Method for processing roasted sand containing iron, indium and zinc through hot-pressing selective leaching
A selective, zinc calcination technology, applied in the field of hydrometallurgy, can solve the problems of long process flow, low recovery rate, large waste gas treatment volume, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing costs and simple source of raw materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
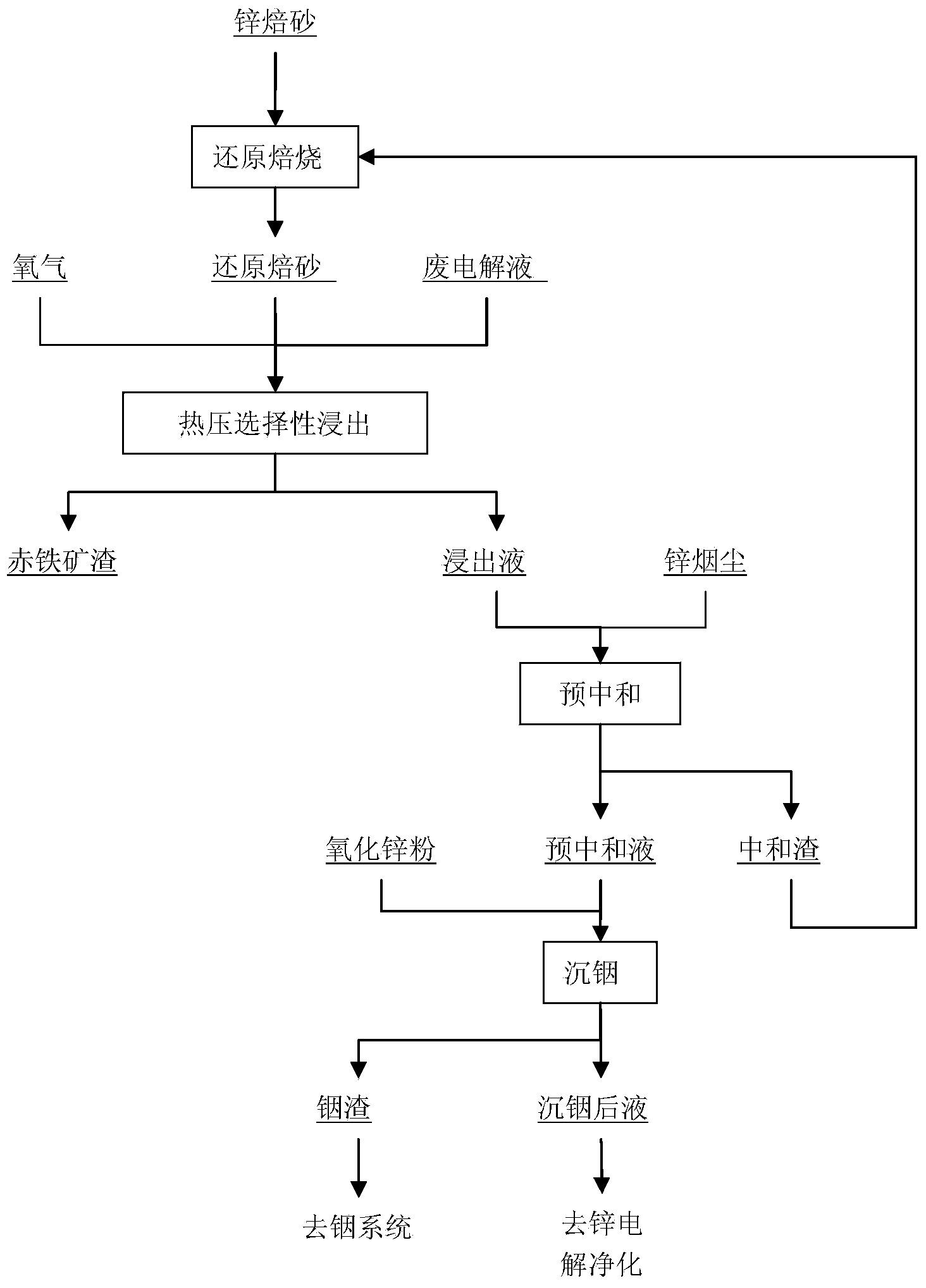
[0019] The first example of the method for hot-pressing selective leaching treatment of iron-containing indium-zinc calcine according to the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0020] Raw materials: high-iron indium-zinc calcine containing Zn52.1%, Fe19.41%, In0.057% somewhere in Guangxi.
[0021] Step 1: The temperature of the rotary kiln is 900°C, zinc calcined sand is mixed with 10% coal powder, and then put into the closed rotary kiln. Lifting plates are installed in the kiln, and the material is rotated in the kiln for 75 minutes to discharge, and the material drops to 100°C in the same reducing atmosphere After that, the reduced zinc calcine is obtained, and the reduction of ferric iron to ferrous iron reaches 92.6%.
[0022] Step 2: The obtained reduced calcine is mixed with an acidic solution, the sulfuric acid content of the acidic solution is 160g / L, the mass ratio of the input reduced calcine to the acidic solution is 1:6, the two are stirred evenly a...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Another example of the method for hot-pressing selective leaching treatment of iron-containing indium-zinc calcine according to the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0028] Raw materials: Calcined sand contains Zn43.8%, Fe22.9%, In0.078%.
[0029] Step 1: Use a rotary kiln to reduce zinc calcine, the temperature of the rotary kiln is 800°C, the amount of reduced coal is 15%, the reduction is 90min, and the reduction rate of ferric iron is 93.8%.
[0030] Step 2: Reducing calcination and mixing with acid solution, the acid solution contains 180% sulfuric acid, the mass ratio of solid to liquid is 1:6, mix well and add to the autoclave.
[0031] Step 3: The reduced calcined sand is subjected to hot-press selective leaching in an autoclave. The leaching rates are: Zn98.9%, Fe8.6%, In94.2%, to obtain 32.8% of iron slag, and the grade of iron in iron slag is 56.1%.
[0032] Step 4: Smoke and dust pre-neutralization, the pre-neutralization end point is 1.5, ...
Embodiment 3
[0035] Another example of the method for hot-pressing selective leaching treatment of iron-containing indium-zinc calcine according to the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0036] Raw materials: Calcined sand contains Zn46.0%, Fe18.02%, In0.049%.
[0037] Step 1: Use a rotary kiln to reduce the zinc calcine, reduce the amount of coal to 8%, reduce the temperature to 850°C, and reduce for 45 minutes to obtain a reduced calcine with a reduction rate of 82.5%.
[0038] Step 2: Reducing calcination and mixing with acid solution, the acid solution contains 180g / L of sulfuric acid, the mass ratio of solid to liquid is 1:5, mix well and add to the autoclave.
[0039] Step 3: The reduced calcine is subjected to hot-press selective leaching in an autoclave. The hot-press reaction temperature is 180°C, the reaction pressure is 1.6Mpa, the leaching solution contains 83.7g / L of zinc, 67mg / L of indium, and 0.62g / L of iron. It is Zn98.8%, In83.2%, Fe1.91%, 38.7% of iron sl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com