Iridium amorphous alloy wire and preparation method thereof
A technology of amorphous alloys and alloy wires, applied in the fields of condensed matter physics and material science, can solve problems such as crystallization of iridium-containing amorphous materials, and achieve the effects of easy molding, reduced energy consumption, and good forming ability of iridium amorphous alloys
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] Embodiment 1, the preparation of master alloy ingot
[0065] After the Ir, Ni, Ta, and B components with a purity of 99.5wt% (weight percent) are prepared in a molar ratio of 35:20:40:5, in an electric arc furnace protected by an argon atmosphere that absorbs titanium, First put tantalum (Ta) and boron (B) with close melting points into the electric arc furnace for smelting. This is because boron is a non-metal, and the arc cannot directly heat it, so the boron is wrapped with high melting point tantalum. After the tantalum is melted, the boron is melted by the temperature of the tantalum to make a tantalum-boron master alloy ingot; then, the tantalum-boron master alloy ingot and the remaining Ir and Ni raw materials are treated in an electric arc furnace protected by an argon atmosphere adsorbed by titanium. Repeated smelting to mix it evenly, each smelting only needs to melt all the components; finally, after cooling, Ir 35 Ta 40 Ni 20 B 5 Master alloy ingot.
Embodiment 2-14
[0066] Embodiment 2-14, preparation of master alloy ingots of various compositions
[0067] Master alloy ingots with various compositions were prepared according to the method of Example 1, and the composition and thermophysical parameters of the obtained amorphous alloy material were measured, and listed in Table 1 below.
[0068] Table 1
[0069]
Embodiment 15
[0070] Embodiment 15, free load traction method prepares Ir 35 Ta 40 Ni 20 B 5 Iridium amorphous alloy wire
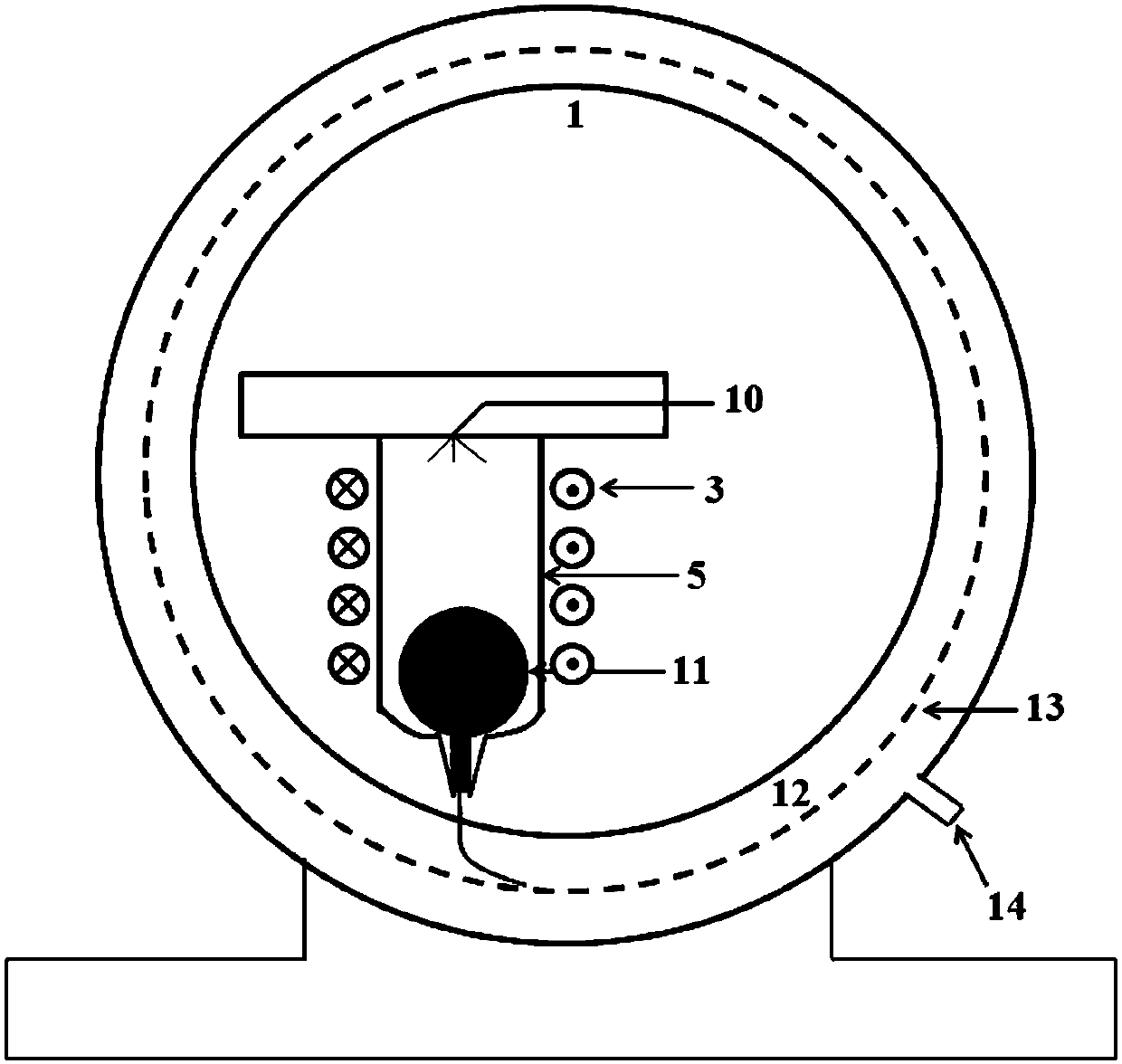
[0071] Using conventional metal mold casting method, the Ir prepared in Example 1 35 Ta 40 Ni 20 B 5 The master alloy ingot is re-melted, and the melt of the master alloy is sucked into the water-cooled copper mold by using the suction casting device in the electric arc furnace. The inner diameter of the water-cooled copper mold is composed of a 2mm part with a length of 1cm and a 1mm part with a length of 4cm , the final composition can be obtained as Ir 35 Ta 40 Ni 20 B 5 An iridium amorphous alloy rod with a head diameter of 2 mm and a length of 1 cm and a tail diameter of 1 mm and a length of 4 cm. Wherein, there is a section of diameter at the head of the bar that is 2mm in order to place the iridium amorphous alloy bar on the figure 1 When placed in the central hole of the graphite cylinder (length 2cm, center diameter 1.5mm) shown, it will not fall o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com