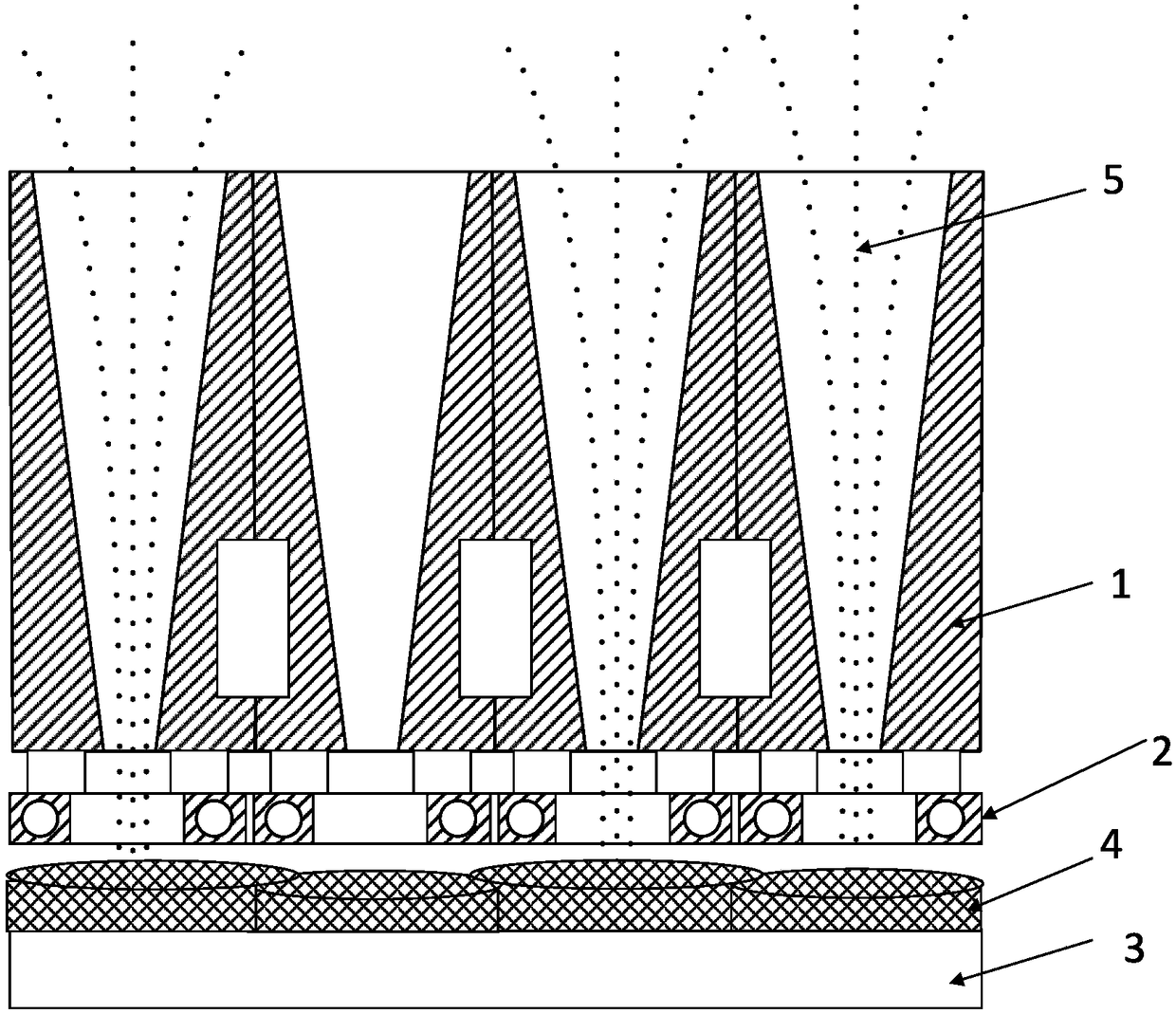
Three-dimensional printing formation method based on induction heating and used for metal nanopowder
A nano-metal powder and three-dimensional printing technology, applied in the field of additive manufacturing, can solve the problems of inability to realize parallel molding, high energy consumption, and slow molding speed, and achieve the elimination of molding thermal stress problems, elimination of residual stress accumulation, and surface roughness Reduced effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0036] The present invention will be described in further detail below in combination with specific embodiments.
[0037] The invention provides a method for three-dimensional printing of nanometer metal powder based on induction heating, which includes the following steps:
[0038] (1) Prepare the CAD data file of the 3D printing molded part, the molded substrate, the metal nanopowder and the nanopowder jet array plate;
[0039] The CAD data file of the 3D printing molded part is carried out by the designer using 3D CAD software to perform 3D modeling of the parts to be processed, and adds necessary auxiliary support structures according to the obtained 3D model size and shape of the parts, and then presses the traditional 3D The principle of laminated manufacturing of printing is to set the layer thickness (the thickness of the single-layer flat layer after the nano-powder is melted) to obtain the closed contour graphic data set after layered slicing;
[0040] The upper sur...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com