New method for obtaining regulatory macrophage
A macrophage, regulatory technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve problems such as changing biological functions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Example 1 Culture, passage and identification of endothelial-like splenic stromal cells (ESSC)
[0024] 1. Materials and methods
[0025] 1. Materials
[0026] C57BL / 6J mice, 1 week old, female, were purchased from the Experimental Animal Center of the Academy of Military Medical Sciences and raised at SPF level. 75% ethanol, normal saline, RPMI-1640 (purchased from Hyclone Company), fetal bovine serum (FBS, Beijing Yuanheng Jinma Biotechnology Development Co., Ltd.), 0.25% trypsin, FACS washing solution, mAnti-PE CD106 (purchased from eBioscience). Vials, test tubes, scissors, tweezers, droppers, pipettes, centrifuges, flow cytometer FACS Calibur (BD, USA), CO 2 Cell incubator (Forma3111 type, Thermo, USA), optical inverted microscope.
[0027] 2. Experimental method:
[0028] (1) Culture and passage of ESSC:
[0029] Aseptically isolate the spleen of 1-week-old C57BL / 6J mice, cut it to a size of 1-2 mm with sterile scissors, and stick it evenly and firmly to the...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Example 2 Co-cultivation of ESSC and bone marrow mononuclear cells
[0036] 1. Materials and methods
[0037] 1. Materials
[0038] C57BL / 6J mice, 6-8 weeks old, female, were purchased from the Experimental Animal Center of the Academy of Military Medical Sciences and raised at SPF level. 75% ethanol, normal saline, RPMI-1640 (purchased from Hyclone Company), fetal bovine serum (FBS, Beijing Yuanheng Jinma Biotechnology Development Co., Ltd.), 0.25% trypsin, FACS washing solution, mAnti-PE CD106 (purchased from eBioscience). Vial, test tube, scissors, tweezers, dropper, pipette, centrifuge, 2ml sterile syringe, flow cytometer FACS Calibur (BD, USA), CO 2 Cell incubator (Forma3111 type, Thermo, USA), optical inverted microscope.
[0039] 2. Experimental method:
[0040] (1) Obtaining bone marrow mononuclear cells
[0041] C57BL / 6J mice were sacrificed by cervical dislocation, soaked in 75% ethanol for 2-3 minutes, wiped off the alcohol with paper, separated the fem...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Characterization of differentiated cells after co-cultivation in Example 3
[0045] 1. Materials and methods
[0046] 1. Materials
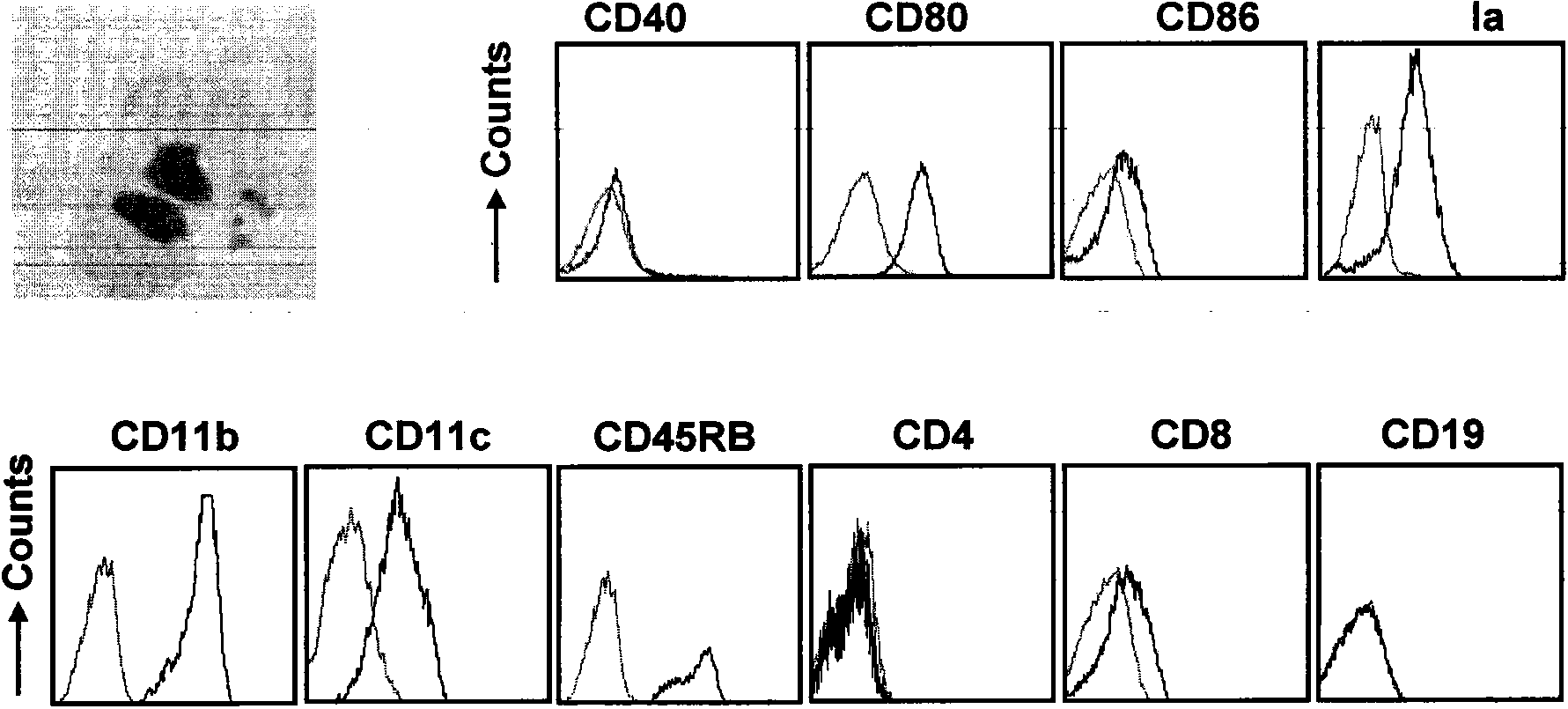
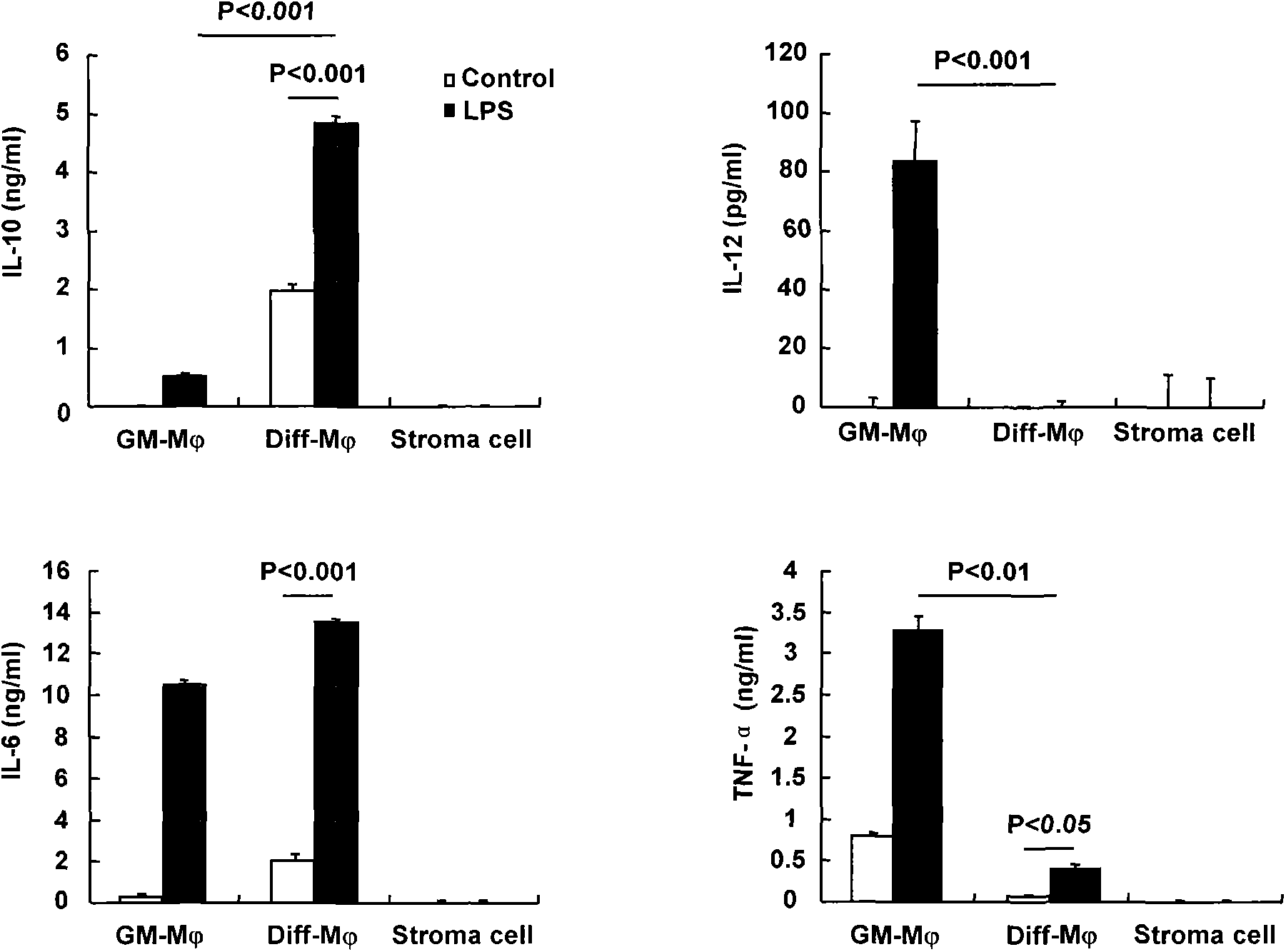
[0047] Anti-mouse F4 / 80, CD14, CD40, CD80, CD86, Ia, CD11b, CD11c, CD45RB, CD4, CD8, CD19 and isotype control antibodies were purchased from eBioscience. IL-6, IL-12, TNF-α ELISA kit (purchased from eBioscience), IL-10 ELISA kit (purchased from Daktronics), LPS (purchased from Sigma). Giemsa reagent.
[0048] 2. Experimental method:
[0049] (1) Giemsa dyeing
[0050] Take differentiated cells 2×10 5 / 50μl 10% RPMI-1640 and throw the cells onto the glass slide with a slide machine; when they are about to dry, fix them with methanol for 10min; When drying, add 100 μl Giemsa stain to the cells and cover it, and stain at room temperature for 30 minutes; after half an hour, pour off the Giemsa stain, wait for it to dry quickly and rinse gently with water, during which time the staining can be observed with a microscope.
[0051] (2)ELIS...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com