Method for recycling textile wastewater to prepare submicron calcium-based rigid material
A sub-micron textile wastewater technology, applied in textile industrial wastewater treatment, chemical instruments and methods, water/sewage multi-stage treatment, etc., can solve solid waste TA problems such as poor purity, no reuse value, and poor dehydration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Step 1: Adjust the pH value of the waste water to 10, add basic aluminum chloride, stir at a speed of 400 rpm for 10 minutes, and then slowly stir at a speed of 100 rpm for 20 minutes, filter the suspension through cinders, and filter the filtrate through activated carbon device to obtain clear liquid.
[0027] Step 2: add sulfuric acid to the clear liquid, adjust the pH to 3.5, precipitate terephthalic acid (TA), and obtain TA emulsion;
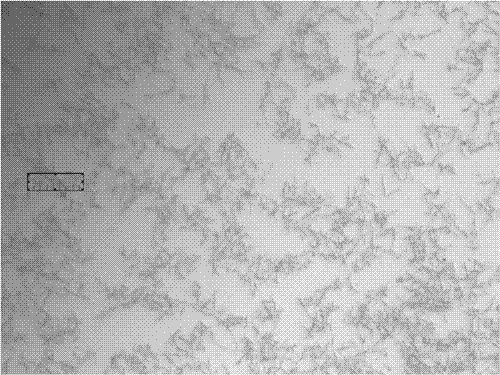
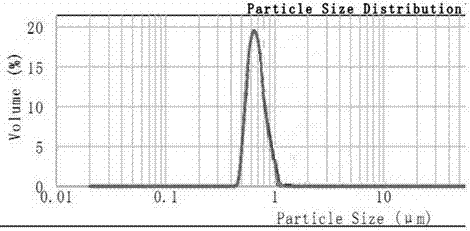
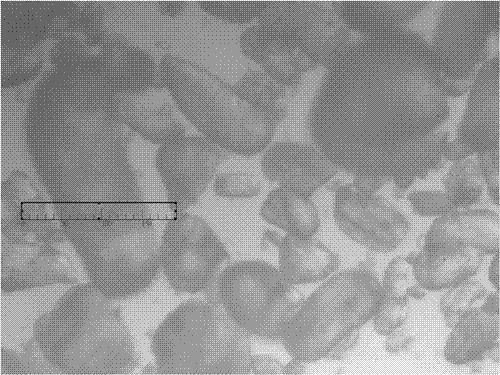
[0028] Step 3: TA emulsion and calcium hydroxide slurry are reacted in an ultrasonically enhanced tubular reactor, and the output is separated from solid and liquid. After drying at 150°C, the filter cake can be used as a functional additive for rubber and plastic materials, and the filtrate is discharged. Enter the biochemical treatment system, and discharge or reuse after further treatment reaches the standard.
[0029] The molar ratio of TA to calcium hydroxide is 1:1.
[0030] The applied frequency of the ultrasonic wave is 55KH...
Embodiment 2
[0034] The difference between embodiment 2 and embodiment 1 is:
[0035] In step 1, adjust the pH value of the wastewater to 11, add basic aluminum chloride, stir at 800 rpm for 3 minutes, and then slowly stir at 300 rpm for 10 minutes.
[0036] In step 2, sulfuric acid was added to the clear liquid to adjust the pH to 4.2.
[0037] The molar ratio of TA to calcium hydroxide is 1:1.1.
[0038] The ultrasonic wave is applied at a frequency of 75KHz and a power of 600W.
[0039] The CODcr detection of the effluent filtrate of step 3 was carried out by the method of test 1, and the results are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0041] The difference between embodiment 3 and embodiment 1 is:
[0042] In step 1, adjust the pH value of the waste water to 10.5, add basic aluminum chloride, stir at a speed of 600 rpm for 7 minutes, and then slowly stir at a speed of 200 rpm for 15 minutes.
[0043] In step 2, sulfuric acid was added to the clear liquid to adjust the pH to 4.0.
[0044] The molar ratio of TA to calcium hydroxide is 1:1.05.
[0045] The applied frequency of the ultrasonic wave is 65KHz, and the power is 500W.
[0046] The CODcr detection of the effluent filtrate of step 3 was carried out by the method of test 1, and the results are shown in Table 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com