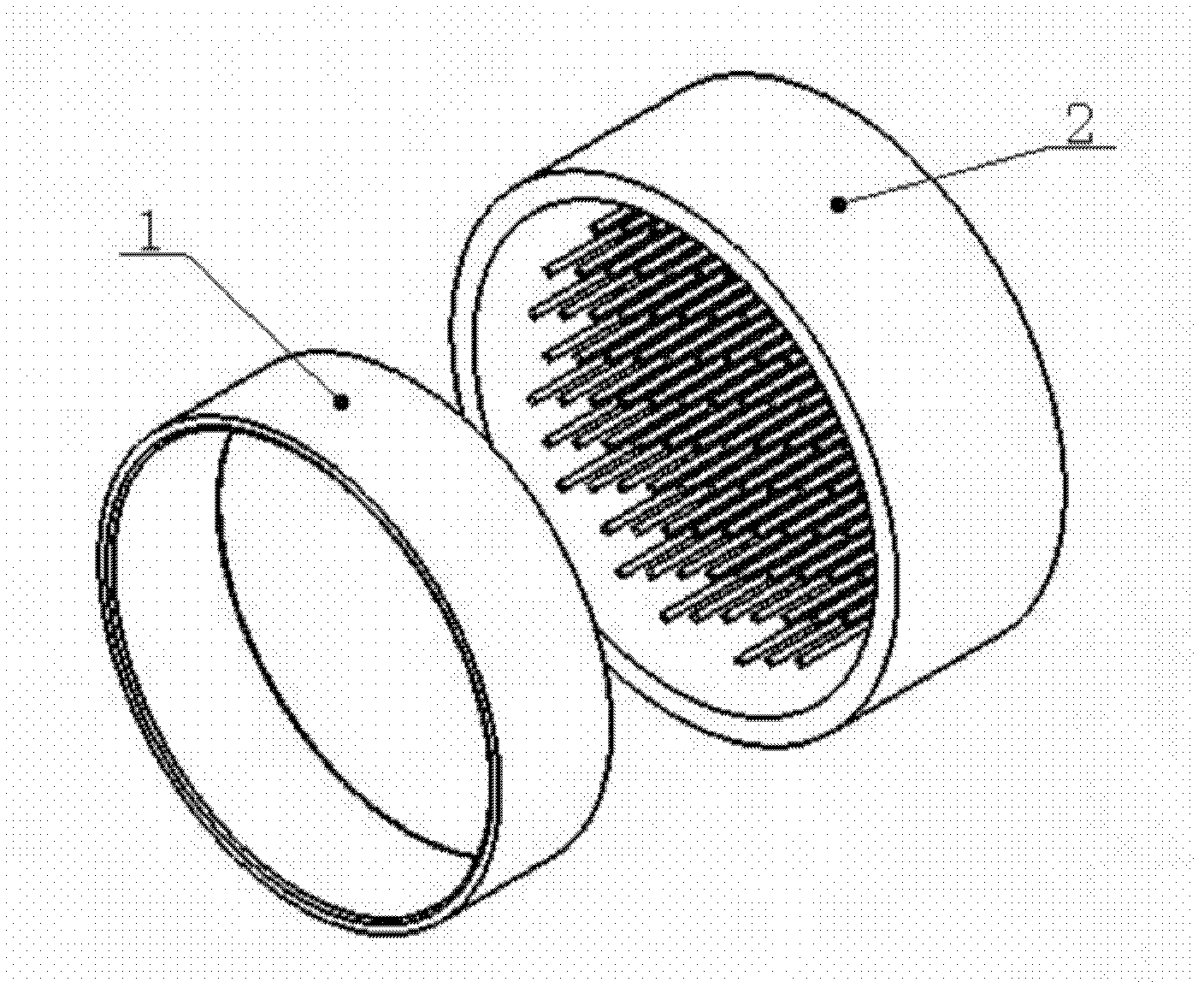
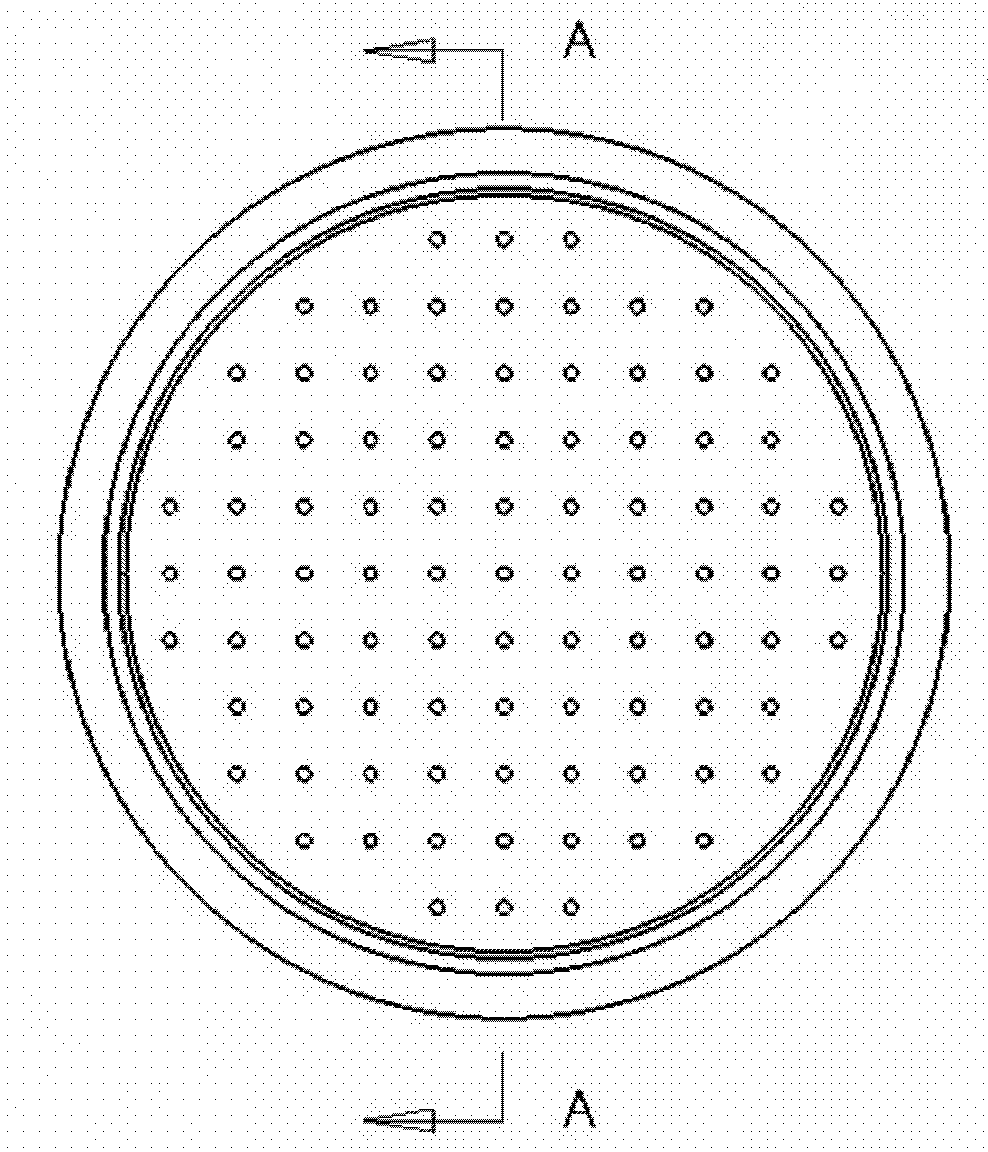
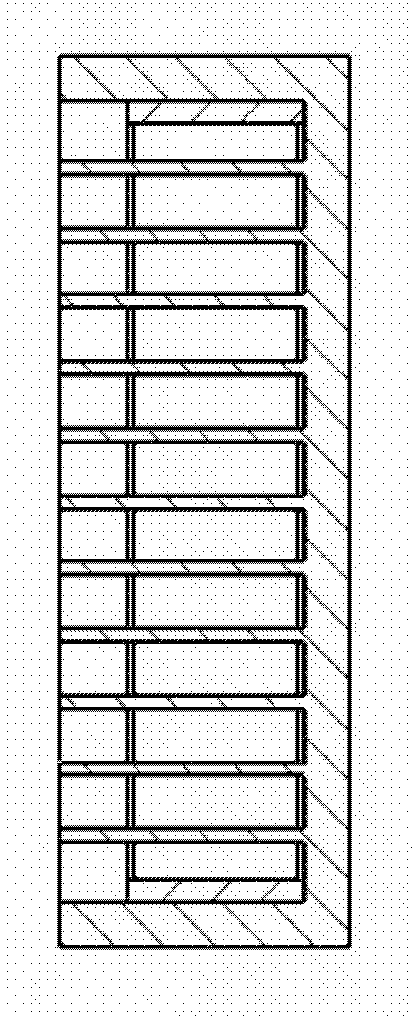
Preparation method of precursor of composite tissues and organs with multichannel multilayer cell structure
A cell structure and composite tissue technology, applied in the direction of prosthesis, medical science, etc., can solve the problems of long time, difficult infiltration of cells, uneven distribution of cells, etc., and achieve the effect of excellent mechanical properties and excellent biocompatibility.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Embodiment 1: 1) Prepare a series of brass material matching combination molds with different sizes; 2) Prepare 50% (W / V) PLGA / 14dioxane solution, add 1% (W / W) Heparin is poured into the master mold. Use the dry film method of natural air drying to form the PLGA bottom support; 2) Prepare the fibrinogen solution, put the inner mold into the main mold, and inject the mixture of gelatin / fibrinogen and endothelial cells into the combined mold, and the cell density is 1× 10 7 3) Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF0.5ng / mL), human platelet-derived growth factor (BB or PDGF-BB 50ng / mL), transforming growth factor β1 (TGFβ1 10ng / mL) and basic fibroblast Cell growth factor (b-FGF 2.5ng / mL). Make the cell natural polymer material evenly distributed, inject thrombin solution (20IU / mL) to make the cell / natural polymer material layer form a stable structure; 4) remove the inner mold, and place the cell / natural polymer material layer on the surface and the inner mold The remaining gaps...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2: 1) Silicon rubber is used to prepare a matching combined mold for multi-channel tissue and organ precursors; 2) 25% polyurethane / ethylene glycol solution is prepared, 5% paclitaxel is added, stirred evenly, and poured into the main mold. Use the cell culture fluid extraction method to form the outer polyurethane layer, and put it into the inner mold; 3) prepare the fibrinogen / endothelial cell mixture containing 5% paclitaxel (the cell density is 1 × 10 7 pcs / mL), perfuse into the combination mold and add thrombin solution (20IU / mL) to form the first layer of main material; 4) inject the mixture of gelatin / fibrinogen and adipose stem cells on the first layer of main material, the cell density 1×10 6 cells / mL to form the second layer of main material; 5) inject fibrinogen / hepatocyte mixture (cell density is 1×10) on the second layer of main material 7 pcs / mL), soak the molded object with thrombin solution (10IU / mL) for 1 minute to form a three-layer structure ...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Embodiment 3: 1) Prepare a series of polytetrafluoroethylene matching combination molds with different sizes; 2) Prepare a polylactic acid / isopropanol solution with a concentration of 30%, add 30% sodium citrate, stir evenly, pour into inside the master mold. Use the PBS extraction method to form the bottom support, and put it into the inner mold; 3) prepare the collagen / endothelial cell mixture of 1% sodium citrate (the cell density is 1×10 7 per mL), poured into the combination mold, and placed at 37°C for 10 minutes to stabilize the structure of the collagen / endothelial cell mixture and form the first layer of main material; 4) inject the collagen / smooth muscle cell mixture on the first layer of main material ( Cell density is 1 x 10 7 cells / mL); placed at 37°C for 10 minutes to stabilize the structure of the collagen / smooth muscle cell mixture and form the second layer of main material; 1), the cell density is 1×10 6 cells / mL, placed in an incubator at 37°C for 1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com