Methods for Elevating Fat/Oil Content in Plants
a technology of fat/oil content and plant cells, applied in the direction of transferases, peptide sources, enzymology, etc., can solve the problems of low abundance of lipid droplets, difficult production of oils in non-seed plant tissues for industrial applications, and insufficient understanding of transient accumulation of stored oils in non-seed tissues, etc., to improve the lipid content of genetically modified plant cells, increase the lipid content of cellular lipid droplets, and reduce lipa activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Increase of Lipid Content and Induction of Lipid Droplet Formation in Plants Using Mammalian Proteins Associated with Lipid Metabolism
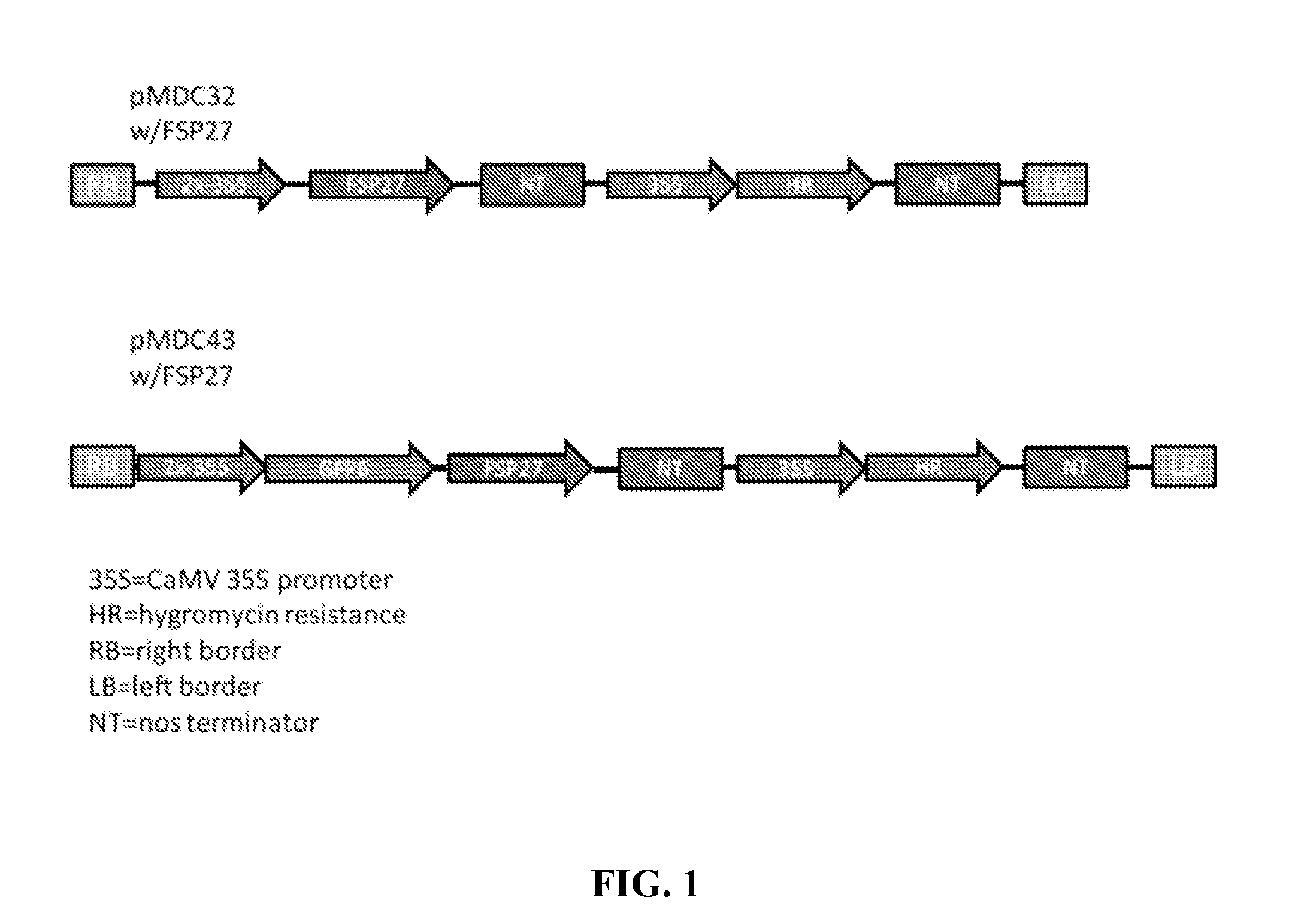
[0328]Plant transformation vectors are constructed and are propagated in Eschericia coli Top 10 cells. The vectors are sequenced for verification. Plasmid vectors are transformed into Agrobacterium, tunefaciens LBA4404, and the clones are selected and verified by PCR. Arabidopsis plants are transformed by the floral dip method as described in Bent and Clough, Plant J. 1998 December; 16(6):735-43, which is herein incorporated by reference in its entirety.
[0329]Both wild-type plants (A. thaliana, ecotype Columbia), and plants with a transfer DNA (T-DNA) insertion mutation in the At4g24160 locus are used for transformations. The T-DNA knockout is in an exon of the Arabidopsis homolog of the human CG1-58 gene. For Arabidopsis plants with CGI-58 mutation, there is an increase in cystosolic lipid droplets in leaves when compared to wild-type plants (James e...
example 2
Generation of FSP27 and PLIN2 Expressing Homozygous Transgenic Plants with High Lipid Content
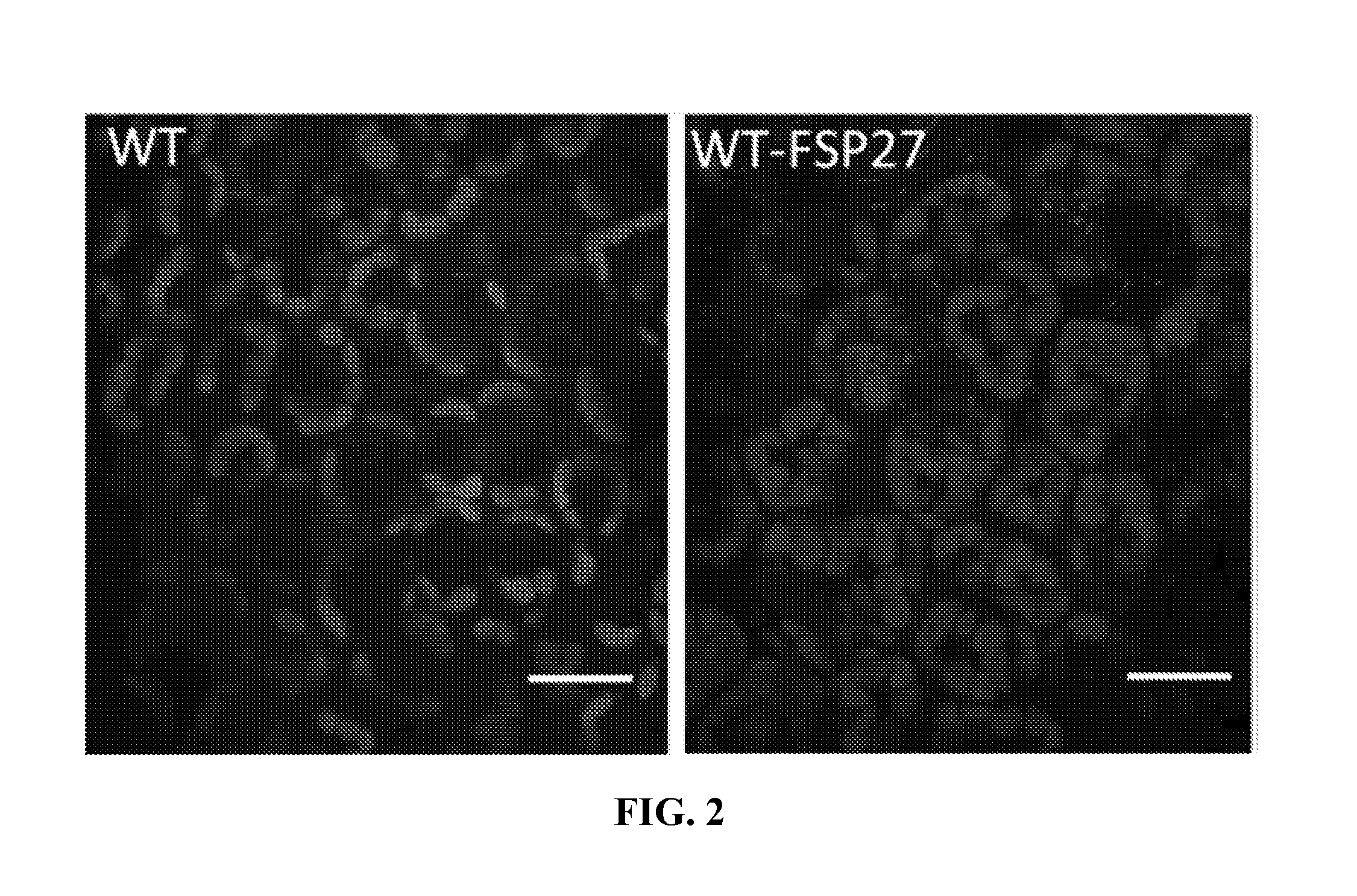
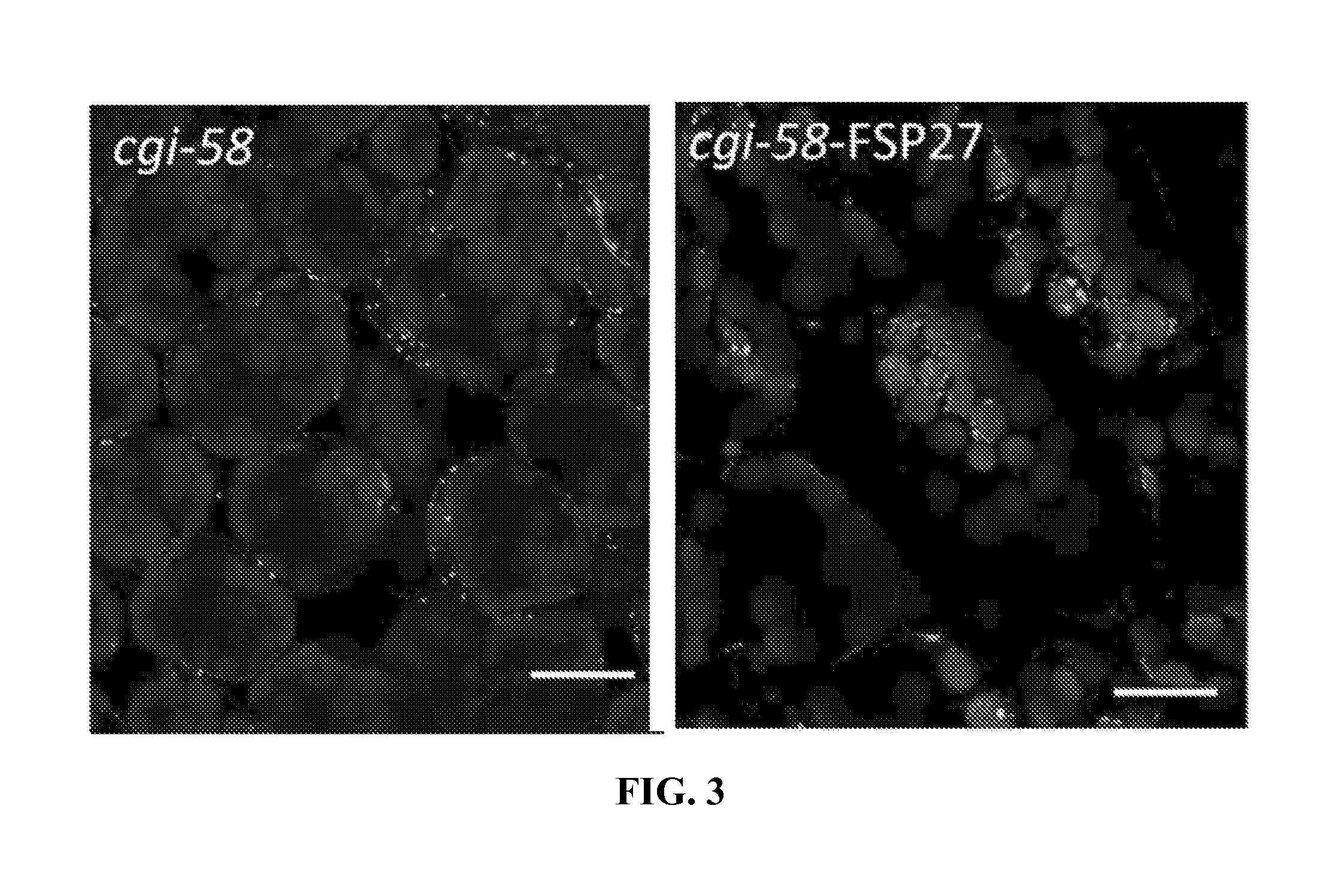
[0334]Seven homozygous lines of FSP27-expressing plants in the cgi58 mutant background, as well as one homozygous line expressing PLIN2 (ADRP) are raised. The new plants are completely viable and healthy with higher lipid accumulation as shown by microscopic data (FIG. 7).
[0335]Seedlings are grown on solidified nutrient medium under selection. Seven Arabidopsis homozygous lines in T2 generation over-expressing the FSP27 in the cgi58 knockout background are identified. Also, one Arabidopsis homozygous line in T2 generation overexpressing the ADRP in the cgi58 knockout background is identified. Lines that are no longer segregating (homozygous) are selected for harvest and extraction. FIG. 7 shows representative confocal images of leaves having preponderance of lipid droplets in both lines as well as the cgi-58 knockout background.
example 3
Identification of Triglyceride-Accumulatory Domain of FSP27
[0336]Using deletion-mutagenesis, the domain of amino acids 120-220 of the mouse FSP27 protein (SEQ ID NO: 2), which is associated with lipid accumulation in adipocytes, is dissected. The domain 120-220 of mouse FSP27 is a core-portion of FSP27 protein. As shown in FIG. 8, adipocytes expressing amino acids 120-220 of the mouse FSP27 protein accumulate lipids faster than adipocytes expressing the full length mouse FSP27 protein.
[0337]The present invention also provides genetically engineered plants expressing only the triglyceride-accumulating domain of FSP27 (such as amino acids 120-220 of mouse FSP27), in order to accumulate lipids / oils at a faster rate than the full length protein. For the plants that need to be harvested from time to time for biofuel production, expressing the triglyceride-accumulating domain can be useful for improving lipid / or production.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tm | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| droplet size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| lipid droplet size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com