Medical devices with lubricious surfaces when wet
A medical appliance and lubricity technology, applied in the field of medical appliances, can solve the problem of high risk of surface lubricating layer peeling off
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
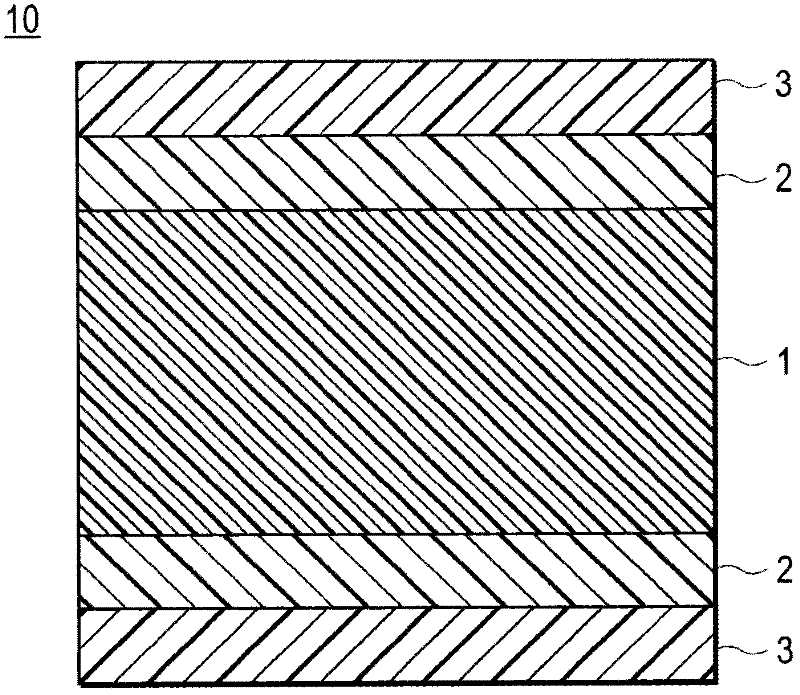
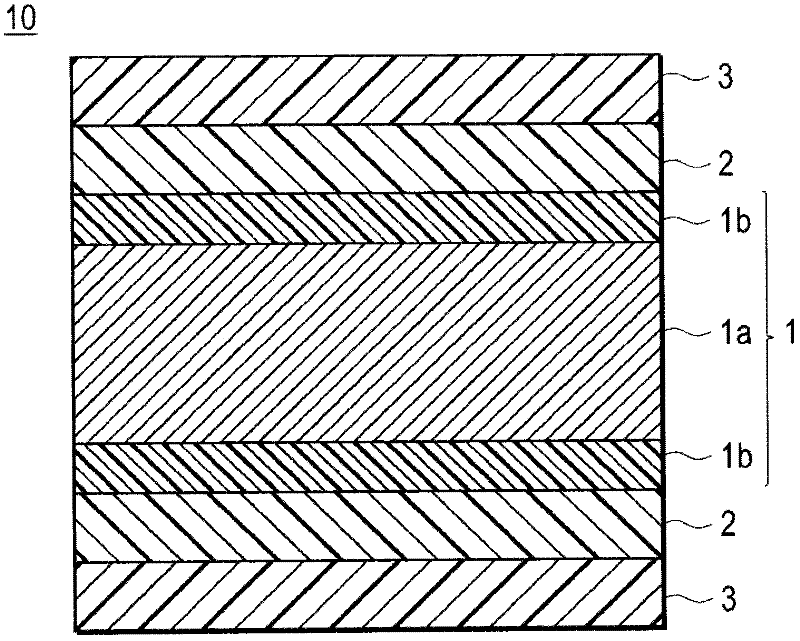
[0065]As a specific embodiment of fixing the thiol compound 2 on the substrate layer 1, the following embodiments can be enumerated: (i) before the solution of the compound having a thiol group is applied to the surface of the substrate layer, the The surface of the substrate layer is irradiated with ionized gas plasma, so that the compound having a thiol group is supported on the substrate layer. Specifically, it is an embodiment in which the surface of the substrate layer 1 is plasma-treated before the solution (thiol compound solution) in which the thiol compound is dissolved is applied on the surface of the substrate layer 1 (before the coating of the thiol compound). body treatment to modify and activate the surface, and then apply the thiol compound solution to react (bond / immobilize) the thiol compound 2 with the surface of the substrate layer 1 . In this embodiment, the thiol compound 2 can be firmly fixed on the surface of the substrate layer 1 . That is, generally, ...
Embodiment 1
[0153] [Example 1] Substrate: Nylon 12
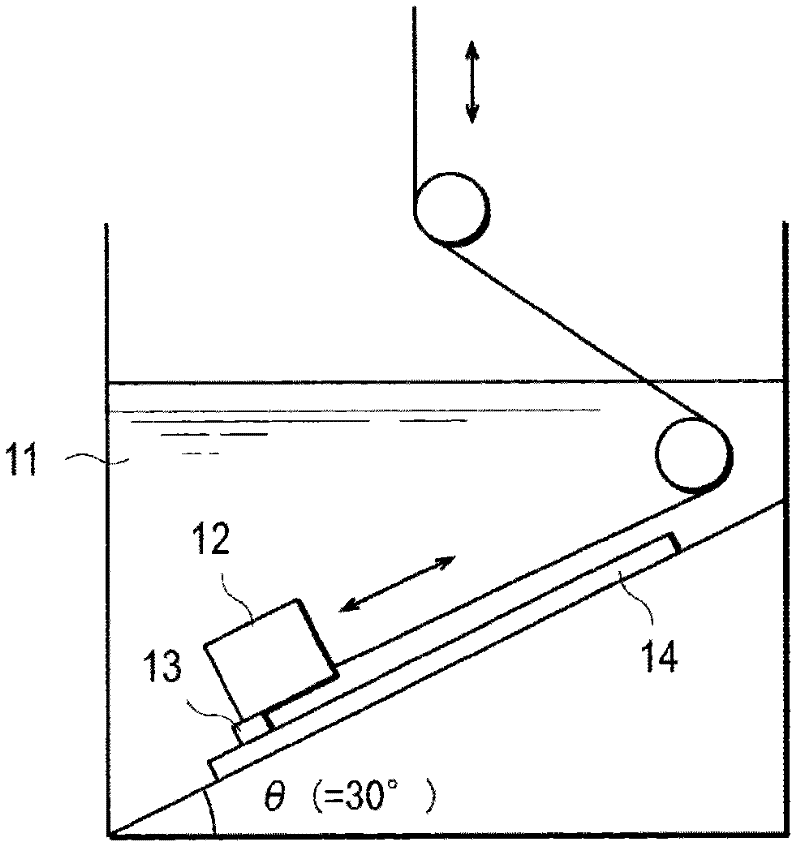
[0154] A thin sheet (length 30 mm x width 50 mm x thickness 1 mm; polymer substrate layer 1) of nylon 12 (Grillamid L 16, manufactured by EMS) was ultrasonically cleaned in acetone, and then a nozzle with a width of 1 inch was installed on the plasma irradiation surface. On the device (DURADYNE, PT-2000P, manufactured by TRI-STAR TECHNOLOGIES), under the conditions of atmospheric pressure, air flow: 15SCFH, plasma current: 2.00A, argon is irradiated from a distance of 10mm to the entire surface of the nylon 12 sheet for 25 seconds Ion plasma (plasma treatment prior to coating of thiol compounds).
[0155] The nylon 12 sheet subjected to the plasma treatment before coating with the above-mentioned thiol compound was immersed in tris-[(3-mercaptopropionyloxy)-ethyl]isocyanurate (TEMPIC) adjusted to a concentration of 20 mM ( (manufactured by SC Organic Chemicals Co., Ltd.) (3 thiol groups per molecule) in DMF solution, after 10 minutes o...
Embodiment 2
[0173] [Example 2] base material: LDPE
[0174] A thin sheet (long 30mm * wide 50mm * thickness 1mm; polymer substrate layer 1) of low density polyethylene (LDPE) (NOVATEC LD LC720, manufactured by Japan Polyethylene Corporation) is carried out ultrasonic cleaning in acetone, then use and embodiment 1 Argon ion gas plasma irradiation (plasma treatment before thiol compound coating) was performed for 25 seconds under the same conditions as in Example 1 using the same plasma irradiation apparatus.
[0175] The LDPE sheet subjected to the plasma treatment before the application of the above-mentioned thiol compound was immersed in a THF solution of TEMPIC adjusted to a concentration of 20 mM, dried naturally for 3 minutes, and then again under the above-mentioned conditions using the above-mentioned plasma irradiation device. Argon ion gas plasma irradiation for 25 seconds (plasma treatment after thiol compound coating). Then, the TEMPIC was immobilized on the surface of the LDP...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com