Preparation method and use of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) microspheres as nucleic acid vaccine vectors
A nucleic acid vaccine and microsphere technology, applied in the field of vaccine carrier system and preparation, can solve the problems of limited size of loaded foreign genes, lack of tissue specificity, low gene transfer efficiency, etc., and achieves convenient preparation, strong versatility, The effect of simple ingredients
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Preparation of PLGA magnetic microspheres
[0042] FeCl 3 and FeCl 2 The solution is mixed according to the molar ratio of 1:2 (Fe 2+ Slight excess), under nitrogen atmosphere, after 30min in 60°C water bath, quickly add a certain amount of ammonia water to the mixture under vigorous stirring, and continue stirring for 30min under nitrogen atmosphere. Stir. After the reaction is completed, use a commercial permanent magnet to absorb the generated Fe 3 o 4 For black particles, pour off the supernatant and wash with high-purity water several times. Its reaction equation: Fe 2+ +2Fe 3+ +8OH - → Fe 3 o 4 +4H 2 o
[0043] Add an aqueous solution containing a polymer (PEI, PLGA, chitosan or dextran) to the obtained magnetic fluid precipitate, resuspend the magnetic fluid, place it for 30 minutes, and then magnetically separate. After repeating 3 times, dilute in PBS with pH 7.2 and set aside.
Embodiment 2
[0045] Characterization of PLGA magnetic microspheres
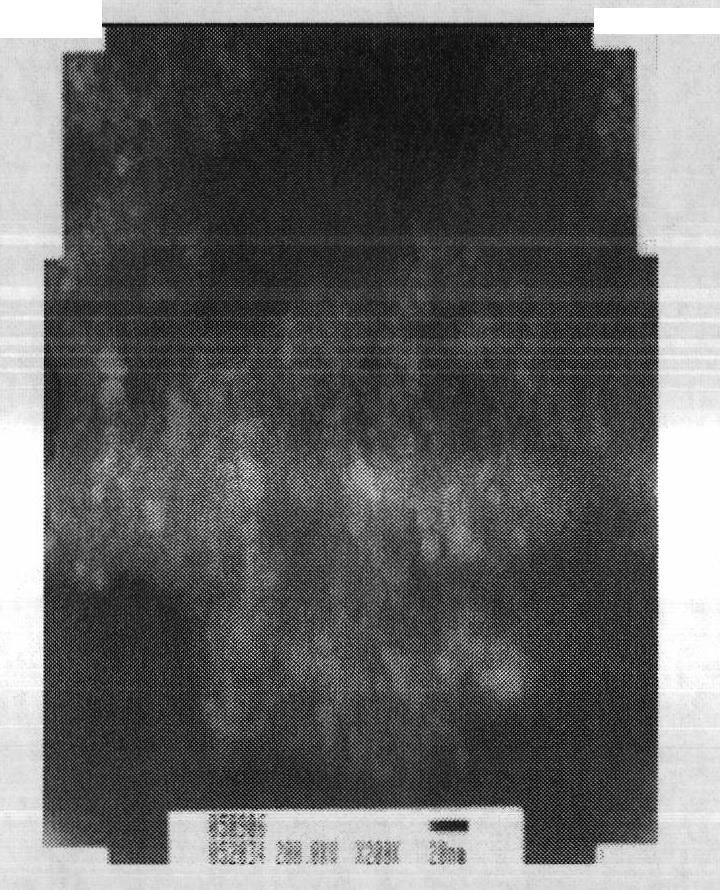
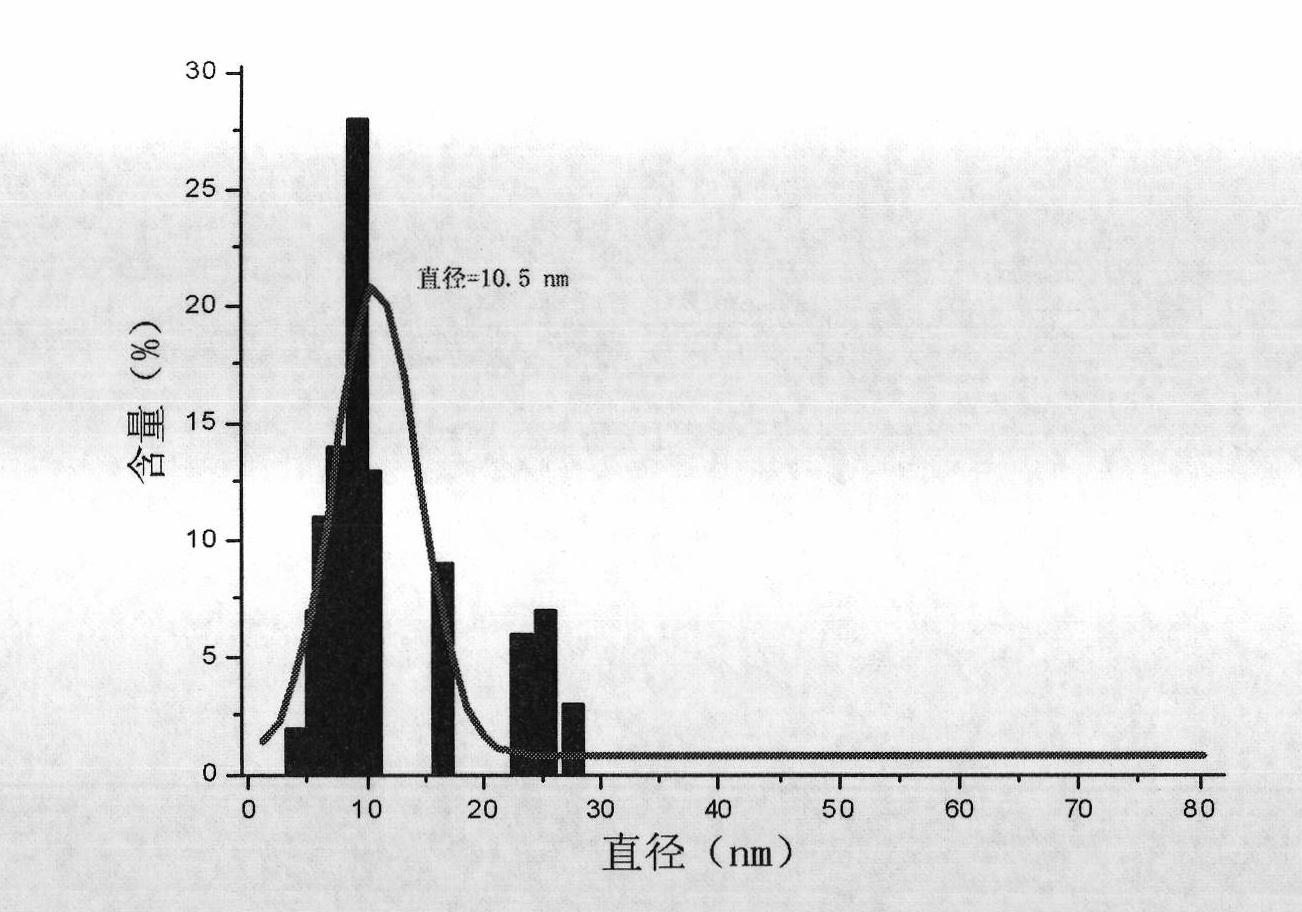
[0046] Fix the pH value and ionic strength of the system, and use the method of rapidly dropping ammonia water to ensure that Fe 3 o 4 The rapid nucleation and stable growth of nanoparticles are beneficial to reduce the size distribution of nanoparticles. The morphology of nanoparticles can be observed and their size can be determined by transmission electron microscopy (TEM).
[0047] like figure 2 As shown, Fe 3 o 4 Nanoparticles have good monodispersity, and the particle size distribution conforms to Gaussian distribution;
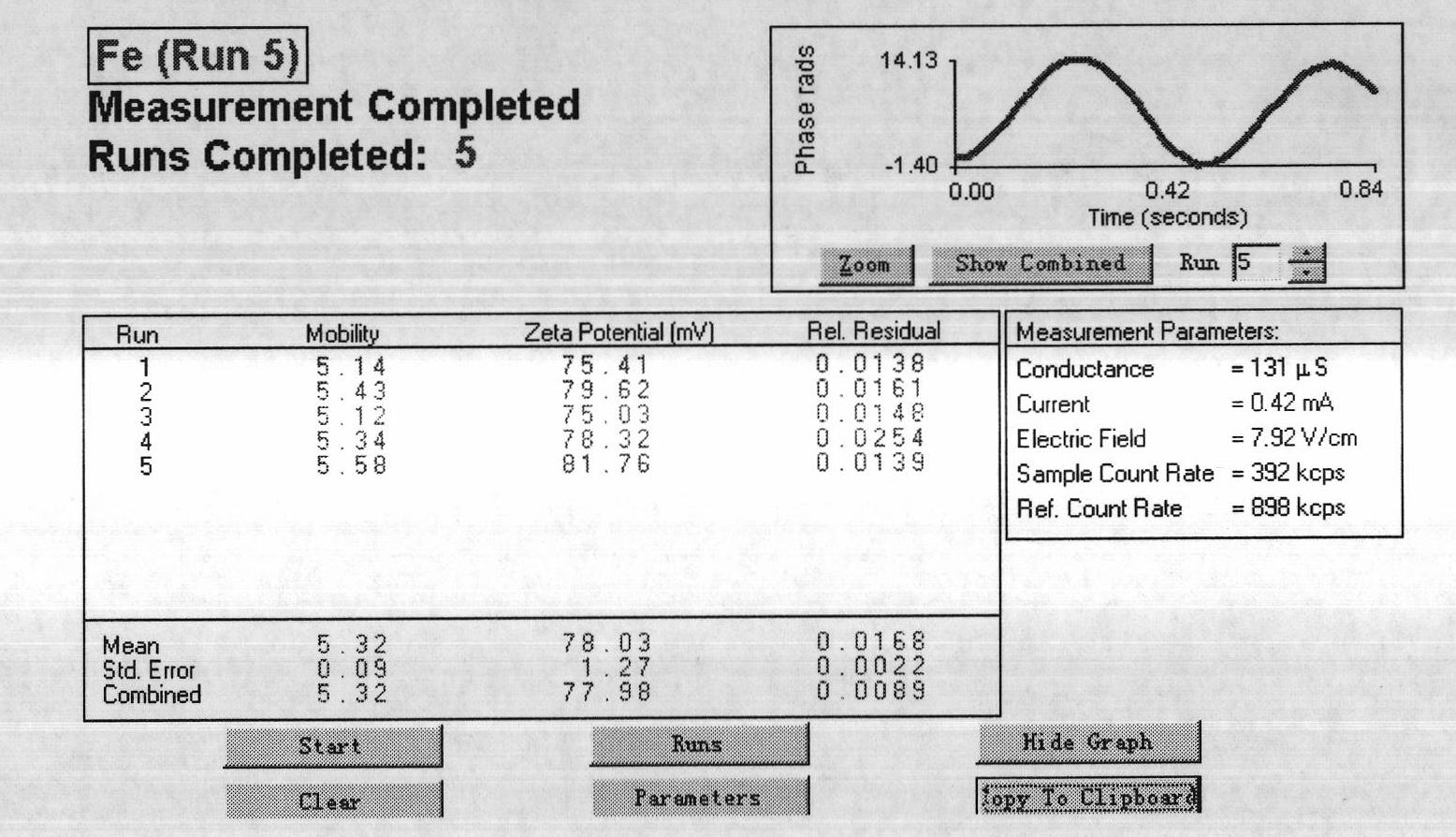
[0048] like image 3 As shown, Fe 3 o 4 The surface potential of nanoparticles has a high positive charge, which can bind and concentrate genetic vaccines.
Embodiment 3
[0050] Gene Vaccine Binding Experiment of PLGA Magnetic Microspheres
[0051] In a fixed buffer system (1×TAE), the quality of the fixed DNA vaccine is constant, and magnetic nanoparticles of different masses (w / w=0.25, 0.5~3.0, 3.5, 4.0) are added to it, and after standing at 4°C for 30 minutes, The results of agarose gel electrophoresis were used to screen for the best (magnetic particle / DNA) ratio. When the magnetic nanoparticles / DNA (w / w) is greater than 3:1, the DNA is completely blocked in the sample hole (such as Figure 4 ). By carrying out electrophoresis analysis to DNA and using computer simulation, the in vitro binding curve (such as Figure 5 ).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com