Lactic acid bacteria extracellular polysaccharide and immune adjuvant
An extracellular polysaccharide and immune adjuvant technology, applied in bacteria, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve problems such as side effects and can not meet the requirements of new vaccine adjuvants
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] Embodiment 1, the acquisition of WXD030
[0058] 1. Isolation and purification of strains
[0059] 1. Dilute the dairy product with sterile water, then take a small amount of liquid and spread it on the MRS solid medium, place it upside down in an anaerobic tank, and incubate at 37°C for 48 hours under anaerobic conditions.
[0060] 2. After step 1 is completed, isolate and mark the strains with the same colony shape, and repeatedly line the isolated strains to purify them. One strain is screened out and named as strain WXD030.
[0061] 2. Identification of strains
[0062] 1. Strain WXD030 is round on MRS solid medium, with medium-sized colonies, raised, slightly white, moist, with neat edges, such as Figure 13 shown. Gram-positive, as in Figure 14 shown.
[0063] 2. The 16S rDNA sequence of the strain WXD030 was amplified and sequenced, and the sequence result was shown in sequence 1 of the sequence table.
[0064] After the above identification, it was determ...
Embodiment 2
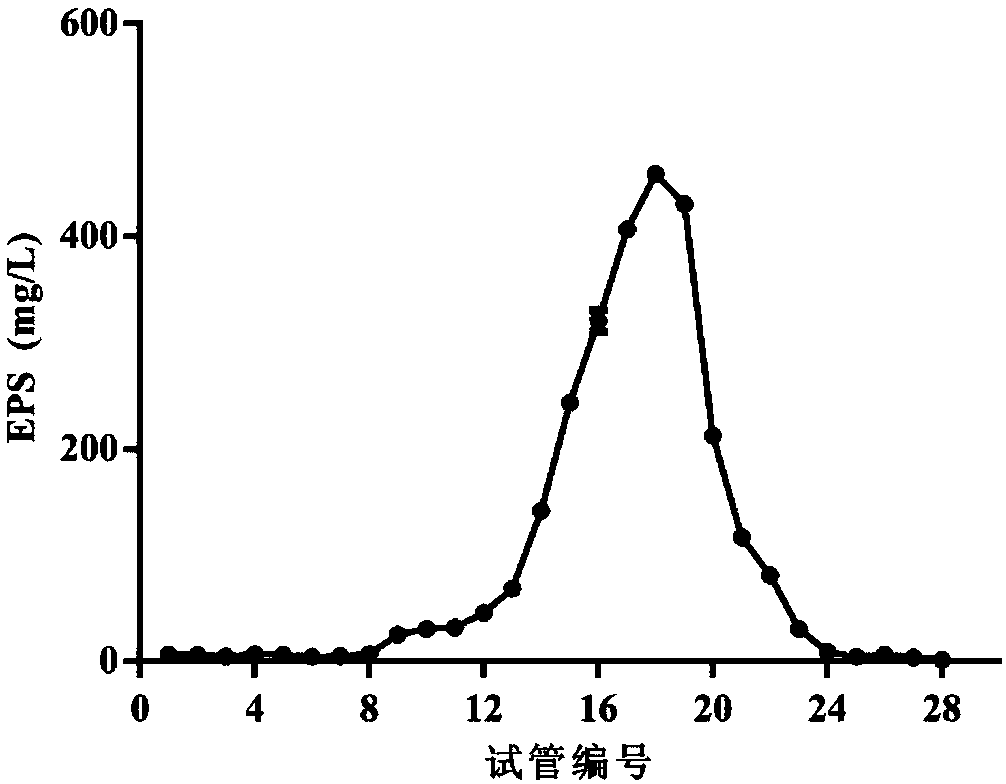
[0067] Example 2, Exopolysaccharide extraction, purification and identification of WXD030
[0068] 1. Extraction of WXD030 Extracellular Crude Polysaccharide
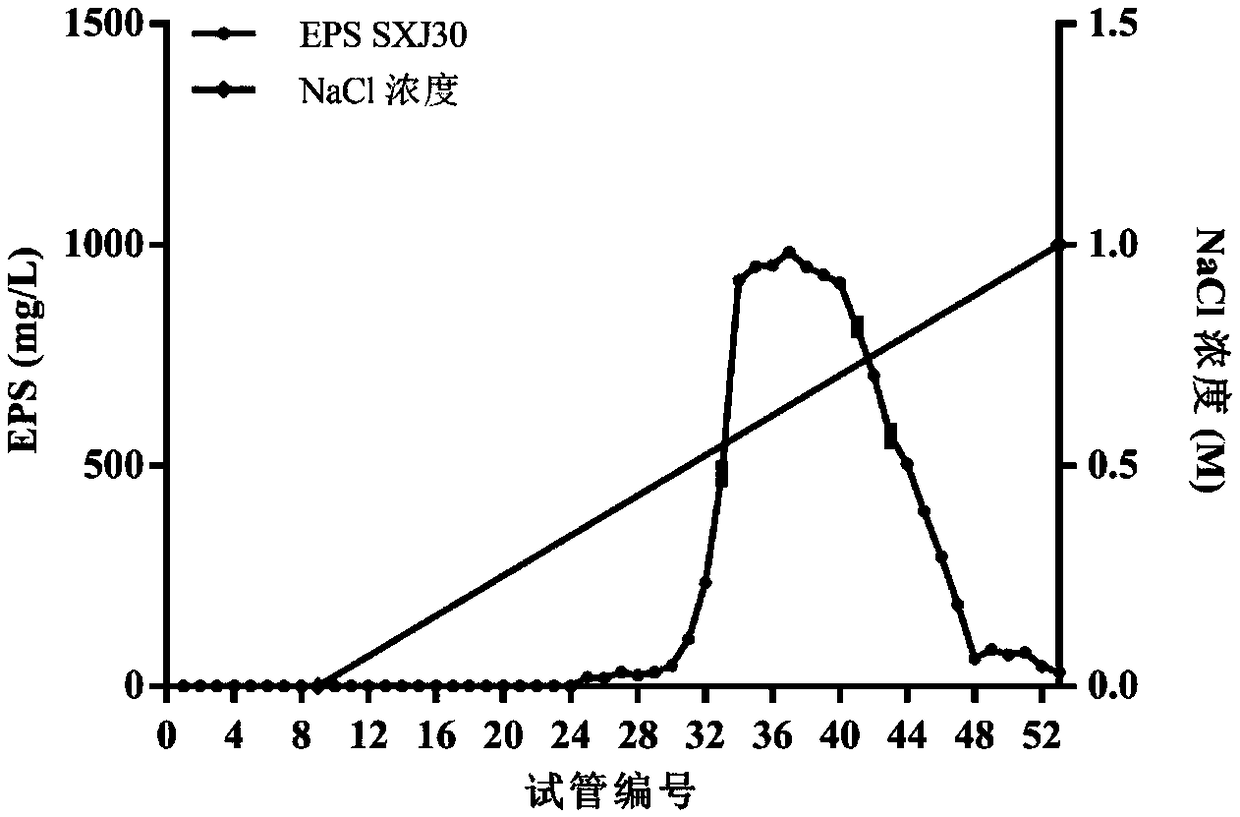
[0069] 1. Inoculate WXD030 in MRS liquid medium, and culture it statically at 37°C for 30 hours to obtain fermentation broth (bacterial concentration is 1×10 9 CFU / mL).
[0070] 2. Centrifuge the fermentation broth obtained in step 1 at 5000 rpm at 4°C for 15 minutes, and take the supernatant.
[0071] 3. Slowly add trichloroacetic acid to the supernatant in step 2 until the concentration of trichloroacetic acid in the supernatant is 40 mg / mL. After standing at 4°C for 8 hours, centrifuge at 10,000 rpm for 10 minutes at 4°C to collect the supernatant.
[0072] 4. Add 4 parts by volume of absolute ethanol to 1 part by volume of the supernatant obtained in step 3, alcohol precipitation overnight at 4° C., centrifuge at 10,000 rpm for 10 minutes at 4° C., and collect the precipitate.
[0073] 5. Dissolve the precipitate...
Embodiment 3
[0113] Example 3. Application research of WXD030 exopolysaccharide as immune adjuvant
[0114] 1. Cytokine secretion of mouse bone marrow-derived cells (BMDCs) stimulated by WXD030 exopolysaccharide
[0115] 1. Follow the steps below to prepare mouse bone marrow-derived cells (BMDCs):
[0116] (1) BALB / c female mice (SPF grade, Beijing Weitong Lihua Experimental Animal Technology Co., Ltd.) aged 6-8 weeks were killed by neck dislocation and soaked in 75% alcohol for 5-10 minutes;
[0117] (2) Aseptically take the femur, tibia and humerus, and place them in PBS for soaking;
[0118] (3) Carefully remove the muscle tissue, connective tissue and cartilage tissue attached to the bone, wash in PBS for soaking, and transfer to fresh PBS for soaking;
[0119] (4) Clamp the bone with sterile tweezers, cut off the epiphysis at both ends, use a 1mL sterile syringe to absorb the RPMI1640 basal medium containing double antibodies, wash repeatedly from one end of the epiphysis until the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com