A kind of method that reclaims iridium, rhodium from iridium-rhodium alloy scrap
A technology of iridium-rhodium alloy and scrap, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, lengthy process flow, poor separation effect and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
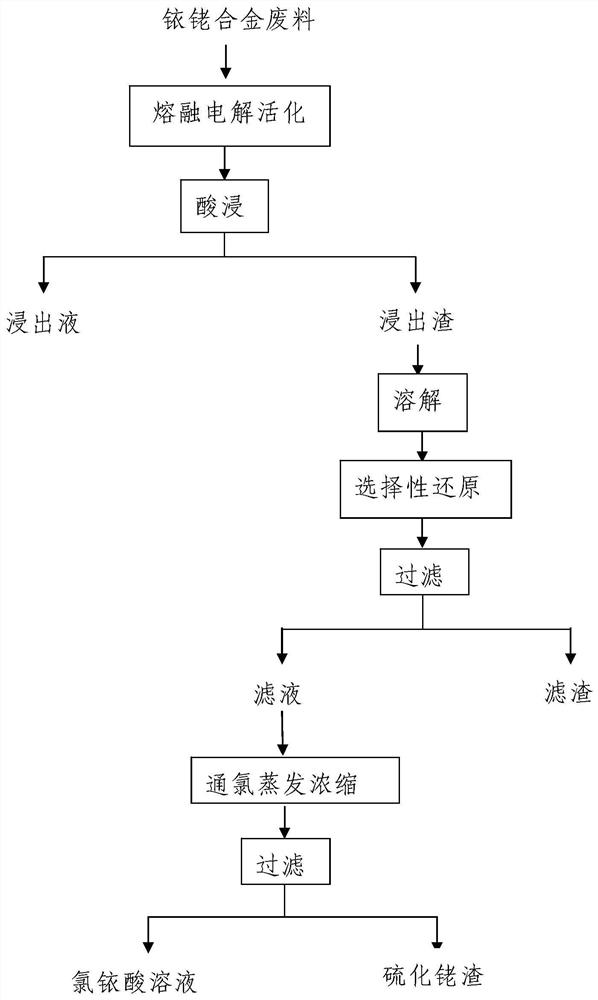
[0021] Such as figure 1 As shown, this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0022] Step 1, after mixing 100g of iridium-rhodium alloy waste and 300g of alumina, put it into the aluminum electrolytic cell of the electrolysis device as an electrolyte, then melt and electrolyze it for 10 hours at a temperature of 900° C. to obtain highly active iridium-rhodium alloy waste; The anode current density is controlled to be 0.5A / cm in the process of molten electrolysis 2 ;
[0023] Step 2, adding a hydrochloric acid solution with a mass concentration of 5% to the highly active iridium-rhodium alloy waste obtained in step 1, performing leaching treatment at a temperature of 80°C, and then filtering, collecting and washing the filter residue;
[0024] Step 3, put the washed filter residue in step 2 into a titanium autoclave, then add a hydrochloric acid solution with a mass concentration of 35% and feed in chlorine gas, dissolve and react for 3 hours at a temperature of 90°C and ...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Such as figure 1 As shown, this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0029] Step 1, after mixing 500g of iridium-rhodium alloy scrap and 1500g of alumina, put it into the aluminum electrolytic cell of the electrolysis device as electrolyte, then melt and electrolyze it for 20h at a temperature of 950°C to obtain highly active iridium-rhodium alloy scrap; In the process of molten electrolysis, the anode current density is controlled to be 1A / cm 2 ;
[0030] Step 2, adding a hydrochloric acid solution with a mass concentration of 5% to the highly active iridium-rhodium alloy waste obtained in step 1, performing leaching treatment at a temperature of 85°C, and then filtering, collecting and washing the filter residue;
[0031] Step 3, put the washed filter residue in step 2 into a titanium autoclave, then add a hydrochloric acid solution with a mass concentration of 35% and feed chlorine gas, and dissolve and react for 4 hours at a temperature of 100°C and a pressu...
Embodiment 3
[0035] Such as figure 1 As shown, this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0036] Step 1, mix 1000g of iridium-rhodium alloy waste and 3000g of alumina and put it into the aluminum electrolytic cell of the electrolysis device as electrolyte, then melt and electrolyze it for 50h at a temperature of 1000°C to obtain highly active iridium-rhodium alloy waste; The anode current density is controlled to be 1.5A / cm in the process of molten electrolysis 2 ;
[0037] Step 2, adding a hydrochloric acid solution with a mass concentration of 5% to the highly active iridium-rhodium alloy waste obtained in step 1, performing leaching treatment at a temperature of 90°C, and then filtering, collecting and washing the filter residue;
[0038] Step 3, put the washed filter residue in step 2 into a titanium autoclave, then add a hydrochloric acid solution with a mass concentration of 35% and feed chlorine gas, and dissolve and react for 5 hours at a temperature of 150° C. and a pressur...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com