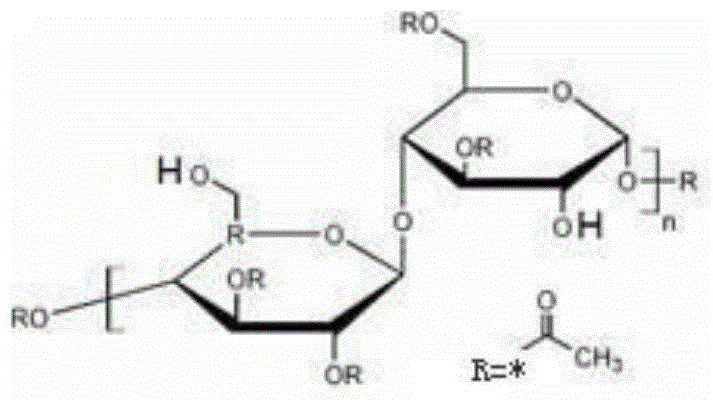
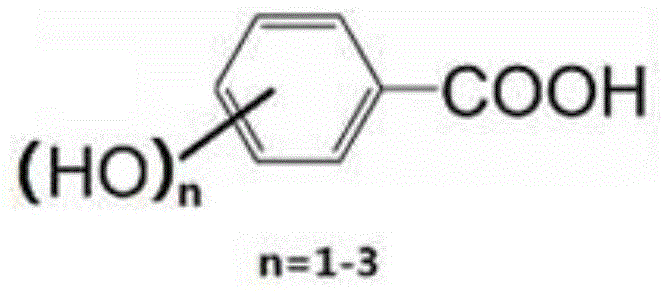
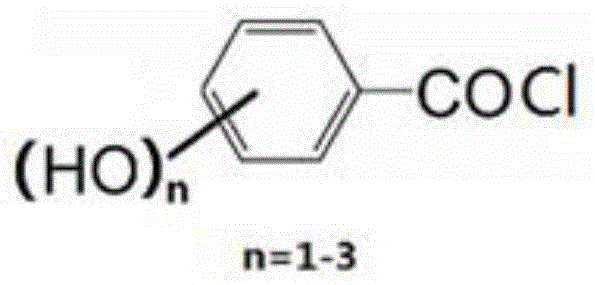
A preparation method of fiber with antibacterial function that can regenerate absorb heavy metal dust
A technology for adsorbing heavy metals and functional fibers, applied in the field of preparation of bacteriostatic functional cellulose acetate, can solve the problems of inability to effectively remove heavy metal dust, limited bacteriostatic effect, difficult biodegradation, etc., so as to inhibit the growth of bacteria and fungi , low cost, good biosafety effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] In the first step, add 10g of cellulose diacetate (80% degree of esterification) into 300mL of acetone, stir and dissolve at room temperature, and slowly and dropwise add 6g of N,N-dimethylformamide at 25-28°C 50 ml of acetone solution, and 50 ml of acetone solution containing 6 g of p-hydroxybenzoyl chloride and 6.5 g of 2,4-dihydroxybenzoyl chloride, were added dropwise in about 25-30 minutes; the reaction was kept at 35-40°C for 120 minutes.
[0035]In the second step, the above-mentioned reaction solution is filtered to remove the hydrochloride precipitate formed by the hydrogen chloride generated by the reaction and the basic catalyst N,N-dimethylformamide, and the filtrate is the acetone solution of polyhydroxy cellulose acetate. Extruded through the spinneret, the solvent is volatilized in the hot air flow, and the fine stream forms fibers. Wash the fiber 3 times with 100 mL of water to wash a small amount of alkaline catalyst adsorbed on the fiber. The fiber wa...
Embodiment 2
[0037] In the first step, add 10g of cellulose diacetate (74% degree of esterification) to 200mL of acetone, stir and dissolve at room temperature, and slowly and simultaneously dropwise add 50mL of acetone solution containing 7g of triethylamine, and 50 mL of acetone solution of 6 g of o-hydroxybenzoyl chloride and 7 g of 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoyl chloride was added dropwise in about 25-30 minutes, and the reaction was kept at 20-22°C for 60 minutes.
[0038] The second step is to filter the above reaction solution to remove the hydrochloride precipitate formed by the reaction hydrogen chloride and the basic catalyst triethylamine. The filtrate is the acetone solution of polyhydroxy cellulose acetate, and the solution is extruded through the spinneret , the solvent is volatilized in the hot air flow, and the fine flow forms fibers. Wash the fiber 3 times with 100 mL of water to wash a small amount of alkaline catalyst adsorbed on the fiber. The fiber was dried at 100° C. for 2...
Embodiment 3
[0040] In the first step, add 10g of cellulose diacetate (95% degree of esterification) into 100mL of dioxane, stir and dissolve at room temperature, and slowly add 50mL of dioxane solution containing 6.1g of pyridine dropwise at 23-25°C , and 50 mL of a dioxane solution containing 3 g of p-hydroxybenzoyl chloride and 10 g of 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoyl chloride, the dropwise addition was completed in about 25-30 minutes, and the reaction was kept at 30-33°C for 120 minutes.
[0041] The second step is to filter the above reaction solution to remove the hydrochloride precipitate formed by the hydrogen chloride generated by the reaction and the basic catalyst pyridine. The filtrate is the dioxane solution of polyhydroxy acetate cellulose, and the solution is extruded through the spinneret , the solvent is volatilized in the hot air flow, and the fine flow forms fibers. Wash the fiber 3 times with 100 mL of water to wash a small amount of alkaline catalyst adsorbed on the fiber. Th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com