Manufacturing method of hydrophilic polyester short fibers for directly spinning spun-laced non-woven fabric
A technology of polyester staple fiber and non-woven fabrics, which is applied in the field of synthetic fibers, and can solve the problem of poor uniformity of treatment agents on the fiber surface and weak adhesion fastness, reduced uniformity of physical and mechanical properties of non-woven fabrics, and processing of spunlace non-woven fabrics. Efficiency reduction and other problems, to achieve the effect of obvious hydrophilic effect, improved hydrophilic effect, and low production cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
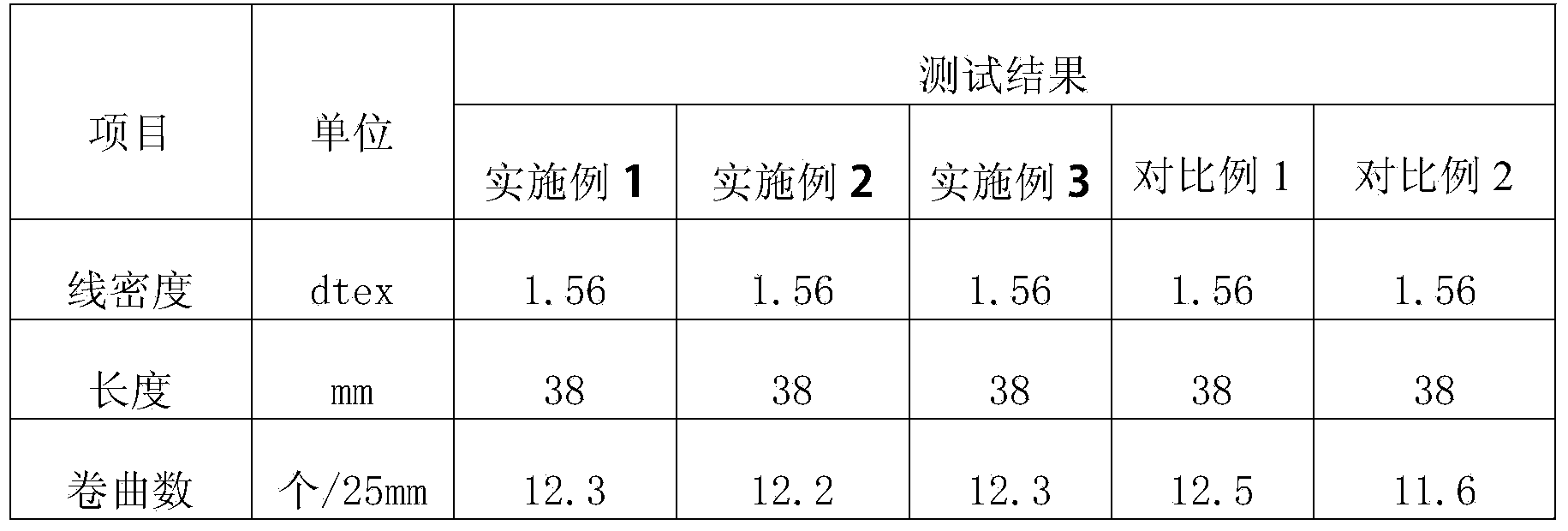
Embodiment 1
[0025] The method for manufacturing hydrophilic polyester staple fibers for direct spinning spunlace nonwovens, the steps include:
[0026] Esterification: Purified terephthalic acid (PTA) and ethylene glycol (EG) are used as raw materials, PTA and EG are prepared according to the molar ratio of 1:1.12 to 1:1.3 for continuous slurry preparation, and esterification tanks are continuously provided for esterification , control the esterification reaction temperature at 261-270°C, and enter the pre-condensation process after the esterification rate exceeds 95%.
[0027]Pre-condensation: In the polymerization production line with a daily output of 200 tons of PET, a certain amount of polycondensation catalyst (antimony ethylene glycol) and matting agent (TiO 2 ), and increase the injection of PEG prepared in EG in the above-mentioned pipeline, the molecular weight is 2000, the addition amount is 0.8%wt of polyester, the pre-condensation reactor is under negative pressure, controlle...
Embodiment 2
[0036] The steps of this example are basically the same as those of Example 1, except that the molecular weight of PEG added in the pre-condensation process is 1500, and the amount added is 1.0%wt of polyester. And the composition of fiber surface finishing agent comprises:
[0037] (1) the aliphatic long-chain ester obtained by the reaction of aliphatic acid and alcohol accounts for 40%wt of the total amount of finishing agent;
[0038] (2) long-chain alkyl polyoxyethylene ether sodium sulfate, accounting for 15%wt of the total amount of finishing agent;
[0039] (3) Fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether, accounting for 45%wt of the total amount of the finishing agent.
Embodiment 3
[0041] The steps of this example are basically the same as those of Example 1, the difference being that the molecular weight of PEG added in the pre-polycondensation process is 1800, and the addition amount is 0.5%wt of polyester. And the composition of fiber surface finishing agent is:
[0042] (1) The aliphatic long-chain ester obtained by the reaction of aliphatic acid and alcohol accounts for 30%wt of the total amount of finishing agent;
[0043] (2) long-chain alkyl polyoxyethylene ether sodium sulfate, accounting for 30%wt of the total amount of finishing agent;
[0044] (3) Fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether, accounting for 40%wt of the total amount of the finishing agent.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com