Stimuli-responsive composite material made from bacterial nano cellulose as well as preparation method and application of stimuli-responsive composite material
A technology of nanocellulose and bacterial cellulose, which is applied in non-active ingredients medical preparations, pharmaceutical formulations, pharmaceutical sciences, etc., can solve high biological toxicity, low biodegradability, surface chemical properties and hydroxyl-rich properties changes, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of low drug permeability and low swelling rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
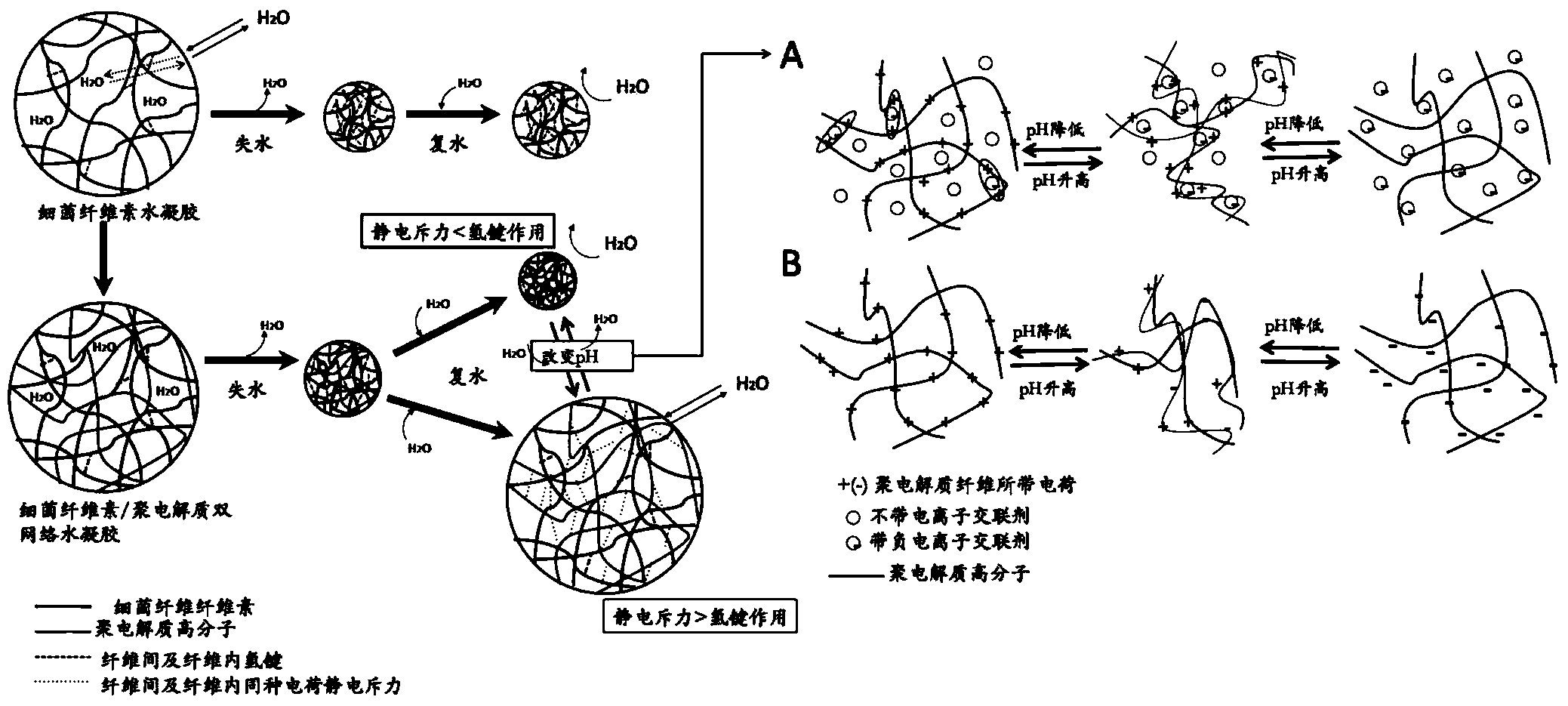
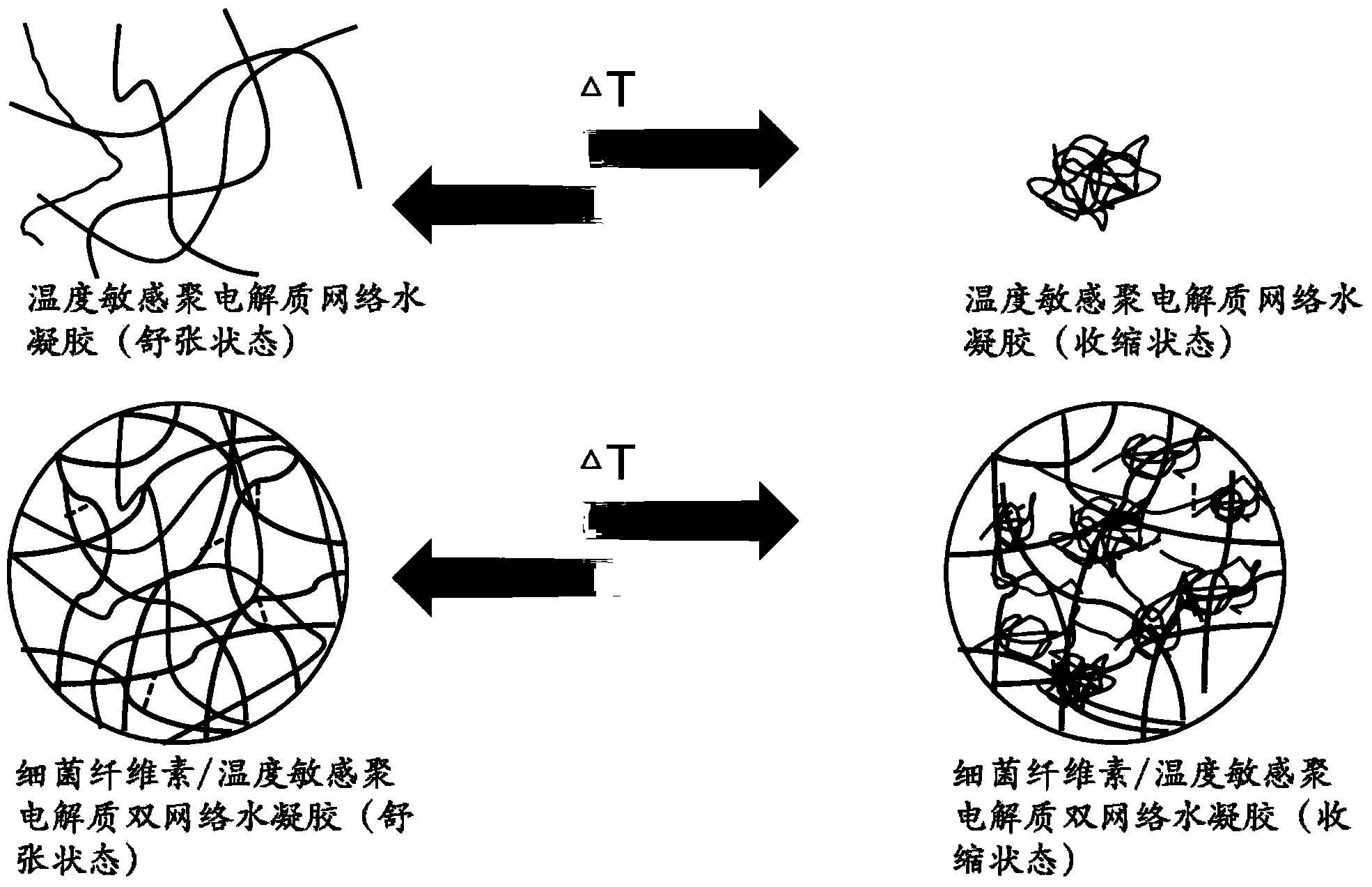
[0054] (1) The selected chitosan has a characteristic viscosity of 50-800mPa·S, a degree of deacetylation of 92.0%, and its isoelectric point pI is 4.9. When the pH is lower than 4.9, the -NH on chitosan 2 Convert to -NH 3 + The ionization balance of is biased toward -NH3 + , zata potential measurement, as the pH decreases, the charging performance of chitosan increases, when the pH is lower than 3.5, the zeta potential exceeds 80mv, the electrostatic repulsion between molecules is larger, and the response swelling pH is pH lower than 3.5.
[0055] (2) The bacterial cellulose hydrogel membrane with a thickness of 2 mm and a water content ratio of 523.9 g / g (water content: material dry weight) was removed by alkali boiling and water boiling to remove bacterial cells and culture medium. The purified bacterial cellulose membrane was dissolved with an appropriate amount of acetic acid to prepare a 2% (w / v) chitosan solution (pH 5.0), soaked at 50°C for 5 days. Rinse the impregn...
Embodiment 2
[0061] (1) According to Example 1, the bacterial cellulose / chitosan hydrogel prepared in steps (1)-(2) was soaked in 2% (w / v) citric acid buffer for 1 hour, so that chitosan Cross-linking with percitrate ions. Then wash off the residual cross-linking solution on the surface with deionized water.
[0062] (2) The obtained bacterial cellulose / chitosan hydrogel was placed on a polyethylene film, and air-dried in a blast drying oven at 25°C to obtain the bacterial cellulose / chitosan interpenetrating composite dry film B.
[0063] (3) According to the method described in step (4) of Example 1, the rehydration swelling performance test was carried out.
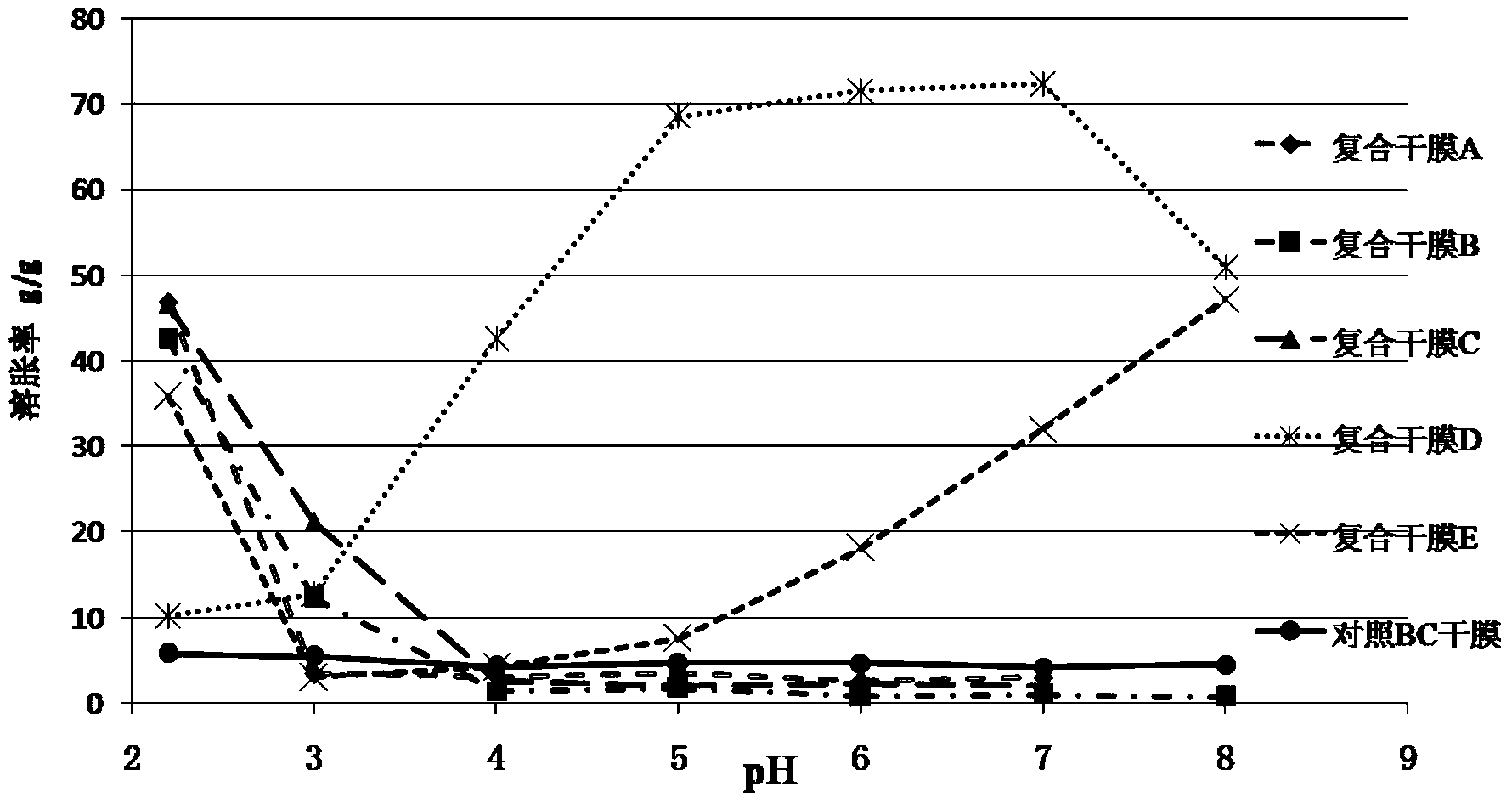
[0064] pH-responsive rehydration characteristics of composite dry film B: (see instructions for swelling rate image 3 , see the physical picture Figure 8 ) After measurement, the composite dry film B, for the composite dry film B between pH 4.0-7.0, does not absorb water and swell, and cannot return to the hydrogel state, and i...
Embodiment 3
[0066] (1) The bacterial cellulose / chitosan hydrogel prepared according to the steps (1)-(2) of Example 1 was soaked in absolute ethanol for 1 hour, so that the chitosan was deposited in the bacterial cellulose network. After the soaked BC was re-soaked in deionized water for 4 hours to replace the ethanol in the hydrogel, the obtained bacterial cellulose / chitosan hydrogel was placed on a polyethylene film and placed in a 25°C blast oven or vacuum Air-dried in a drying oven to obtain a bacterial cellulose / chitosan semi-interpenetrating composite dry film C.
[0067] (2) According to the method described in Example 1, step 4, the rehydration swelling performance test was carried out.
[0068] pH-responsive rehydration characteristics of composite dry film C: (See image 3 ) After testing, the composite dry film C and the composite dry film B between pH 4.0-7.0 do not swell upon water absorption and cannot return to the hydrogel state, and the swelling rates are (2.60, 2.05, 2....
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com