Three-dimensional isinglass multi-hole bracket and the preparing method
A porous scaffold and three-dimensional gelatin technology, which is applied in medical science, prosthesis, coating, etc., can solve the problems of plasticity, mechanical properties and microstructure that are difficult to meet the needs of tissue engineering
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0066] Preparation of three-dimensional gelatin porous scaffold material I
[0067] Put 1 g of gelatin into 100 ml of water, and magnetically stir for 60 min in a water bath at 30° C. to completely dissolve the gelatin in the water to prepare a 1% gelatin solution. Store at -4°C for later use.
[0068] Take 10ml of 1% gelatin solution and stir it magnetically in a water bath at 30°C. Gradually, 10ml of n-pentanol was added in portions to form a white emulsion. Take 0.5ml of 0.5% glutaraldehyde, stir it with magnetic force for 1min, pour it into a mold, and put it into a -20°C refrigerator to pre-freeze for 24h. The frozen gelatin is taken and dried in a freeze dryer to obtain a rough product of the porous gelatin scaffold material.
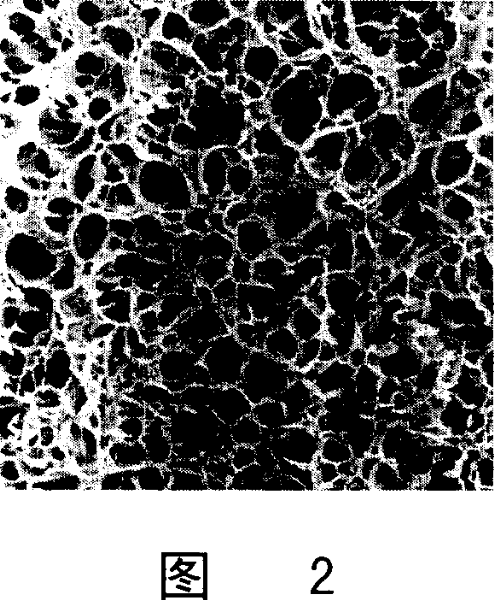
[0069] Soak the gelatin scaffold material with ethanol, and then rinse it with deionized water to remove organic solvents and residues. Freeze-dry again to obtain the three-dimensional gelatin porous scaffold material I. See attached picture ...
Embodiment 2
[0072] Preparation of three-dimensional gelatin porous scaffold II
[0073] Put 2 g of gelatin into 100 ml of water, stir magnetically in a water bath at 35° C. for 60 min to completely dissolve the gelatin, and prepare a 2% gelatin solution. Store at -4°C for later use.
[0074] Take 10ml of 2% gelatin solution and stir it magnetically in a water bath at 35°C. Gradually and in portions, 15 ml of n-propanol was added to form a white emulsion. Take 1ml of 0.5% glutaraldehyde, stir it magnetically for 2 minutes, pour it into a mold, and put it in a -20°C refrigerator for 24 hours. Get the frozen gelatin and dry it in a freeze drier to obtain a white porous material.
[0075] Soak the white gelatin porous material with ethanol, then soak and rinse with deionized water, remove free glutaraldehyde with 5% sodium borohydride, and wash with a large amount of deionized water to remove organic solvents and residues. Freeze-dry again to obtain the three-dimensional gelatin porous sc...
Embodiment 3
[0078] Preparation of Three-dimensional Gelatin Porous Scaffold III
[0079] Put 5 g of gelatin into 100 ml of water, and magnetically stir in a water bath at 37° C. for 60 min to completely dissolve the gelatin in the water to prepare a 5% gelatin solution. Store at -4°C for later use.
[0080] Take 10ml of 5% gelatin solution and stir it magnetically in a water bath at 37°C. Gradually, add 20ml of n-butanol in batches to form a white emulsion. Take 0.5ml of 1% glutaraldehyde, stir it magnetically for 3 minutes, pour it into a mold, and put it in a -25°C refrigerator for at least 24 hours. Get the frozen gelatin and dry it in a freeze dryer to obtain a white porous material.
[0081] Soak the white gelatin porous material with ethanol, then soak and rinse with deionized water, remove free glutaraldehyde with 5% sodium borohydride, and wash with a large amount of deionized water to remove organic solvents and residues. Freeze-dry again to obtain the three-dimensional gelat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com