Degradable zinc base alloy implant material and preparation method and application thereof
A technology for implanting materials and alloys, which is applied in the field of medical devices, can solve problems such as uncertainty and potential safety hazards, and achieve the effects of improving mechanical properties, easy processing and shaping, and beneficial to the recovery of body functions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Embodiment 1: Zinc-iron-copper alloy
[0043] The degradable zinc-based alloy implant material in this embodiment is a zinc-iron-copper alloy, and the preparation process specifically includes the following steps:
[0044] 1) According to the mass percentage content, 1wt% of Fe, 1wt% of Cu and the remainder of Zn (total impurity content 6 (1vol.%) and CO 2 In the atmosphere, add high-purity graphite crucible to mix and smelt to obtain zinc-based alloy.
[0045] 2) After smelting, extrude the obtained zinc-based alloy into rods with a diameter of 10 mm and a length of 50 cm.
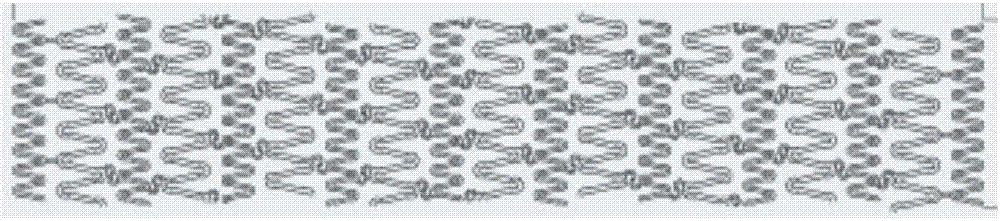
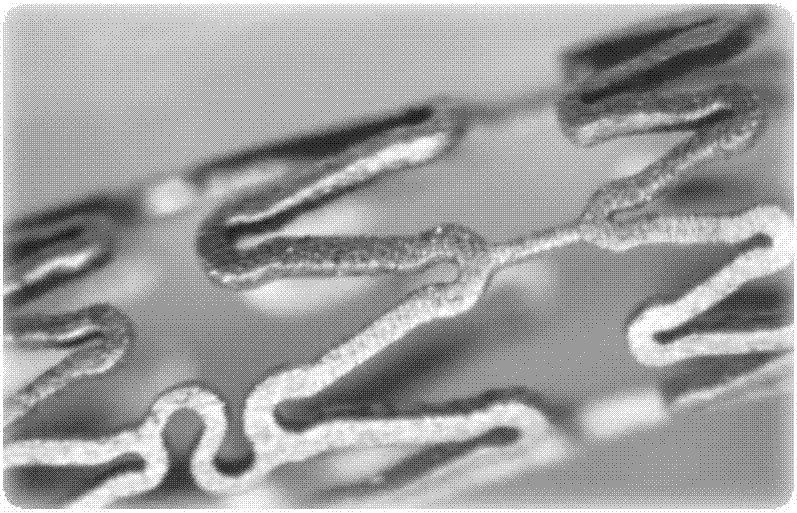
[0046] 3) After repeated annealing (temperature 200°C-500°C, 30min), the obtained rod is drawn into a pipe with an outer diameter of 0.15mm±0.013mm and a wall thickness of 0.1mm±0.013mm, and the design pattern is 3.0 The bracket of ×20 is formed by femtosecond laser engraving (see engraving pattern figure 1 ), the electrochemical polishing method removes the edges and corners of the material to ...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Embodiment 2: zinc-iron-copper alloy
[0053] The degradable zinc-based alloy implant material in this embodiment is zinc-iron-copper alloy, containing 0.14wt% iron-1.8wt% copper, the balance is zinc, and the total content of impurities is controlled to be <0.001wt%. The preparation process is the same as the implementation example 1.
[0054] Effect verification:
[0055] The zinc-based alloy implant material prepared by the above method has an elastic modulus of 75GPa, a yield strength of 210MPa, and a tensile strength of 240MPa. Ideal coronary stent material. The degradation rate measured according to the ASTM_G31-1972 method is 0.19mm / year; the blood compatibility is tested according to the GB16886 series method, and the hemolysis rate is 1%, which is 5% lower than the standard value; the cytotoxic reaction is grade I, no intradermal Stimulation, sensitization rate 0%.
Embodiment 3
[0056] Example 3: Zinc-iron-strontium-calcium alloy
[0057] The degradable zinc-based alloy implant material in this embodiment is a zinc-iron-strontium-calcium alloy, containing 0.5wt% iron-0.5wt% strontium-0.5wt% calcium, and the balance is zinc. The preparation process is the same as in Example 1. .
[0058] Effect verification:
[0059] The zinc-based alloy implant material prepared by the above method has an elastic modulus of 80GPa, a yield strength of 233MPa, and a tensile strength of 270MPa, which can meet the mechanical performance requirements of fracture and bone fixation in load-bearing parts. The degradation rate measured according to the ASTM_G31-1972 method is 0.38mm / year; according to the GB16886 series of methods, there is no obvious cytotoxicity, intradermal irritation, sensitization rate and genotoxicity. Since the elastic modulus (60-70Gpa) of the zinc-based alloy implant material is closer to human cortical bone (about 20Gpa) than traditional internal f...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com