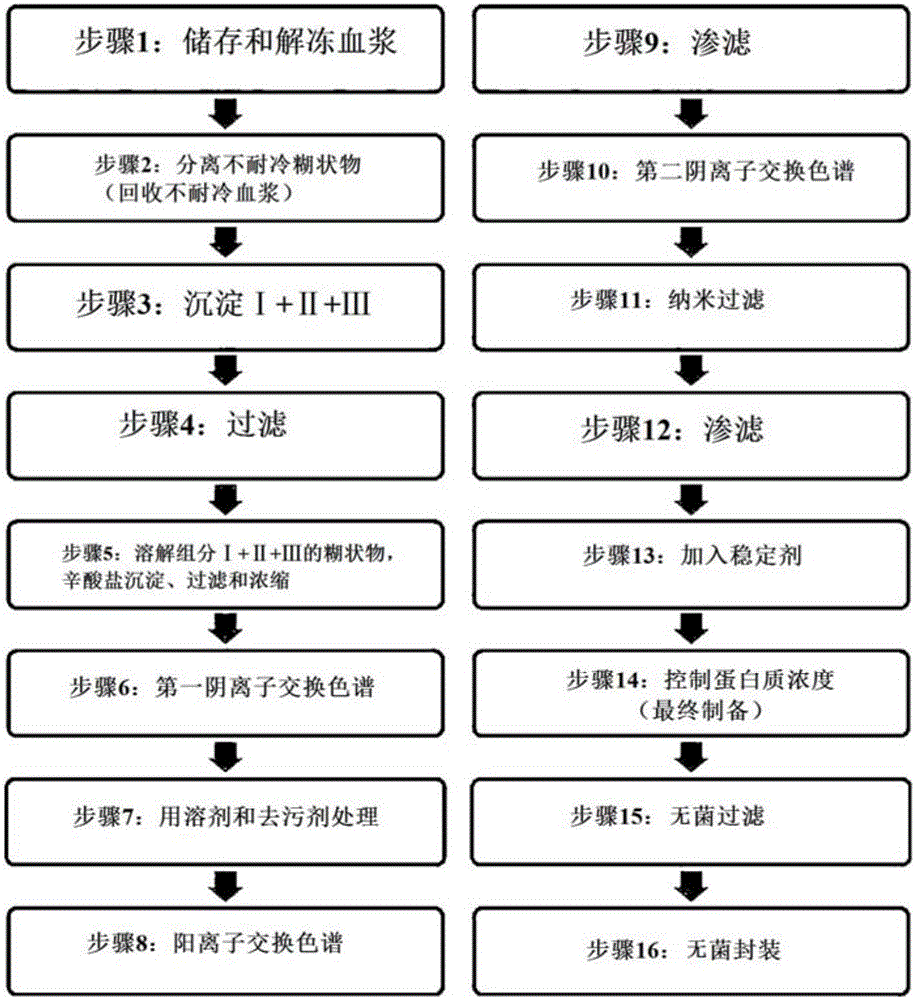
Method for purifying immunoglobulin
A technology of immunoglobulin and cation exchange, which is applied in the direction of immunoglobulin and peptide preparation methods, chemical instruments and methods, etc., which can solve the problems of immunoglobulin pain, reduce the activity of immunoglobulin antibody, complex production, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0076] Example 1: Preparation of intravenous immunoglobulin
[0077] 1-1: Preparation of plasma
[0078] For plasma, use FDA-approved plasma with bioassays that include nucleic acid amplification for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), hepatitis C virus (HCV), hepatitis B virus (HBV), and parvovirus B19 testing and serological testing.
[0079] In the present invention, plasma derived from the United States (Lot No. 600B0491) was used. Plasma was stored at -20°C or below until use. The vials containing the plasma were opened with a bottle cutter and the plasma was thawed by incubation at 1-6°C for 12-72 hours in a jacketed vessel.
[0080] When plasma is thawed under the above conditions, cryopreserves containing fibrinogen and coagulation factors are produced. The resulting condensed protein was removed by centrifugation and the remaining cryolabile plasma was recovered.
[0081] 1-2: Precipitation Ⅰ
[0082] Add 96% ethanol to the cold-labile plasma recovered in ...
Embodiment 2
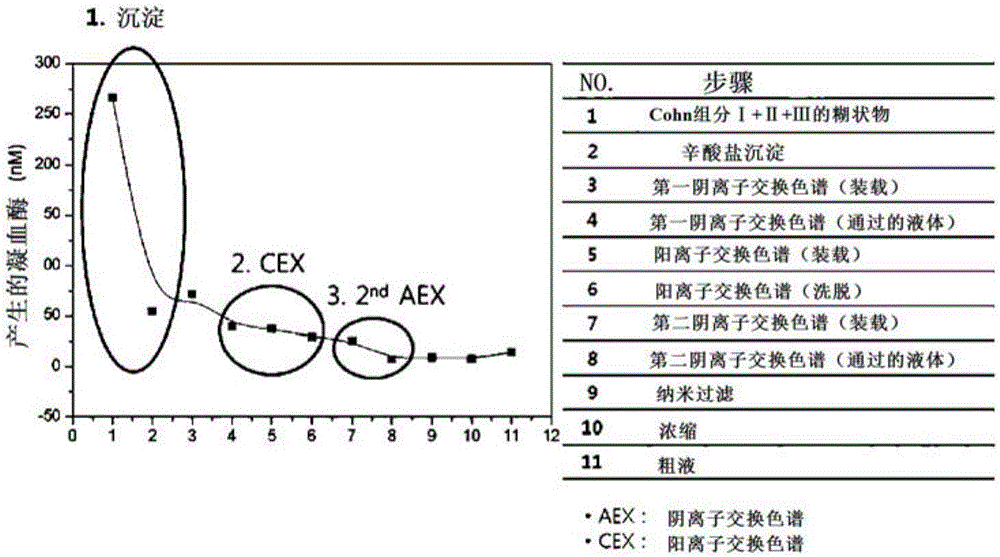
[0113] Example 2: Measurement of thrombin / IgG (thromboembolic risk) produced in immunoglobulin solutions at each preparation step risk)
[0114] The purity (thrombin / IgG) of the immunoglobulin preparation sampled in each preparation step of Example 1 was measured.
[0115] 2-1: Experimental method
[0116] In the present invention, according to the Thrombin Generation scheme (CBER Thrombin Generation protocol 01Experiment (100916)a) provided by CBER (Center for Biological Products Evaluation and Research), one of FDA's six affiliated analytical institutions, implement the immunization in each step of Example 1 Measurement of thromboembolic risk of globulin solutions.
[0117] 2-2: Experimental results
[0118] The immunoglobulin purification process according to the present invention includes Cohn's plasma fractionation method and ion exchange chromatography purification technology. as below figure 2 As shown in Table 1, it can be seen that the octanoate precipita...
Embodiment 3
[0122] Example 3: Measuring the concentration of FXI (human coagulation factor XI) in the filtrate or precipitate at each preparation step
[0123] In order to detect the degree of coagulant removal, the filtrate and precipitate sampled in each preparation step of Example 1 were measured by ELISA (AssayMax Human Factor XI(FXI) ELISAKit; ssaypro, Cat. No. EF1011-1) and SDS-PAGE. Concentration of FXI (human coagulation factor XI).
[0124] Table 2: FXI Content of Purification Process Products
[0125]
[0126] The FXI content of the product of the purification process according to the invention can be measured by ELISA and SDS-PAGE. Therefore, as in Table 2 above and image 3 As shown, FXI was almost removed in zincate precipitation, cation exchange chromatography and anion exchange chromatography.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com