L-lactic acid producing strain and method for producing L-lactic acid using same
A technology for producing bacterial strains and lactic acid, which is applied in the field of genetic engineering and microbial fermentation to achieve the effects of reducing energy consumption, increasing the speed of acid production, and improving the performance of acid production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] Example 1: strain isolation and identification
[0051] Isolation of strains: Dilute yogurt samples from Xinjiang pastoral areas by 1 time with sterile normal saline, mix well for 30 minutes; take the above diluted solution 10-fold gradient dilution and spread it on a medium containing 1% (w / v) CaCO 3 (neutralizing agent) MRS solid medium, cultured at 37°C for 24 hours, picked a single colony with a large transparent circle to inoculate the screening medium, cultivated at 37°C for 24 hours, and detected the production of L-lactic acid and glucose residue with a biosensor. Select the strains with high L-lactic acid production and basically equal to glucose consumption, that is, the lactic acid bacteria with high L-lactic acid content in the fermentation product, and detect the optical purity of L-lactic acid by liquid phase.
[0052] Strain identification: The selected strains have the characteristics of milky white colonies, neat and smooth edges, and positive Gram stai...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Embodiment 2: strain mutagenesis and high temperature screening
[0055] The Lactobacillus rhamnosus Lr-ALT strain obtained in Example 1 was activated by streaking on a plate and then transferred to MRS medium, cultured at 150 rpm at 37°C until OD=1, and the bacterial solution was diluted with normal saline to OD=0.6 , for atmospheric room temperature plasma (ARTP) mutagenesis. Use helium as the working gas of the plasma, power 100W, gas flow rate 10slpm, treatment time 120s, 150s, 180s, add MRS medium at 37°C and 150rpm to recover for 1 hour, and use sterile saline to gradiently dilute and spread the bacterial solution in high glucose MRS+CaCO 3 On a solid plate, place the plate in a 45°C incubator for cultivation, and observe the calcium-dissolving circle after forming a single colony.
[0056] Select a single colony on the plate that grows faster and has a larger calcium-dissolving circle, and then transfer it to MRS medium, cultivate it at 37°C and 150rpm until OD...
Embodiment 3
[0061] Example 3: Production of L-lactic acid by bacterial strain fermentation
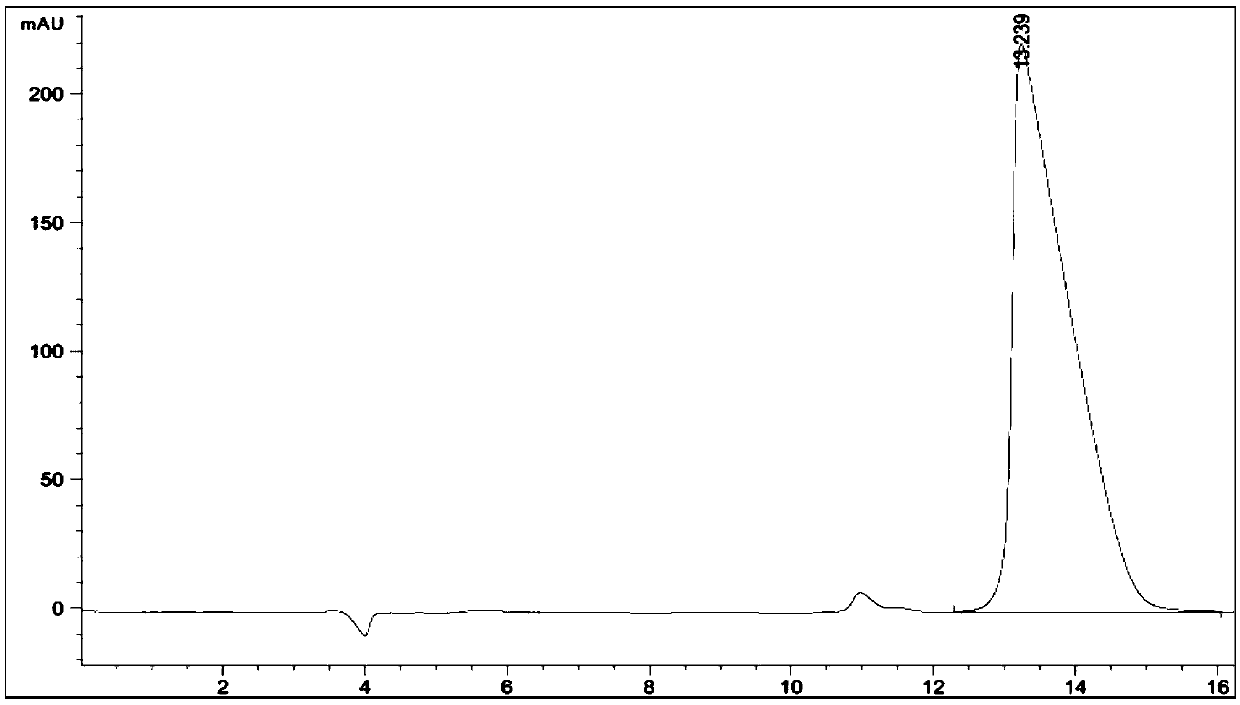
[0062] The L-lactic acid producing strain Lr-ALTHT obtained in Example 2 was inoculated into the MRS medium, and cultivated overnight at 37° C. at 150 rpm to obtain seed liquid. Then, inoculate the above-mentioned seed solution in 200mL acidogenic fermentation medium according to the ratio of 10% (v / v), and cultivate it on a shaker at 37°C for 6 hours at 150rpm to allow the strain to grow, then raise the temperature to 48°C, and continue to cultivate it on a shaker at 150rpm for 70 Obtain fermented liquid (total fermentation time length 76 hours) in hour. Lactic acid production and optical purity were determined by high performance liquid chromatography after fermentation.
[0063] As a result, in the case of enlarged culture scale, the wild-type Lactobacillus rhamnosus strain Lr-ALT can ferment and produce 123.2 g / L of lactic acid for 76 hours, the conversion rate of sugar and acid is more than ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Conversion rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com