Method for preparing high-coercivity neodymium-iron-boron magnet through grain boundary diffusion
A technology with high coercivity and grain boundary diffusion, which is applied in the manufacture of magnetic objects, magnetic materials, inductors/transformers/magnets, etc. Diffusion process and uniformity of magnet structure and properties, suitable for mass continuous production, high bonding strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] Example 1: Sintered NdFeB magnets are hot dipped with Pr 68 Cu 32 Preparation of High Coercive Force Magnet by Post-Grain Boundary Diffusion Heat Treatment of Alloy
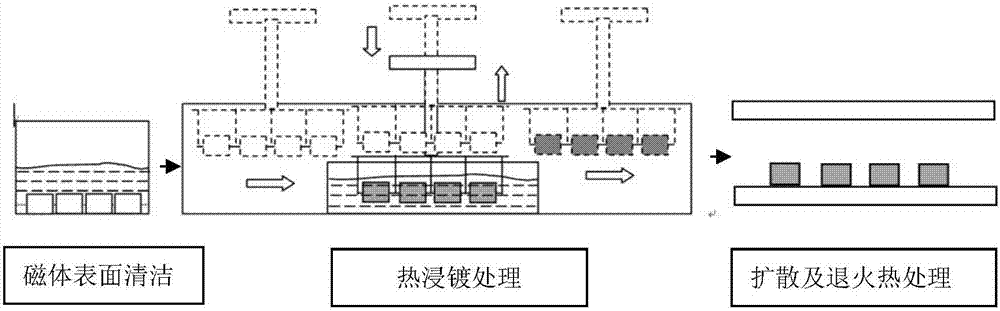
[0022] (1) Clean the surface of the NdFeB magnet;
[0023] (2) Vacuum melting Pr 68 Cu 32 alloy (atomic fraction);
[0024] (3) Pr 68 Cu 32 The alloy is heated to about 500°C in a vacuum plating tank to melt the alloy into a uniform melt;
[0025] (4) After the magnet is vacuum preheated at about 500°C for about 1-3 minutes, it is immersed in the alloy melt for hot-dip plating, and then cooled after taking it out;
[0026] (5) The magnet is subjected to diffusion and annealing heat treatment in a vacuum furnace. The diffusion heat treatment temperature is 900° C. for 2 hours, and the annealing temperature range is 480° C. for 2 hours.
[0027] (6) After surface treatment, the desired high coercivity NdFeB magnets are obtained.
Embodiment 2
[0028] Example 2: Sintered NdFeB magnets are hot dipped with Nd 60 Dy 20 Al 20 Preparation of High Coercive Force Magnet by Post-Grain Boundary Diffusion Heat Treatment of Alloy
[0029] (1) Clean the surface of the NdFeB magnet;
[0030] (2) Vacuum melting Nd 60 Dy 20 Al 20 alloy (atomic fraction);
[0031] (3) Nd 60 Dy 20 Al 20 The alloy is heated to about 680°C in a vacuum plating tank to melt the alloy into a uniform melt;
[0032] (4) After the magnet is vacuum preheated at about 680°C for about 1-3 minutes, it is immersed in the alloy melt for hot-dip plating, and then cooled after taking it out;
[0033] (5) The magnet is subjected to diffusion and annealing heat treatment in a vacuum furnace. The diffusion heat treatment temperature is 900°C for 2 hours, and the annealing temperature range is 500°C for 2 hours.
[0034] (6) After surface treatment, the desired high coercivity NdFeB magnets are obtained.
Embodiment 3
[0035] Example 3: Hot dip coating of sintered NdFeB magnets with Al 70 Cu 30 Preparation of High Coercive Force Magnet by Post-Grain Boundary Diffusion Heat Treatment of Alloy
[0036] (1) Clean the surface of the NdFeB magnet;
[0037] (2) Vacuum melting Al 70 Cu 30 alloy (atomic fraction);
[0038] (3) Al 70 Cu 30 The alloy is heated to about 640°C in a vacuum plating tank to melt the alloy into a uniform melt;
[0039] (4) After the magnet is vacuum preheated at about 640°C for about 1-3 minutes, it is immersed in the alloy melt for hot-dip plating, and then cooled after taking it out;
[0040] (5) The magnet is subjected to diffusion and annealing heat treatment in a vacuum furnace. The diffusion heat treatment temperature is 900°C for 2 hours, and the annealing temperature range is 500°C for 2 hours.
[0041] (6) After surface treatment, the desired high coercivity NdFeB magnets are obtained.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com