Method for manufacturing printing plate
A manufacturing method and printing plate technology, applied in the field of plate manufacturing, can solve problems such as difficult to judge, difficult to obtain water-ink balance, not beneficial to printing, etc., to achieve enhanced storage stability, short plate-making time, and high printing quality excellent effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
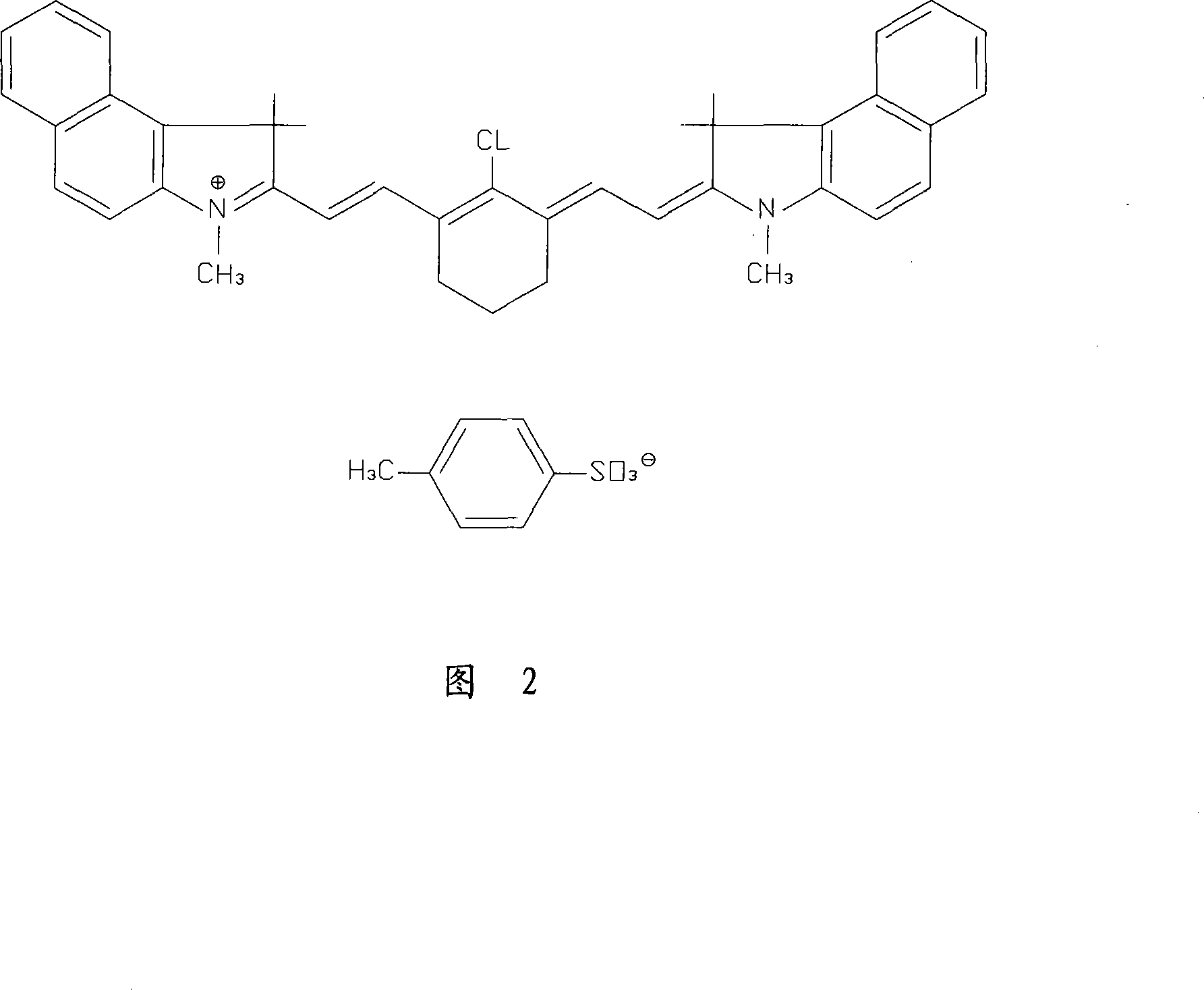
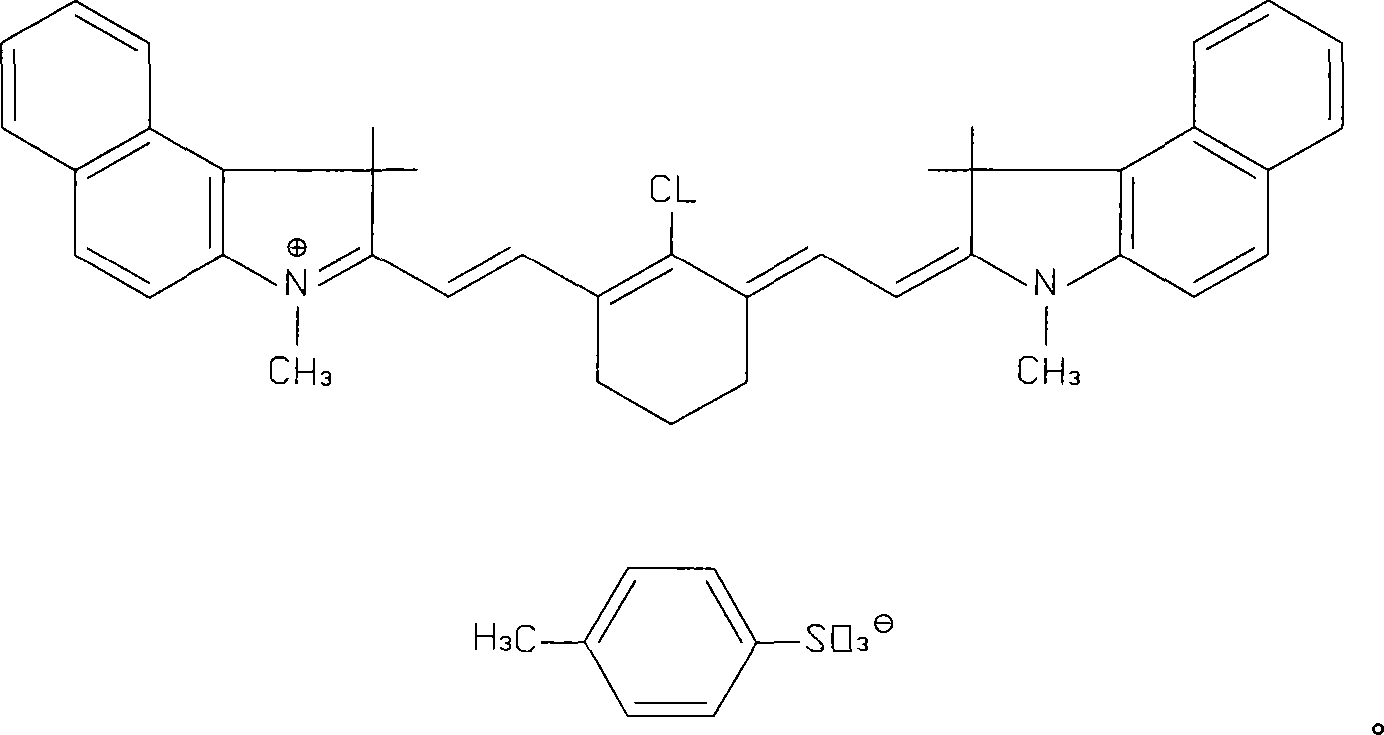
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
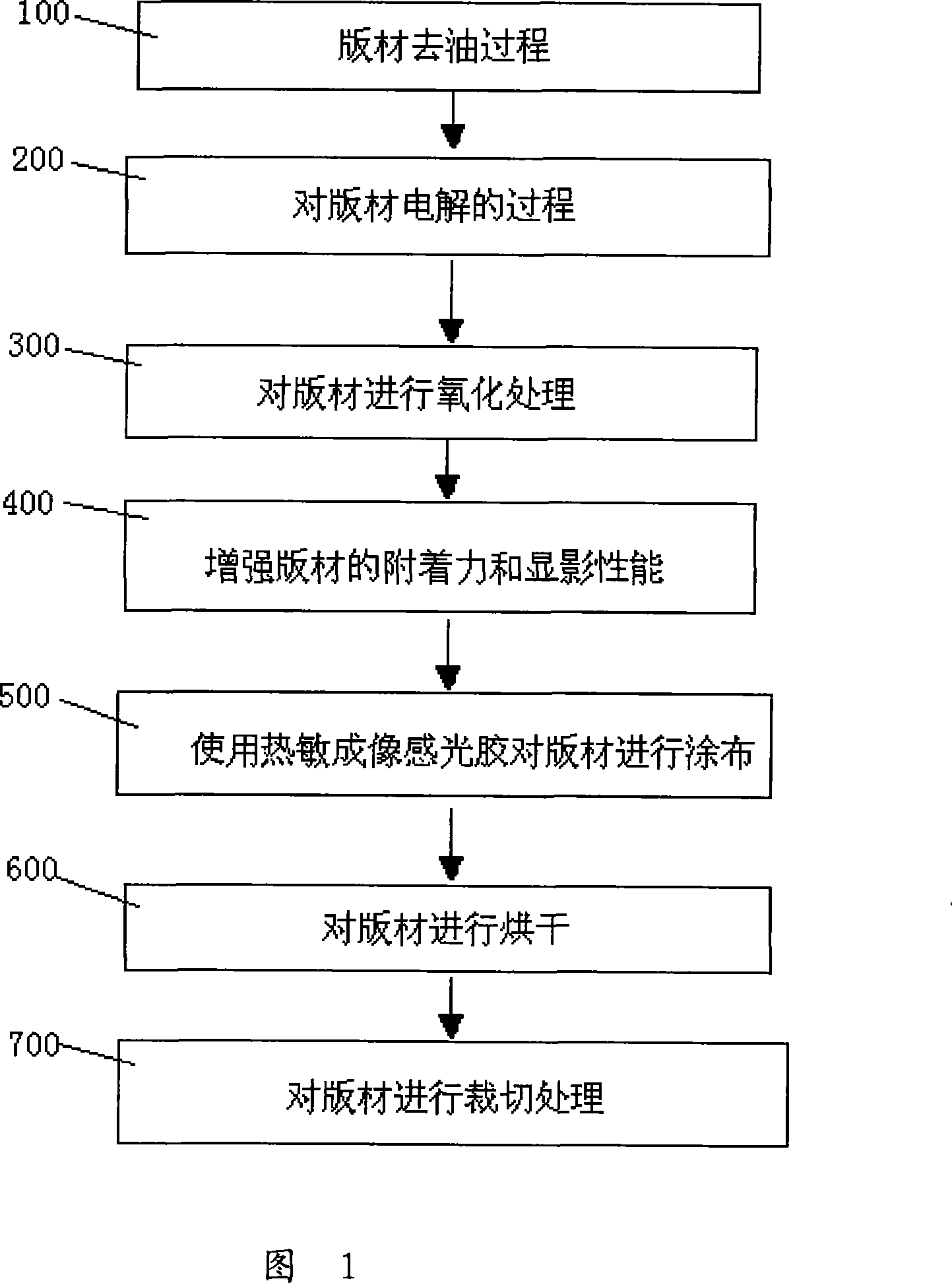
[0046] Please refer to Fig. 1, the method for producing positive-type thermal printing plates of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0047] Step 100: plate degreasing process
[0048] Use a degreasing solution to remove grease from the surface of the plate, including sodium hydroxide.
[0049] Step 200: the process of electrolyzing the plate
[0050] Plates use alternating current when electrolyzing grains. The electrolyte is usually (but not limited to) nitric acid or hydrochloric acid. In order to control the grain profile, some corrosion inhibitors are usually added, such as boric acid, acetic acid, phosphoric acid, sulfuric acid or It is their salts to ensure that no particularly deep pits (valley bottoms) will appear during the electrolysis of the plate.
[0051] In the process of electrolysis, the valley peaks and contours of the grain surface of the plate are not important for the storage quality of infrared sensitive printing plates, especially pos...
Embodiment 2
[0080] The producer takes a 1030mm aluminum coil and produces printing plates on a roll-to-roll line.
[0081] The production process includes the following steps:
[0082] Oil removal step: use 32 g / L sodium hydroxide, the treatment temperature is 50° C., and the treatment time is 30 seconds.
[0083] Electrolysis step: use an electrolytic solution including 8.5 g / L hydrochloric acid and 13.5 g / L acetic acid, and process for 80 seconds at a processing temperature of 30° C., an AC voltage of 11.5 V, and a current of 1000 A.
[0084] Decontamination step: use 7.0 g / L sodium hydroxide, the treatment temperature is 25°C, and the treatment time is 70 seconds.
[0085] Oxidation step: use 200 g / L of sulfuric acid for 80 seconds at a DC voltage of 30 volts, a current of 1000 A, and a temperature of 35° C.
[0086] Post-processing: use polyvinyl phosphoric acid (the original text is Poly(vinyl phosphonic acid)) for 30 seconds at 85°C.
[0087] Then rinse off with clean water and d...
Embodiment 3
[0104] This embodiment and embodiment 2 are comparative examples.
[0105] Get the same quality and batch of aluminum coils in Example 2, use the production process in Example 2 to process and coat, but use the following electrolyte:
[0106] Contains 12 g / l hydrochloric acid and 4 g / l acetic acid.
[0107] After testing, the Ra value of the aluminum plate treated by the above process is 0.7um, and the Rv value is 4.3.
[0108] Coat and dry the same as the aluminum plate in Example 2, and store the aluminum plate in a warehouse at 35° C. for 90 days.
[0109] After processing through the steps in Example 2, it was found that the whole plate base was blue, and it was checked with a magnifying glass of 50 times, and it was found that there were a large number of blue spots on the plate after electrolytic sand molybdenum.
[0110] Because the blue dot absorbs ink during the printing process, the blank part of the printed matter is also colored, so this plate is obviously not su...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com