Microcrystal catechin and preparation method thereof
A technology of catechins and microcrystals, which is applied in the field of medicine, can solve the problems of unresolved tea polyphenols anti-oxidation, unstable quality of tea polyphenols, and poor functionality, so as to achieve excellent anti-oxidation performance and prevent atherosclerosis Strong effect of hardening and quality stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] Embodiment 1: Preparation of the microcrystalline catechin of the present invention
[0056] The specific process is as follows:
[0057] (1) Steaming: Put green tea and deionized water into a pot to heat and cook, so that the effective substances in the tea can be dissolved in water. The ratio of deionized water to dry green tea is (2.5-3): 1, and the heating temperature is 85-100 ℃, the heating time is 15-30 minutes, then filter the tea soup into the container.
[0058](2) Membrane technology: The filtered tea soup is treated with an ultrafiltration membrane to remove impurities in the tea soup and concentrate it to 40-50% strong tea soup.
[0059] (3) Ethyl acetate extraction: pump the strong tea soup obtained in step (2) into the extraction tower, add ethyl acetate to extract catechins, the weight ratio of ethyl acetate to strong tea soup is 2:1, and the extraction time is 50- 80 minutes.
[0060] (4) Recovery of ethyl acetate: pump the two liquids obtained in st...
Embodiment 2
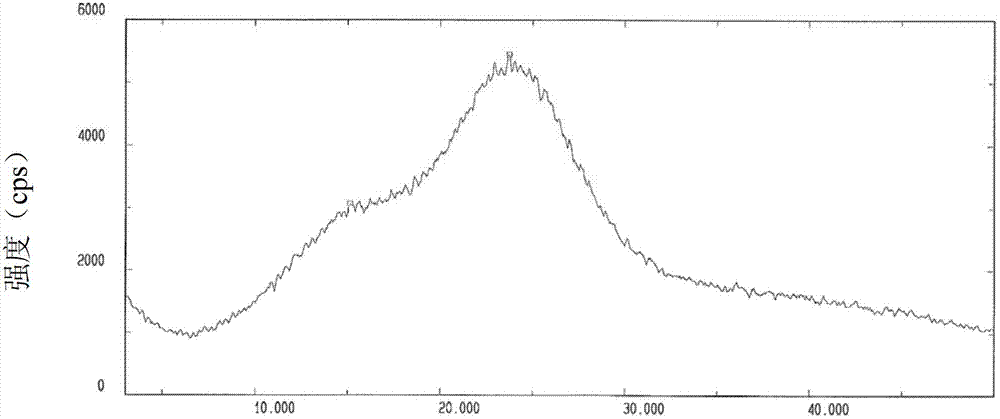
[0063] Embodiment 2: X-ray powder diffraction spectroscopic analysis of the microcrystalline catechin of the present invention
[0064] The microcrystalline catechin prepared in Example 1 was subjected to X-ray powder diffraction, using Cu-Kα radiation, and sent to the Central Laboratory of Nankai University for X-ray diffraction analysis.
[0065] Instrument: Rigaku D / MAX-2500 diffractometer
[0066] Target: Cu-Kα radiation (λ=1.5405A), 2θ=3°~50°
[0067] Step angle: 0.04°
[0068] Pipe pressure: 40KV
[0069] Pipe flow: 100mA
[0070] Scanning speed: 8° / min
[0071] Filter: graphite monochromator
[0072] Counter: Blink Counter
[0073] The microcrystalline catechin x-ray powder diffraction pattern prepared by embodiment 1 is as follows figure 1 As shown, using Cu-Kα radiation, the X-ray powder diffraction spectral characteristics expressed in 2 θ angles are shown in the table below.
[0074] 2θ
[0075] The sample (TPI) was analyzed to be microcrystalline....
Embodiment 3
[0076] Example 3: Microcrystalline catechin component analysis
[0077] The content of the microcrystalline catechin of the present invention, composition determination are as follows:
[0078] Measurement items
standard
The measurement results
test results
Polyphenol content%
≥40
97.1
Standards compliant
Loss on drying%
≤5.0
4.4
Standards compliant
Ignition residue %
≤0.5
0.13
Standards compliant
Arsenic (calculated as AS)%
≤0.0002
0.00003
Standards compliant
Lead (calculated as Pb)%
≤0.0004
<0.00004
Standards compliant
[0079] Microcrystalline catechins (tea polyphenols) also have a strong hydrogen-supplying capacity, utilizing the ability of catechins to scavenge free radicals up to 98% in the xanthine-xanthine oxidase system. The Institute of Molecular Medicine of Zhejiang University ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com