Strain with chromium tolerance and Cr(VI) removal ability and application of the same in in-situ remediation of moderately and mildly chromium contaminated soil
A chromium-contaminated soil, in-situ remediation technology, applied in the restoration of contaminated soil, bacteria, microorganism-based methods, etc., can solve problems such as low crop production, achieve simple operation, easy acceptance and promotion, and ensure successful colonization. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Embodiment 1: the separation of cellulosic bacteria Cr8
[0020] Soil was collected from an abandoned chromium salt factory in Jinzhong City, Shanxi Province (N37°34′34.01, E113°43′42.06), and the collected fresh soil was fully mixed and cultured with “selective medium + dilution coating” method for isolating bacteria. Weigh 10g of soil into a sterile Erlenmeyer flask, add 100mL of sterile water, and shake for 30 minutes to obtain 10 -1 Soil suspension, draw 1mL with a sterile pipette tip in an ultra-clean bench 10 -1 Soil suspension into 9mL sterile water, that is, 10 -2 Soil suspension was prepared in this way until 10 -8 soil suspension. Draw 200 μL of the soil suspension of -6, -7, and -8 dilution gradients and apply it in the solution containing 1000 μg / mL K 2 Cr 2 o 7 cultured in the dark at 30°C for 3 days, and obtained a strain with fast growth and large colonies, which was purified by streaking until a pure culture was obtained, and a single colony was ...
Embodiment 2
[0021] Embodiment 2: the identification of cellulosic bacteria Cr8
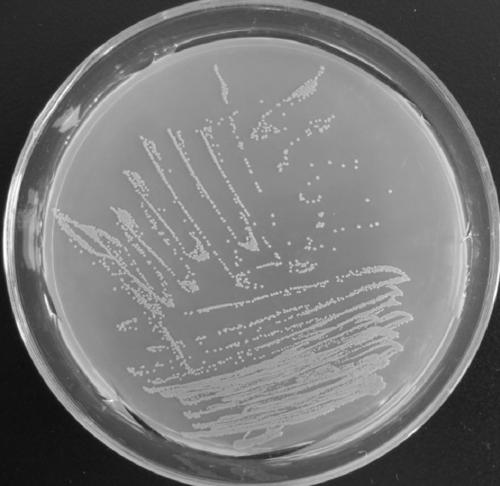
[0022] Morphological characteristics: For the colony characteristics of the strain numbered Cr8 on the LB culture plate, see figure 1 , is: round, yellow, with a diameter of about 1 mm, a protrusion in the middle, and a moist surface. Observe the morphology of Cr8 cells after simple staining, see figure 2 , found that the bacteria were rod-shaped or club-shaped, without spores. In addition, some physiological and biochemical indicators of Cr8 are shown in Table 1.
[0023] Table 1 Physiological and biochemical indicators of strain Cr8
[0024] index
result
index
result
index
result
s
+
Nitrate reduction
+
-
Produce IAA experiment
-
-
+
Cellulose degradation
-
-
Oxidase assay
-
+
+
+
...
Embodiment 3
[0027] Embodiment 3: Determination of chromium-resistant ability of cellulosic bacteria Cr8:
[0028] Determination method: Pick a single Cr8 colony, insert it into LB liquid medium, and culture it on a shaker at 30°C and 180 rpm for 24 hours to make a seed solution. After centrifuging and discarding the supernatant, add LB liquid medium to adjust its OD value to 0.5, and add K 2 Cr 2 o 7 LB liquid medium, K 2 Cr 2 o 7 Concentrations were set at 4 gradients of 0, 300, 500 and 1 000 μg / mL, and cultured on a shaking table at 30 °C and 180 rpm for 2 h, 4 h, 8 h, 12 h, 24 h, 48 h and 72 h. Measure its OD value at a wavelength of 600 nm, see image 3 .
[0029] From image 3 It can be seen that Cr8 can grow very well in the chromium-containing medium, and in both the chromium-containing and chromium-free medium, it enters the logarithmic growth phase when it is cultivated for 12H, and enters the stable growth phase when it is cultivated for 48H. Low concentration of chro...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Upper caliber | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Lower caliber | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com