Separation and purification method of silicon wafer cutting waste mortar
A purification method and silicon wafer cutting technology, which are applied in chemical instruments and methods, silicon compounds, inorganic chemistry, etc. Well-designed effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
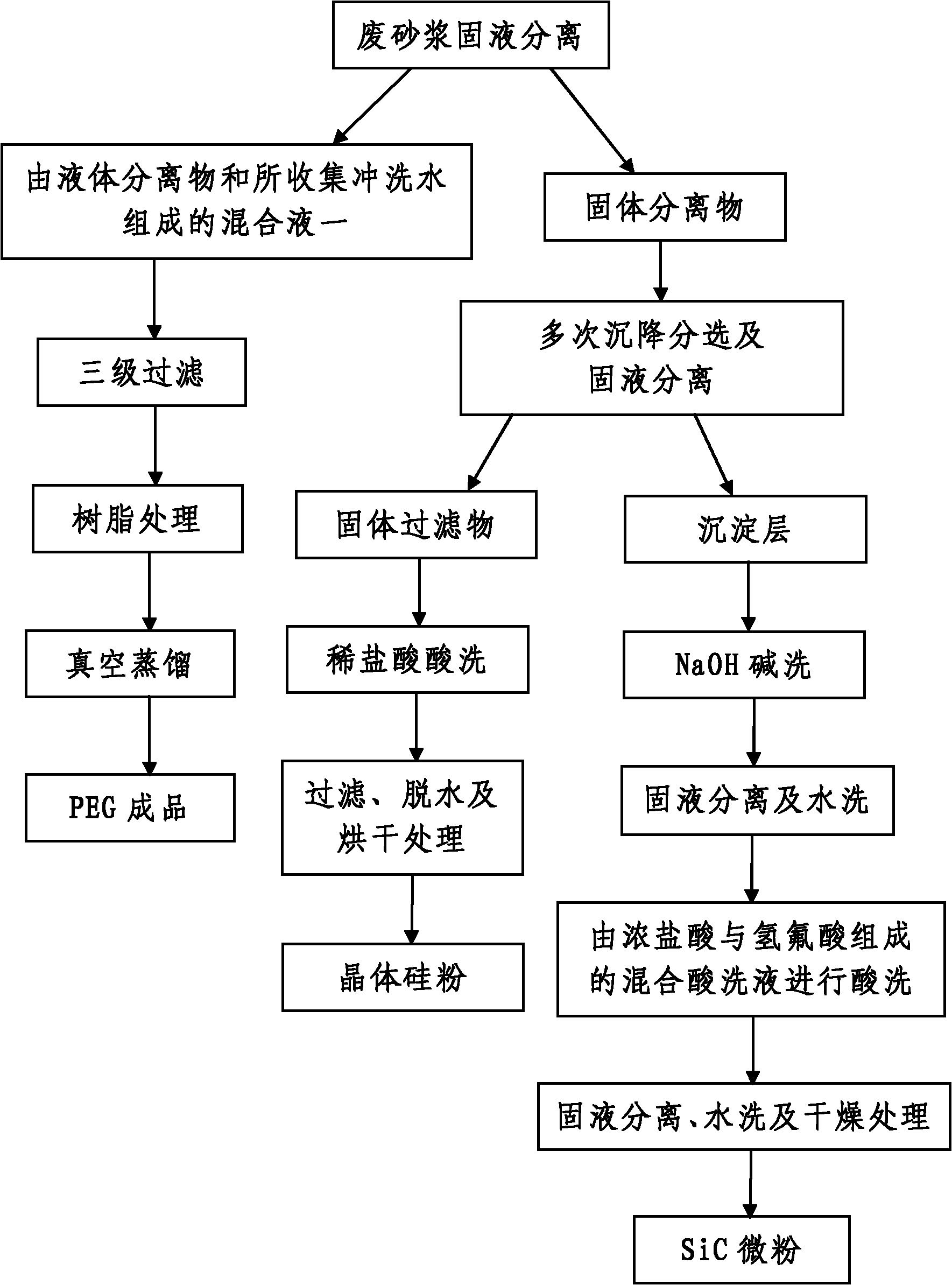
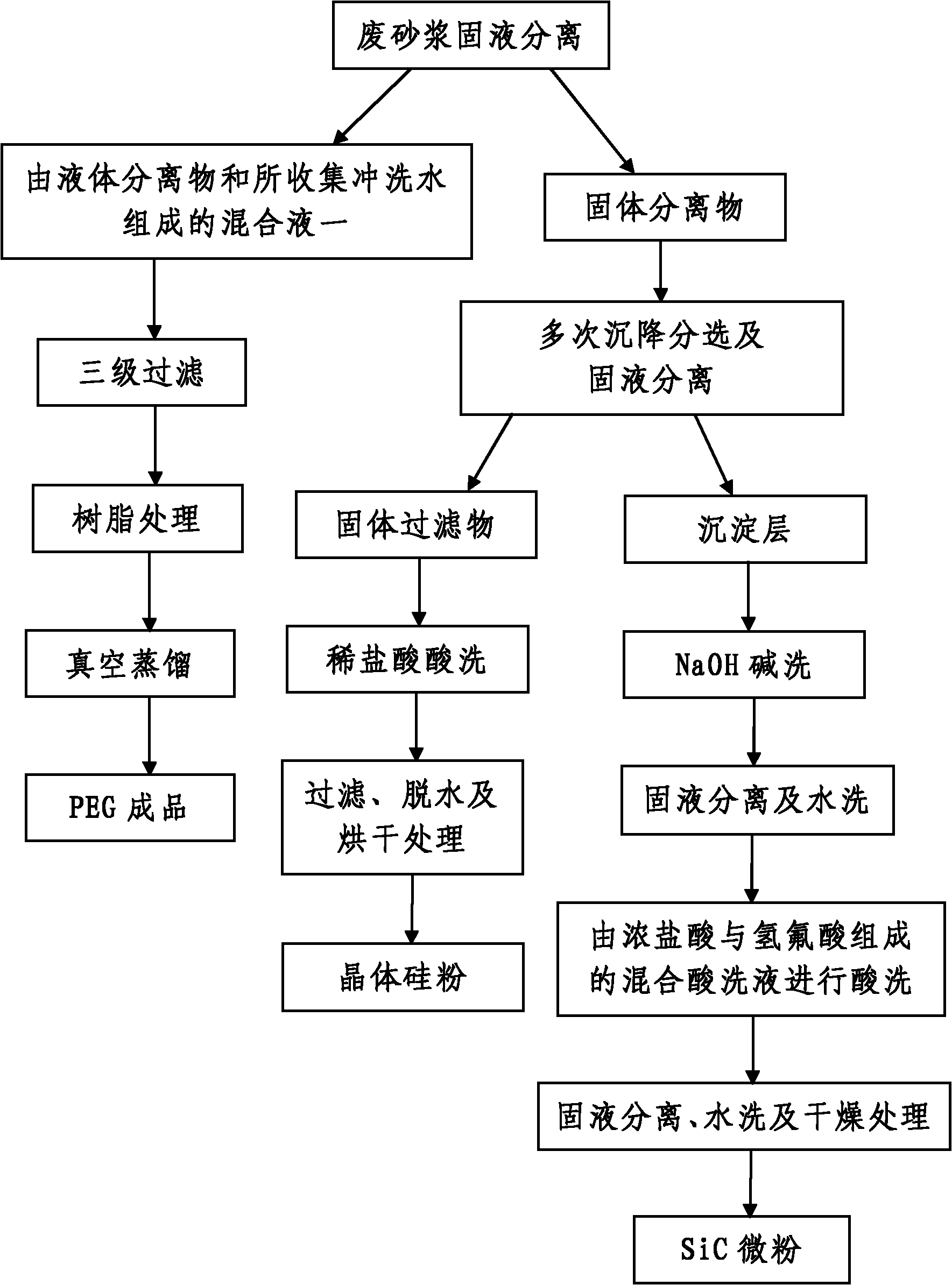
[0055] In the present embodiment, when the waste mortar is separated and purified, the separation and purification process is as follows:
[0056]Step 1. Solid-liquid separation of waste mortar: use heating equipment to heat the processed waste mortar in a stirring state until the processed waste mortar is heated to 65°C; after that, use pumping equipment to pump the heated waste mortar to The solid-liquid separation device performs solid-liquid separation, and obtains the liquid separation and the filter cake layer; then, pumps hot water at a temperature of 65°C into the solid-liquid separation device with pumping equipment to rinse the filter cake layer, And the flushing water is collected, and the volume of the pumped hot water is 6 times the volume of the liquid isolate; after the flushing is completed, the solid isolate and a mixed solution consisting of the liquid isolate and the collected flushing water are obtained.
[0057] In this embodiment, the solid-liquid separat...
Embodiment 2
[0080]In this example, the difference from Example 1 is that when the waste mortar to be treated is heated in step 1, the waste mortar to be treated is heated to 50°C and the stirring speed is 1000r / min. The water temperature of the water is 50°C and the volume of the pumped hot water is 4 times the volume of the liquid isolate; the pore size of the precision filter described in step 201 is 3 μm, and the pore size of the microporous filter or molecular sieve filter is 0.1 μm, The aperture of the ultrafiltration filter is 500 angstroms; the vacuum degree of the vacuum distillation equipment adopted in the step 203 is 2000Pa and the temperature is 50 ℃; in the step 301, the volume of pure water added in the solid isolate described in the step 1 is 2 times the volume of the solid isolate, the volume ratio of the added water-soluble surfactant to the solid-liquid mixture is 0.001%; in step 301, the suspension on the upper part of the precipitation layer is pumped to the solid by ...
Embodiment 3
[0082] In this example, the difference from Example 1 is that when the waste mortar to be treated is heated in step 1, the waste mortar to be treated is heated to 80°C and the stirring speed is 500r / min, and the heat added during solid-liquid separation The temperature of the water is 80°C and the volume of the pumped hot water is 3 times the volume of the liquid isolate; the pore size of the precision filter described in step 201 is 7 μm, the pore size of the microporous filter or molecular sieve filter is 1 μm, ultra The pore diameter of filter filter is 1000 angstroms; The vacuum tightness of vacuum distillation equipment adopted in step 203 is 4900Pa and temperature is 90 ℃; In step 301, the volume of adding pure water in the solid isolate described in step 1 is described 6 times the volume of the solid isolate, the volume of the added water-soluble surfactant is 0.01% of the volume of the solid-liquid mixture; in step 301, the suspension on the upper part of the precipitat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com