Technology of extracting and separating valuable metals such as Pb, In, Sb, Cu and Sn from lead smelting converter slags
A technology of lead, indium, antimony, copper, tin, and valuable metals, which is applied in the field of non-ferrous metal extraction, and can solve the problems of less recycling of tin and antimony and less consideration of recycling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
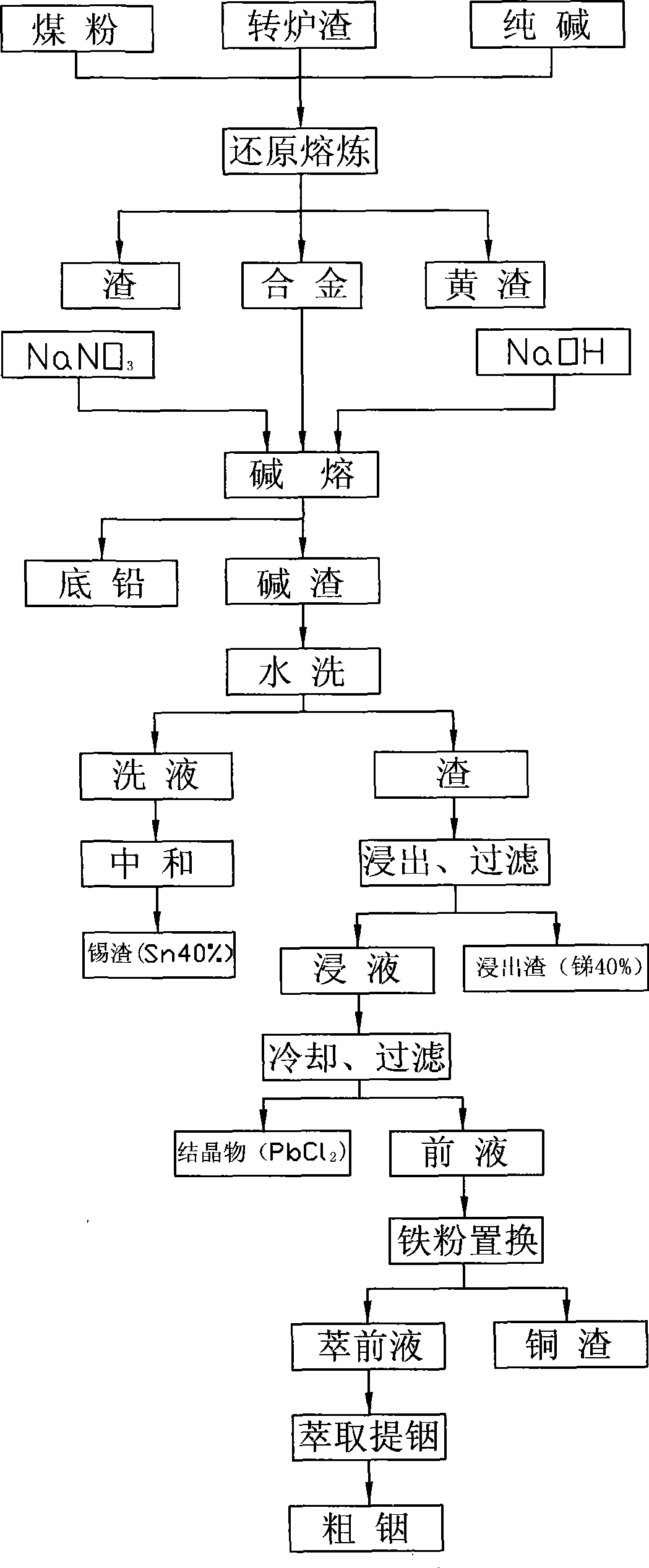
[0011] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing and embodiment the present invention is further described:
[0012] see figure 1 , a process for extracting and separating valuable metals of lead, indium, antimony, copper, and tin from lead smelting converter slag. The raw material is crude copper that is blown in a converter to produce oxide slag containing indium, lead, antimony, copper and tin. The main metals and their contents in the raw material are respectively Is: Pb15~23%, In0.15~0.3%, Sn4.5~6.5%, Sb4.7~5.87%, Cu4.2~8.92%, first of all, the material is mixed with soda ash and anthracite, and the proportion is converter slag : soda ash: anthracite = 1000:12:8; smelting in an electric furnace at 1100°C for 2 hours to obtain an alloy with a content of: In1-3%, Pb45-60%, Sn10-20%, Sb5-15%, Cu10-20% , The direct recovery rate of indium in this process is about 90%, and that of other metals is above 90%.
[0013] Then in the reverberatory furnace at 600-650°C, add ca...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com