Collagen-g-polymer/Ag multi-hole nano antibacterial film material and preparation method thereof
A collagen, film material technology, applied in the fields of botanical equipment and methods, chemicals for biological control, animal repellants, etc., to achieve the effect of good wetting performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
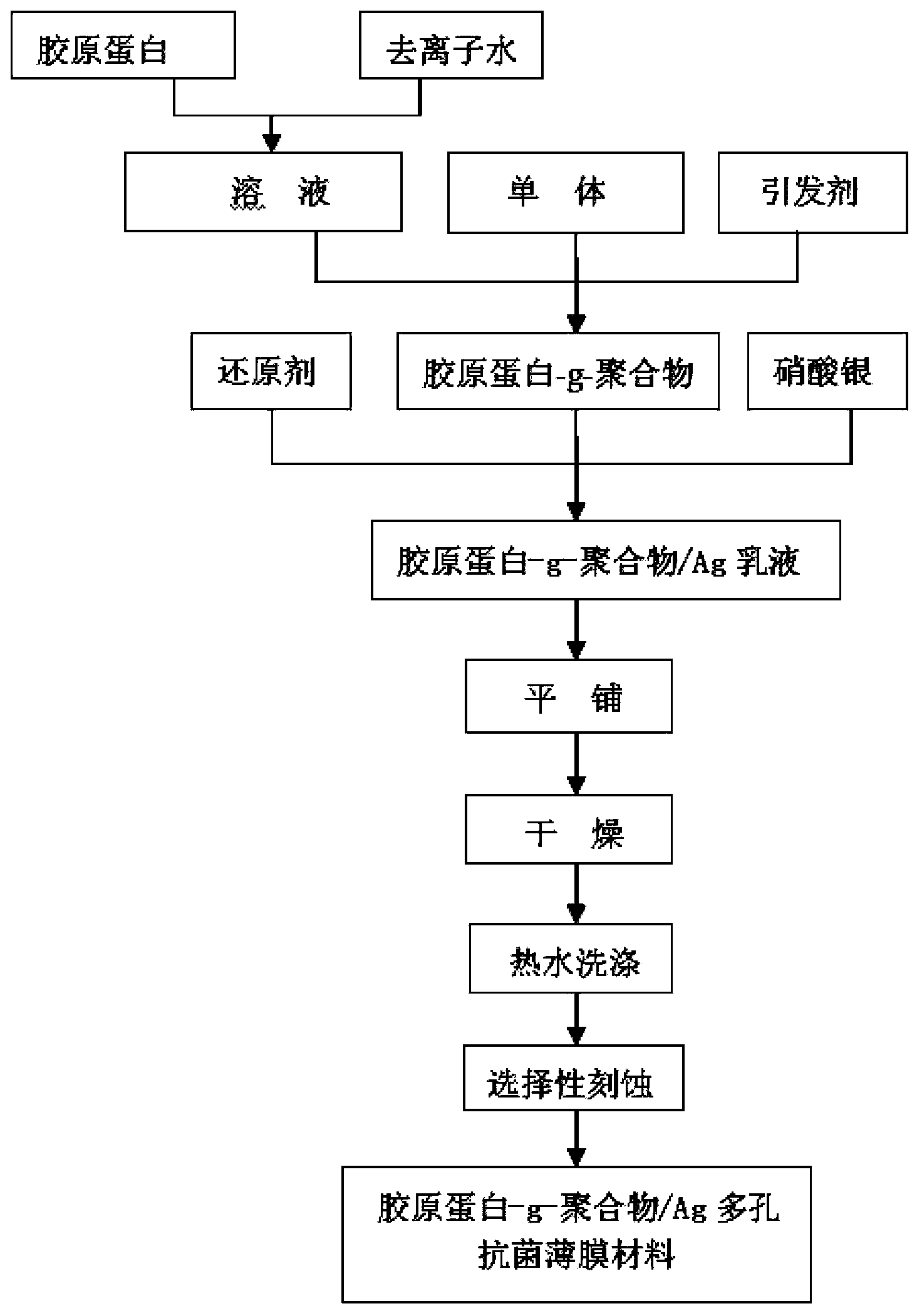
[0027] Step 1. Dissolve 4g collagen (commercially available) in 96 mL 40~60 o C hot water;
[0028] Step 2, add 0.2g styrene monomer to step 1, pass N under constant temperature 2 ;
[0029] Step 3, add 0.002g potassium persulfate initiator in the mixed solution of step 2, 60 o C reaction 3h;
[0030] Step 4, add 4mL of 1g / L silver nitrate solution to the mixed solution of step 3,
[0031] Step 5, adding sodium borohydride reducing agent to step 4 solution;
[0032] Step 6, cooling to room temperature, spreading it on the glass slide, and solidifying it to form a film;
[0033] Step 7, remove unreacted collagen and residual potassium persulfate initiator in the film with hot water;
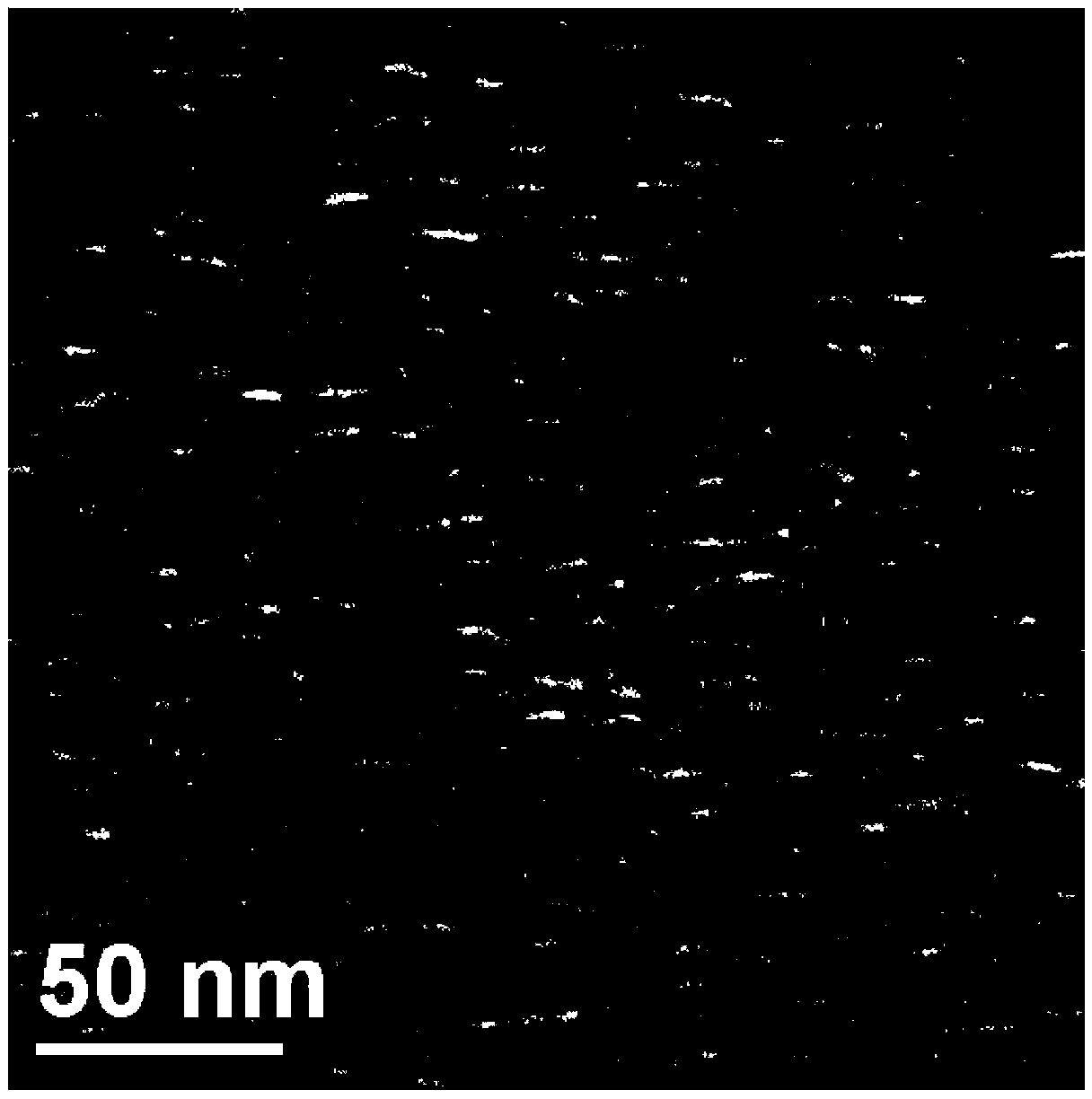
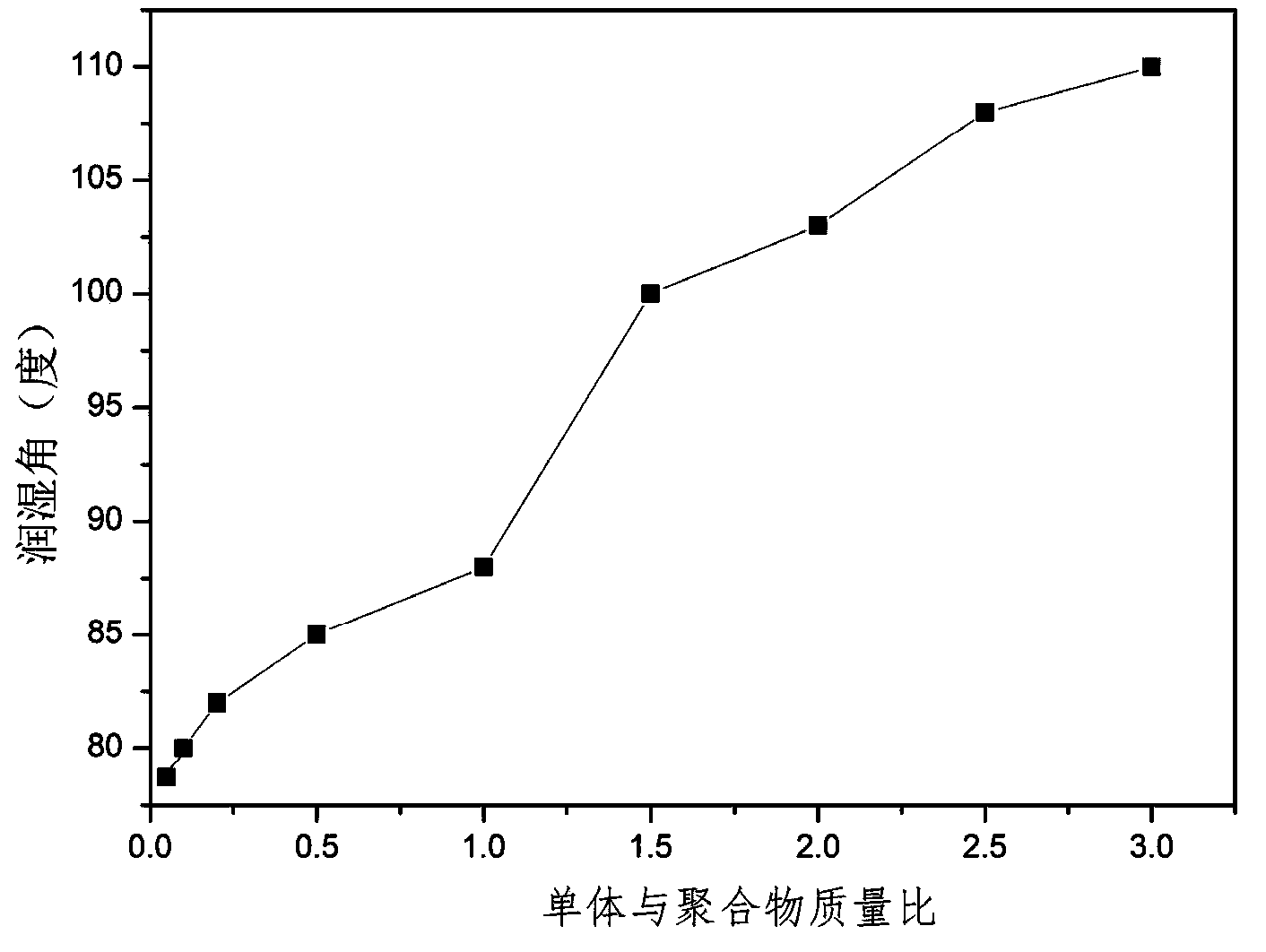
[0034] Step 8, place the film obtained in step 7 in a Soxhlet extractor, etch the by-product polystyrene microspheres with acetone solvent to obtain a porous collagen-g-polymer / Ag antibacterial film material, collagen grafted The ratio is 4%, and the wetting angle is 76 o , the size of Ag ...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Step 1. Dissolve 1g collagen in 99 mL 40~60 o C hot water;
[0037] Step 2, add 1g vinyl acetate monomer in step 1, lead N under constant temperature 2 ;
[0038] Step 3, add 0.01g hydrogen peroxide solution (50%) in the mixed solution of step 2 as initiator, 80 o C reaction 1h;
[0039] Step 4, add 5mL of 1g / L silver nitrate solution to the mixed solution of step 3;
[0040] Step 5, adding potassium borohydride reducing agent to step 4 solution;
[0041] Step 6, cooling to room temperature, spreading it on the glass slide, and solidifying it to form a film;
[0042] Step 7, removing unreacted collagen in the film with hot water;
[0043] Step 8, place the film obtained in step 7 in a Soxhlet extractor, and after etching the by-product polyvinyl acetate microspheres with acetone solvent, the porous collagen-g-polymer / Ag antibacterial film material is obtained, and the collagen is bonded to The branch rate is 42%, and the wetting angle is 88 o , the size of Ag na...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Step 1. Dissolve 1g collagen in 99mL 40~60 o C hot water;
[0046] Step 2, add 0.2g vinyl chloride monomer to step 1, pass N under constant temperature 2 ;
[0047] Step 3, add 0.001g copper potassium dihydroxydiperiodate in the mixed solution of step 2 as initiator, 100 o C reaction 1h;
[0048] Step 4, add 1mL of 1g / L silver nitrate solution to the mixed solution in step 3;
[0049] Step 5, adding hydrazine hydrate reducing agent to step 4 solution;
[0050] Step 6, cooling to room temperature, spreading it on the glass slide, and solidifying it to form a film;
[0051] Step 7, removing unreacted collagen and dihydroxy diperiodate copper potassium initiator in the film with hot water;
[0052] Step 8, place the film obtained in step 7 in a Soxhlet extractor, and after etching the by-product polyvinyl chloride microspheres with chloroform solvent, obtain the porous collagen-g-polymer / Ag antibacterial film material, collagen grafted The ratio is 15%, and the wett...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com