Nano-antibody for specifically recognizing duck hepatitis A virus 1
A duck hepatitis A virus and nanobody technology, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems of high detection cost, limited sources of polyclonal antibodies, and complexity, and achieve the effect of good stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] Embodiment 1: the construction of anti-DHAV-1 single domain heavy chain antibody (that is, the single domain heavy chain antibody against DHAV-1) immune library
[0053] Take 3ml of DHAV-1 inactivated vaccine to immunize Bactrian camels by subcutaneous multi-point injection. Booster immunization with 3ml of DHAV-1 inactivated vaccine was carried out at intervals of 2 weeks. Blood was collected 7 days after each immunization, and serum titer was determined by indirect ELISA method. The sample with the highest serum titer was selected to separate lymphocytes and extract RNA.
[0054] The extraction of RNA was carried out according to the instruction manual of RNAiso reagent from TAKARA company. Using RNA as a template and oligo dT as a primer, the first strand of cDNA was synthesized according to the instructions of TAKARA reverse transcriptase.
[0055] The gene encoding the variable region of the heavy chain antibody was obtained by nested PCR using PrimeSTAR high-fide...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Example 2: Panning and Identification of Anti-DHAV-1 Single Domain Heavy Chain Antibody
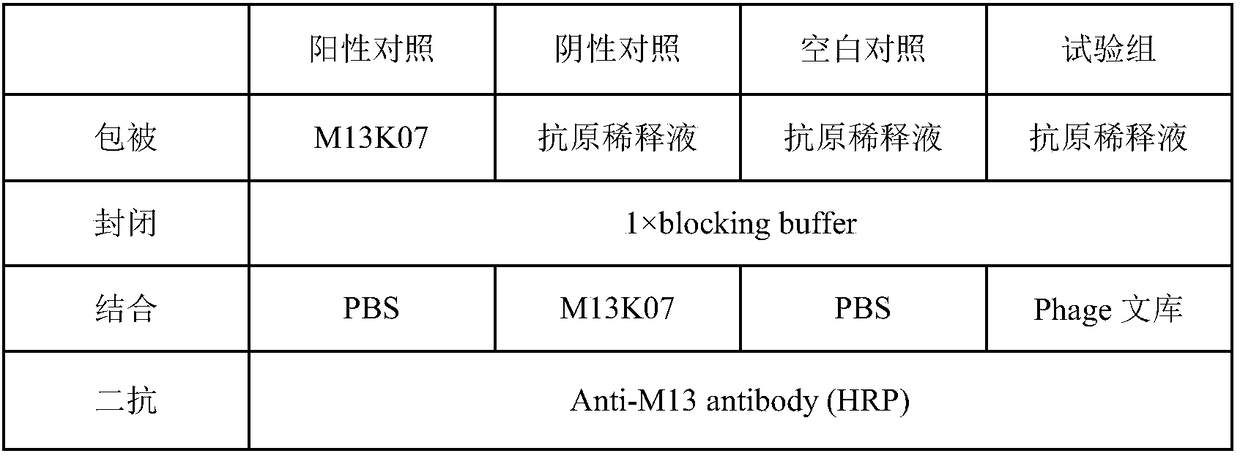
[0064] The single-domain heavy-chain antibody against DHAV-1 was panned from the anti-DHAV-1 single-domain heavy-chain antibody immune library obtained in Example 1 by solid-phase affinity panning. Add 100 μL of DHAV-1 VP1 protein diluted with PBS to each enzyme-labeled well, and coat overnight at 4°C. The coating concentrations of each round of panning are 100, 80, and 40 μg / mL; aspirate the coating solution, PBS Wash the plate 5 times, add 200 μL 5% skimmed milk powder to each well, block for 2 hours at 37°C; wash the plate 5 times with PBS, add 100 μL phage antibody library (about 5×10 10 CFU), 37°C, incubate for 2h; aspirate unbound phage, wash the plate with PBST (containing 0.5% Tween-20) for 3-5 times (increase 5 times for each round), and then wash the plate with PBS for 15-25 times; 100 μL of eluent (glycine-hydrochloric acid, pH 2.2) was used to elute the phage adsorbed ...
Embodiment 3
[0069] Example 3: Scale preparation of anti-DHAV-1 single domain heavy chain antibody
[0070] Acquisition of the DNA fragment encoding the anti-DHAV-1 single domain heavy chain antibody: the variable region encoding gene of the heavy chain antibody was obtained by PCR using the EX Taq DNA polymerase of TAKARA company (see Table 3 for the primers used), agarose gel The anti-DHAV-1 single domain heavy chain antibody gene was recovered by electrophoresis.
[0071] Table 3: Primers for Amplifying Heavy Chain Antibody Variable Regions
[0072] Primer name
Primer sequence (5'-3')
serial number
VHH-F
GGG GGATCC CAGGTCCAACTGCAGGAGTCT
SEQ ID NO.8
VHH-R
GCC AAGCTT TGAGGAGACGGTGACCTGGG
SEQ ID NO.9
[0073] Note: The underlined sequences are restriction enzyme sites.
[0074] The obtained anti-DHAV-1 single-domain heavy-chain antibody gene fragment was cloned into the expression vector pET28as (6XHis tag and SUMO tag were fused a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com