Nano-flaky porous transition metal oxide/carbon composite material and preparation method thereof
A technology of carbon composite materials and transition metals, which is applied in the field of electrochemical materials, can solve the problems of limiting the practical application of porous transition metal oxide/carbon composite materials, reducing the porosity of composite materials, and the uncontrollable reaction process, etc., to achieve excellent large magnification Effects of discharge performance, suppression of dissolution loss, and good cycle stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Example 1: Preparation of nanosheet-shaped porous trimanganese tetraoxide / carbon composite material and electrochemical performance test of a simulated battery assembled with lithium.
[0028] Put 6mmol of manganese acetate and 100ml of ethylene glycol into the autoclave, then vigorously stir and dissolve, heat at 170°C for 2h, and cool naturally to obtain the white sheet-like manganese-based complex Mn-EG, centrifuge, wash, vacuum dry. Put the obtained manganese-based complex Mn-EG into a tube furnace filled with nitrogen or argon, and thermally decompose it at 500°C for 2 hours to obtain a nanosheet-like structure of trimanganese tetraoxide / carbon composite material.
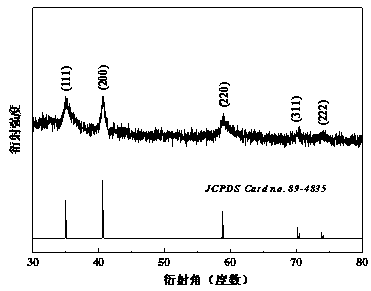
[0029] The resulting product was analyzed by X-ray diffraction as follows: figure 1 The shown diffraction pattern shows that the product is trimanganese tetraoxide without any impurity; the scanning electron micrograph is as follows figure 2 As shown, the nanodisc structure is assembled and stacked b...
Embodiment 2
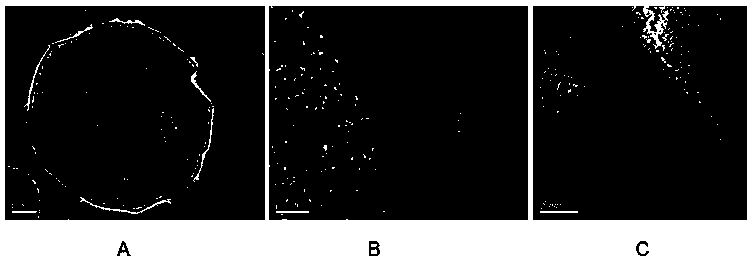
[0032] Replace the manganese acetate in Example 1 with ferrous chloride. The difference is that 5 mmol of ferrous chloride and 100 ml of ethylene glycol are put into a high-pressure reactor and stirred vigorously to dissolve, heated at 100°C for 5 hours, cooled naturally, and decomposed The condition is to thermally decompose at 450° C. for 6 hours, and the other process steps are the same as in Example 1 to obtain the ferric oxide / carbon composite negative electrode material with a nano-flaky structure, and its scanning electron microscope picture is as follows: image 3 As shown in the figure, it can be seen that the material has a nano-disc structure, which is assembled and stacked by spherical particles, and the surface of these nano-spheres is uniformly coated with a layer of carbon film, and the particles are connected by a carbon network. Under the current density of 100 mA / g, the charge and discharge test results of the first three weeks are as follows: Figure 5 shown...
Embodiment 3
[0034]Manganese acetate in Example 1 was replaced by manganese acetate tetrahydrate. The difference was that 60 mmol of manganese acetate tetrahydrate and 100 ml of ethylene glycol were put into a high-pressure reactor and stirred vigorously to dissolve, heated at 180 ° C for 2 hours, cooled naturally, and decomposed conditions In order to thermally decompose at 600°C for 0.5h, the other process steps are the same as in Example 1 to obtain the nanosheet-shaped porous trimanganese tetraoxide / carbon composite material. At a current density of 100 mA / g, the charge and discharge test results for the first three weeks are as follows: Figure 6 shown. The charge and discharge capacities in the first three weeks were 1239 / 1863, 1245 / 1371, and 1252 / 1357 mAh / g, respectively.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com