Lithium ion battery conducting material and preparation method and application thereof
A lithium-ion battery and conductive material technology, applied in battery electrodes, circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve the problem of no lithium-ion battery negative electrode materials, etc., and achieve the effects of low cost, simple process, and low energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
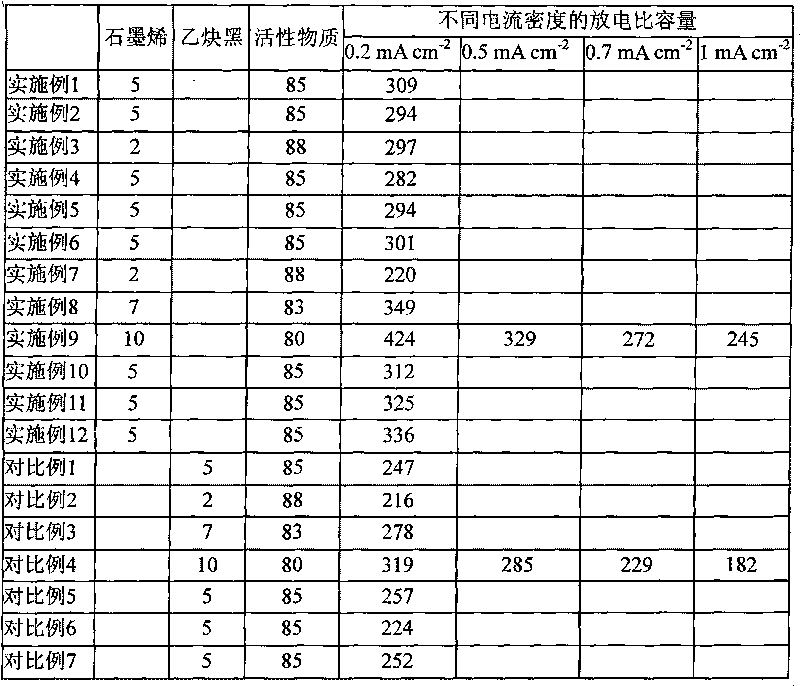
[0023] A: Weigh 5.5g of artificial graphite (the anode material of lithium-ion batteries for industrial use, the particle distribution is 10-15μm, and the specific surface area is 4m 2 / g, the ash content is 4-6%), added to the mixture of 95mL concentrated sulfuric acid (concentration 98%) and 47.5mL concentrated nitric acid (concentration 65-67%) at 0-4°C, and then added 5 1 gram of potassium chlorate, 55 grams in total, the reaction temperature is controlled at 0-4°C, after 90 hours of continuous reaction, first rinse with 0.1mol / L dilute hydrochloric acid and then with deionized water until no chlorine ions are detected and the pH value reaches neutral . Graphite oxide powder was obtained after vacuum drying at 40°C.
[0024] B: put the graphite oxide powder into the crucible and put it into a muffle furnace with an air atmosphere at 1000°C for rapid heat treatment for 20 seconds (that is, leave it for 20 seconds) to obtain exfoliatable graphite.
[0025] C: Using an ultr...
Embodiment 2
[0028] The preparation method of graphite oxide powder is the same as in Example 1. Put the graphite oxide powder obtained in step A into a crucible and put it into a muffle furnace with an air atmosphere at 1000°C for rapid heat treatment for 10 seconds to obtain peelable graphite. Use a probe ultrasonic cell pulverizer Under 400W power, in ethanol solvent, disperse for 4 hours to obtain graphene suspension, and vacuum dry at 40°C to obtain graphene conductive agent. The prepared graphene nanosheets have a thickness of 5-10nm and an area of 2-4μm 2 . The tap density is 0.74~0.78g / cm 3 , the conductivity at room temperature is 900~950S cm -1
[0029] The preparation of the electrode sheets, the assembly and testing of the simulated battery are the same as in Example 1. Measured at a current density of 0.2mA / cm 2 When the discharge capacity is 294mAh / g.
Embodiment 3
[0031] The preparation method of graphene conductive agent is the same as in Example 1 except that the oxidation reaction time of step A is 72 hours, and the thickness of the prepared graphene nanosheets is 7-9 nm, and the area is 1-5 μm 2 . The tap density is 0.76~0.77g / cm 3 , the conductivity at room temperature is 950~1150S cm -1 .
[0032] The preparation of the electrode sheets, the assembly and testing of the simulated battery are the same as in Example 1. Measured at a current density of 0.2mA / cm 2 When the discharge capacity is 297mAh / g.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com