Wastewater treatment method by ultrasonic reinforcement micron-scale iron-copper bimetallic particle
A micron-scale wastewater treatment technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water/sewage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problem of limited formation of macroscopic primary batteries and galvanic corrosion, and unfavorable fillers in fixed bed structures Fluidization, waste water treatment efficiency reduction and other problems, to achieve the effect of improving waste water treatment efficiency, enhancing mass transfer efficiency, and promoting water phase combustion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
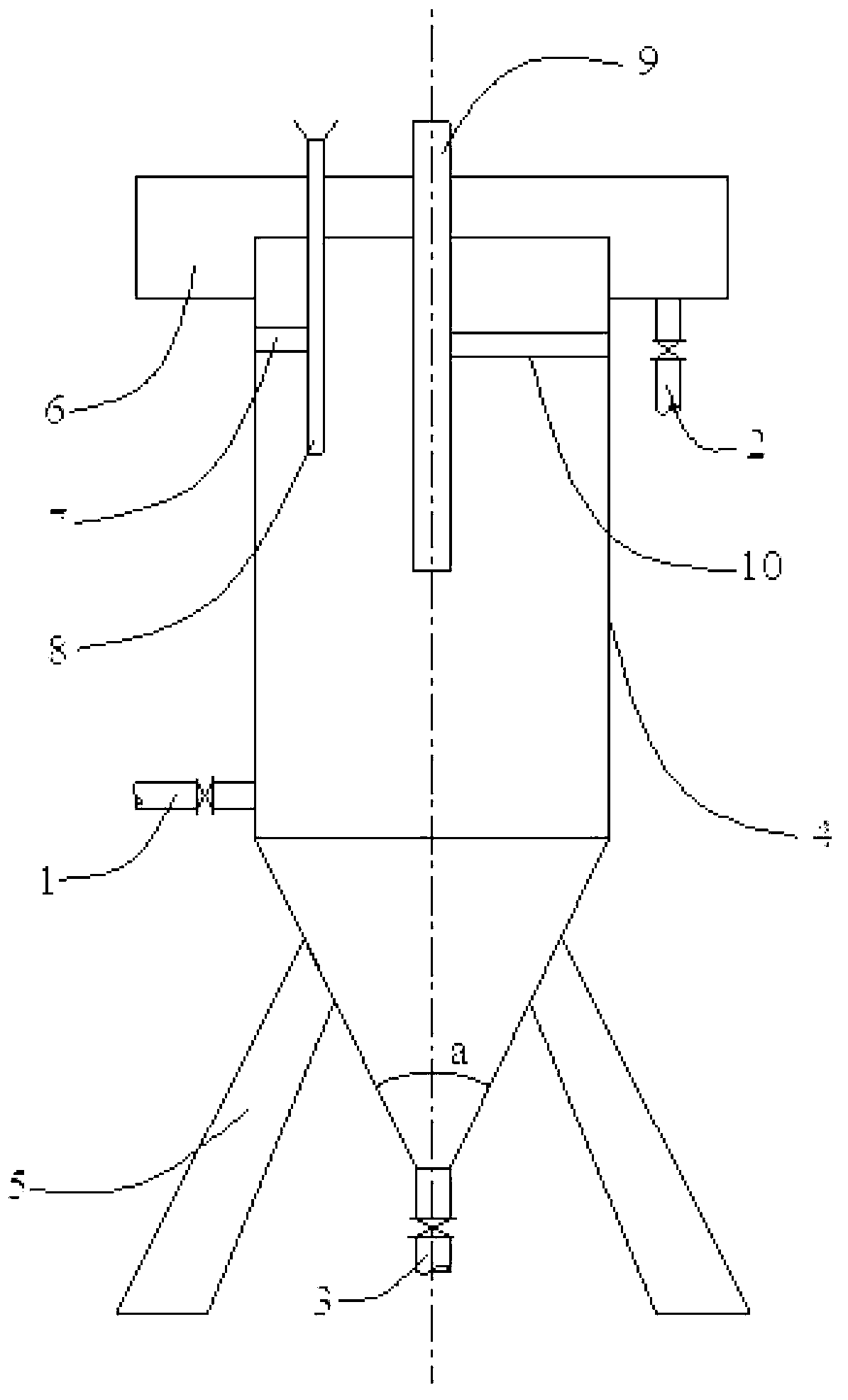
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] This embodiment uses the method of the present invention to treat simulated p-nitrophenol wastewater. The p-nitrophenol concentration in the simulated wastewater is 5000 mg / L, the COD concentration is about 8000 mg / L, and the electrolyte Na 2 SO 4 The concentration is 50 mmol / L, and the pH value of the simulated wastewater is adjusted to 6.0 with 10% sulfuric acid.
[0032] The preparation method of the micron-sized iron-copper bimetallic particles is as follows:
[0033] Add iron powder with an average particle size of 50 μm to the copper sulfate aqueous solution at a stirring speed of 500 r / min at room temperature and normal pressure. After the iron powder is added, continue to stir for 15 minutes, and then let it settle for 15 minutes before being discharged. Clear liquid, wash the obtained solid particles with deionized water to remove the salt impurities on the surface to obtain micron-sized iron-copper bimetallic particles. The obtained micron-scale iron-copper bimetall...
Embodiment 2
[0039] This embodiment uses the method of the present invention to treat acid orange 7 simulated wastewater. The acid orange 7 concentration in the simulated wastewater is 10000 mg / L, the COD concentration is about 9300 mg / L, and the electrolyte Na 2 SO 4 The concentration is 50 mmol / L, and the pH value of the simulated wastewater is adjusted to 8.0 with 2 mol / L sodium hydroxide solution.
[0040] The preparation method of the micron-sized iron-copper bimetallic particles is as follows:
[0041] Add iron powder with an average particle size of 500 μm to the copper sulfite aqueous solution at a stirring speed of 500 r / min at room temperature and normal pressure. After the iron powder is added, continue to stir for 20 minutes, and then let it settle for 12 minutes before being discharged The supernatant is washed with tap water to remove the salt impurities on the surface of the solid particles, and then micron-sized iron-copper bimetallic particles are obtained. The obtained micron-s...
Embodiment 3
[0047] This embodiment uses the method of the present invention to treat the simulated reactive brilliant red wastewater. The concentration of reactive brilliant red in the simulated wastewater is 10000 mg / L, the COD concentration is about 9600 mg / L, and the electrolyte Na 2 SO 4 The concentration is 50 mmol / L, and the pH value of the simulated wastewater is adjusted to 7.0 with 2 mol / L sodium hydroxide solution.
[0048] The preparation method of the micron-sized iron-copper bimetallic particles is as follows:
[0049] Add iron powder with an average particle size of 900 μm to the copper chloride aqueous solution at a stirring speed of 500 r / min at room temperature and normal pressure. After the iron powder is added, continue to stir for 20 minutes, and then leave to settle for 5 minutes before being discharged The supernatant is washed with tap water to remove the salt impurities on the surface of the solid particles to obtain micron-sized iron-copper bimetallic particles. The obt...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com