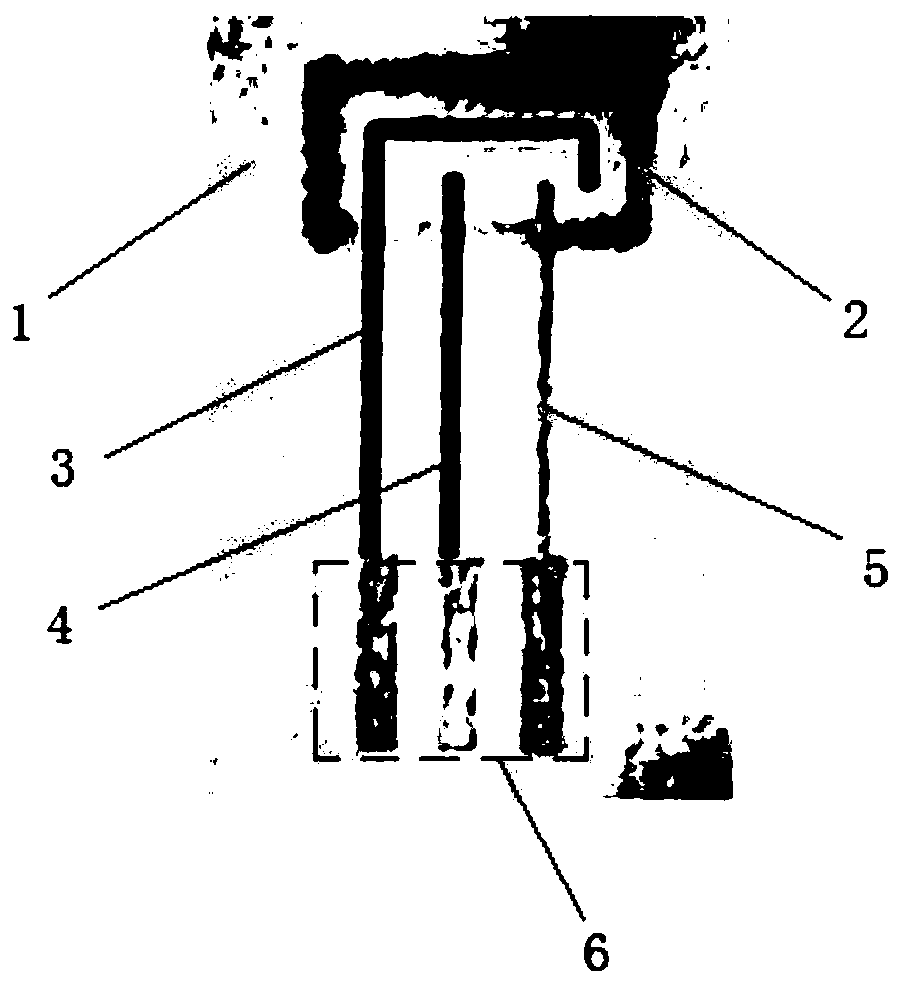
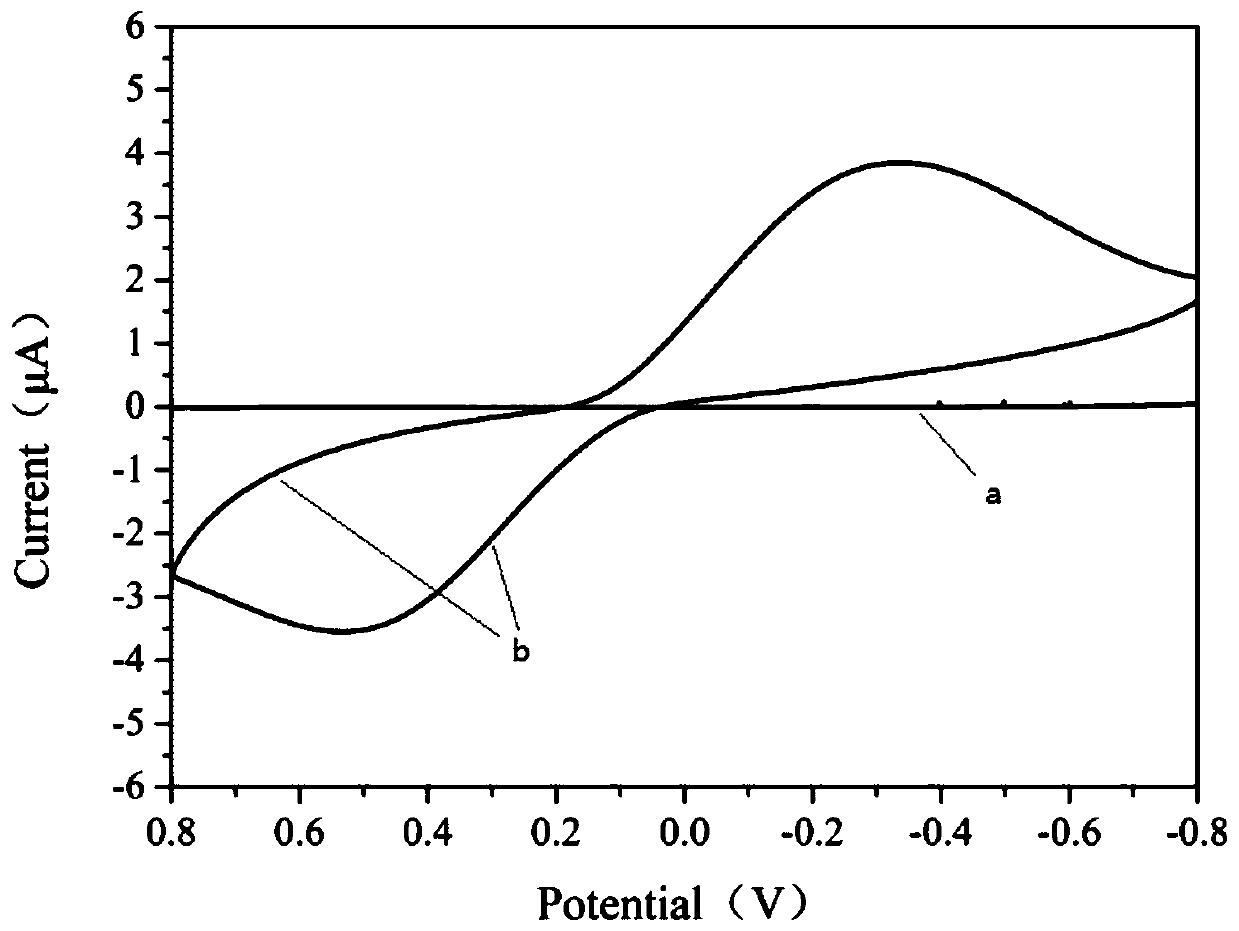
Construction method of nanocellulose paper-based biosensor
A nanocellulose, biosensor technology, applied in instruments, scientific instruments, material electrochemical variables, etc., can solve the problems of poor detection efficiency and accuracy, rough surface, large internal pores, etc., to achieve smooth surface and increase added value , the effect of high light transmittance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0050] Specific embodiment one: The construction method of nanocellulose paper-based biosensor in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0051] One, the preparation of nanocellulose:
[0052] The cellulose raw material is sequentially subjected to extraction treatment and delignification treatment to obtain hemicellulose, and then mechanical pretreatment, chemical mechanical mixing pretreatment or biomechanical mixing pretreatment is performed to obtain hemicellulose-containing nanocellulose aqueous solution;
[0053] Described mechanical pretreatment, concrete operation steps are as follows:
[0054] ① Adding deionized water to the helium cellulose until the mass fraction of the helium cellulose is 0.1% to 0.3%;
[0055] ② Then use a 600bar high-pressure homogeneous mechanical treatment for 30-40 minutes to obtain a nano-cellulose aqueous dispersion containing hemicellulose, wherein the hemicellulose accounts for 20%-30% of the total cellulose mass;
[0056] The sp...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0075] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: the specific steps of the extraction process described in step one are:
[0076] Crush the cellulose raw material into 90-120 mesh powder, and then carry out extraction treatment with benzyl alcohol for 10-12 hours. The benzyl alcohol is a mixture of toluene and absolute ethanol in a volume ratio of 2:1. Others are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0077] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: the specific steps of delignification treatment described in step one are:
[0078] ① Immerse the extracted cellulose powder in a sodium chlorite solution with a mass concentration of 1% to 1.2%, adjust the pH value of the solution to 4 to 5 with glacial acetic acid, and then magnetically place it in a constant temperature water bath at 75 to 80°C. Heat and stir for 1 to 1.5 hours;
[0079] ②Immerse the cellulose powder obtained in step ① into a sodium chlorite solution with a mass concentration of 1% to 1.2%, adjust the pH value of the solution to 4 to 5 with glacial acetic acid, and then magnetically heat it in a constant temperature water bath at 75 to 80°C Stir for 1~1.5h;
[0080] ③ Repeat step ② for 5-6 times to basically remove the lignin, then filter and wash the obtained liquid with a Buchner funnel until the filtrate is neutral, and finally obtain hedophilic cell...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| quality score | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| porosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com