Method for crystallizing germanium antimony tellurium materials through electronic beam irradiation induction
A technology of electron beam irradiation, germanium antimony tellurium, applied in metal material coating process, ion implantation plating, coating and other directions, can solve the problem of phase change material stay, etc., to facilitate in-situ observation and microstructure characterization, Achieve the effect of in-situ performance testing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] In this implementation, the phase change material GeSb 2 Te 4 As an example, a cubic phase nanograin with a grain size of about 30nm is prepared, and the sample is prepared on a TEM standard copper grid for easy observation. The specific process is as follows:
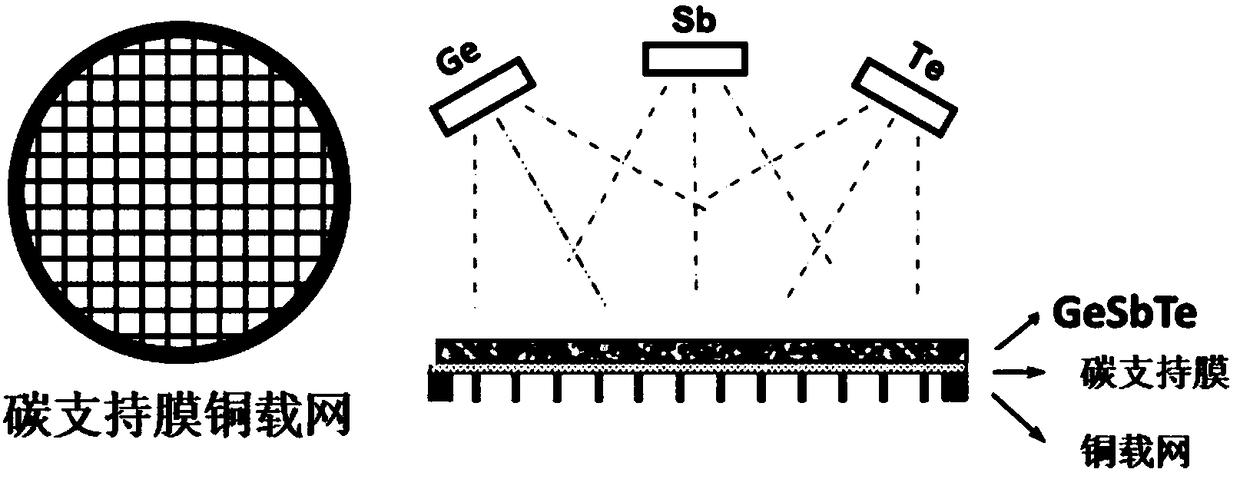
[0046] Step 1: Select a TEM standard size copper grid with an ultra-thin carbon support film (3-5nm) on the surface as the film substrate, and deposit 80nm thick GeSb by magnetron sputtering 2 Te 4 Amorphous thin films (such as figure 1 shown).
[0047] Step 2: Load the sample onto the TEM sample holder and perform plasma cleaning.
[0048] Step 3: Use TEM to find a clean and flat area on the film, as shown in Figure 3(a).
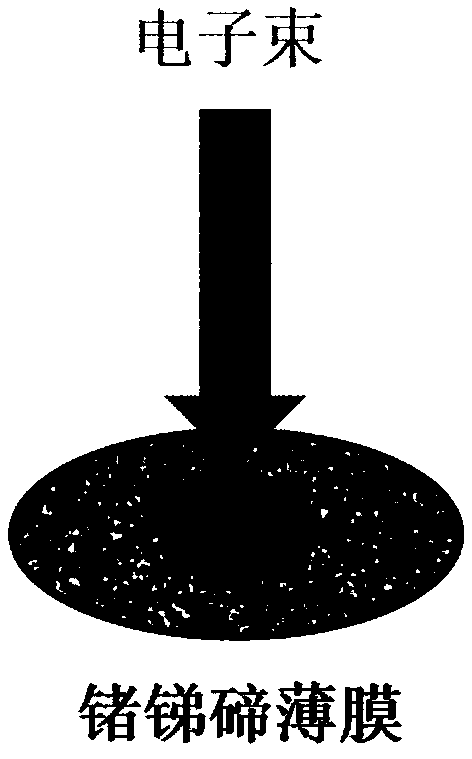
[0049] Step 4: Set the TEM voltage to 200kV, focus the electron beam to 0.3μm, and set the electron beam intensity to 1×10 25 m -2 the s -1 ,Such as figure 2 shown.
[0050] Step 5: Observe the crystallization process in real time (as shown in Figure 3(a)-(d)), after 10 minutes th...
Embodiment 2
[0053] In this implementation, the phase change material Ge 2 Sb 2 Te 5 As an example, cubic phase nanocrystals with a grain size of about 35nm were prepared, and the samples were prepared on silicon wafers for electrical performance testing. The specific process is as follows:
[0054] Step 1: Select a silicon wafer as a thin film substrate, and deposit 200nm thick Ge by molecular beam epitaxy 2 Sb 2 Te 5 Amorphous thin film.
[0055] Step 2: Using ion thinning technology to perform electron microscope sample pretreatment on the substrate for preparing the germanium antimony tellurium amorphous thin film, the thickness of the sample is 90nm.
[0056] Step 3: Use an electron microscope to find a clean and flat area on the film.
[0057] Step 4: Set the electron microscope voltage to 200kV, focus the electron beam to 1μm, and set the electron beam intensity to 1×10 23 m -2 the s -1 .
[0058] Step 5: Observe the crystallization process in real time. After 40 minutes, ...
Embodiment 3
[0061] In this implementation, the phase change material GeSb 2 Te 4 As an example, a hexagonal phase nanograin with a grain size of about 300nm was prepared, and the sample was prepared on a heating chip for external field loading experiments. The specific process is as follows:
[0062] Step 1: Select the heated chip as the thin film substrate, and deposit GeSb with a thickness of 70nm by physical vapor deposition 2 Te 4 Amorphous thin film.
[0063] Step 2: Using focused ion beam technology to perform electron microscope sample pretreatment on the substrate for preparing the germanium antimony tellurium amorphous thin film.
[0064] Step 3: Use an electron microscope to find a clean and flat area on the film.
[0065] Step 4: Set the electron microscope voltage to 120kV, focus the electron beam to 5μm, and set the electron beam intensity to 1×10 26 m -2 the s -1 .
[0066] Step 5: Observe the crystallization process in real time under in-situ heating conditions. Aft...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com