Porous ceramic material preparation method with intrinsic pore formation
A porous ceramic and pore-forming technology, which is applied in ceramic products, applications, household appliances, etc., can solve the problem of high compressive strength, and achieve the effects of easy operation, simple preparation process, and convenient performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0028] The invention provides a method for preparing an intrinsically pore-forming porous ceramic material.
[0029] In the method, firstly, the raw materials are mixed and batched without adding a pore-forming agent; then, a green body is processed according to a traditional ceramic preparation method; finally, a porous ceramic material is obtained through drying and sintering.
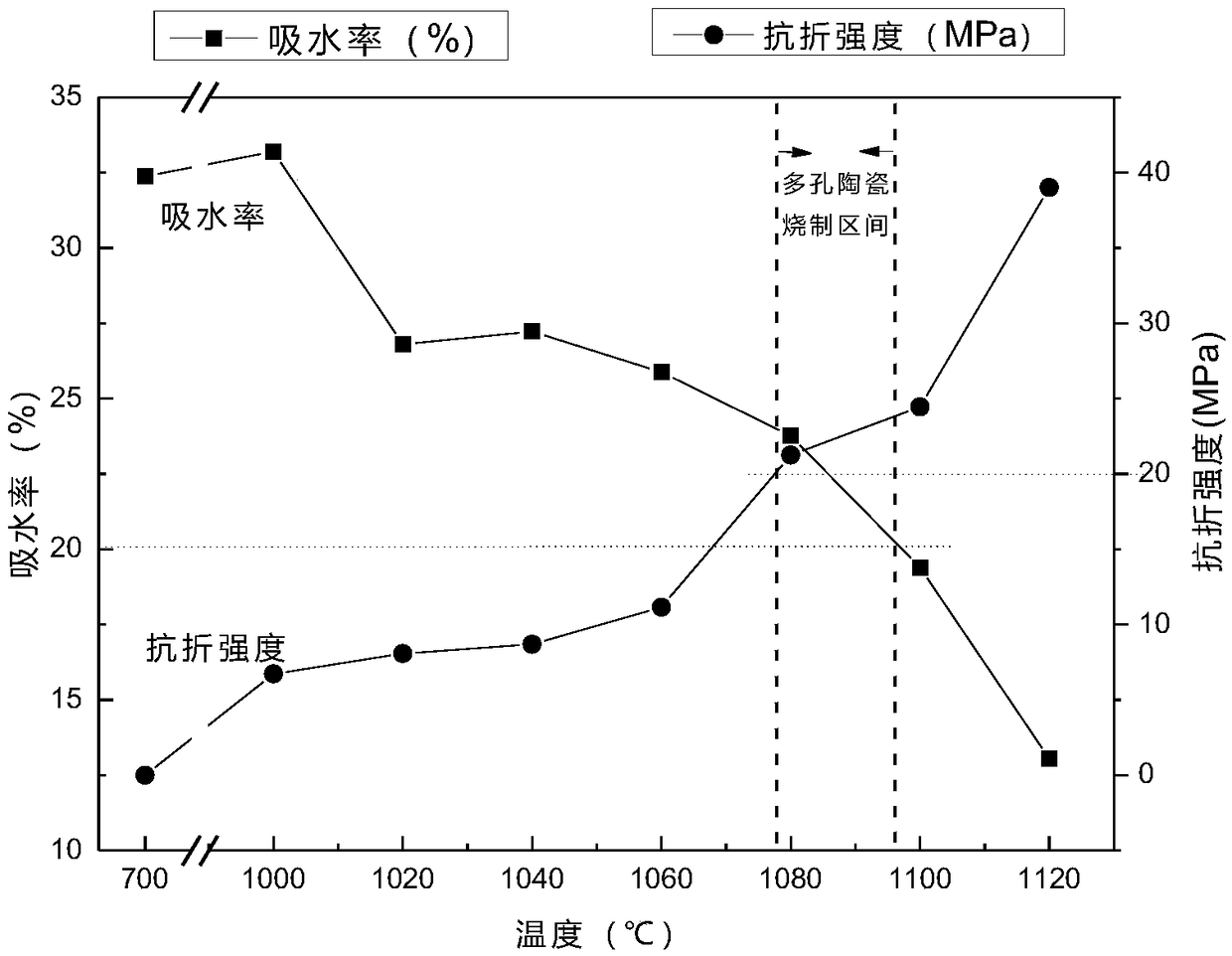
[0030] The traditional ceramic sintering process is mainly divided into two types: solid phase sintering and liquid phase sintering, and the sintering process is relatively complicated. The sintering process can be divided into three stages: the first stage belongs to the stage of mineral loss of volatile matter, decomposition and crystal phase reaction, and some chemical reactions mainly occur, resulting in some mineral phase transformation; the second stage belongs to the densification stage, in which there will be Accompanied by the generation of liquid phase and the further reaction of crystal ph...
Embodiment 1
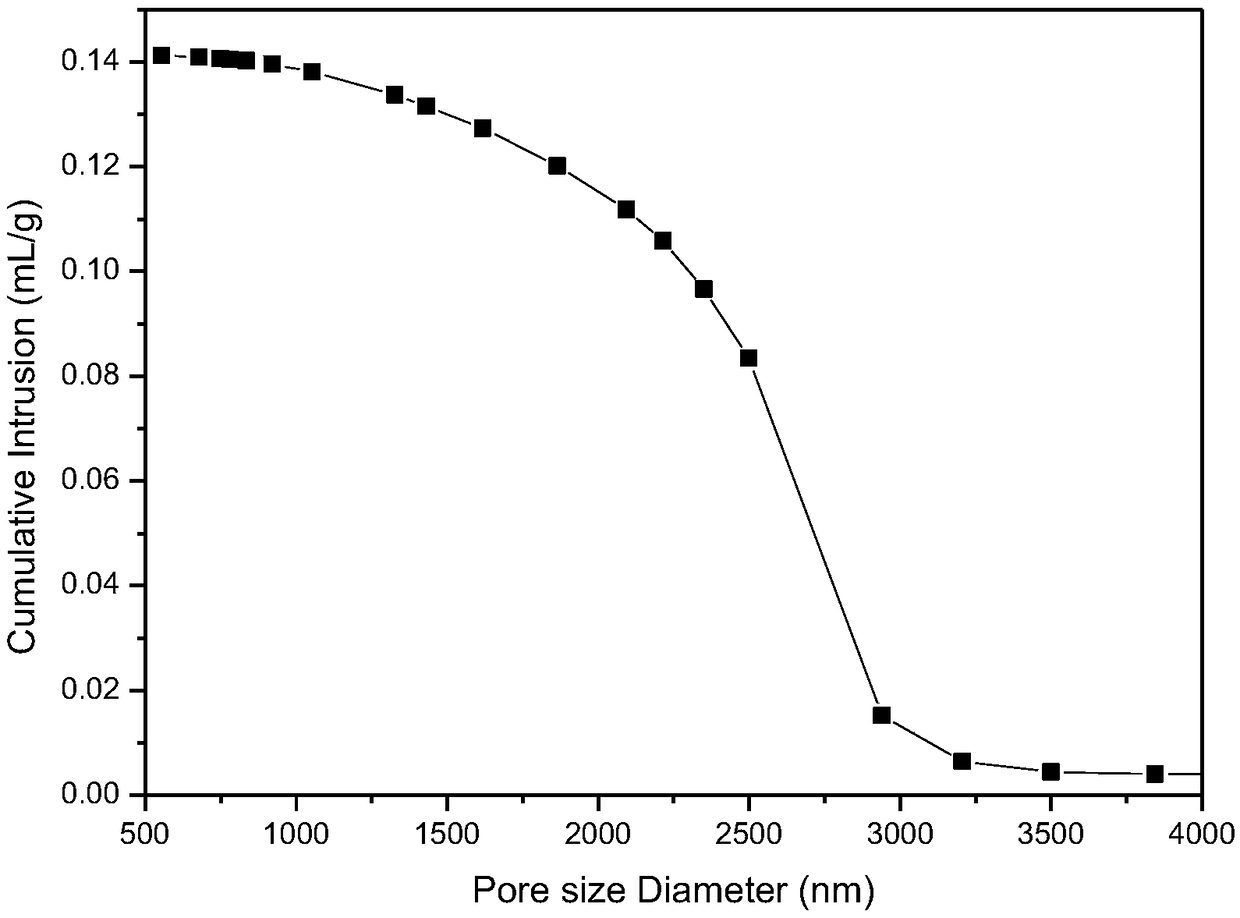
[0035] Refining slag, Laiyang soil, pyrophyllite, and quartz are used as raw materials, and the crystal phase does not contain pyroxene phase. The chemical composition of the ceramic prepared after the raw materials are mixed is 17.08%, and the content of CaO is 17.08%. 2 61.52%, MgO 3.69%, Al 2 o 3 9.54%, Fe 2 o 3 0.72%, Na 2 O+K 2 O is 1.81%. The mixed raw materials are traditionally ground, granulated, dried, and shaped to obtain a green body. The green body is dried and sintered. The firing temperature is 1080°C, which is 50°C lower than the firing temperature. The obtained ceramic material has a flexural strength of 23.07Mpa, a water absorption rate of 23.56%, a porosity of 38.12%, and an average pore diameter of 3.18 μm. It is a porous ceramic material with high strength, and its crystal phase contains a pyroxene phase. Its SEM photo, the obtained porous ceramic material pore size distribution and firing temperature are determined as follows figure 1 , figure 2 ...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Refining slag, Laiyang soil, pyrophyllite, and quartz are used as raw materials, and the crystal phase does not contain pyroxene phase. The chemical composition of the ceramic prepared after the raw materials are mixed is 17.08%, and the content of CaO is 17.08%. 2 61.52%, MgO 3.69%, Al 2 o 3 9.54%, Fe 2 o 3 0.72%, Na 2 O+K 2 O is 2.81%, and the difference from Example 1 is the external doping of 1% Na 2O (added in the form of soda ash). The mixed raw materials are traditionally ground, granulated, dried, and shaped to obtain a green body, which is then dried and sintered at a firing temperature of 1020°C, which is 50°C lower than the firing temperature. The obtained ceramic material has a compressive strength of 51.2 MPa, a water absorption rate of 23.58%, a porosity of 37.77%, and an average pore diameter of 1.27 μm. It is a porous ceramic material with high strength, and its crystal phase contains a pyroxene phase.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| flexural strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com