Application of Phyllostachys polysaccharide component in the preparation of anti-hepatitis B virus medicine
A bead polysaccharide and anti-hepatitis B technology, applied in the field of medicine, can solve the problems of low price, need for in-depth research, few adverse reactions of Chinese herbal medicine, etc., and achieve the effects of less dosage, improved immunity, and high development value.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Example 1 Extraction of Phyllostachys polysaccharide
[0023] 1 Materials and methods
[0024] 1.1 Materials (omitted)
[0025] 1.2 Experimental method
[0026] 1.2.1 Phyllostachys pretreatment
[0027] The whole plant of Phyllostachys phylloxera was washed with distilled water to remove the soil, dried at 50°C, crushed, and sealed for later use. Its powder is yellow-green.
[0028] 1.2.2 Extraction method of Phyllostachys polysaccharide
[0029] Petroleum ether reflux at 80 °C to degrease → 95% ethanol at 80 °C to remove small molecule sugars → 90 °C water to reflux for three times, combine the filtrate for three times and centrifuge at 4000r / min, concentrate to 1 / 4 volume → add 4 times the volume of 95% ethanol , stand still for 24 hours, centrifuge, redissolve in distilled water → remove protein by sevag method (chloroform: n-butanol = 4:1, polysaccharide solution: mixed solution = 3:1), magnetically stir for 30 minutes, fully stand for stratification, repeat 7~...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Example 2 Separation and Purification of Phyllostachys polysaccharide
[0060] 1 Materials and methods
[0061] 1.1 Materials (omitted)
[0062] 1.2. Experimental method
[0063] 1.2.1 DEAE-52 column separation
[0064] 1.2.1.1 DEAE-52 filler pretreatment
[0065] Soak DEAE-52 cellulose filler in distilled water for 48 hours, change the water once every 4 to 5 hours, remove suspended impurities by pouring method, and then carry out alkali-acid-alkali treatment. First soak in 0.5 mol / L NaOH solution for 30 minutes, then wash with distilled water until neutral, then soak in 0.5 mol / L HCl solution for 30 minutes, then wash with distilled water until neutral, and finally soak in 0.5 mol / L NaOH solution for 30 minutes After washing with distilled water to neutrality, OH - type cellulose. Wet column packing (column size 500×50mm), equilibrated with distilled water for 48 hours, avoiding bubbles and faults during column packing.
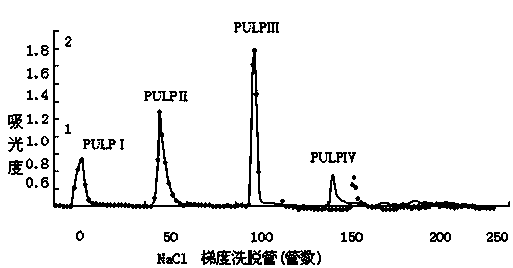
[0066] 1.2.1.2 Separation and purificat...
Embodiment 3
[0086] Embodiment 3 Physicochemical properties and structural analysis of PULPⅡ
[0087] 1. Physical and chemical properties
[0088] PULPⅡ is a khaki powder, easy to absorb moisture. Soluble in water, insoluble in ethanol, acetone and other organic solvents. Molish reaction, phenol-sulfuric acid reaction, sulfuric acid-carbazole reaction are positive, ninhydrin reaction, iodine-potassium iodide reaction, Fehling reaction, ferric chloride reaction and sulfate group reaction are negative.
[0089] The physical and chemical properties, uronic acid content determination, elemental analysis, infrared and ultraviolet, and HPLC comprehensive analysis show that PULP II is a kind of acidic polysaccharide that does not contain N and S elements, and the relative average molecular weight is 579962.6.
[0090] 2. Infrared absorption spectrum of PULPⅡ
[0091] Infrared spectrum shows that PULP Ⅱ is at 3100~3500 cm -1 , 2800~2900 cm -1 , 1400~1530 cm -1 , 1000~1100 cm -1 There are obvi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| absorbance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com