Method for sustainably preparing nanometer cellulose
A nanocellulose and cellulose technology, applied in the field of natural polymer material preparation, can solve the problems of water and air pollution, human irritation, explosion danger, etc. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0045] In the preparation method according to the present invention, the cellulose raw material is reacted with an organic acid to realize hydrolysis and esterification of cellulose, and the organic acid includes: one or more mixtures of malic acid, pyruvic acid, tartaric acid and lactic acid; these acids The pKa values of all are about 3, preferably between 2.49-3.86, are all easily soluble in water, have one or more carboxylic acid groups, are all organic acids with relatively strong acidity, and are safe to the human body and the environment. If the pKa of the acid is too large, the acidity will be insufficient, and the preparation efficiency of nanocellulose will be too low, which is not conducive to realizing industrialization. In addition, these acids are commonly used in the fields of medicine and food industry, and can be obtained through fermentation or widely present in living organisms. They have little toxic and side effects on the human body, and are less corrosi...
Embodiment 1
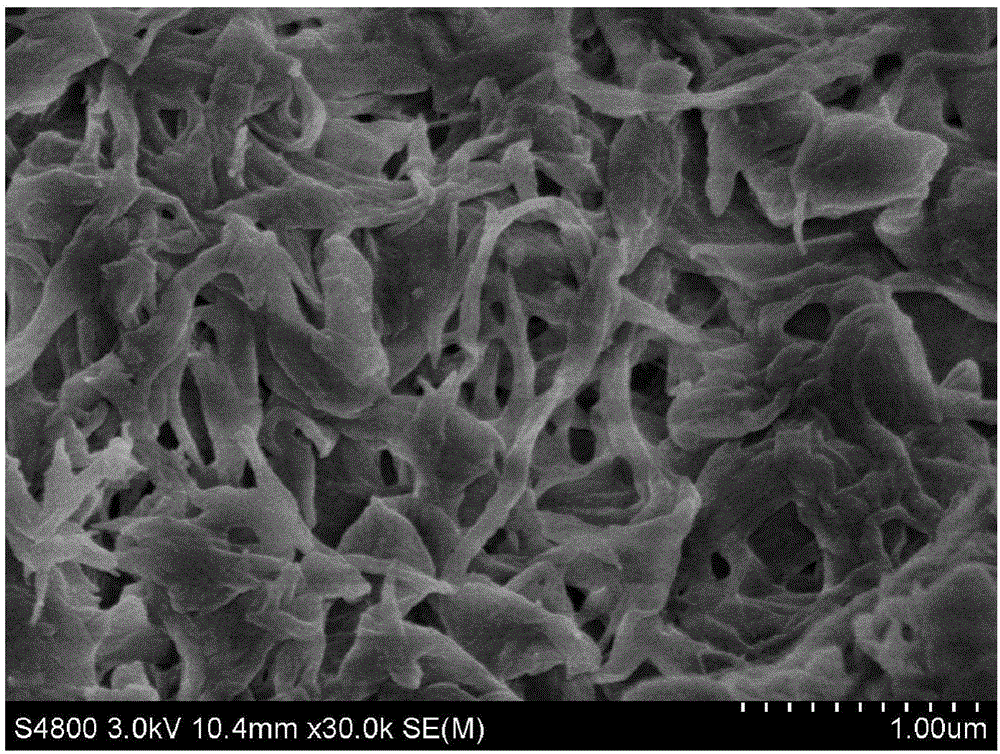
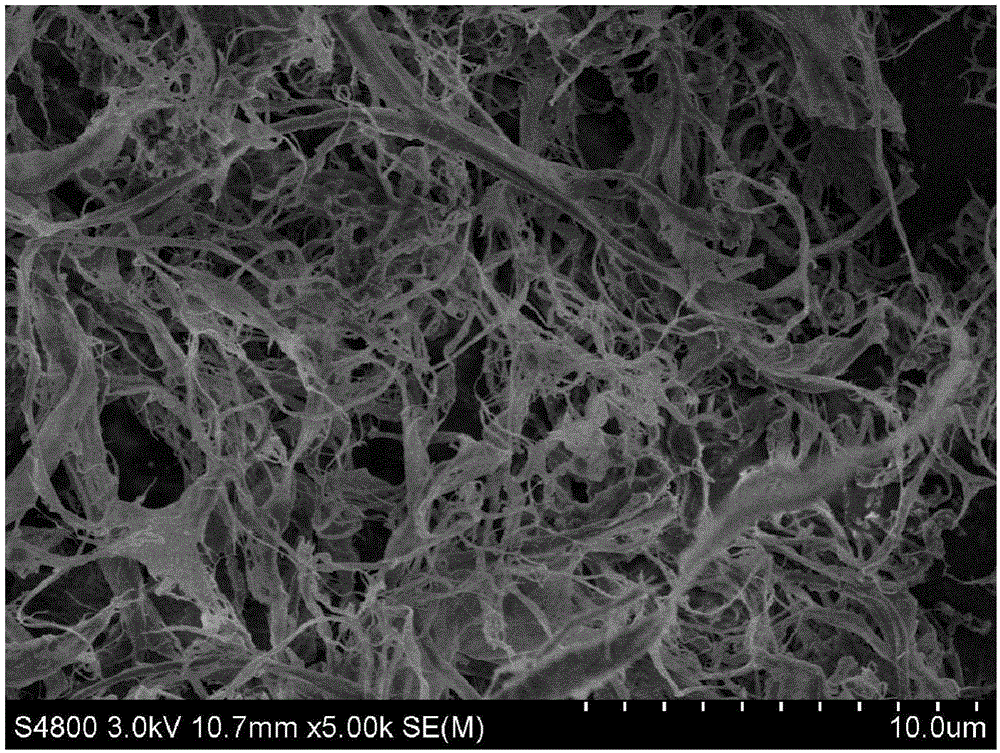
[0049] Weigh 5g of dry bleached eucalyptus pulp into a 250mL round bottom flask, add 100mL of 80wt% tartaric acid solution, and stir magnetically at 120°C for 5h. After the reaction, the flask was quickly placed in a cold water bath to cool to room temperature, and then the reaction mixture was transferred into a centrifuge tube and centrifuged at 8000 rpm for 5 min. The precipitated colloid was centrifugally washed with distilled water to neutrality, and the centrifuged product was diluted to a concentration of 0.2 wt% with distilled water, and then homogenized 6 times at 50 MPa by a high-pressure homogenizer to obtain a viscous product. The yield of cellulose nanofibrils prepared in this example was 71% (relative to the original dry bleached eucalyptus pulp), and the aqueous suspension of cellulose nanofibrils with good dispersibility was left for 24 hours without sedimentation. The transmission electron micrographs (SEM photos) of cellulose nanocrystals and cellulose nanofi...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Weigh 3g of absolute dry furfural residue into a 150mL round bottom flask, add 60mL of 70wt% tartaric acid solution, and stir magnetically at 130°C for 5h. After the reaction, the flask was quickly placed in a cold water bath to cool to room temperature, and then the reaction mixture was transferred into a centrifuge tube and centrifuged at 8000 rpm for 8 min. After the precipitated jelly was centrifuged and washed 3 times with distilled water, the residual acid and degradation by-products were removed by dialysis. The obtained product was diluted with distilled water to a concentration of 5 wt%, and the upper layer of cellulose nanocrystal suspension was taken out after standing for 24 hours. The cellulose solid in the lower layer of the suspension was diluted with distilled water to 0.3 wt%, and then homogenized 7 times by a high-pressure homogenizer at 60 MPa to obtain a viscous cellulose nanofibril product. The total yield of nanocellulose obtained in this example ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com