Methods of robust and efficient conversion of cellular lipids to biofuels
A cell and biomass technology, applied in the field of sufficient and efficient conversion of cell lipids to biofuels
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
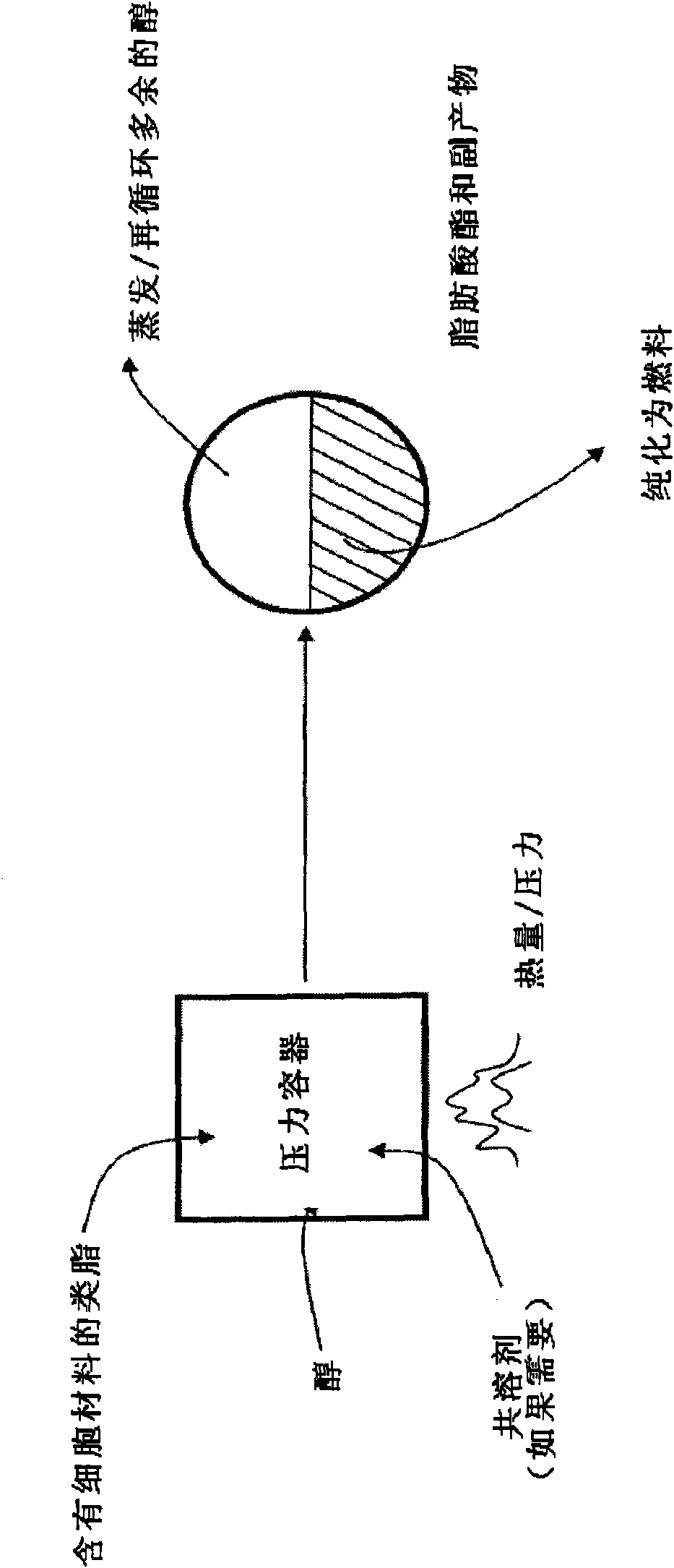
[0091] [88] Live cultures of Chlorella sp. microalgae were centrifuged at 1 kgf for 5 min. The resulting plug of cellular material was mixed with an equal amount of technical grade methanol and then transferred to a stainless steel cylindrical pressure vessel. The vessel was closed with a screw stopper and placed in a 350°C molten tin bath for 12 minutes. After cooling in a water bath for several minutes, the container was opened and the brown solution was evaporated to dryness at room temperature. The residue was partitioned between hexane and water, and the hexane layer was analyzed by GCMS chromatography. Analysis showed the presence of C12-C20 fatty acid methyl esters in amounts, and less than 10% of a mixture of fatty acids and monoglycerides. To detect unreacted triglycerides.
Embodiment 2
[0093] [89] pumped a 20% w / v slurry of mixed species of microalgae and bacteria (from a sewage treatment tank) through a length of 6 mm internal diameter 316 stainless steel pipe maintained at 340°C via a peripheral raw aluminum cylinder that passed The resistance sleeve is heated. The system pressure is maintained at 20MPa through an adjustable back pressure safety valve. The pumping rate was adjusted to allow a heated residence time in the tubing of 16 minutes. The output from the system containing a near brown suspension (maintained for 4 hours) was separated into a smaller dense layer containing almost all fatty acids and small amounts of hydrophobic degradation compounds, and an aqueous layer containing mainly amino acids, Sugars, minerals and heterocyclic bases.
Embodiment 3
[0095][90] A slurry of proprietary microalgae containing 0.58 grams (dry weight) of cells in 8 mL of water and 3.5 mL of technical grade hexane was added to a stainless steel vessel. The container was sealed and heated to 350°C for 20 minutes, then cooled and opened. The hexane layer was combined with an equal amount of technical grade methanol, then sealed and reheated at 350° C. for an additional minute in the pressure vessel. The resulting reaction mixture was dried at 80°C until there was no further weight loss. A residue weighing 0.24 g (based on GCMS chromatographic analysis) indicated a near pure mixture containing C10-C22 fatty acid methyl esters. The yield of algae from methyl esters was over 49%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com