Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
153results about How to "Easily access" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
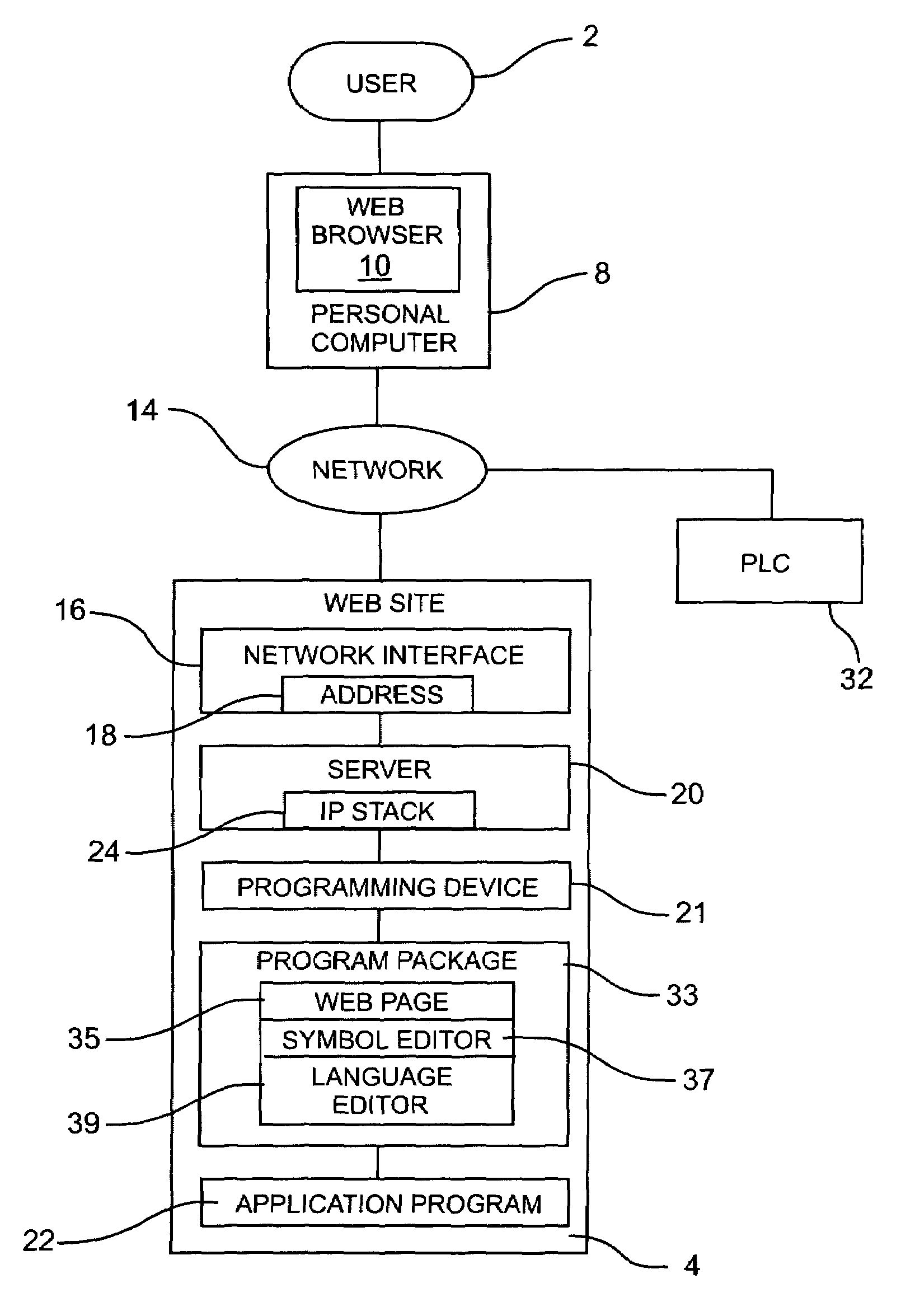
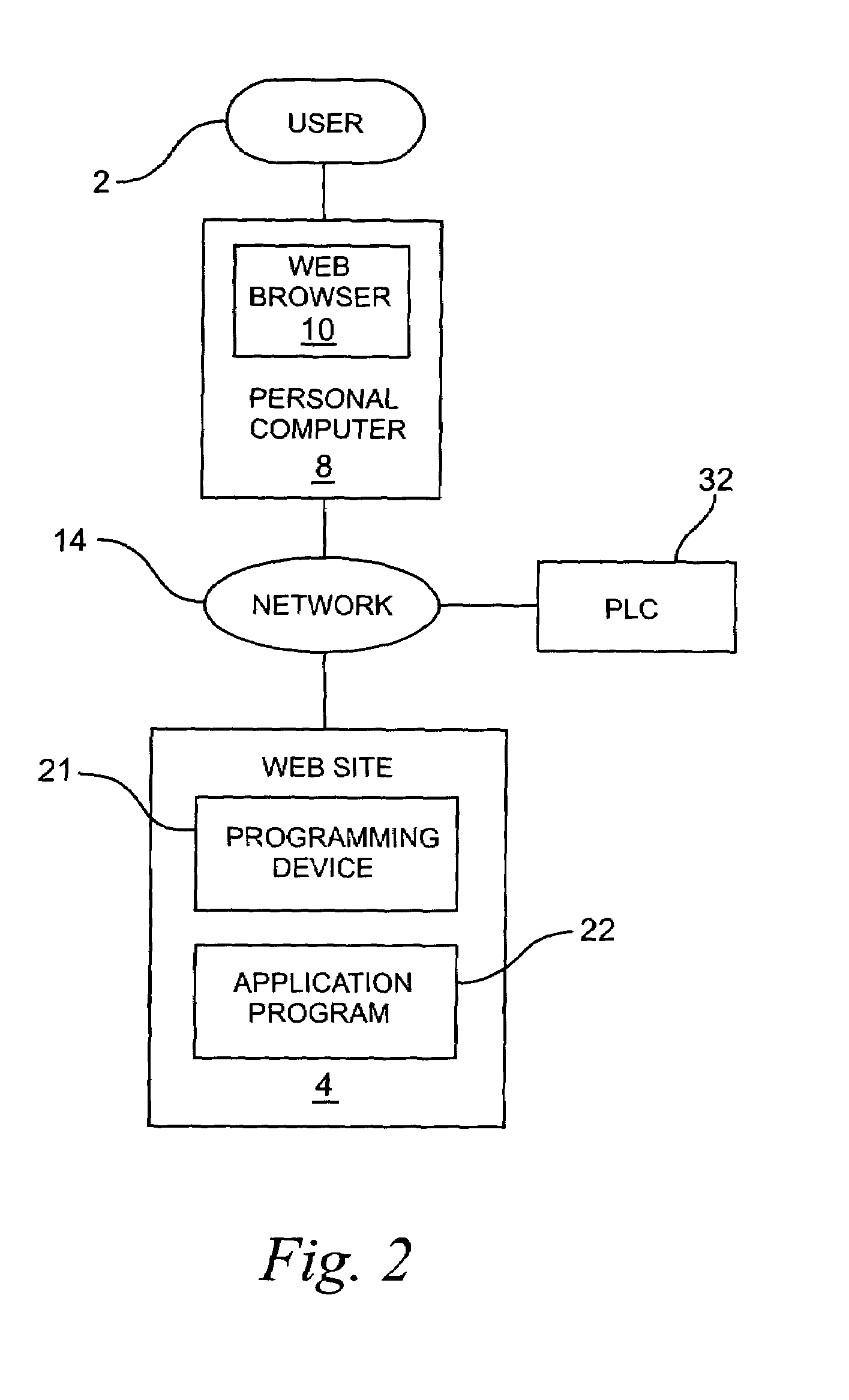
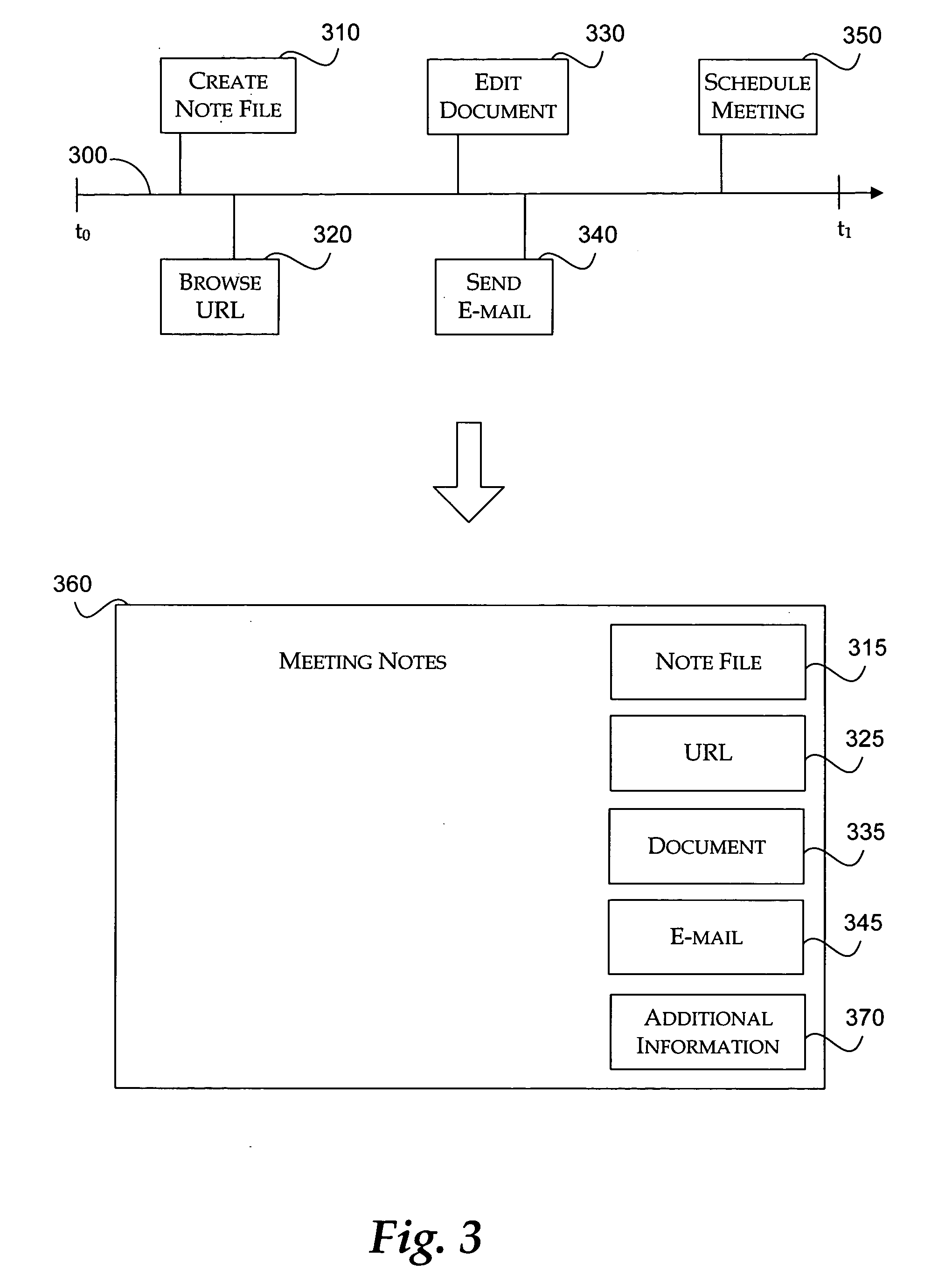
System for programming a factory automation device using a web browser
InactiveUS7035898B1Easily accessEasy accessTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsComputer controlEmbedded systemApplication software
A control system for programming an application program controlling a factory automation device on a communication network having a programming device operably connected to the communication network. A program package is embedded in the programming device and is used for creating and editing the application program. At least one web page is resident on the programming device and operably connected to the program package. The web page is accessible to a user using a web browser to edit the application program controlling the factory automation device.
Owner:SCHNEIDER AUTOMATION INC
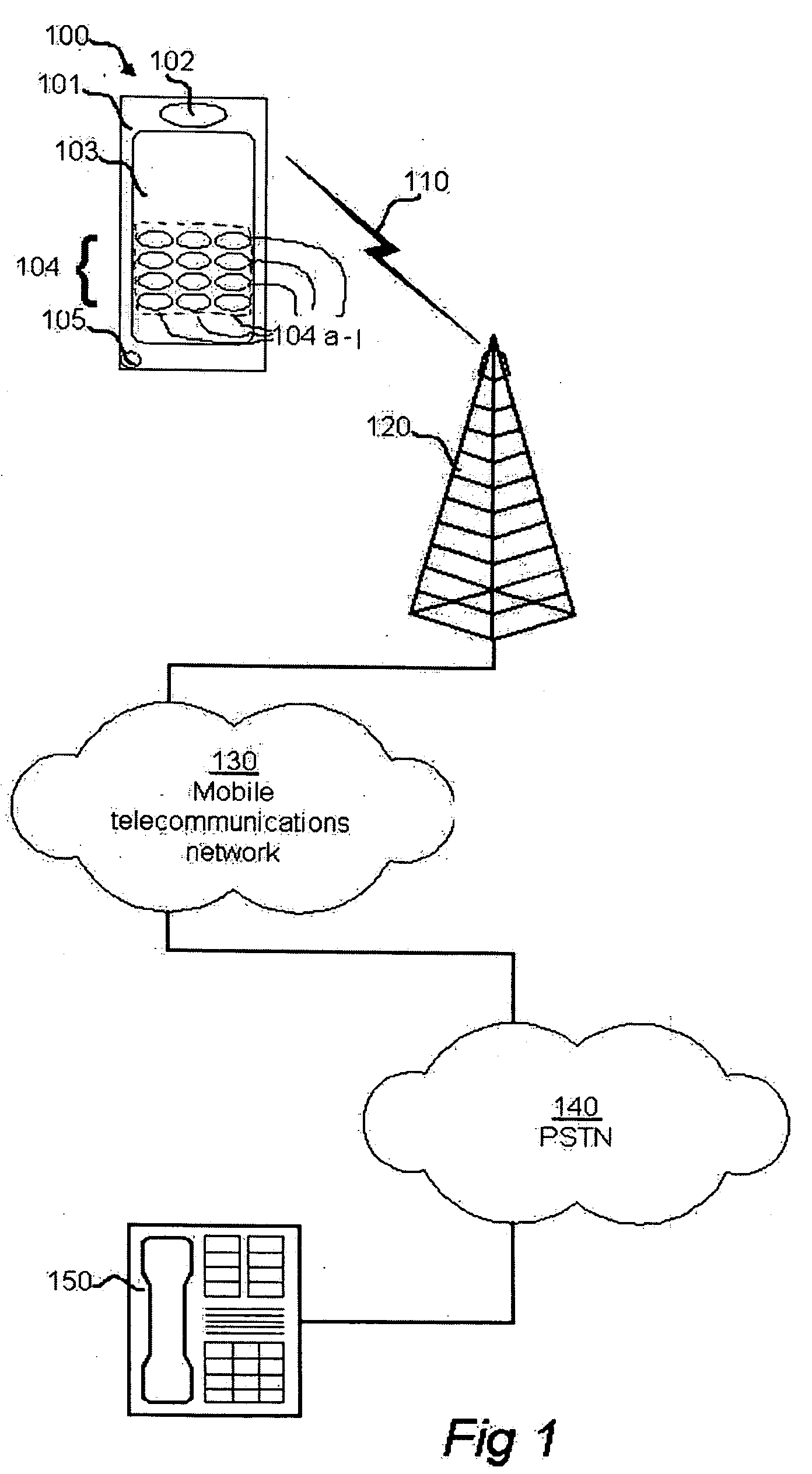
Electronic device having an imporoved user interface
InactiveUS20060007178A1Easily reachEasily accessCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingVirtual keyboardDisplay device
Owner:NOKIA CORP
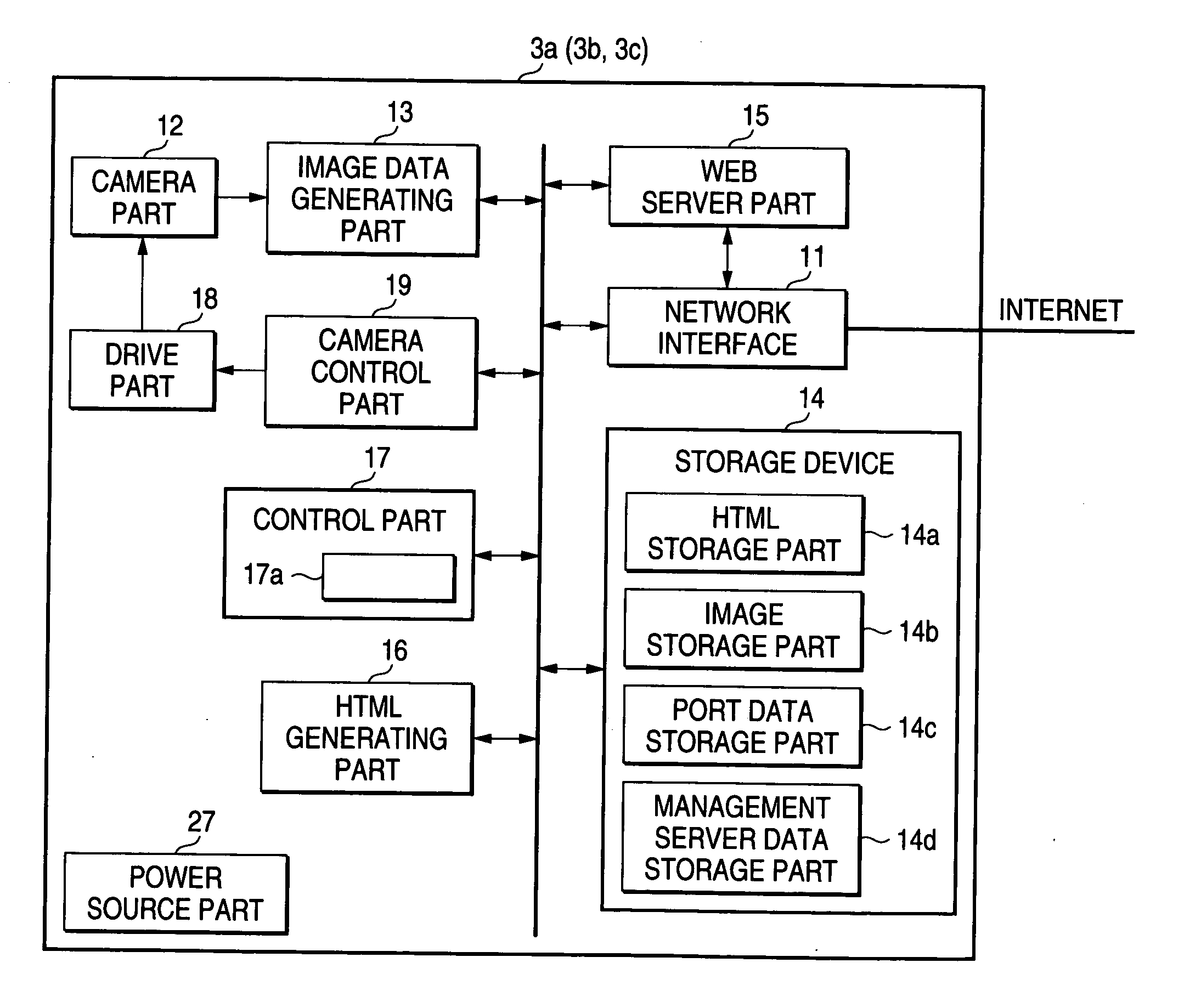
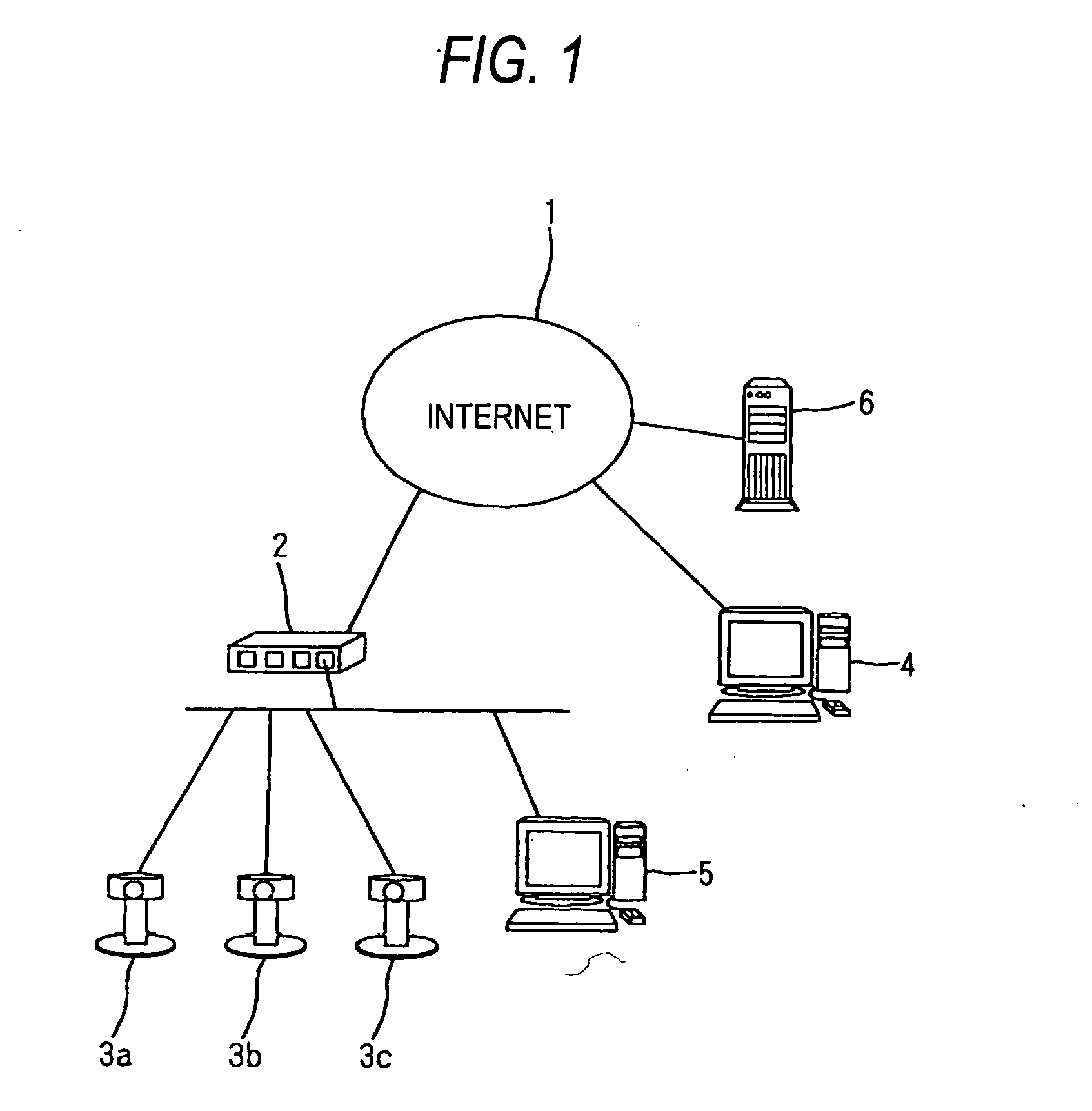
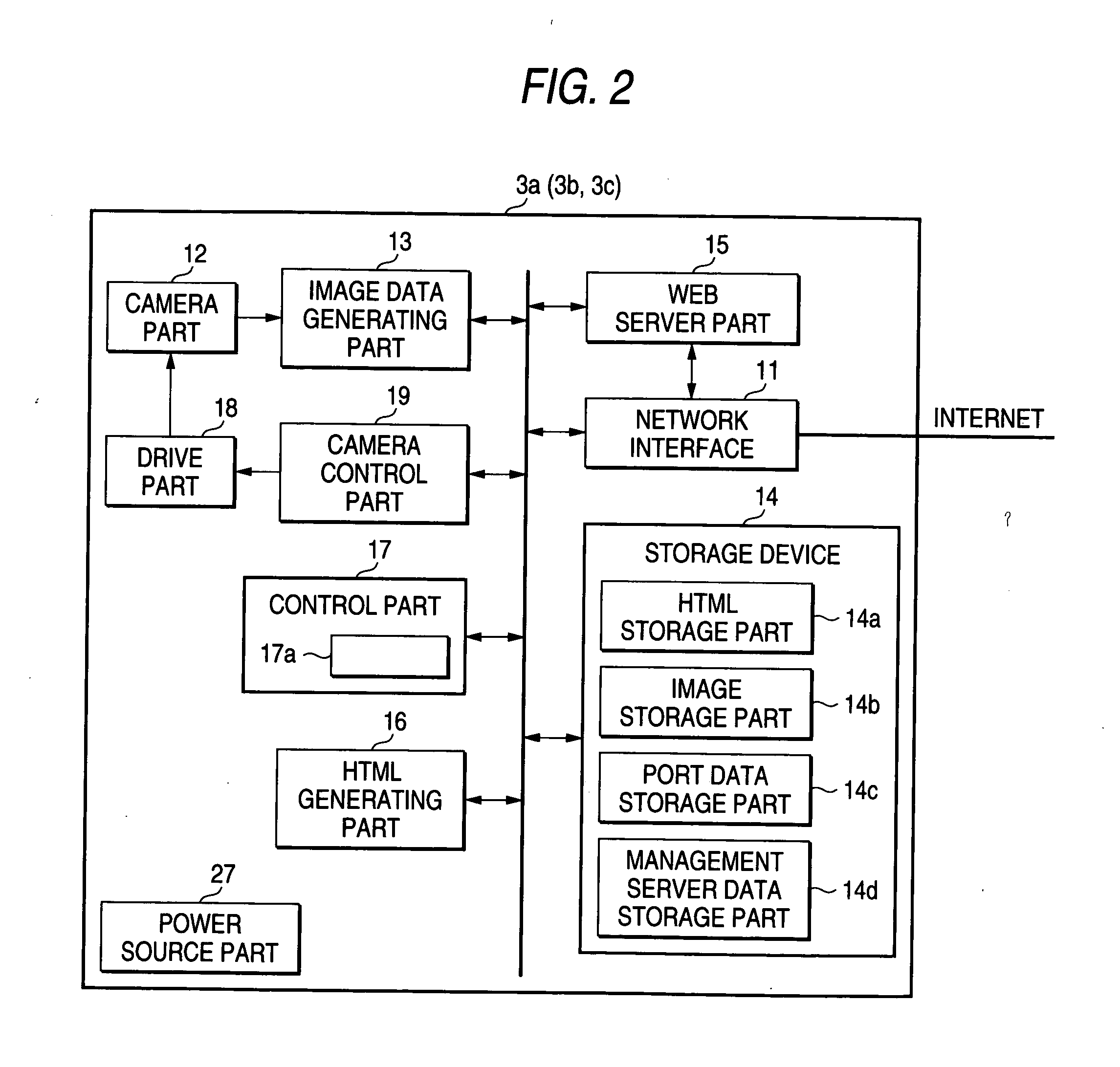
IP device, management server, and network system
InactiveUS20050152287A1Easily accessEasy accessData switching by path configurationNetwork cameraNetworked system
An IP device (for example, network cameras 3a, 3b, and 3c) connectable to a router (for example, a router 2) makes a request to the router for assignment of a port number when a predetermined operation is performed, and notifies a management server 6 connected to a wide area network of address data containing an assigned port number when the port number is assigned from the router, wherein address data containing the port number can be registered in the management server 6 on the wide area network, so that, even when access is made from the terminal 4 on the wide area network side with a port number that is locally updated, access is made possible by transmitting address data of the IP device to the terminal 4.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Universal holder and flexible member for mounting, holding, and adjustably positioning electronic products and accessories
InactiveUS20100288895A1Easily accessEasy accessPipe supportsCandle holdersElectronic componentEngineering
In the first embodiment, a universal flexible connector or gooseneck and a movable holding device are provided for adjustably positioning electronic accessories relative to a TV or furniture. A mounting lug is connected to the flexible connector for mounting electronic accessories relative to a TV frame, wherein the TV frame is for mounting a TV on a wall. The holding device has adjustable arms for receiving any electronic component or accessory or media playing device (MPD), wherein said holding device is removably connected to the other end of the flexible connector. The flexible connector and holding device for holding the electronic component or accessory or media playing device (MPD) are movable as a unit to different positions relative to a TV, outside the periphery of the TV, for easy access to the electronic component or accessory by the user.
Owner:SHAMIE STEVEN
Video data stream concept
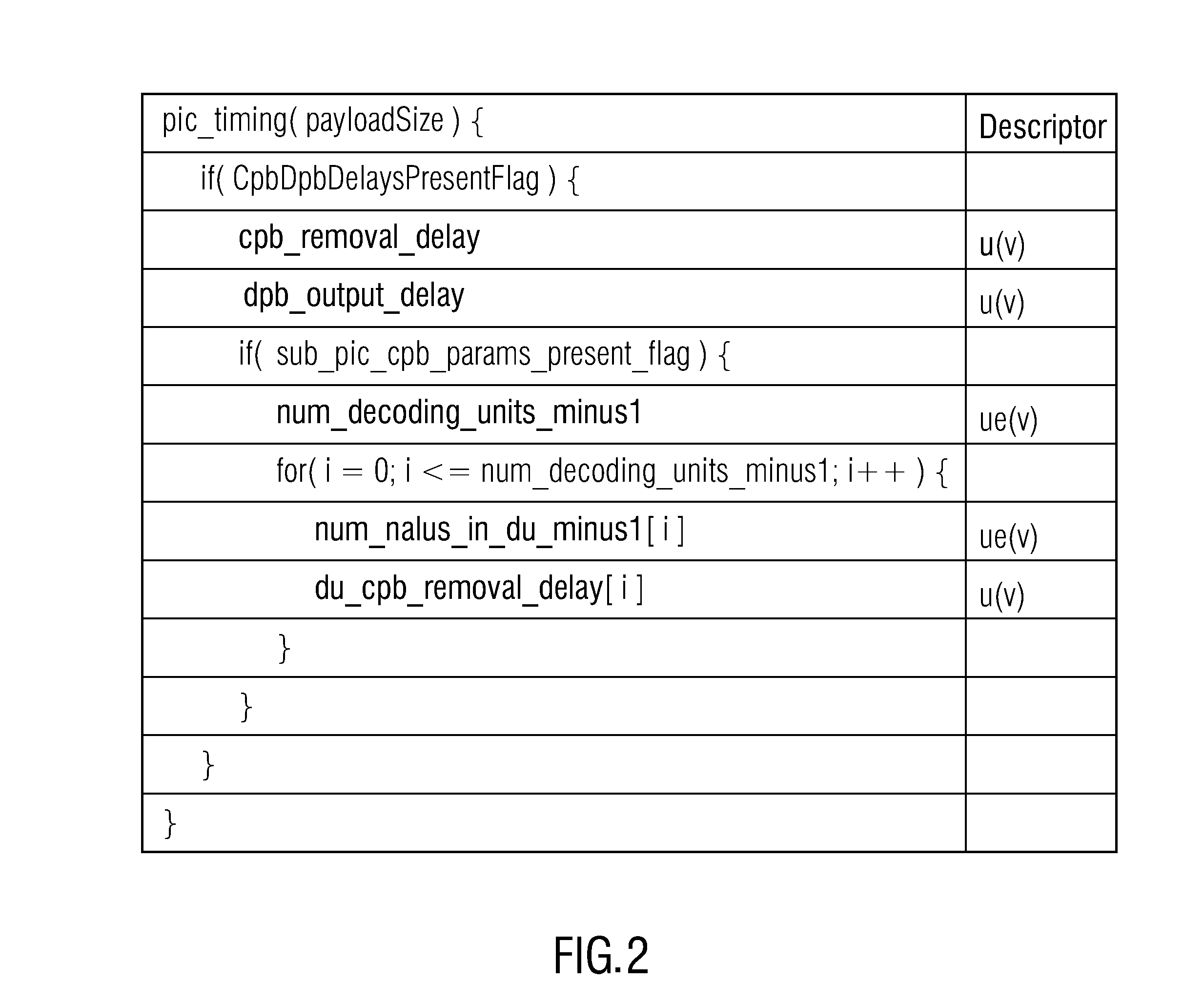
ActiveUS20150208095A1Easily accessLow end-to-end delayPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningComputer networkData stream
Decoder retrieval timing information, ROI information and tile identification information are conveyed within a video data stream at a level which allows for an easy access by network entities such as MANEs or decoder. In order to reach such a level, information of such types are conveyed within a video data stream by way of packets interspersed into packets of access units of a video data stream. In accordance with an embodiment, the interspersed packets are of a removable packet type, i.e. the removal of these interspersed packets maintains the decoder's ability to completely recover the video content conveyed via the video data stream.
Owner:GE VIDEO COMPRESSION LLC
Methods and systems for generating wind energy
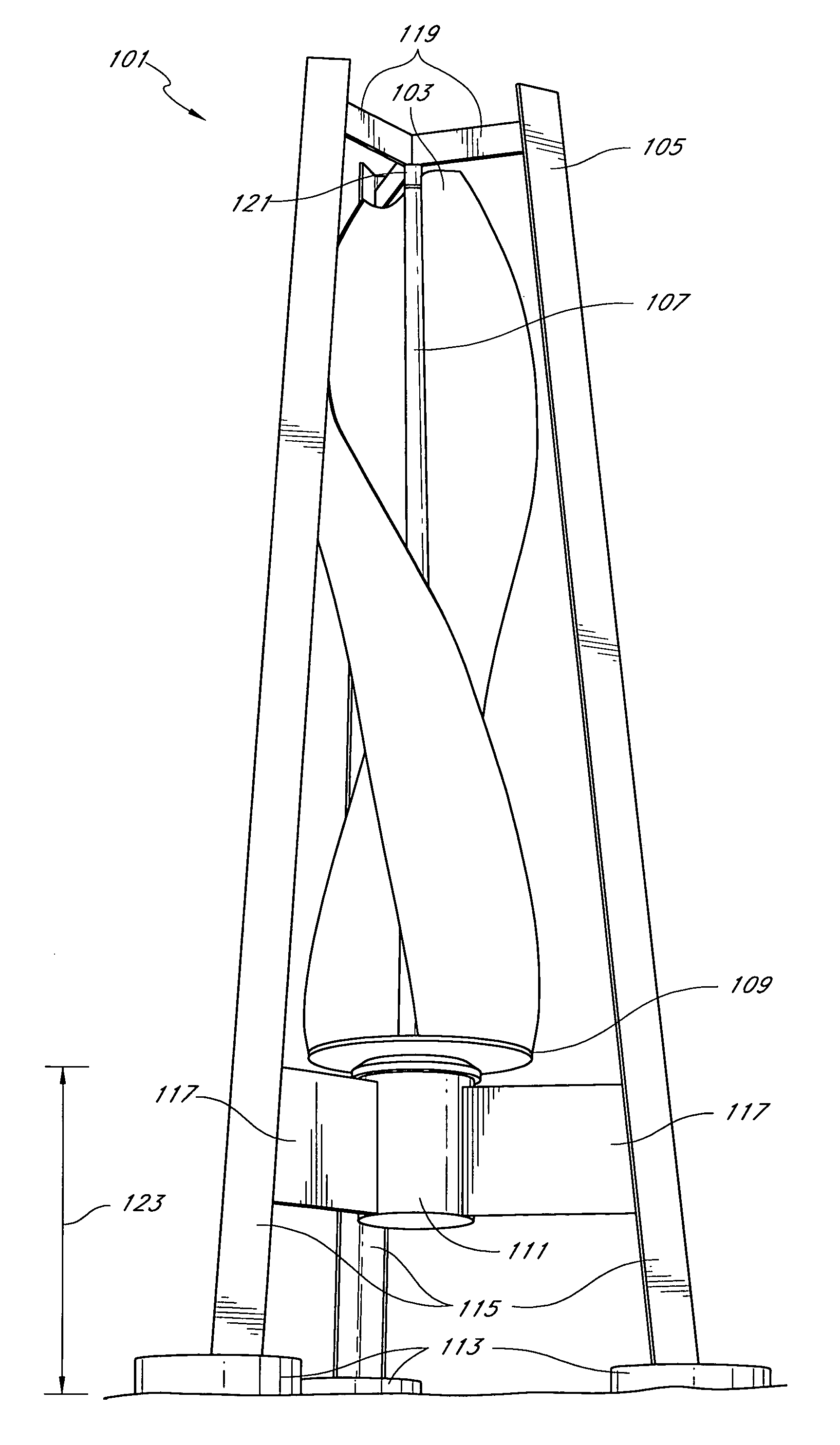
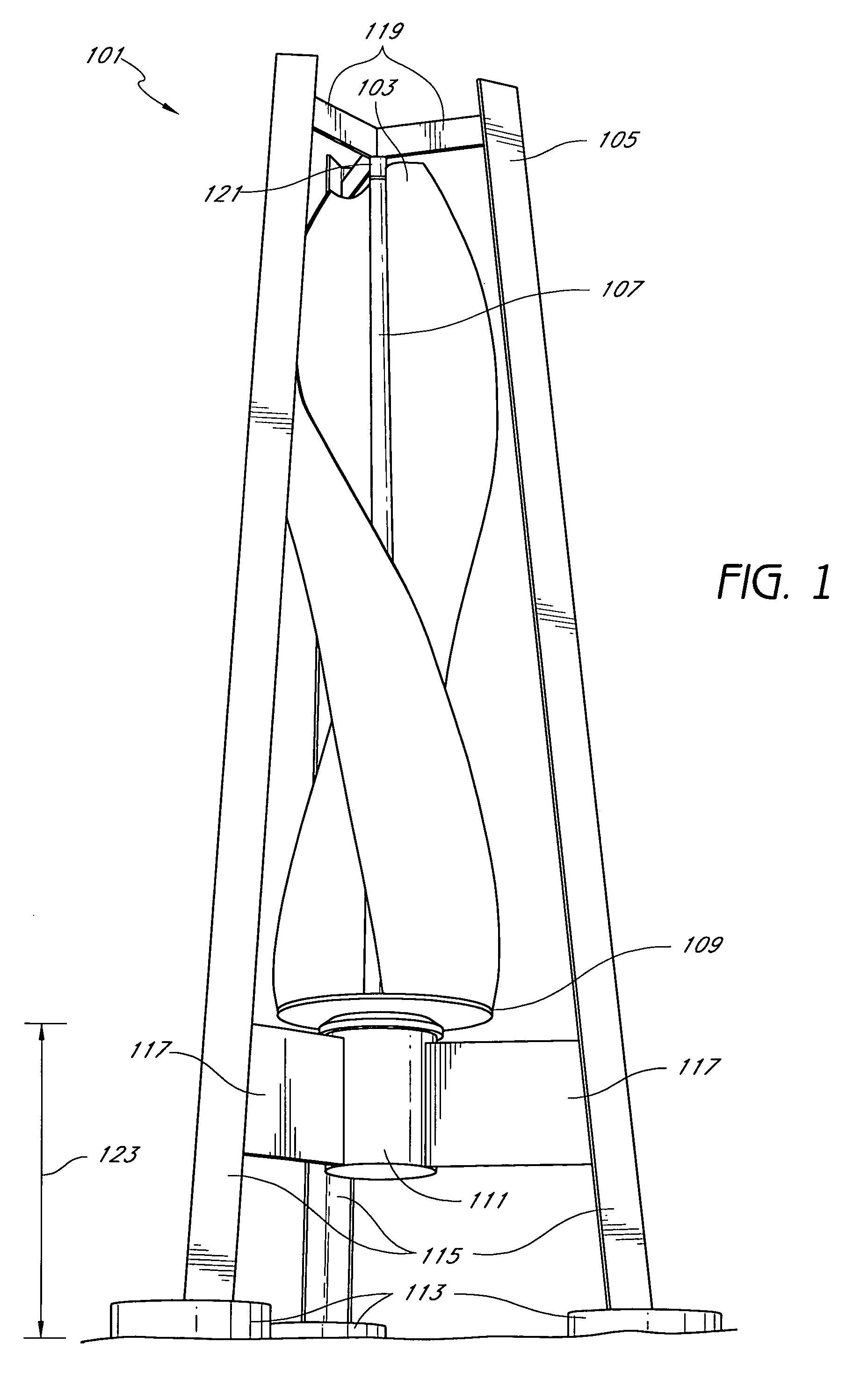
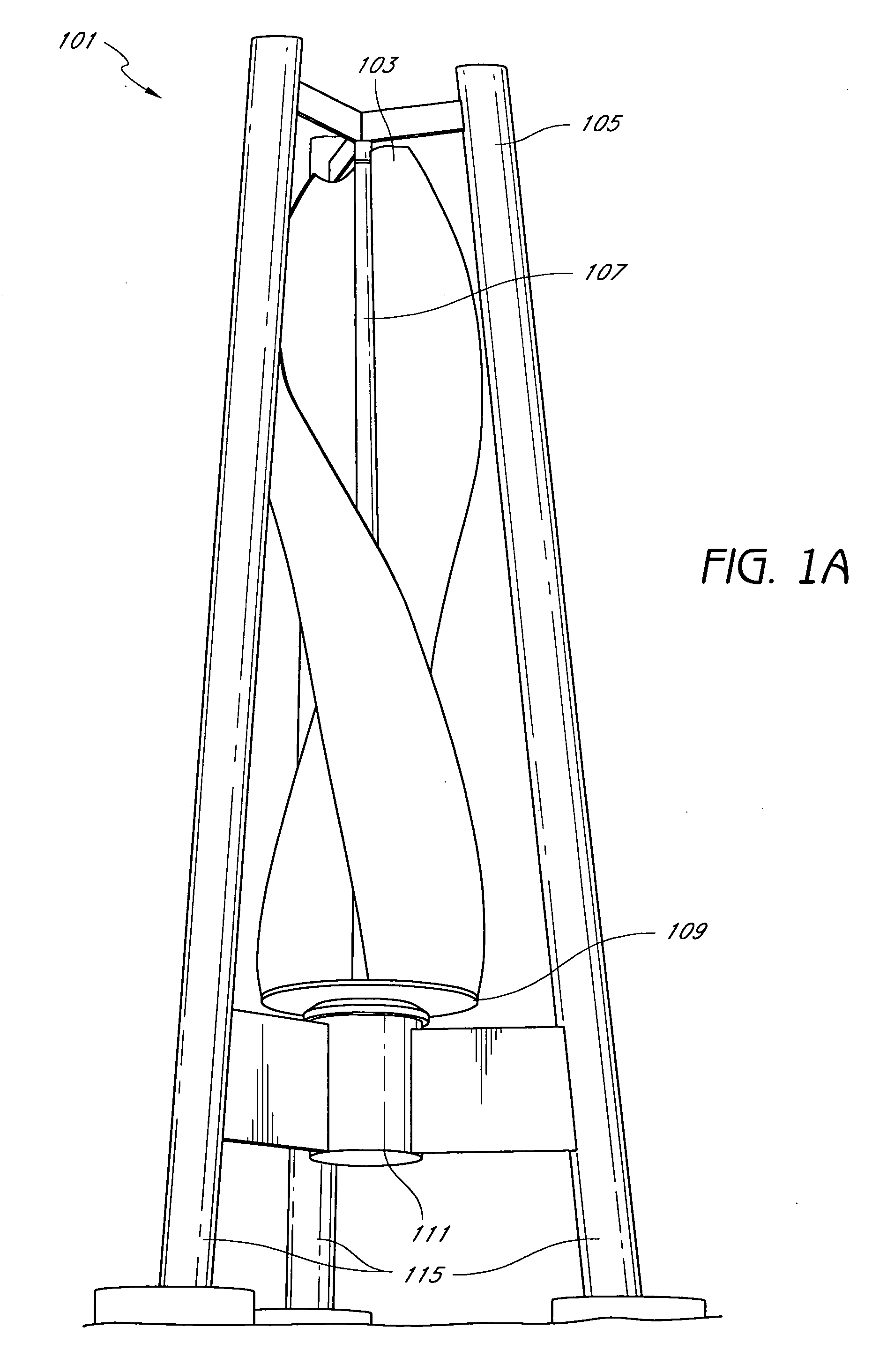
InactiveUS20070029807A1Lower maintenance costEasily accessMachines/enginesWind motor combinationsWind forceElectricity
The present disclosure disclosures methods and systems for harnessing wind to create electricity. The present disclosure discloses a helical blade vertical axis wind generator. One or more blades are spun by the force of wind which in turn spins a generator and produces electricity.
Owner:SPIRA INT
Sportsman's box portable cooler
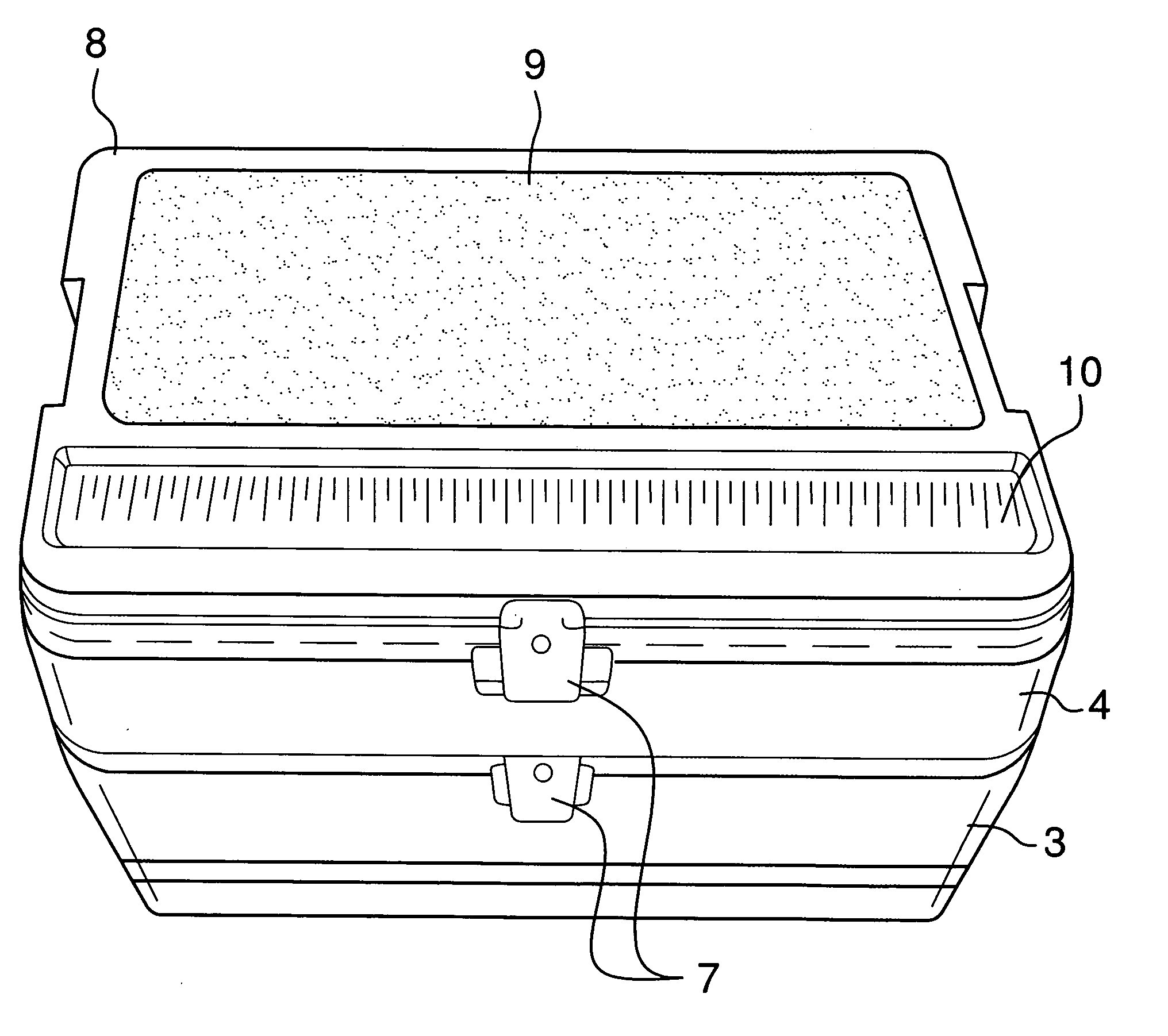
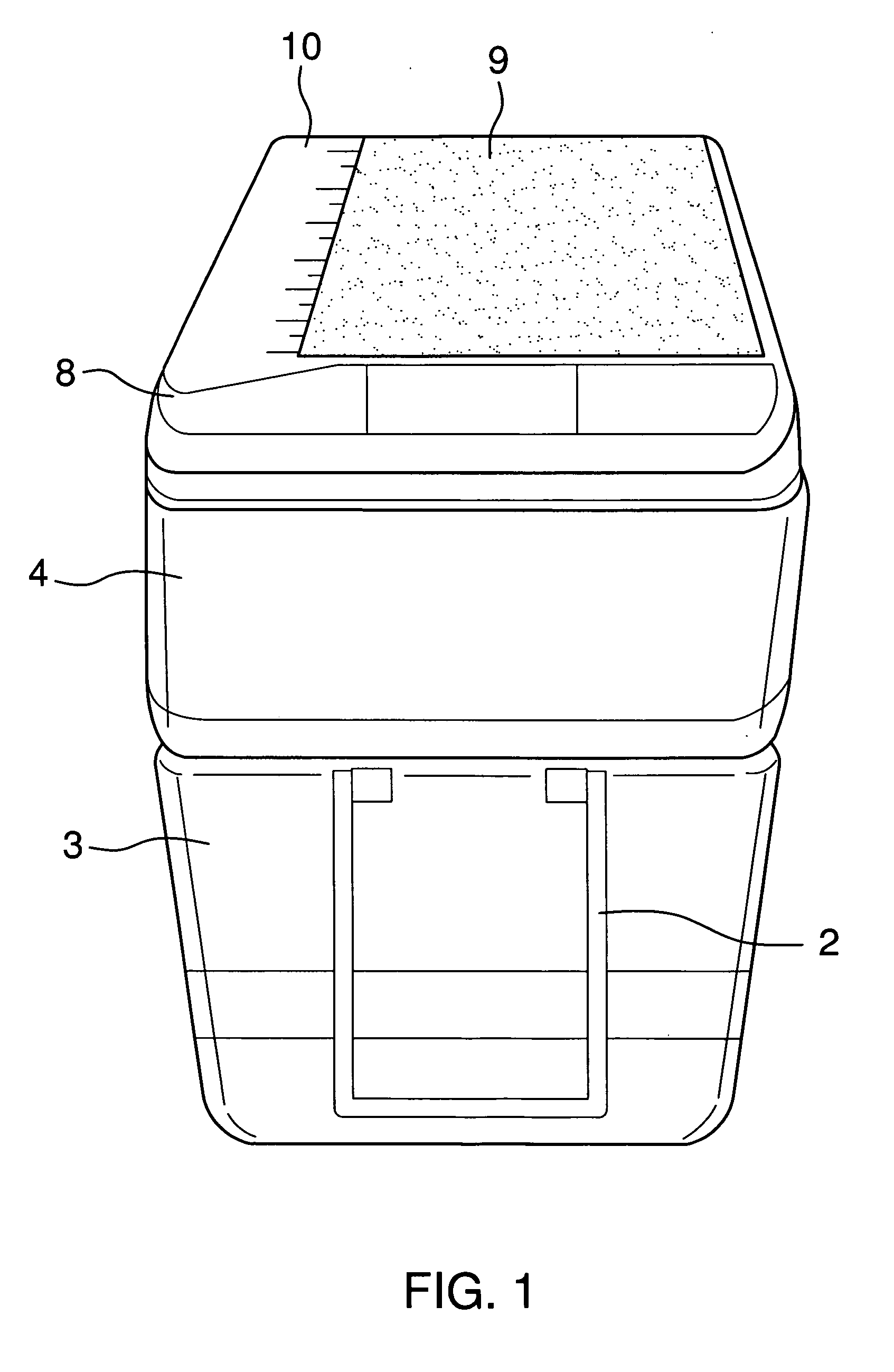
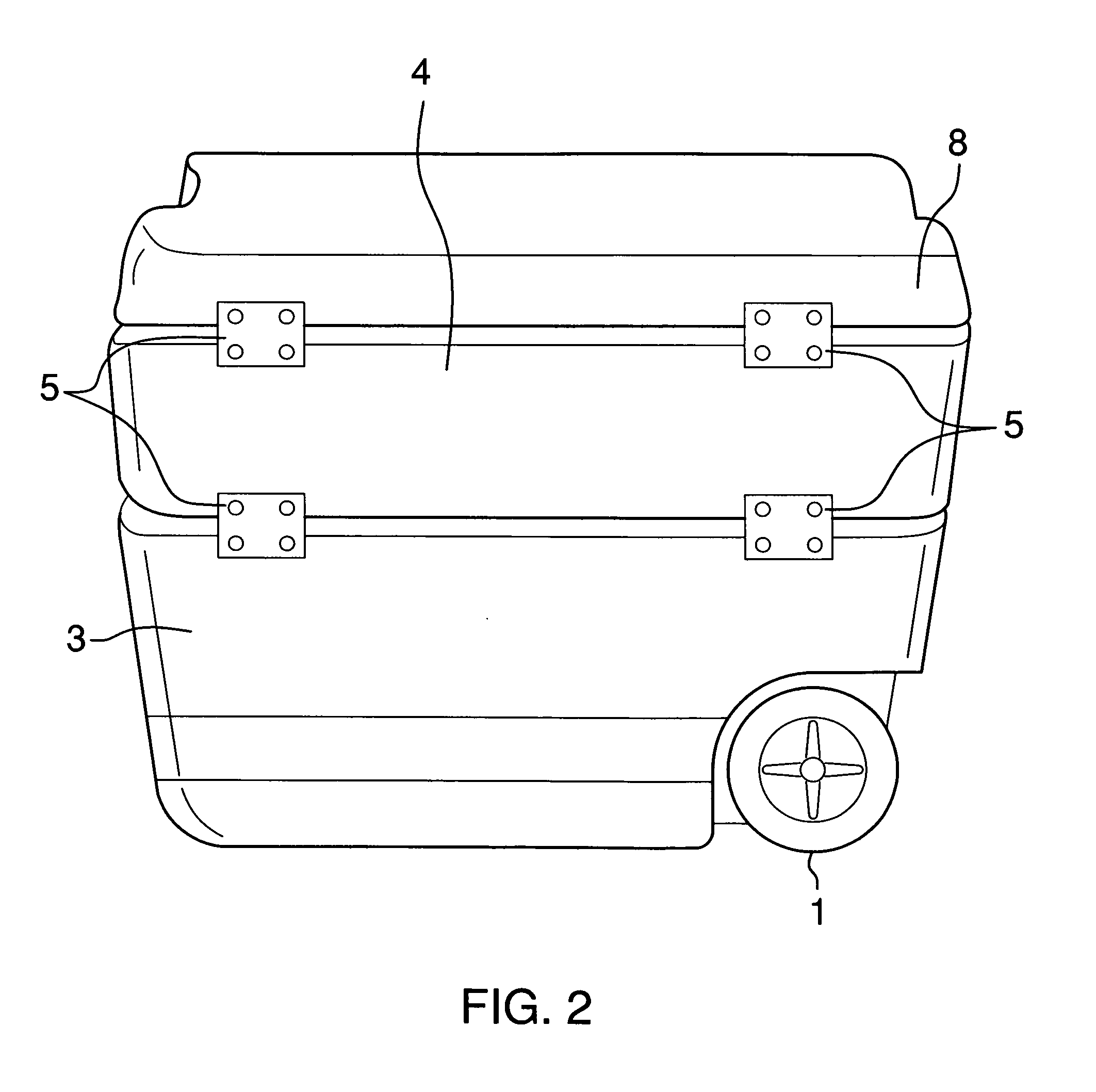
InactiveUS20110226785A1Easily transportEasily accessDomestic cooling apparatusLighting and heating apparatusEngineeringDry storage
The sportsman box is a wheeled cooler with a lid and cover to that lid forming a compartment for containing a tackle box or a dry storage box or a condiment container with a cutting board and built in ruler. The cooler has a handle for pushing or pulling. In some models, the cooler has a split cover which allows the user to gain access to the cold section of the cooler for inserting or removing items such as food, beverages, and the like without requiring the user to remove all items from the other side of the lid. The cooler may be made in a variety of sizes and colors to suit the wishes of the user.
Owner:SAKELL JAMES
Child resistant dispenser
InactiveUS6866164B2Easily accessAvoid accessDecorative coversClosure decorative/protective coversEngineering
Owner:BERRY PLASTICS CORP
Airport map system with compact feature data storage
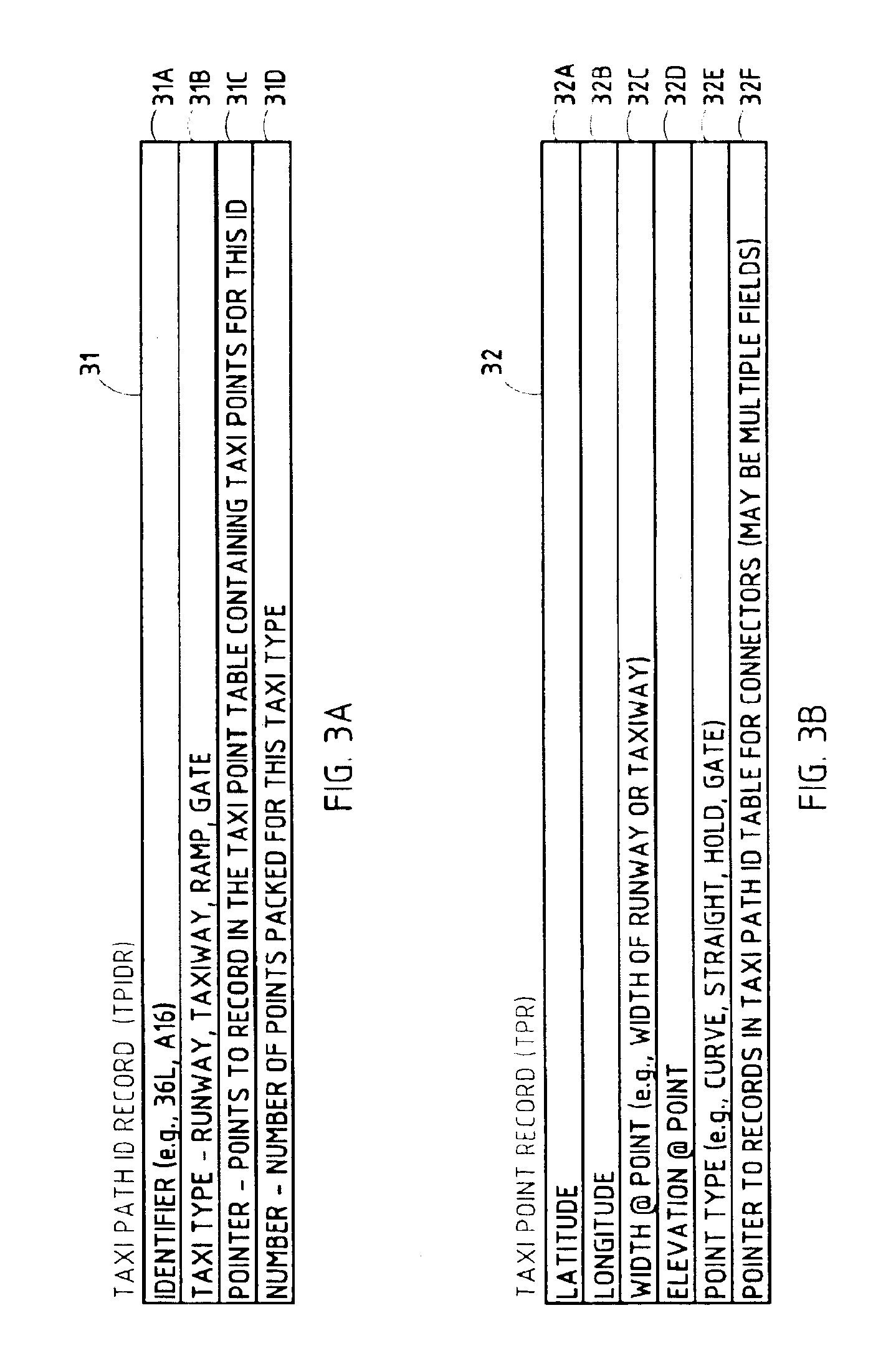
InactiveUS6862519B2Reduced space requirementEasily accessAnalogue computers for vehiclesHelicopter landing platformData pointAirplane
An airport map display system for an aircraft displays the airport paved surfaces and structures to a pilot or crew member. The system displays runways, taxiways, connectors, ramps, gates, and buildings. Hold and yield points may also be displayed. A compact set of specific data points and associated pavement width values is used to store unique data for each airport.
Owner:SMITHS AEROSPACE INC
System and method for using interactive electronic representations of objects
InactiveUS20040122731A1Quickly locateEasily accessAdvertisementsMultimedia data retrievalComputer visionReproduction
The present invention provides a method for providing, with respect to a media source, an interactive electronic reproduction of a media object that includes a secondary object appearing in the media source.
Owner:TANGELO IP LLC
Reservation of TCP/UDP ports using UID, GID or process name
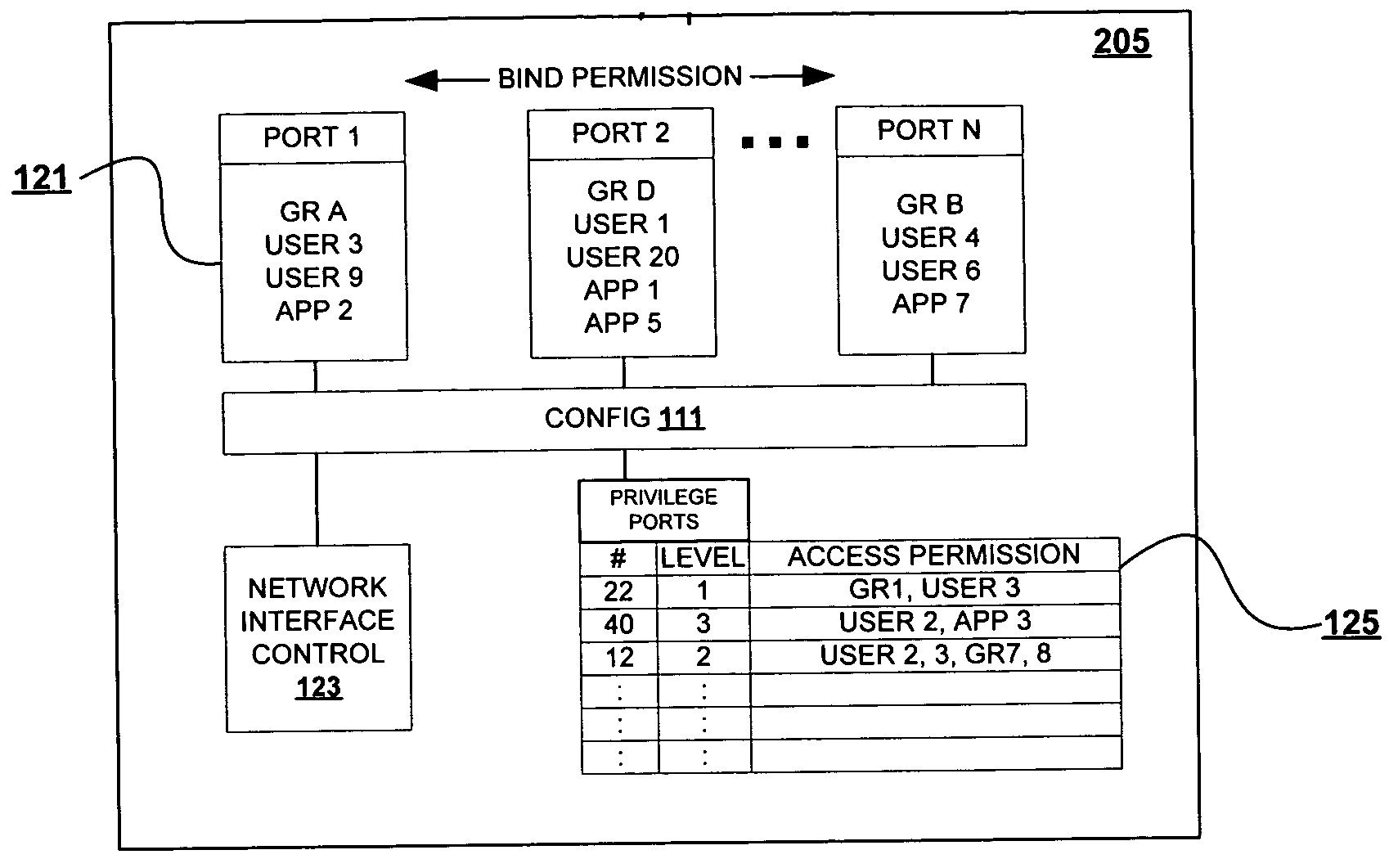
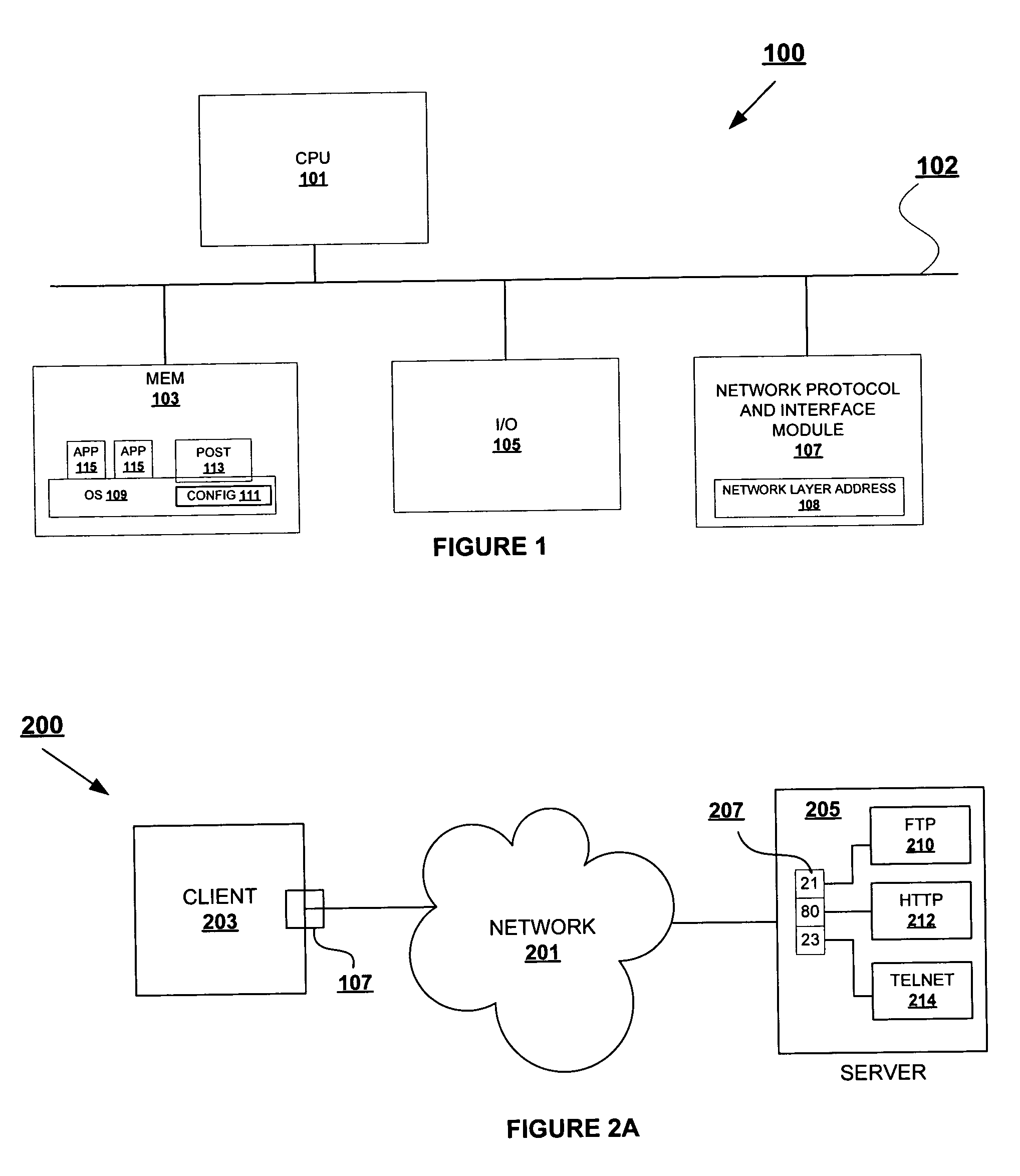
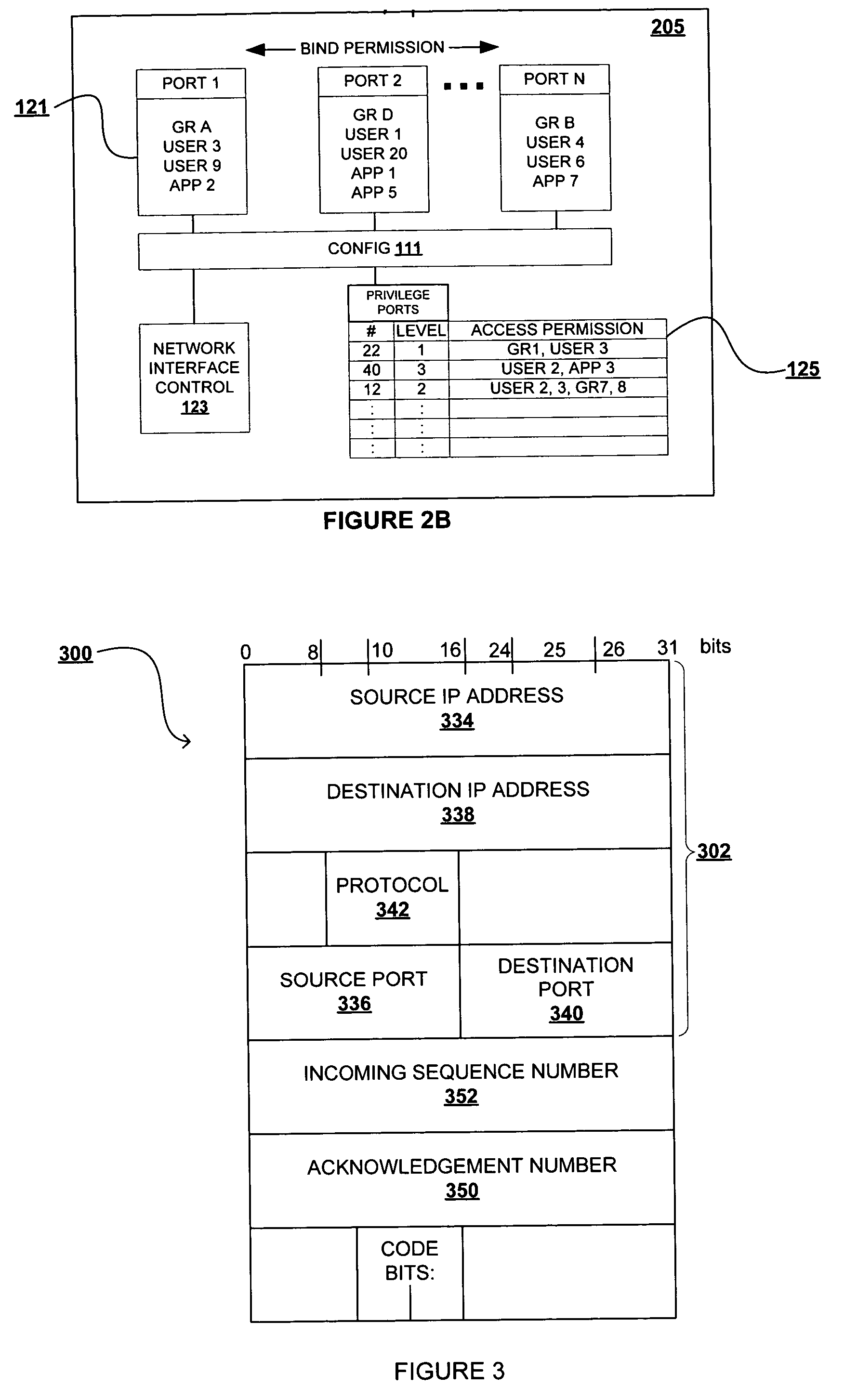
ActiveUS20050044227A1Maintain securityEasily accessDigital computer detailsElectric digital data processingSystem administratorAccess port
A method for enhancing port allocation procedures in a computer network by reserving specific ports to particular users and processes. Access protocol for ports are modified to enable a system administrator to defined / pre-select particular users and processes that may access the specific ports. A table structure is provided with the list of users and processes with bind authority for the particular port. When a bind request is received the ID of the user or process is confirmed against those within the table of the requested port. Bind access is provided only when the user ID or process ID matches one that is within the table. The port is allocated to the user / program until the user / process is complete, and other requests for access to the port are ignored until final completion of the ongoing process, even when a temporary disconnect of the port occurs.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Television schedule system
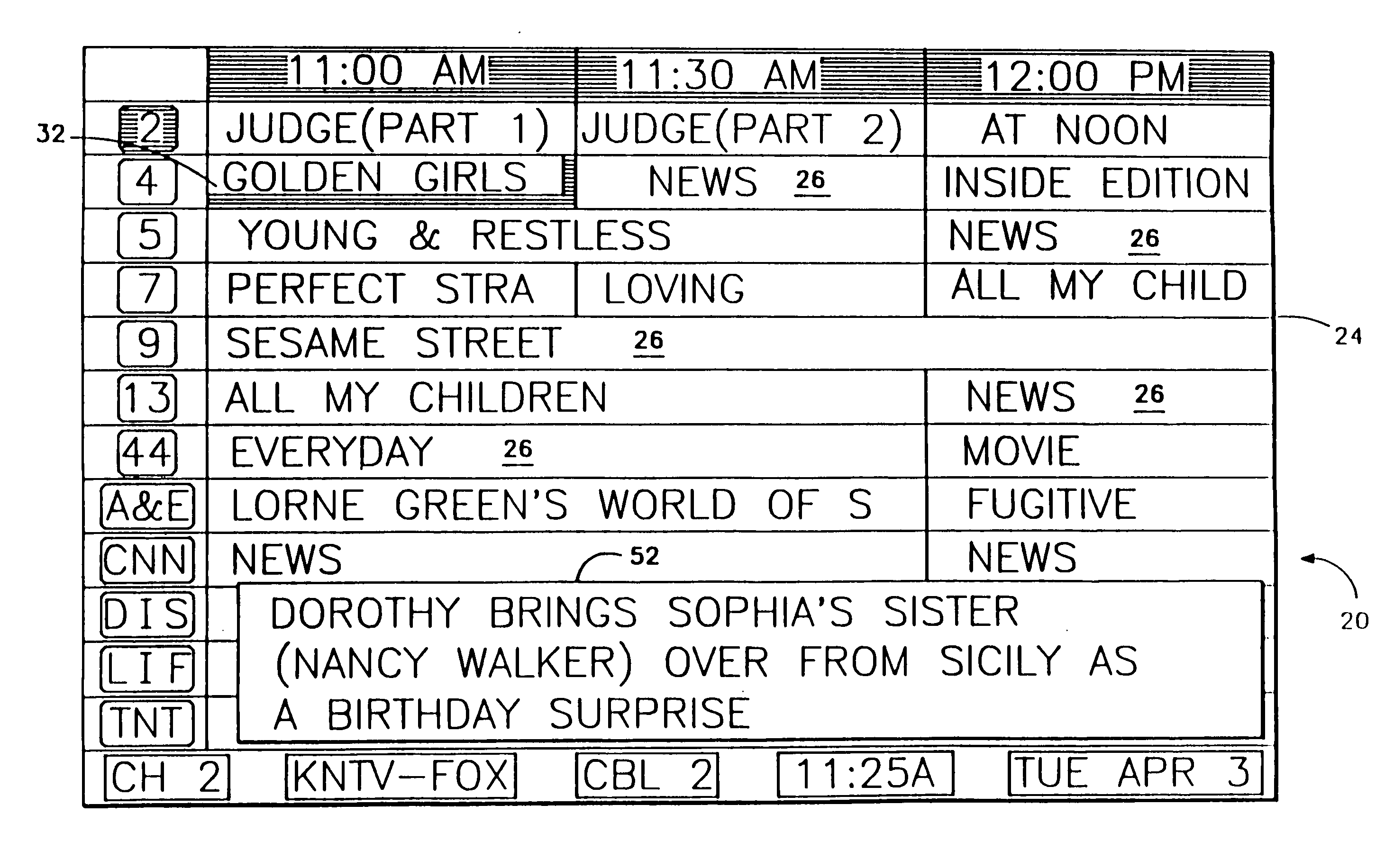
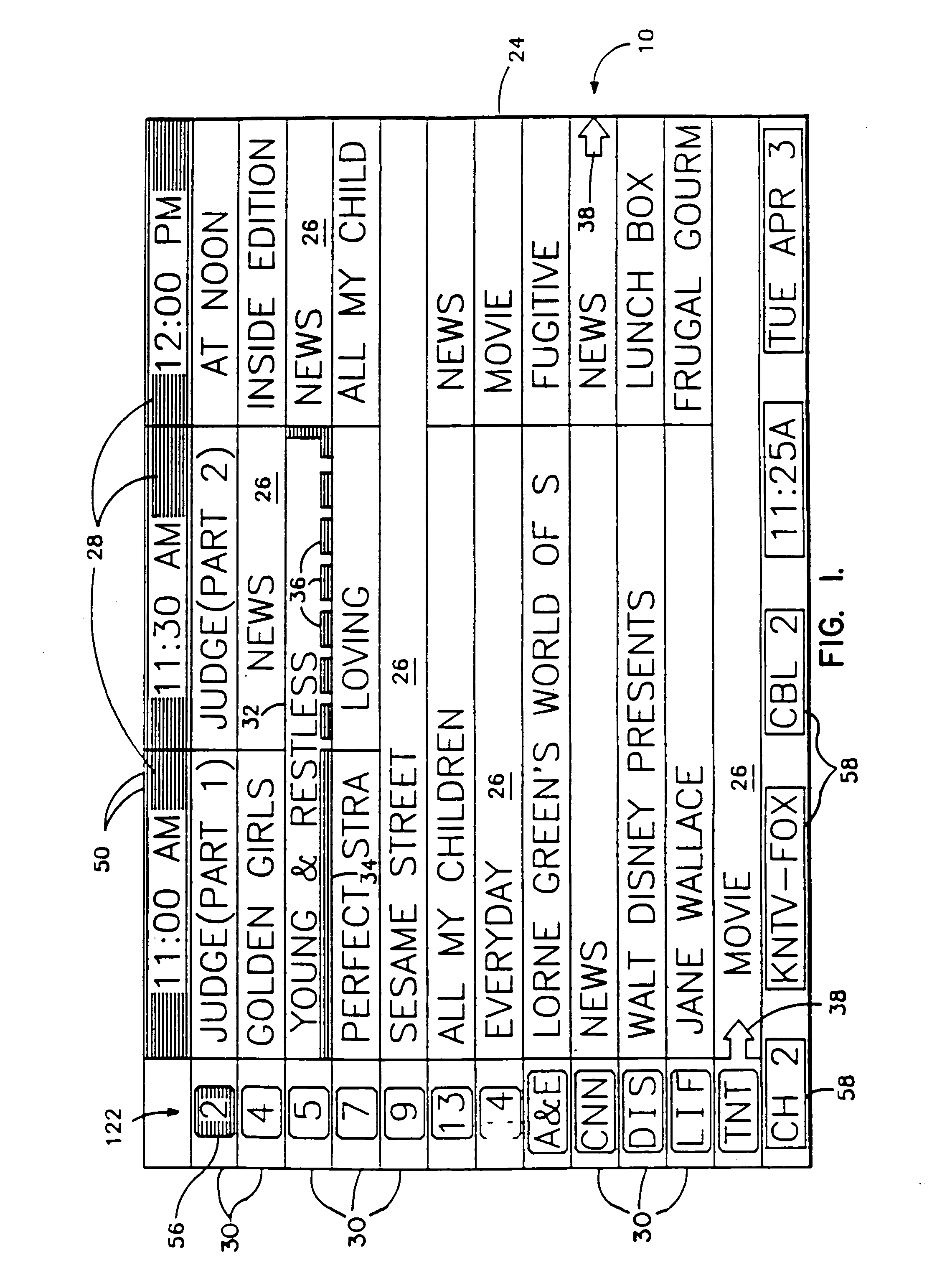
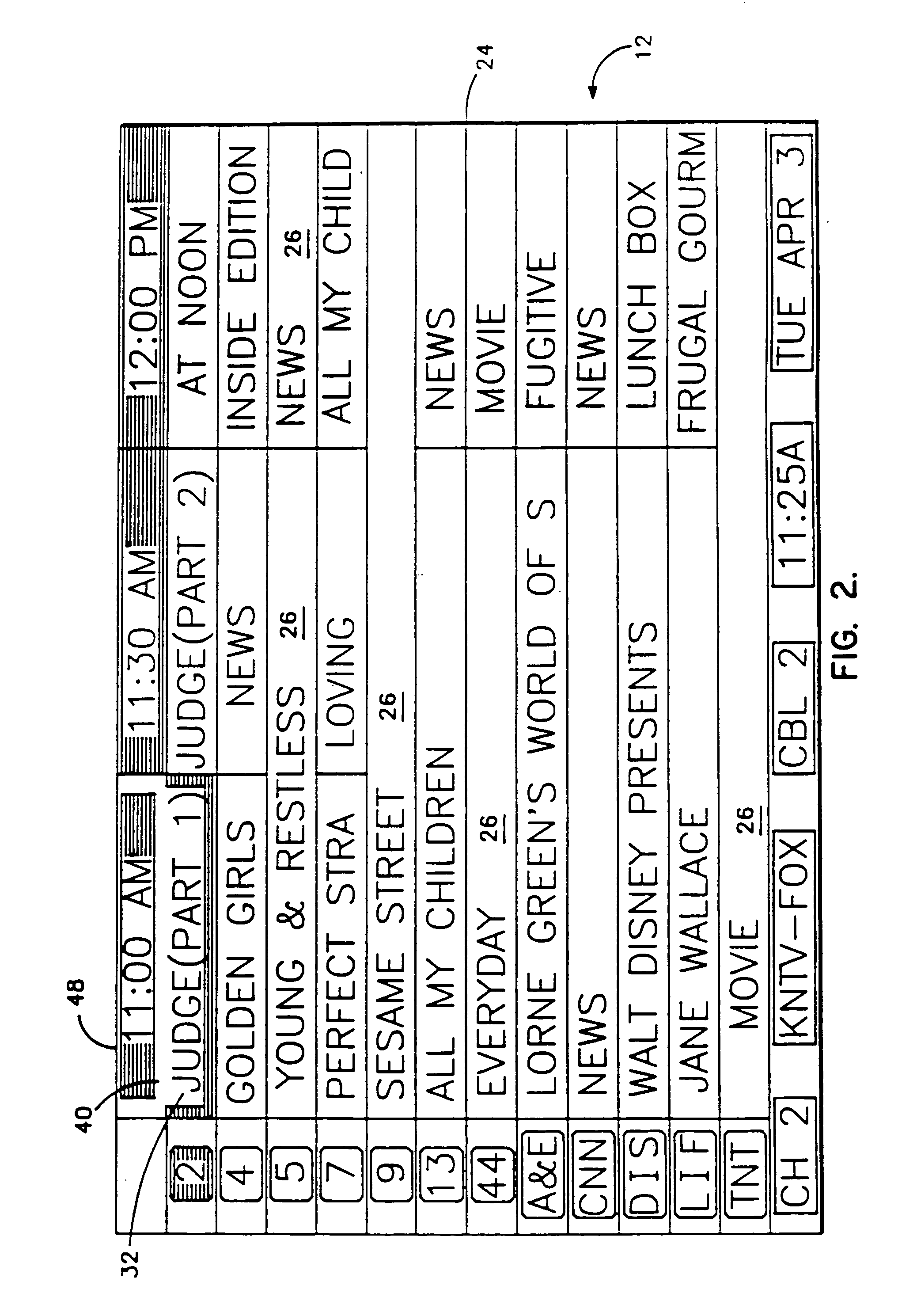
InactiveUS20050251828A1User control be simplifyEasily accessTelevision system detailsTime indicationWrap aroundEntire cell
Screen (10) for a user interface of a television schedule system and process consists of an array (24) of irregular cells (26), which vary in length, corresponding to different television program lengths of one half hour to one-and-one half hours or more. The array is arranged as three columns (28) of one-half hour in duration, and twelve rows (30) of program listings. Some of the program listings overlap two or more of the columns (28) because of their length. Because of the widely varying length of the cells (26), if a conventional cursor used to select a cell location were to simply step from one cell to another, the result would be abrupt changes in the screen (10) as the cursor moved from a cell (26) of several hours length to an adjacent cell in the same row. An effective way of taming the motion is to assume that behind every array (24) is an underlying array of regular cells. By restricting cursor movements to the regular cells, abrupt screen changes will be avoided. With the cursor (32) , the entire cell (26) is 3-D highlighted, using a conventional offset shadow (34). The offset shadow (34) is a black bar that underlines the entire cell and wraps around the right edge of the cell. To tag the underlying position—which defines where the cursor (32) is and thus, where it will move next—portions (36) of the black bar outside the current underlying position are segmented, while the current position is painted solid.
Owner:ALL MEDIA GUIDE +10
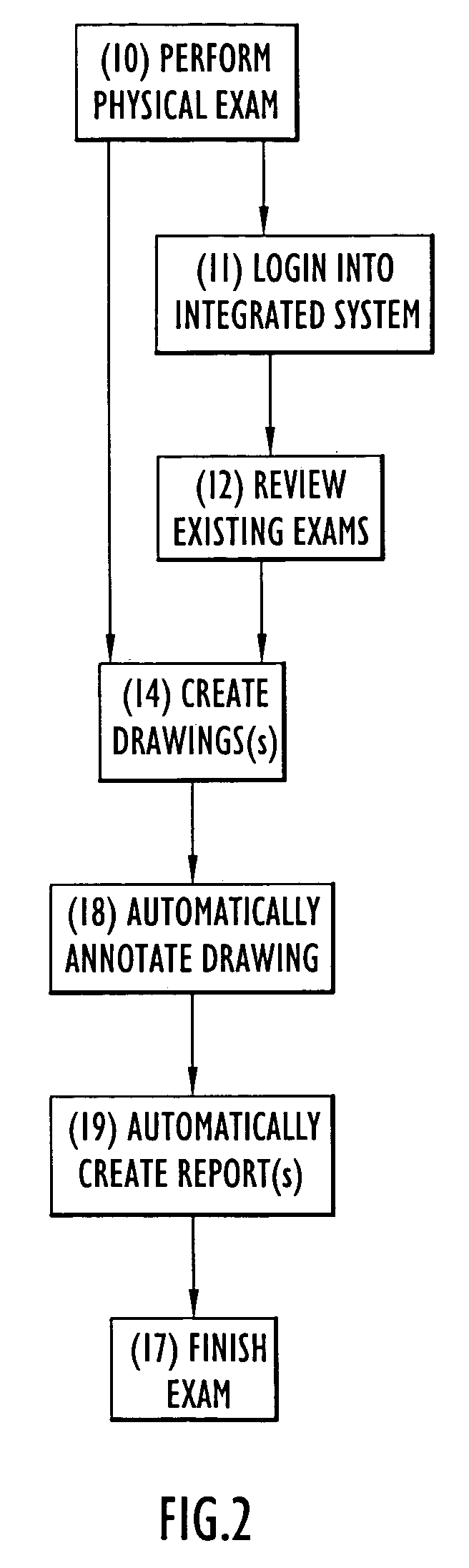
System and method for automated report generation of ophthalmic examinations from digital drawings
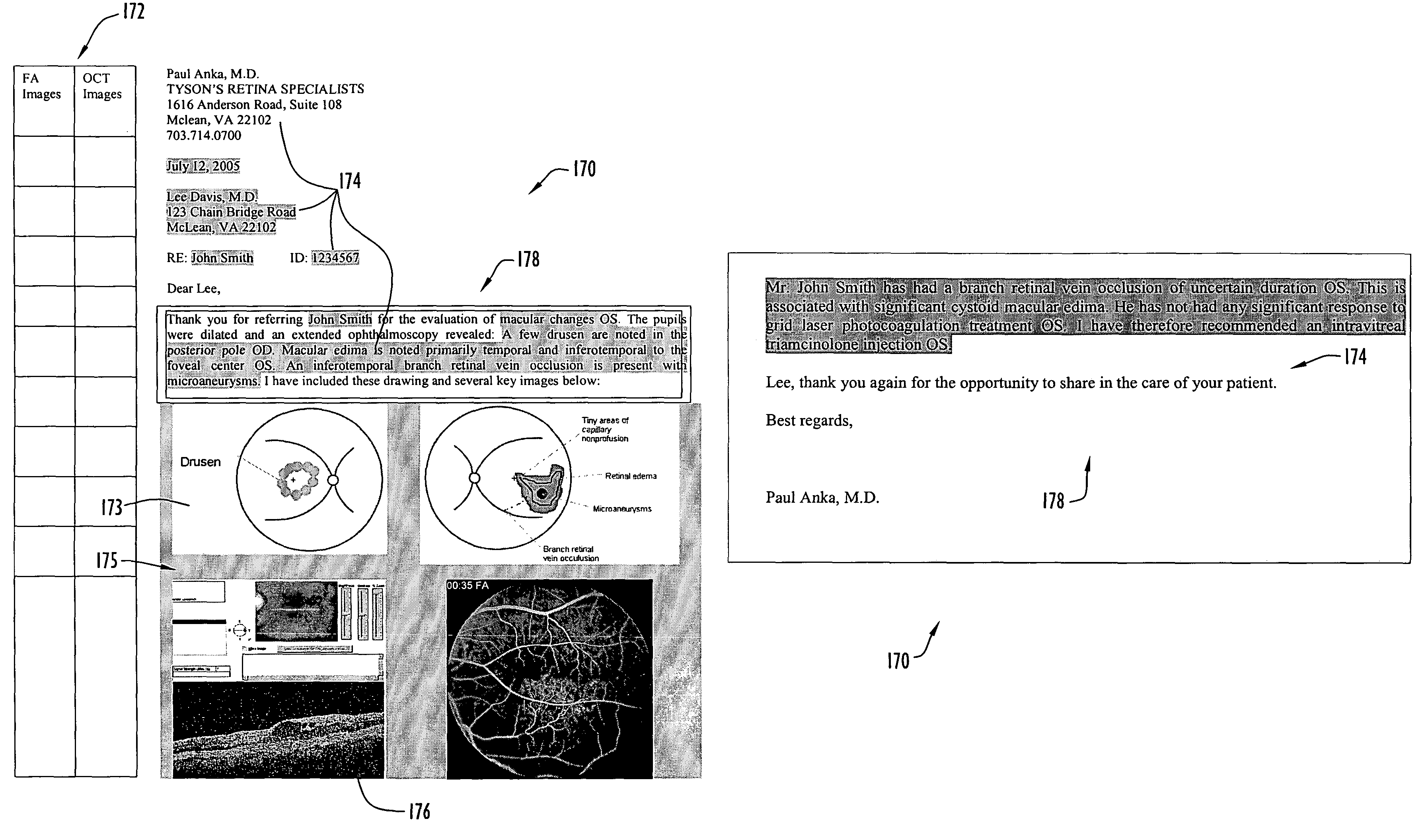
ActiveUS7793217B1Easily accessEasy accessMedical communicationMedical report generationData conversionPhysician roles
The present invention is a combined image viewing, drawing, and reporting system, which provides: an easy way to access digital images while creating a digital drawing; and an automated method of creating medical reports by translating the drawing data into standard reports. The present invention system provides automated medical drawings and creates medical reports as a result of translating drawing results. The system provides invaluable tools for drawing, diagnosing and treating ophthalmic and / or other types of diseases by generating an automated translation report based on the physician drawing. Customized reports (e.g., a medical drawing report, a referral note, a medical letter, billing based information, a proofsheet for the patient chart, etc.) can be added by the user. A physician can design a format for a report via system utility tools. The present invention may be a stand-alone system, and / or connected to a network.
Owner:ANKA SYST INC
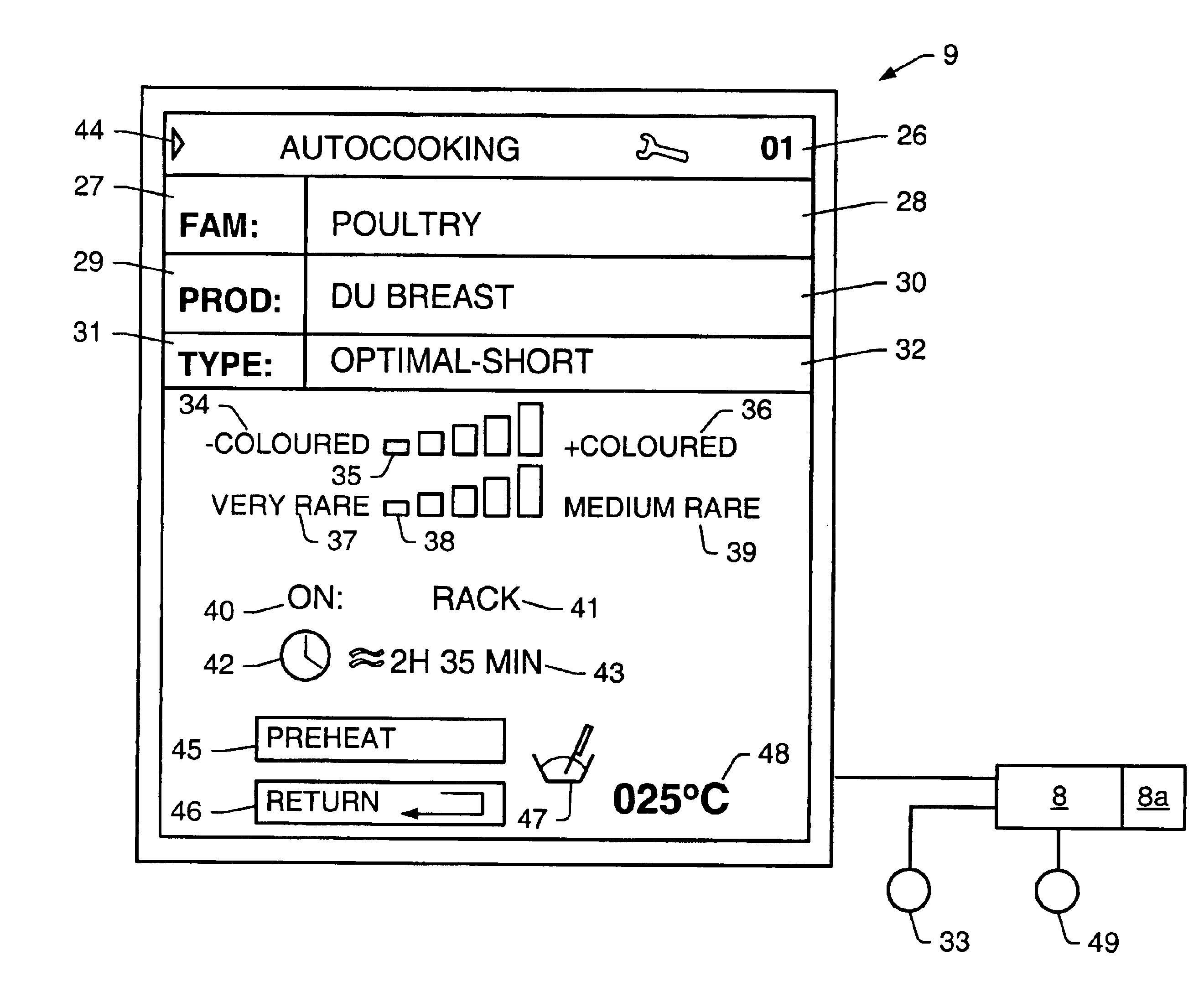
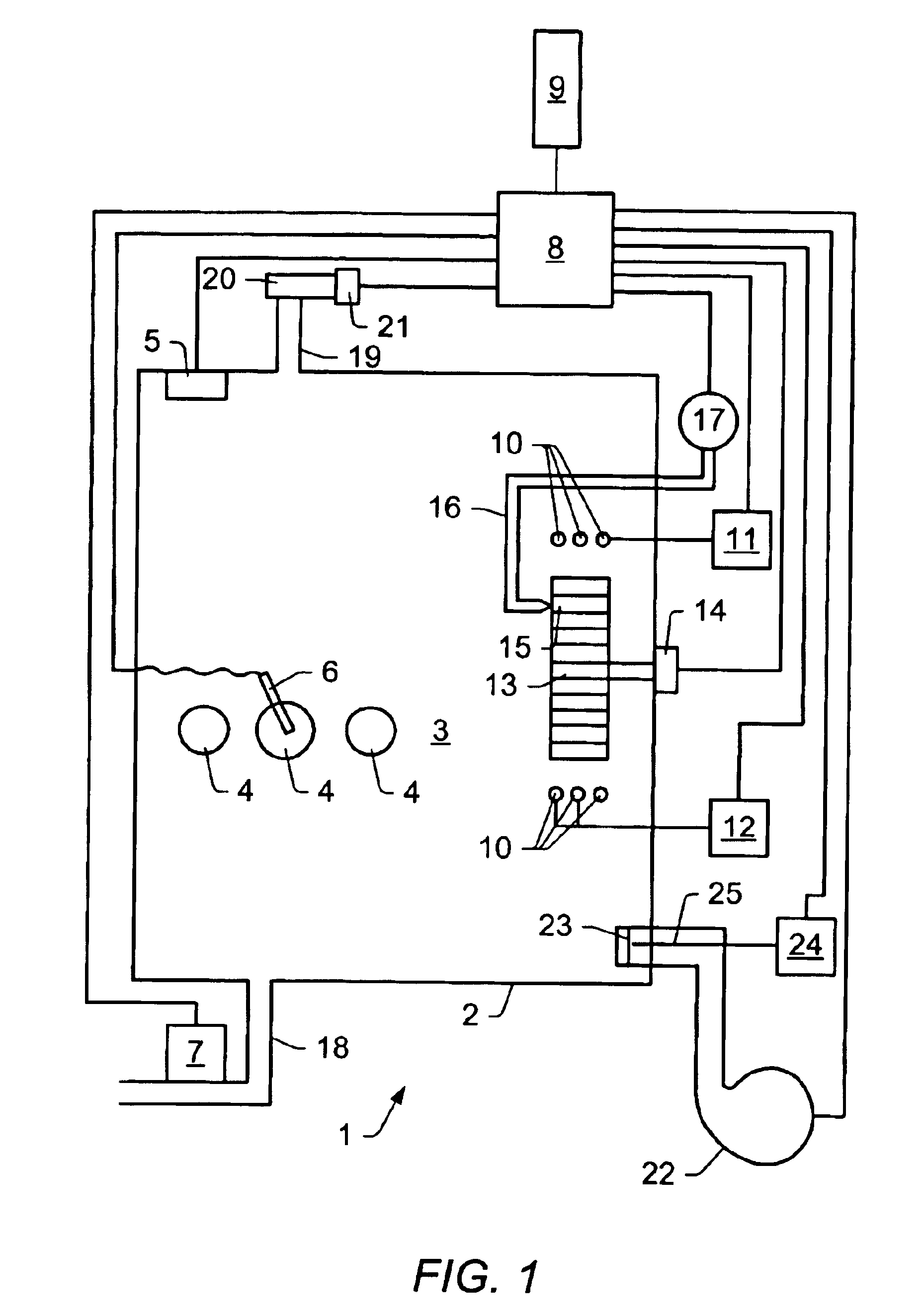
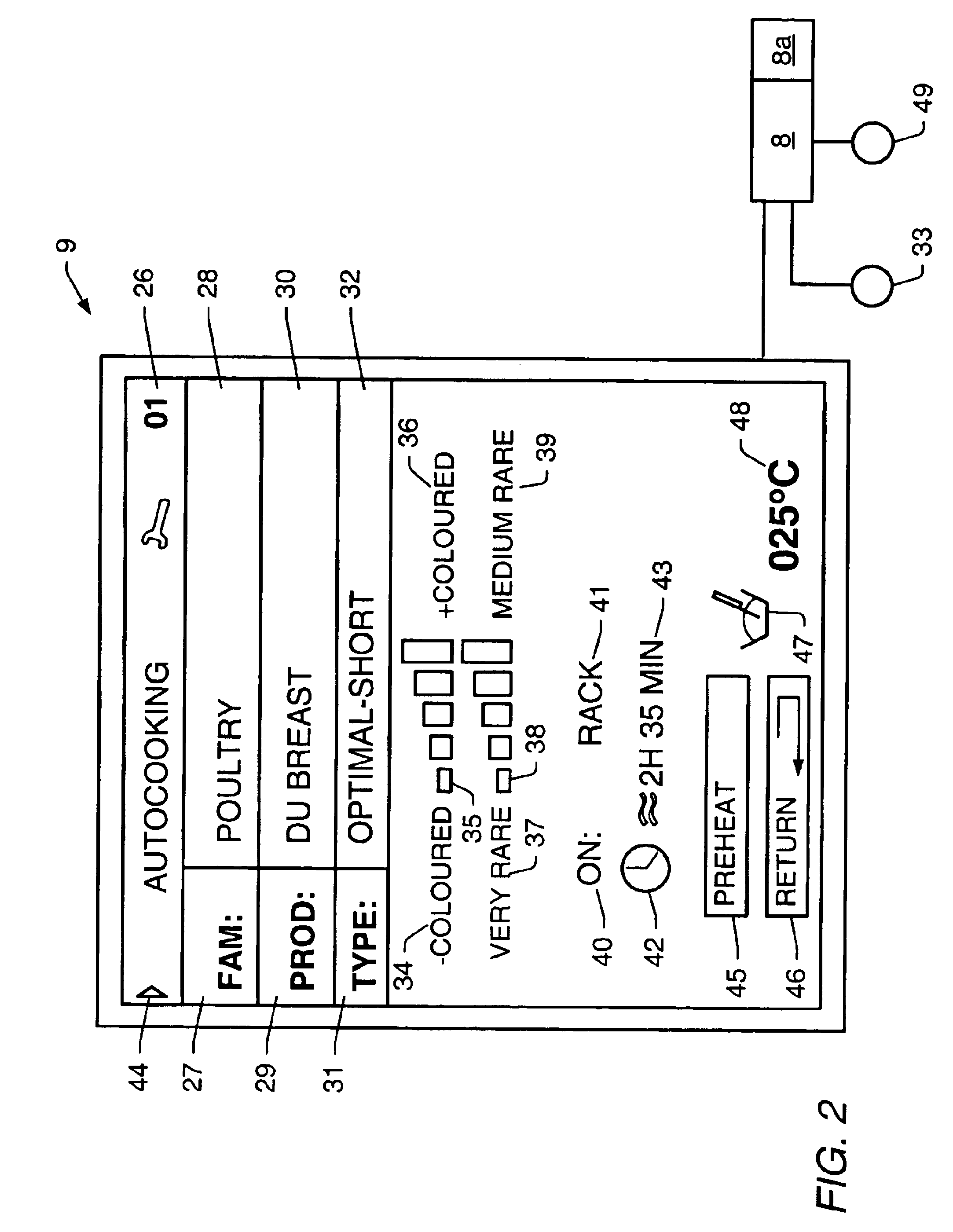
Oven control system
InactiveUS7057142B1Easily accessEasy accessDomestic stoves or rangesLighting and heating apparatusData entryProduct family
Oven control system, comprising a display screen 9, a data input means 32 and a calculation unit 8 able to send instructions to the display screen 9 and to receive instructions from the data input means, the said calculation unit 8 comprising a means for grading cooking programmes at least as a function of a first criterion of family of products to be cooked, of product to be cooked within a family, or of recipe or of method of cooking, and a means for adjusting the cooking programme according to at least one second internal final criterion and one third external final criterion, the display screen 9 being able to simultaneously display the selected values of the said criteria or the values of the said criteria currently being selected by a user, with a zone for displaying the values of the second and third criteria and which is designed to also display unselected values of the said criteria in such a way that the selected values can be read graphically, the said display zone being able to display a window adapted to each type of product.
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
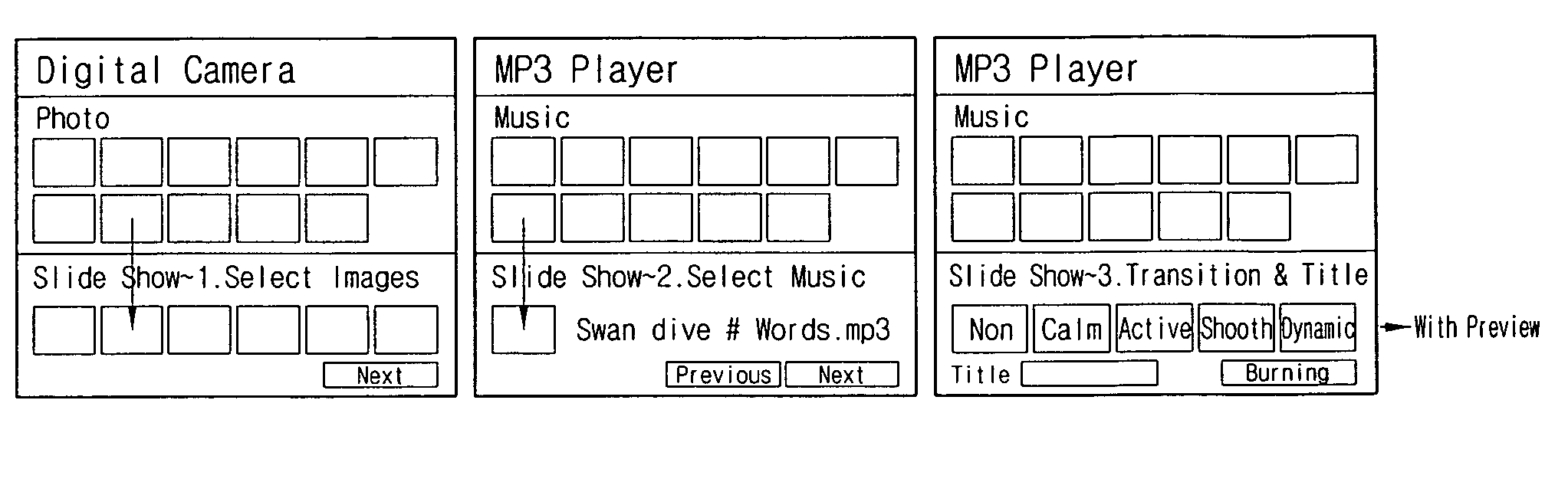
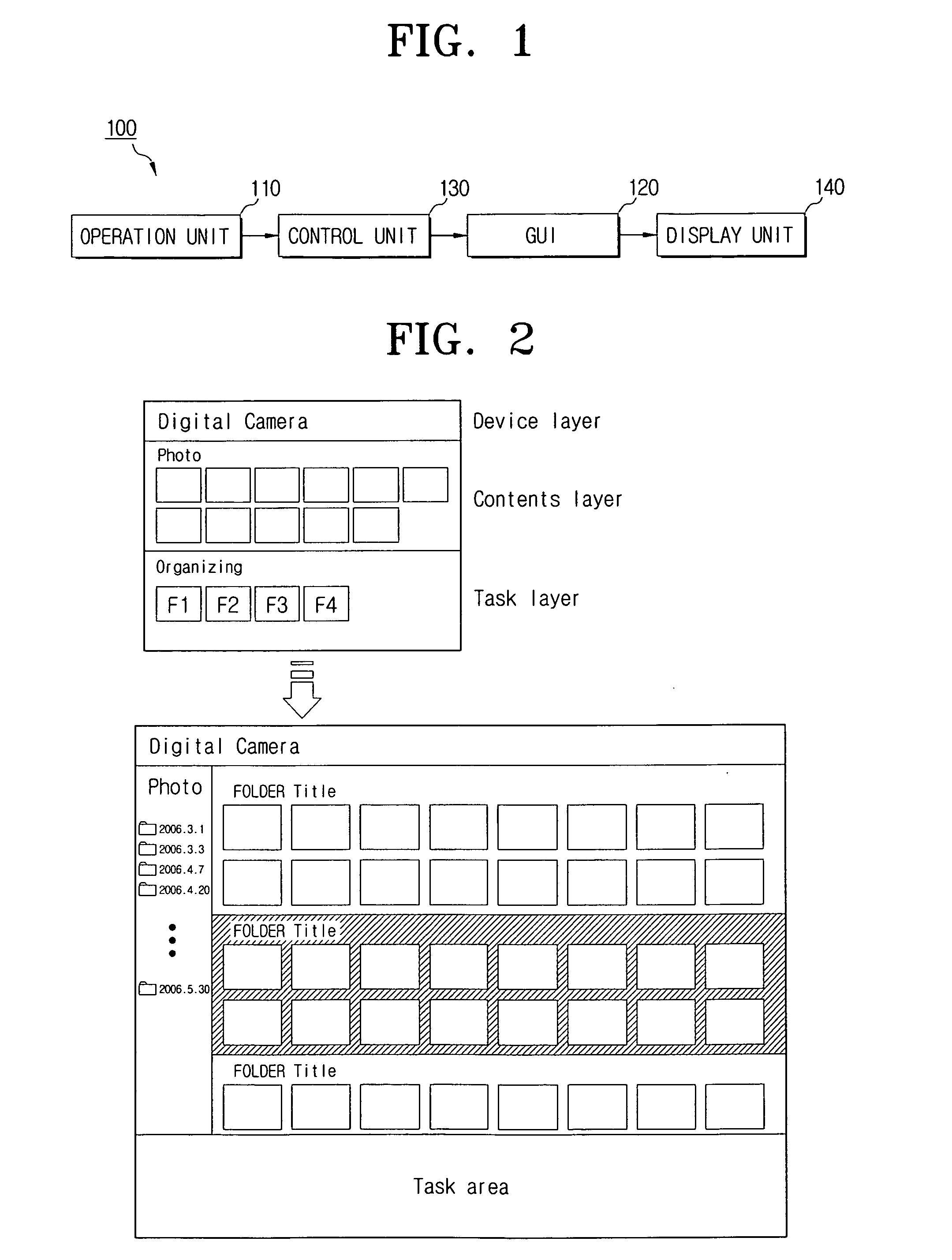
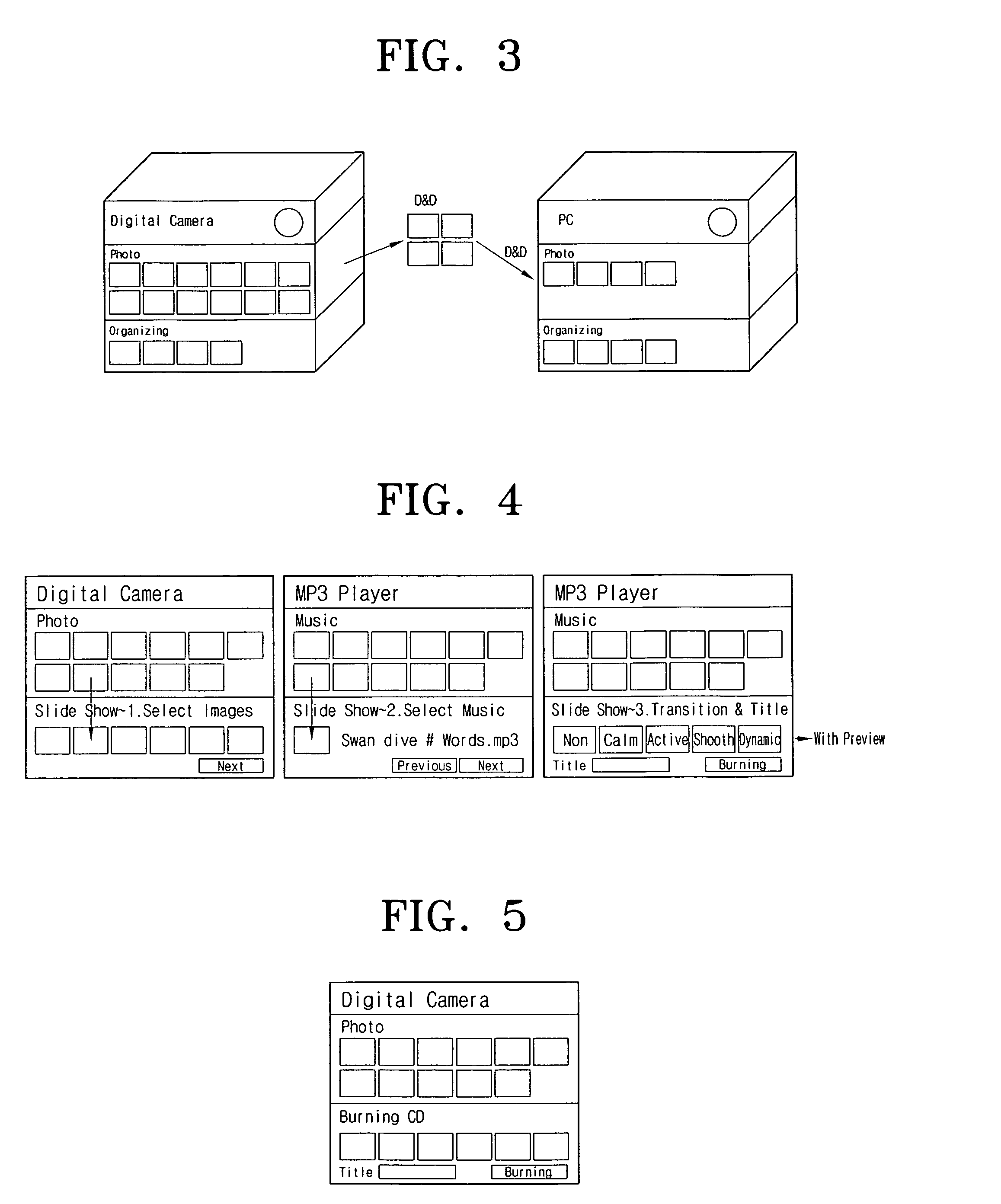
Electronic device for providing 3D user interface and method of providing a 3D user interface
InactiveUS20080016471A1Easily accessEasy accessInput/output processes for data processingGraphical user interfacePersonalization
Electronic devices providing three-dimensional user interface and methods therefore are provided. The electronic device includes a graphical user interface (GUI) unit for producing a GUI, the GUI including a device layer for displaying device information using at least one of side surfaces of a first polygonal pillared shape, and a content layer for displaying content information using at least one of side surfaces of a second polygonal pillared shape; and a control unit for controlling the GUI producing operation of the GUI unit. The devices allow for efficiently operating menus and operating personalized menus according to user's preferences by providing a three-dimensional GUI having a plurality of independently movable layers.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
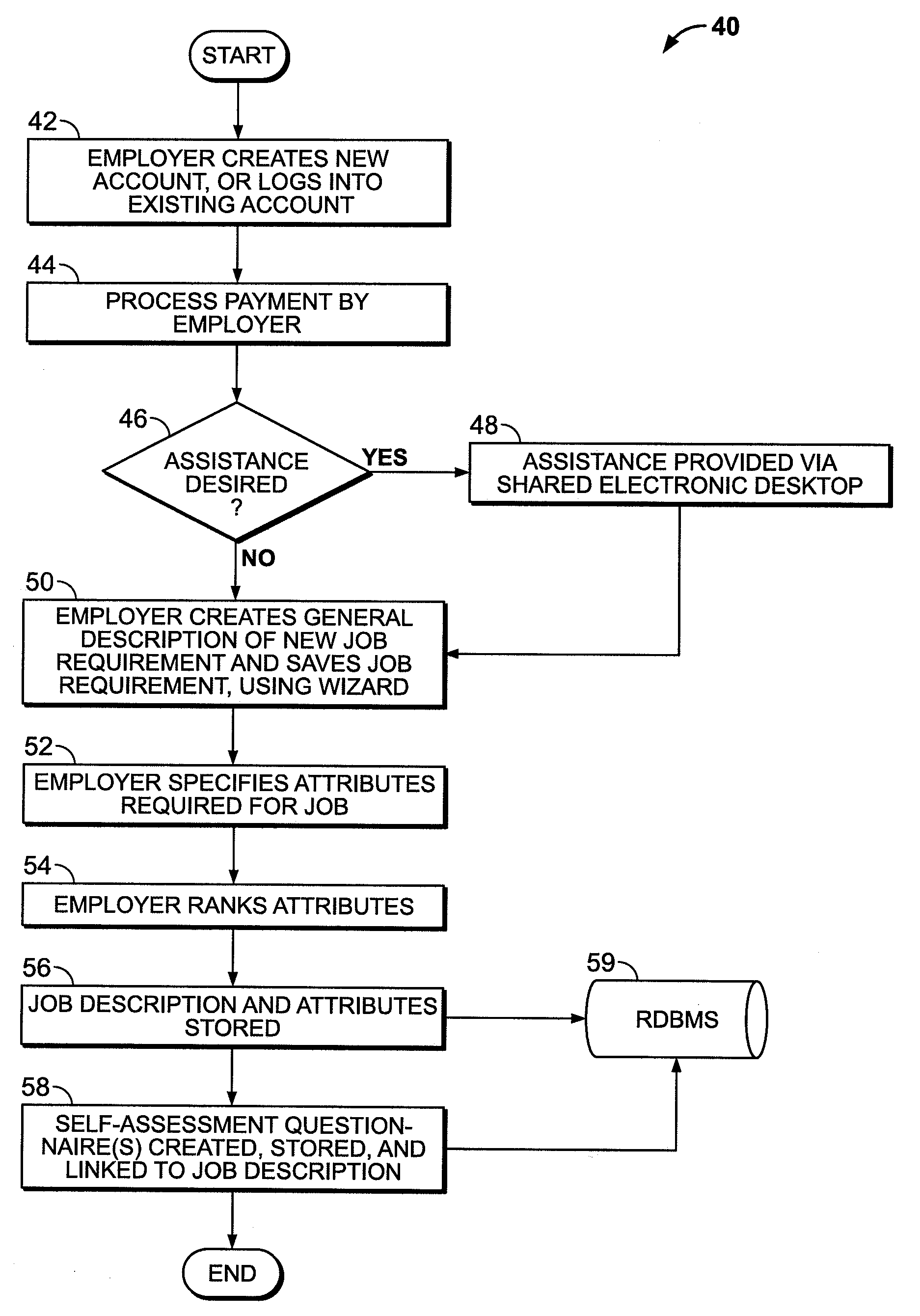
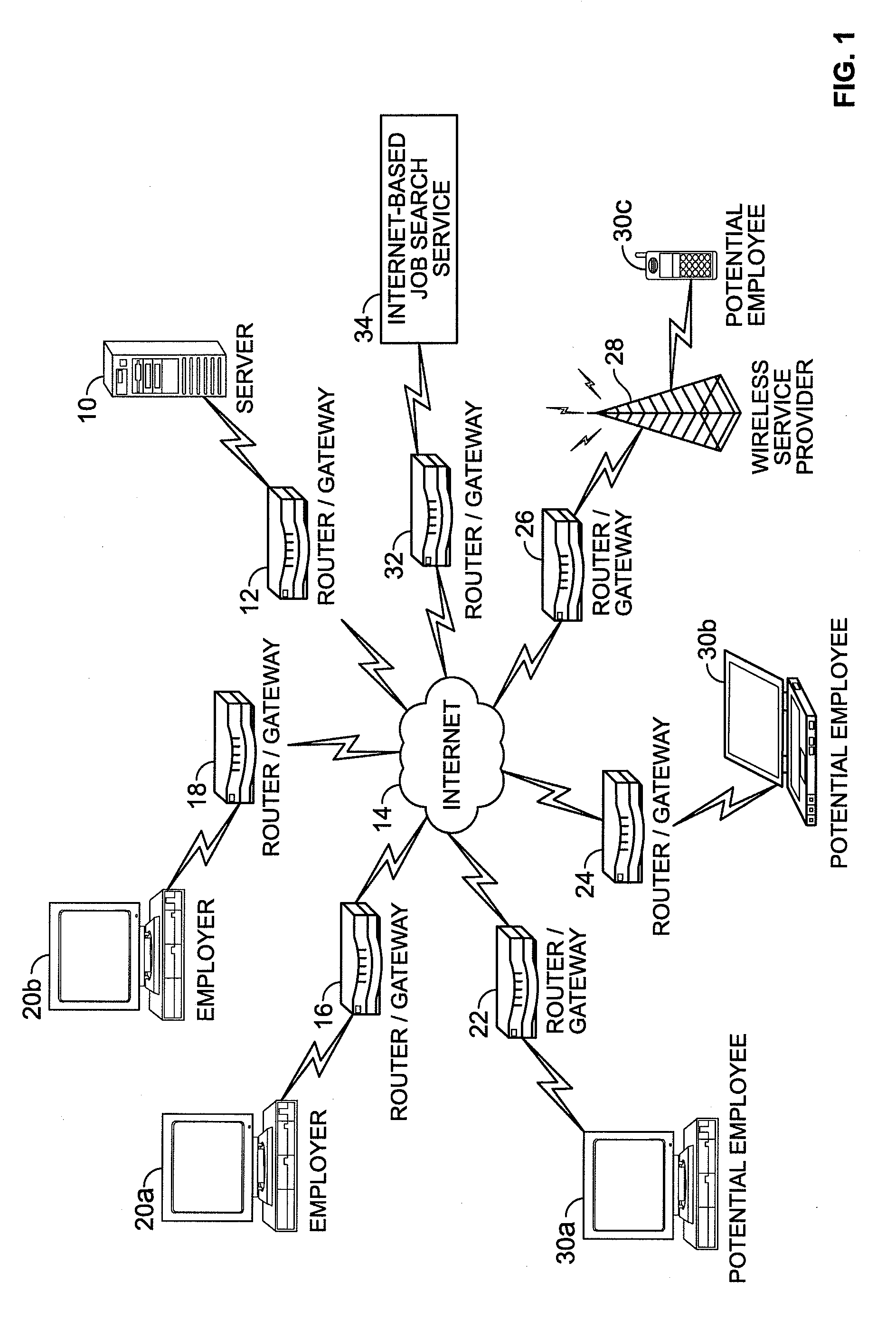
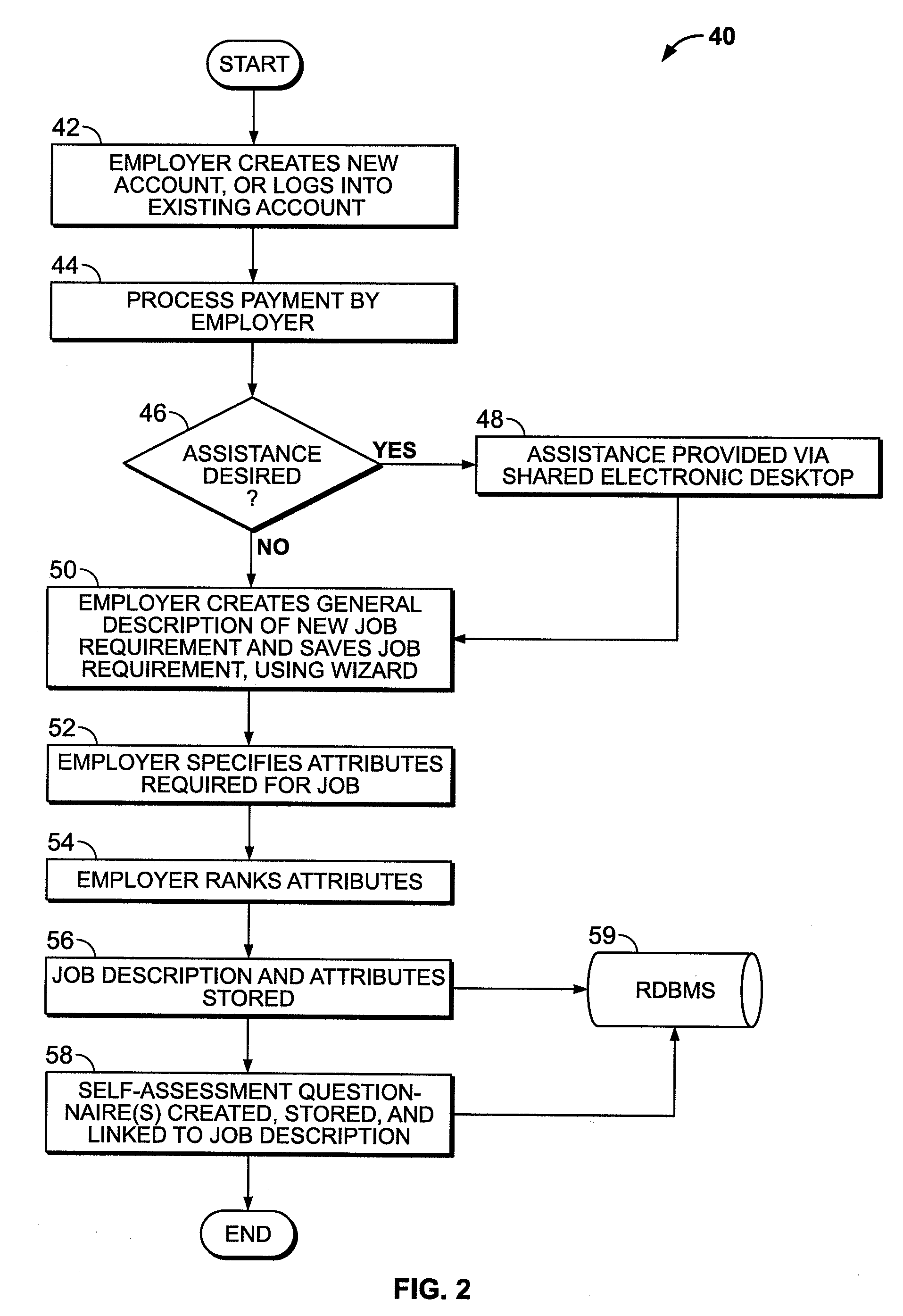
System and Method for Online Employment Recruiting and Evaluation
A system and method for online employment recruiting and evaluation is provided. An online, web-based environment allows employers to create job descriptions for posting on an Internet-based job search service in communication with the web-based environment, and allows for online recruitment and review of hiring candidates using a multi-phase approach. An employer can create an initial questionnaire associated with the job descriptions, which must be answered by potential employees as part of the recruitment and hiring process. A virtual dossier is created for each potential employee, is stored in a database, and can be reviewed by the employer. An employer can select desired candidates based upon information provided in response to the initial questionnaire, and selected candidates can be provided with a second questionnaire which asks the selected candidates to provide information about previous employers / supervisors. A subset of candidates can then be selected for a telephone interview, which is recorded and stored as part of the virtual dossier. Each employer / supervisor specified by the candidate is also interviewed, and the interview is recorded and is stored as part of the candidate's virtual dossier. A final group of candidates is then selected for an in-person interview, which is recorded and made part of the candidate's virtual dossier. A final review of the updated virtual dossiers is conducted by the employer so that the employer can select a final candidate for hiring. The virtual dossier can be made part of the hired candidate's personnel file, and provides a digital, comprehensive, and easy-to-access record of the recruitment and evaluation process of the candidate.
Owner:INTERVIEWSTREAM INC
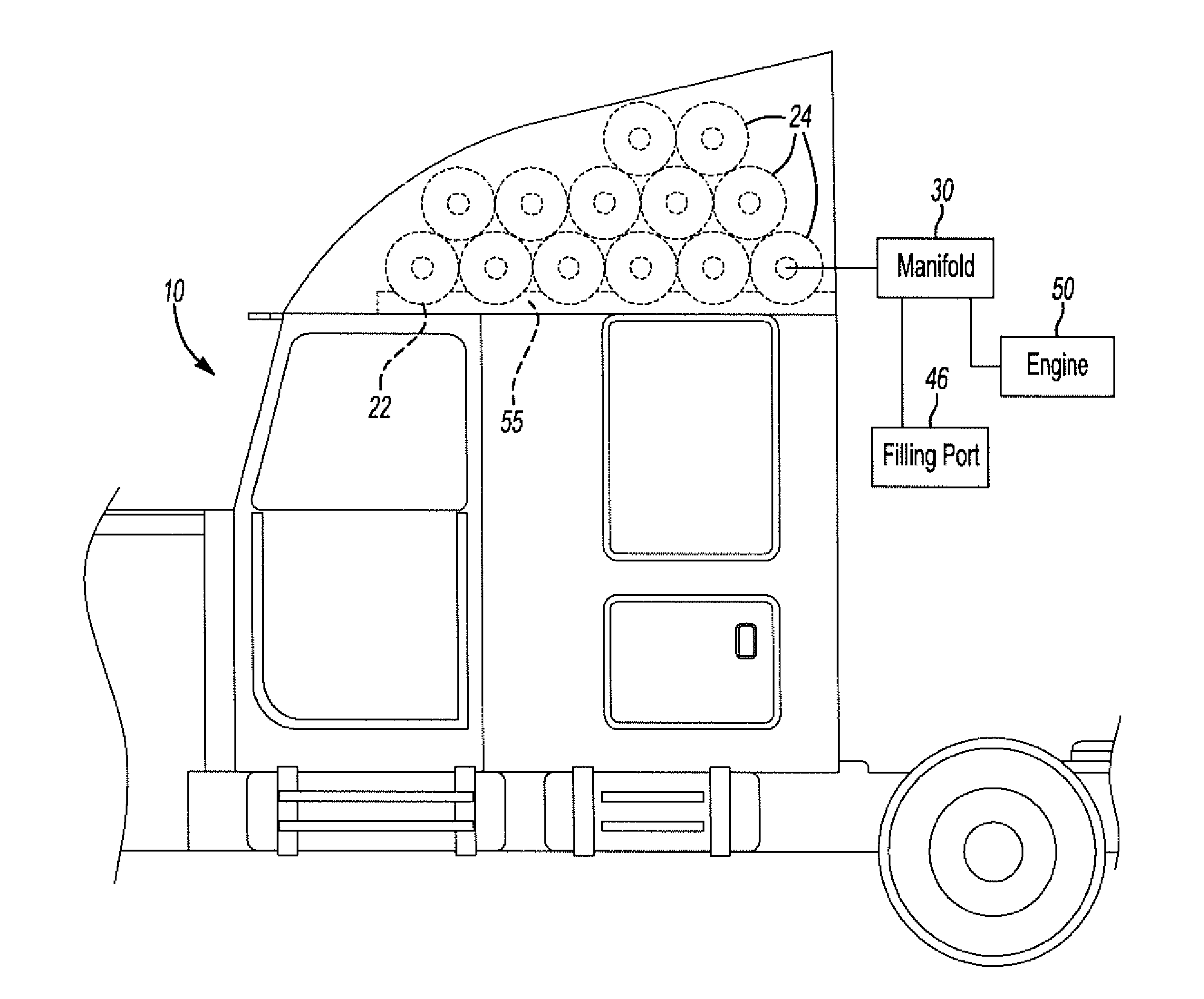
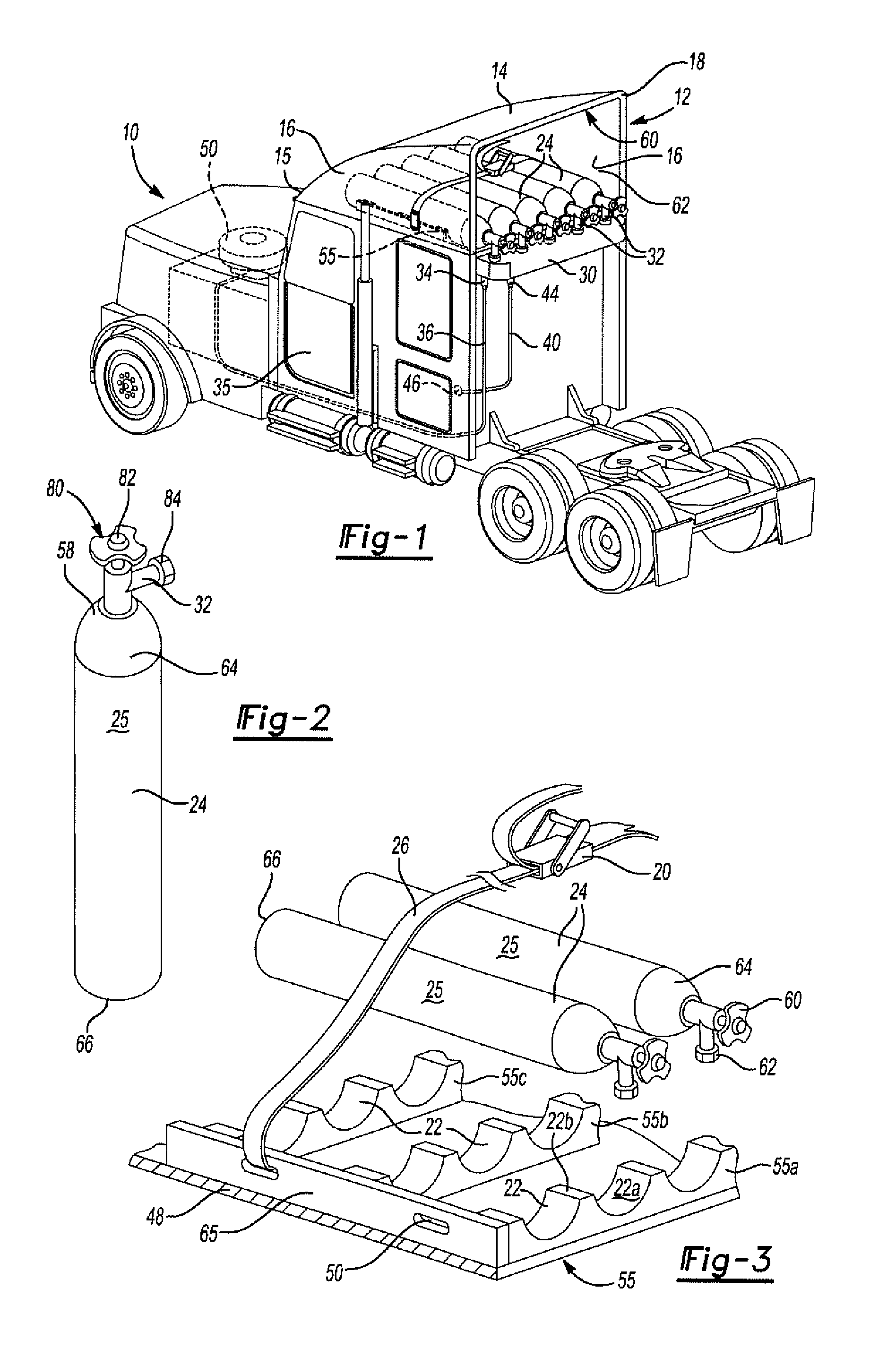
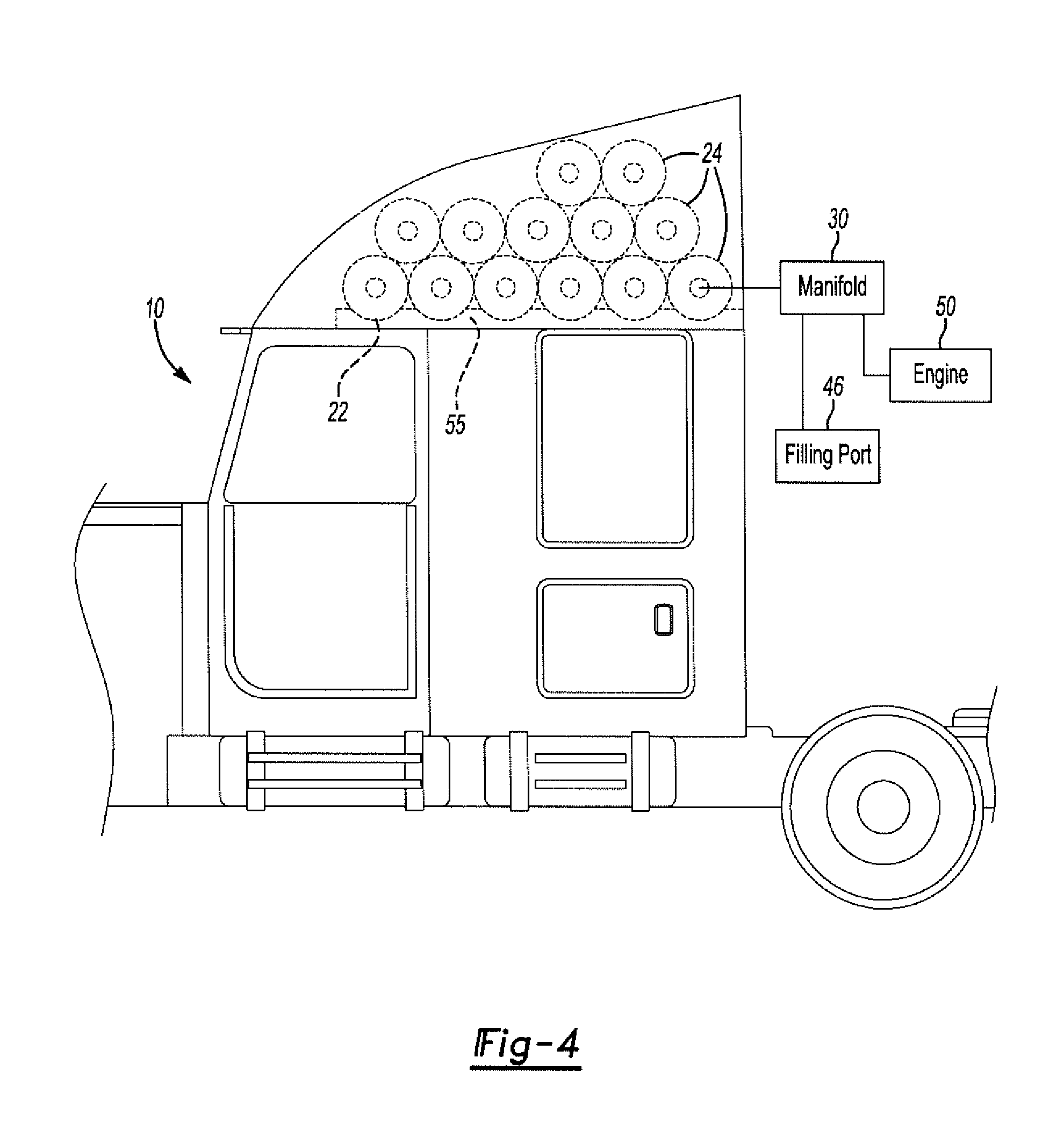
Method and apparatus for mounting cng/ang tanks to heavy trucks
A system and method for storing fuel on a semitrailer truck vehicle. The system includes a fairing mounted to the exterior surface of a vehicle. The fairing includes an outer surface to deflect air as the vehicle moves forward. The fairing further includes an inner surface forming a cavity. A fuel tank, or a plurality of fuel tanks are provided to mount within the cavity of the fairing. The fuel tanks are specifically adapted to hold CNG or ANG fuel.
Owner:ALTERNATIVE FUEL CONTAINERS
Diagnostic system and method for phonological awareness, phonological processing, and reading skill testing
InactiveUS20050106540A1Easily accessWeakened areaReadingElectrical appliancesDiagnostic systemSpeech sound
A diagnostic system and method for evaluating one or more phonological awareness, phonological processing and reading skills of an individual to detect phonological awareness, phonological processing and reading skill deficiencies in the individual so that the risk of developing a reading deficiency is reduced and existing reading deficiencies are remediated. The system may use graphical games to test the individual's ability in a plurality of different phonological awareness, phonological processing and reading skills. The system may use speech recognition technology to interact with the games. The system may include a module for providing motivation to a user of the system being tested.
Owner:COGNITIVE CONCEPTS INC
Dunnage converter system
ActiveUS6918489B2Easily accessEasy accessMechanical working/deformationPaper/cardboard articlesEngineeringDunnage
An easy load packaging system, and a stand and a dunnage conversion machine therefor are disclosed. The stand includes a base and a pair of upright guide members mounted to the base and supporting at the upper ends thereof a dunnage conversion machine. The guide members define there between a channel for guiding sheet stock material to the dunnage conversion machine. The dunnage conversion machine is pivotable relative to the stand between an operating position and a servicing / loading position whereat access to internal components of the machine is simplified. A stack of sheet stock material is jacketed and / or baled for simplified loading into a packaging system or stand. An adhesive layer on the bottom or top of the stack enables the stack to be easily spliced to another stack.
Owner:RANPAK CORP
Wireless well communication system and method
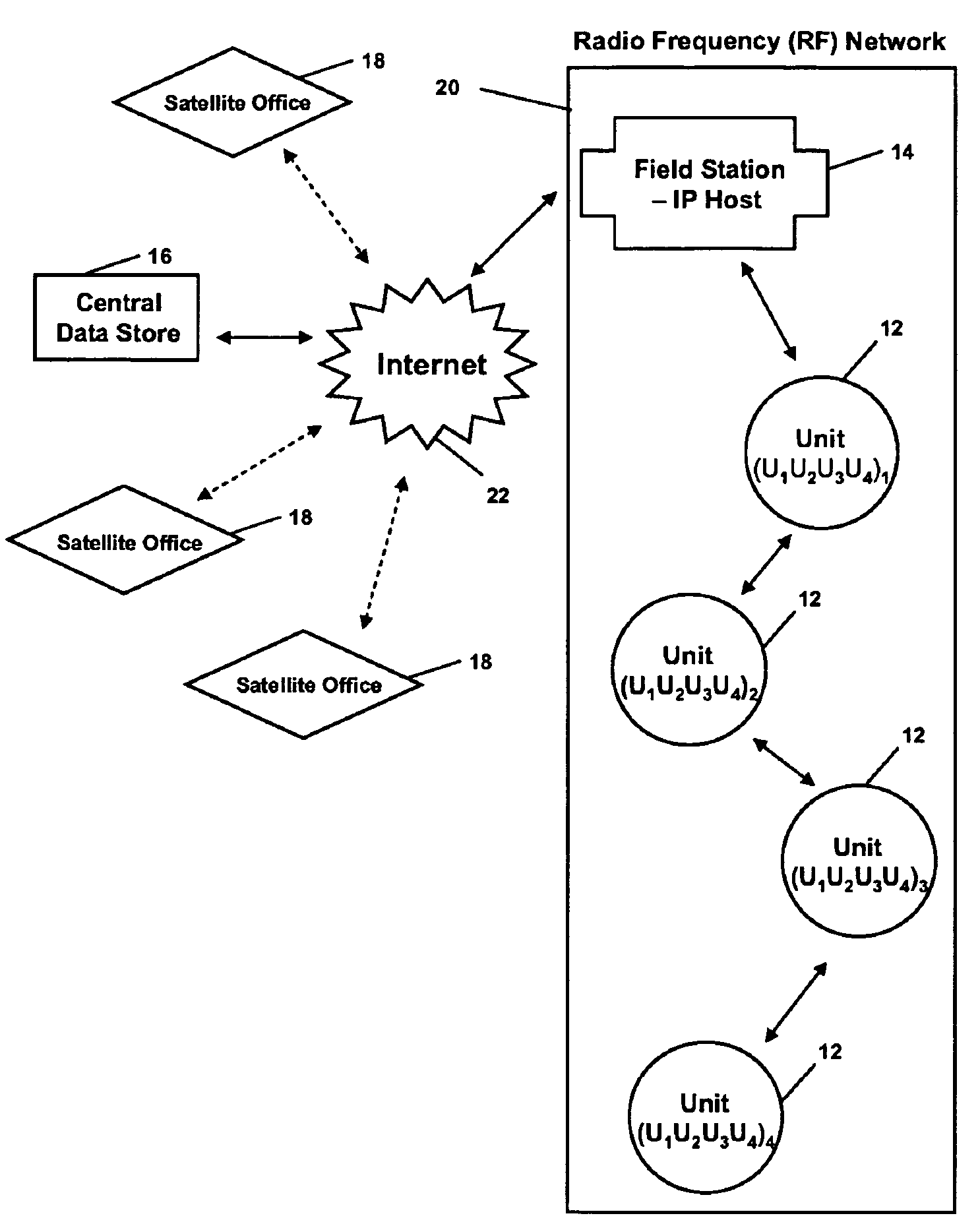
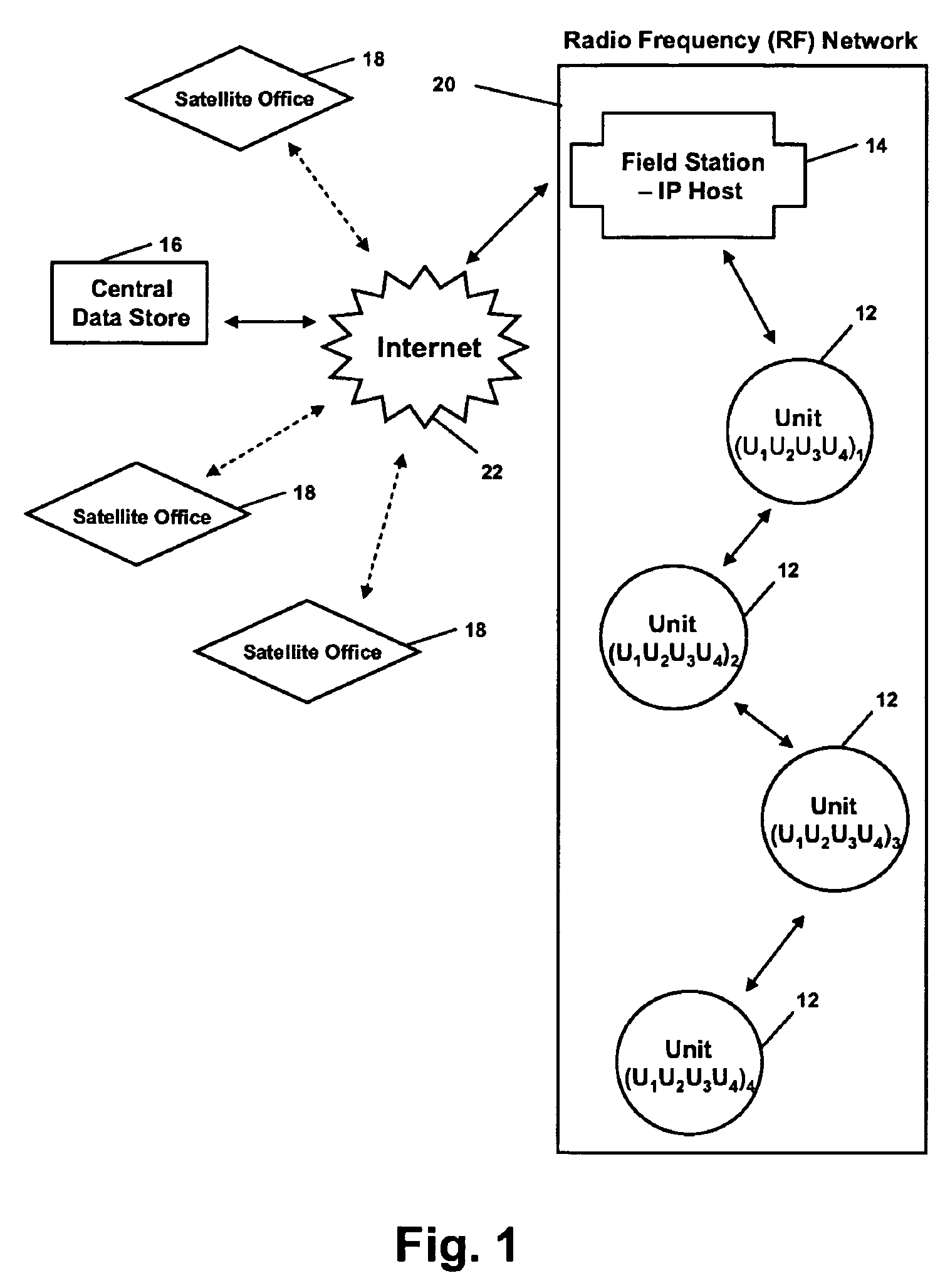
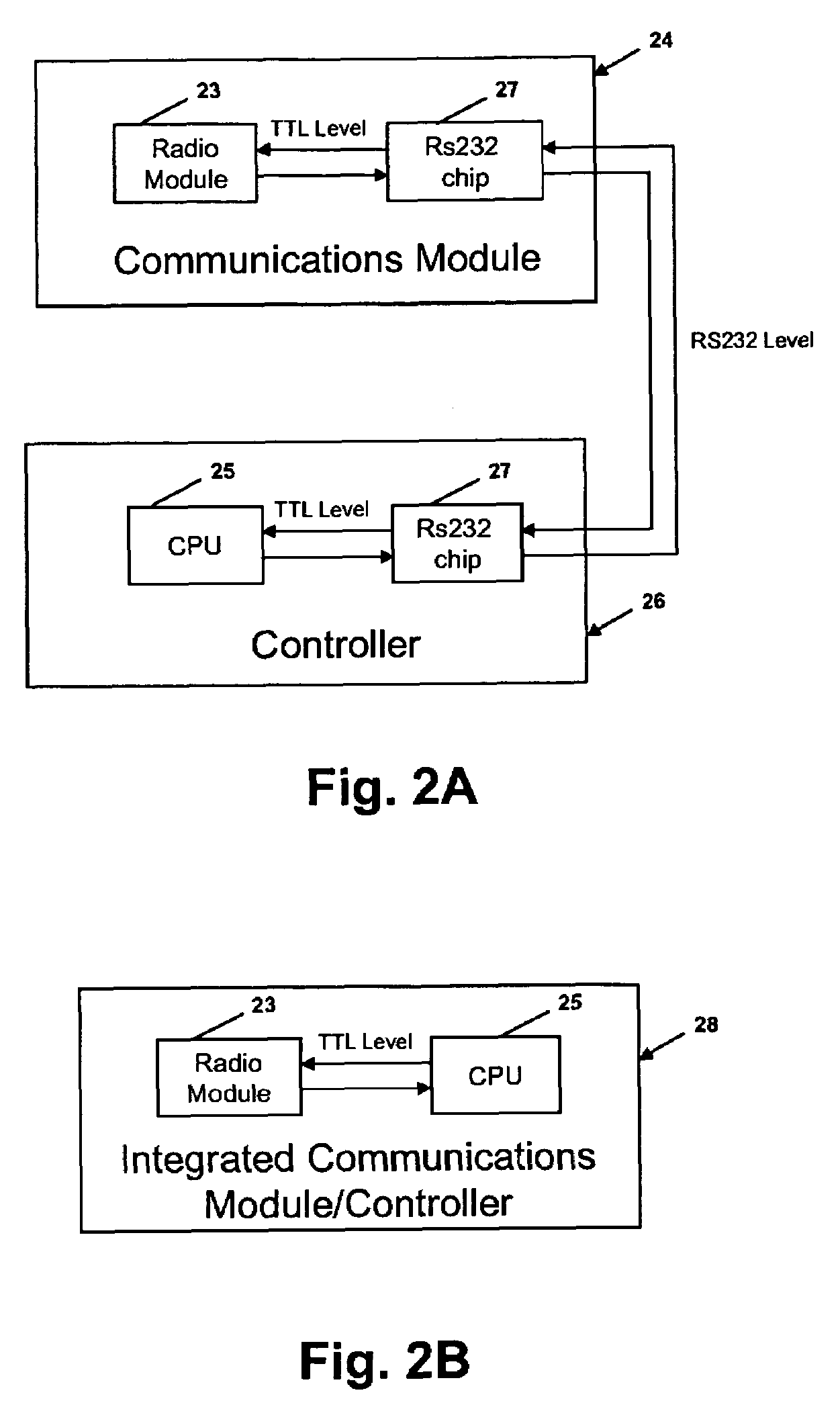
Well data and production control commands are transmitted from a remote central data store to wells at a remote location with a well hopping system and method, preferably through a radio frequency (RF) network. Request packets are sent through a field station to one or more well units until it reaches the destination well unit. The destination well unit executes the data request or the command and sends a response data packet back to the central data store through the RF network using the same well hopping system and through the field station. The central data store reads and stores the data. One or more satellite offices are connected to the central data store and can download data from the central data store or send / receive data packets to / from the well units. Oxygen content in production gas can be detected and transmitted to the central store for monitoring and reporting.
Owner:SILVERSMITH
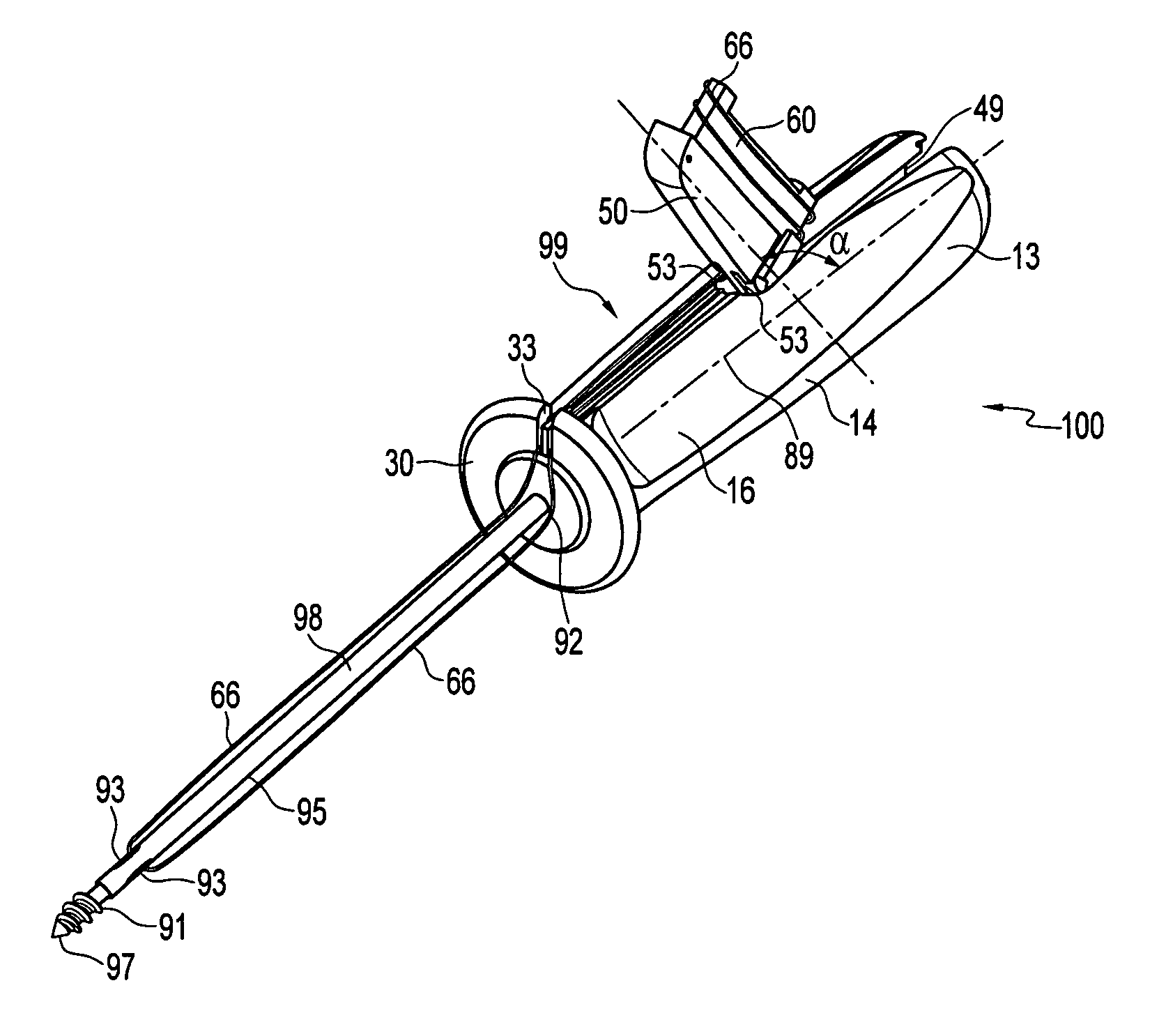
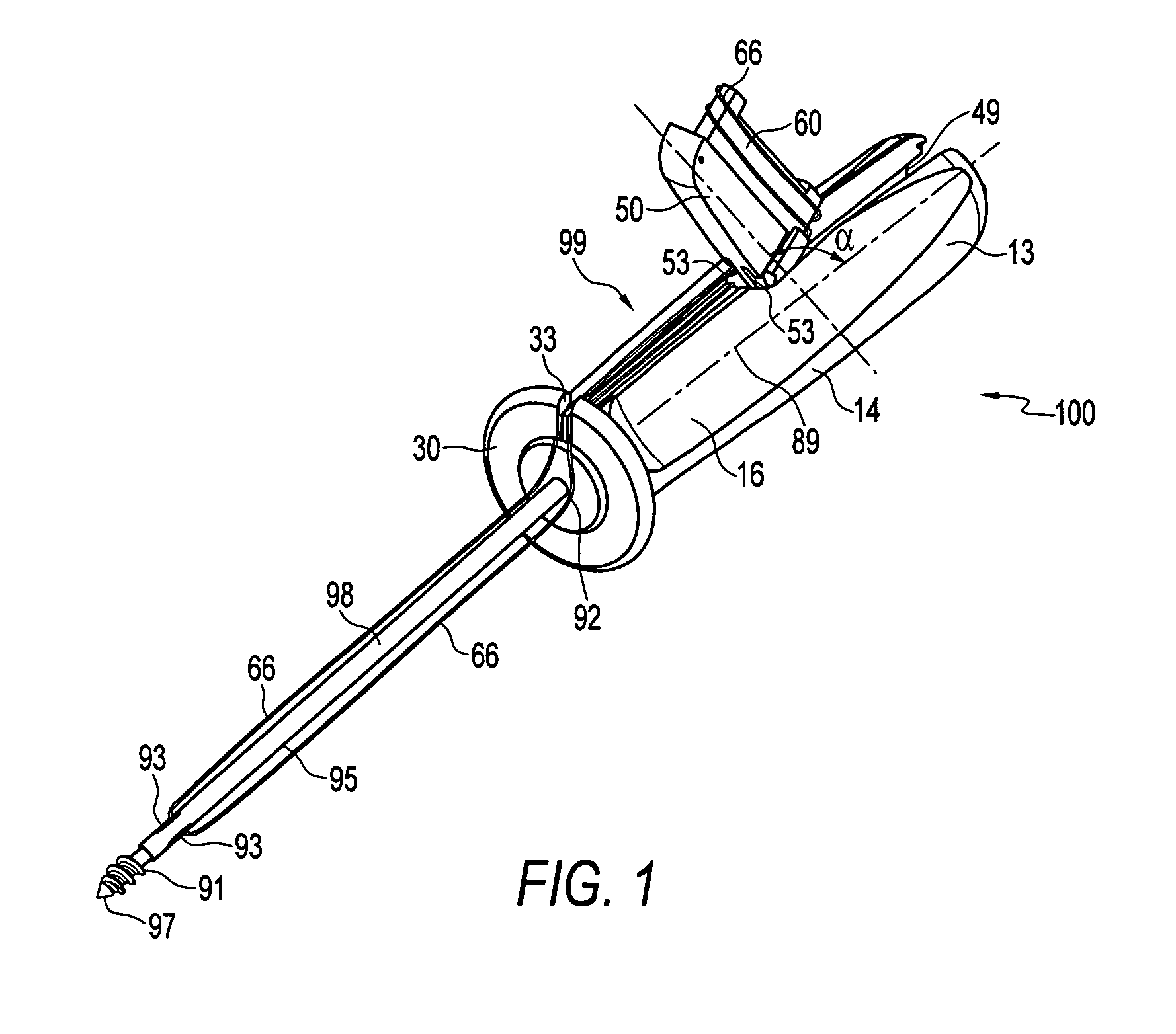
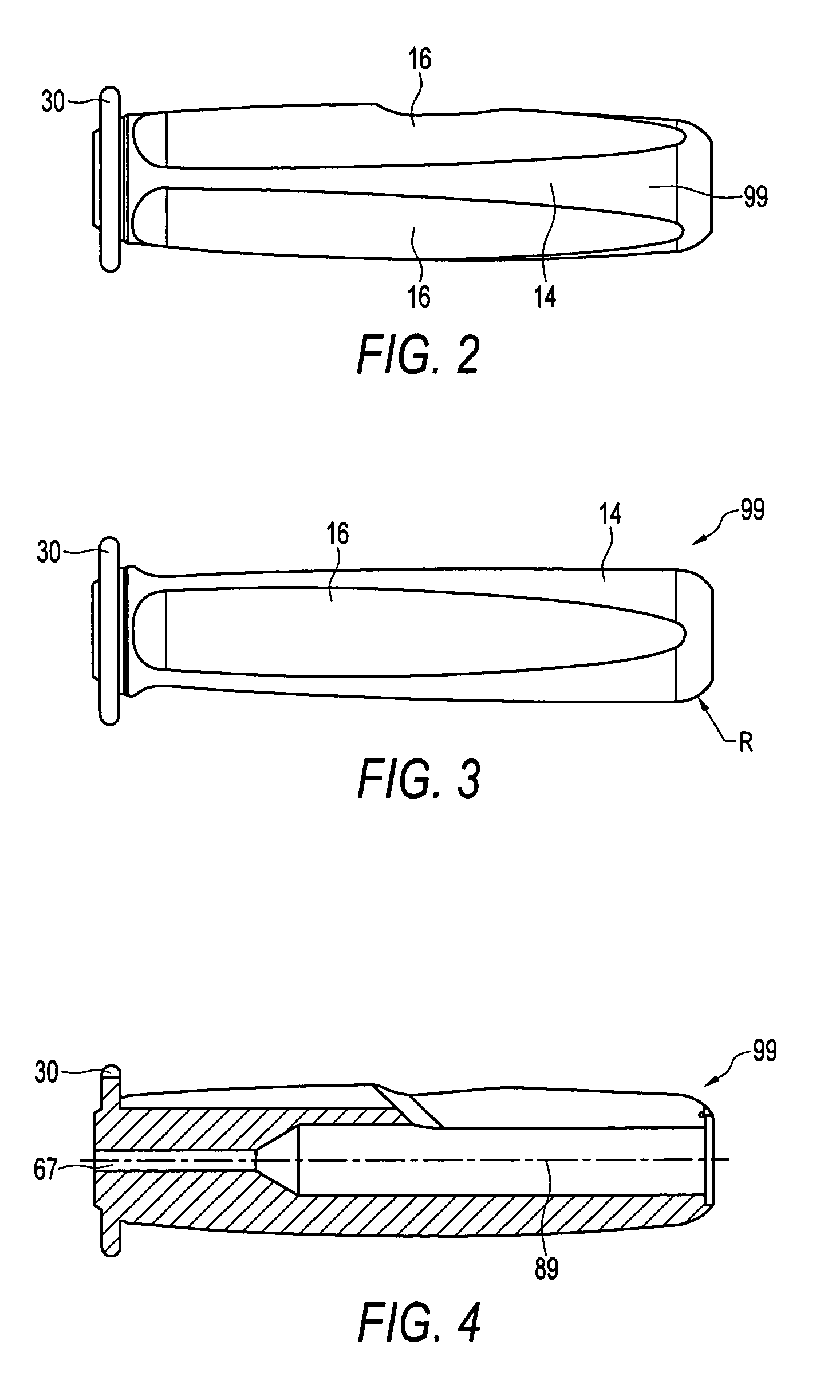
Instrument handle for storing suture and needles
InactiveUS7329264B2Easily accessOvercome disadvantageSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesSurgical departmentWrap around
An instrument handle for storing of suture which can be easily accessed by a surgeon. The handle is provided with a cavity for housing sutures and needles. The cavity is accessed by opening a pivotable hatch. The suture is wrapped around a tie-down bar disposed on the inside of the pivotable hatch. If desired, a surgical needle may be attached to the suture and stored within a slot of the tie-down bar of the pivotable hatch.
Owner:ARTHREX
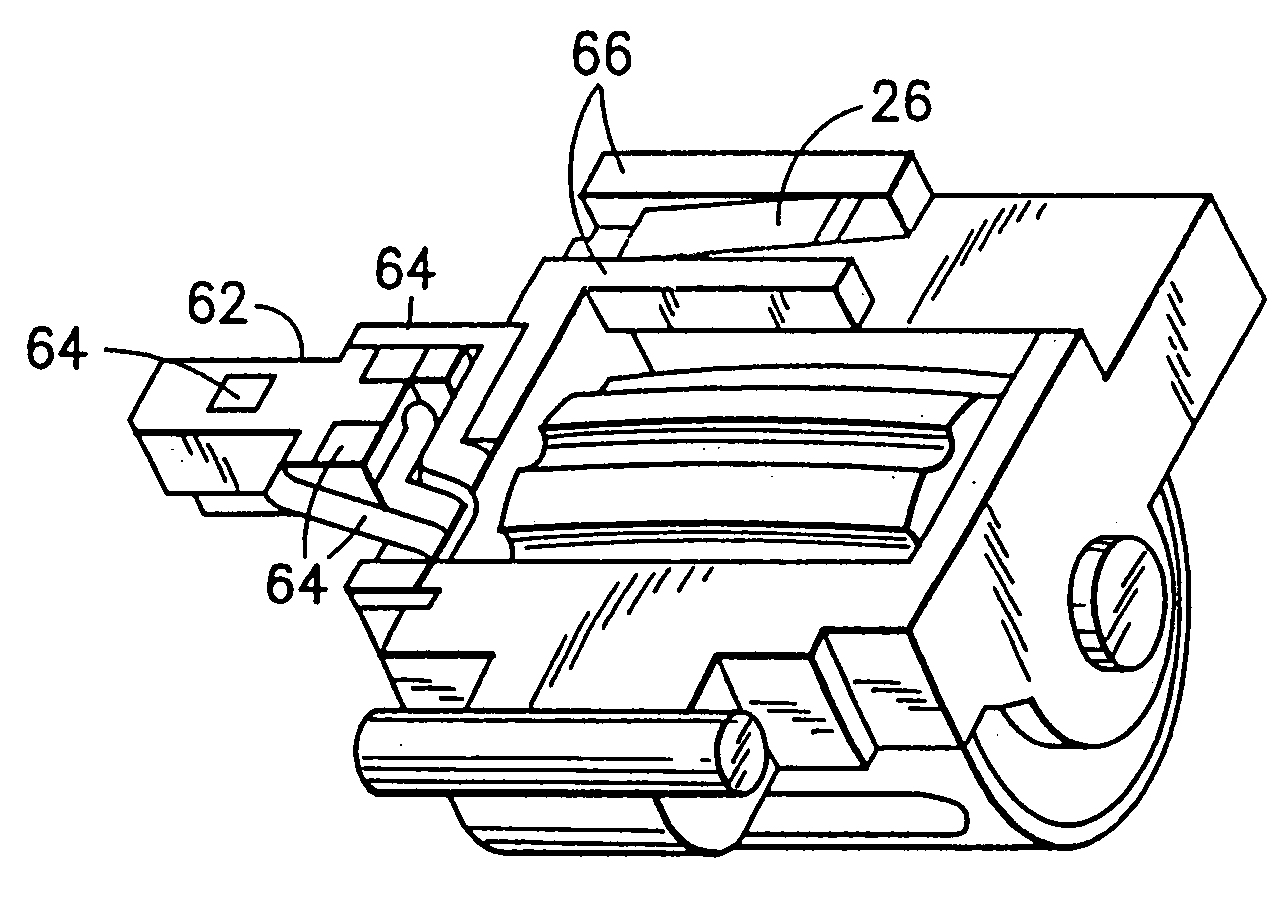
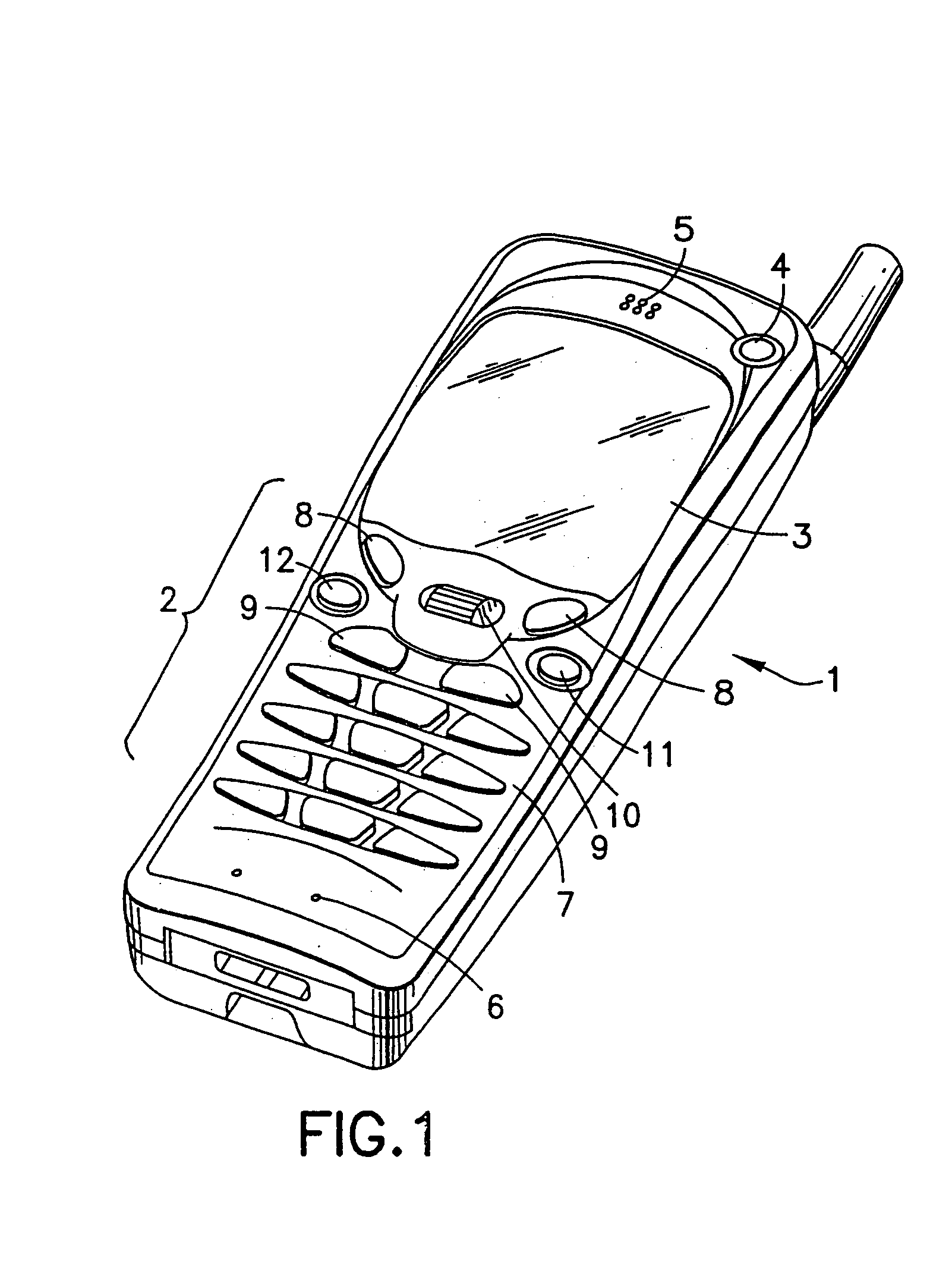
Navigation key for a handset
InactiveUS6965782B1Easily accessSmall sizeInput/output for user-computer interactionInterconnection arrangementsHandsetEngineering
A telephone handset comprises a front surface with a display and a keypad. The keypad includes a group of keys for entering alphanumeric signs and a key for navigating a cursor in the display. The navigation key is placed in the front surface of the phone between the display and the group of alphanumeric keys, and it includes a roller body which extends partly though an opening in the front surface of the phone. The roller body is essentially cylindrical with a length and diameter of the same size as the width of the keys in said group of keys for entering alphanumeric signs.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
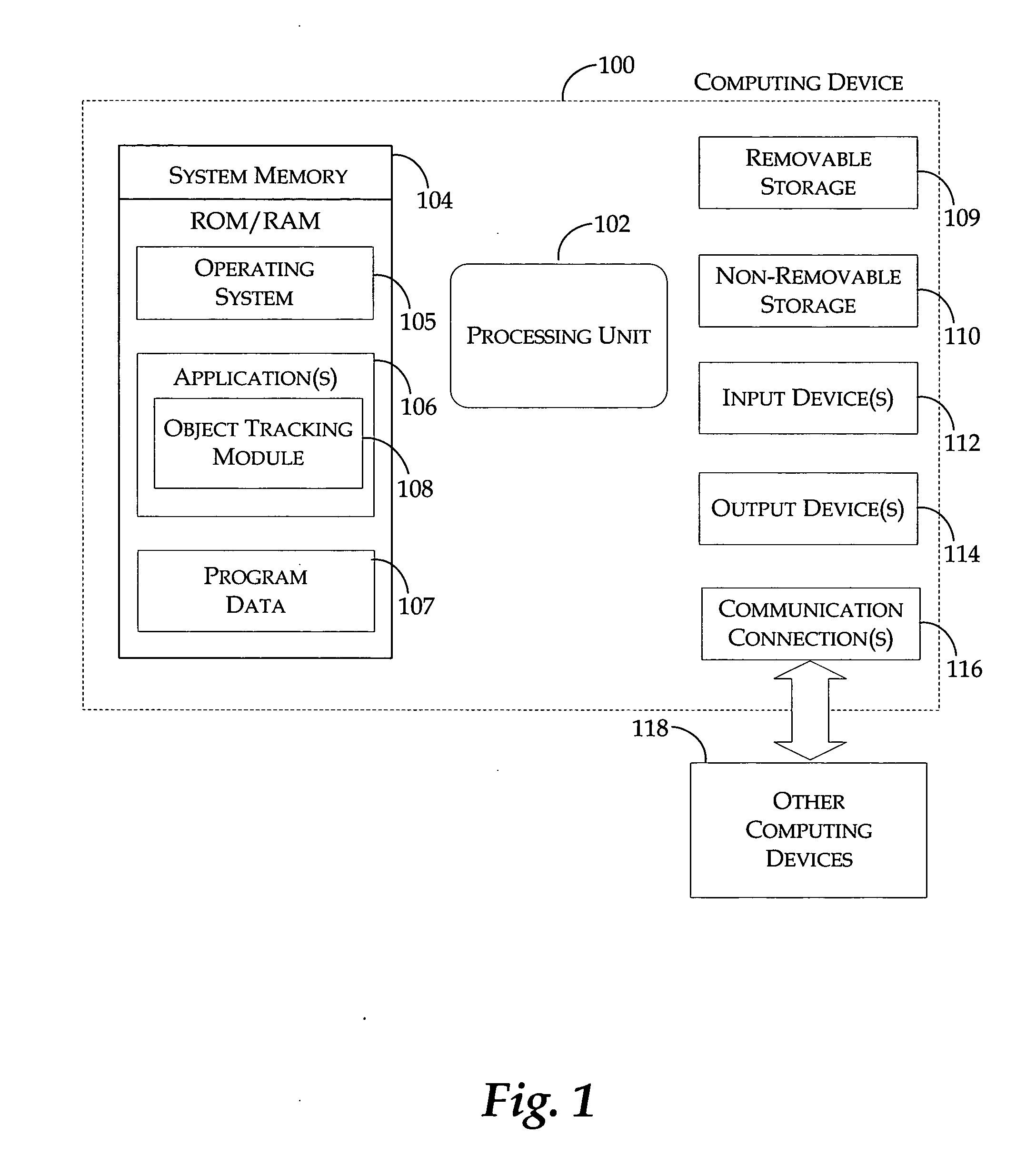
Method and system for tracking objects associated with an activity
ActiveUS20060136357A1Easily accessDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsData miningData objects
An object tracking module establishes relationships between different types of data objects associated with application programs while a particular activity occurs. Contextual information associated with the data objects and the activity is collected to establish the relationship. The contextual information may include data objects that are accessed or created while the activity is in progress, or any other information associated with the activity. When an event related to the activity occurs, the object tracking module locates data relevant to the event based on the established relationships. The relevant data is presented in the same information space where the event occurs. A user may easily access the relevant information without manually searching for the data. The object tracking module may determine the degree of relevance between the data objects and the event such that only the most relevant objects are displayed.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
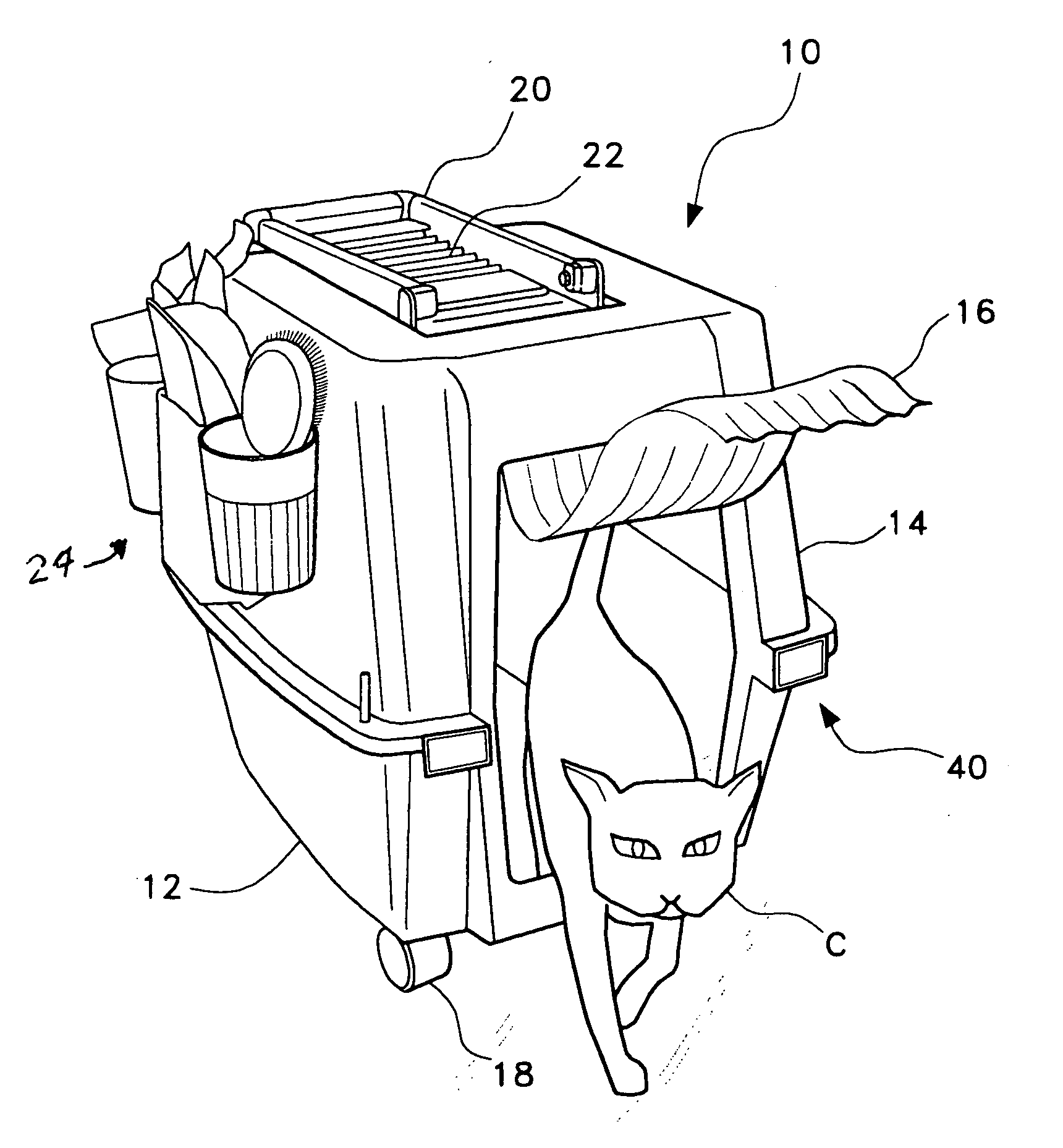
Wheeled litter box
InactiveUS20060005777A1Easily accessEffectively wasteAnimal housingOther apparatusEngineeringLitter box
A wheeled housing having separable top and bottom components. A covered opening is formed in the housing to provide for easy entrance and exit by a pet. The housing has an air filter positioned on the top component. An extendable handle is affixed to the top adjacent the filter. Brakes are provided for the rear wheels to prevent the housing from being pushed by the pet.
Owner:GALINDO ANABELLA V +1
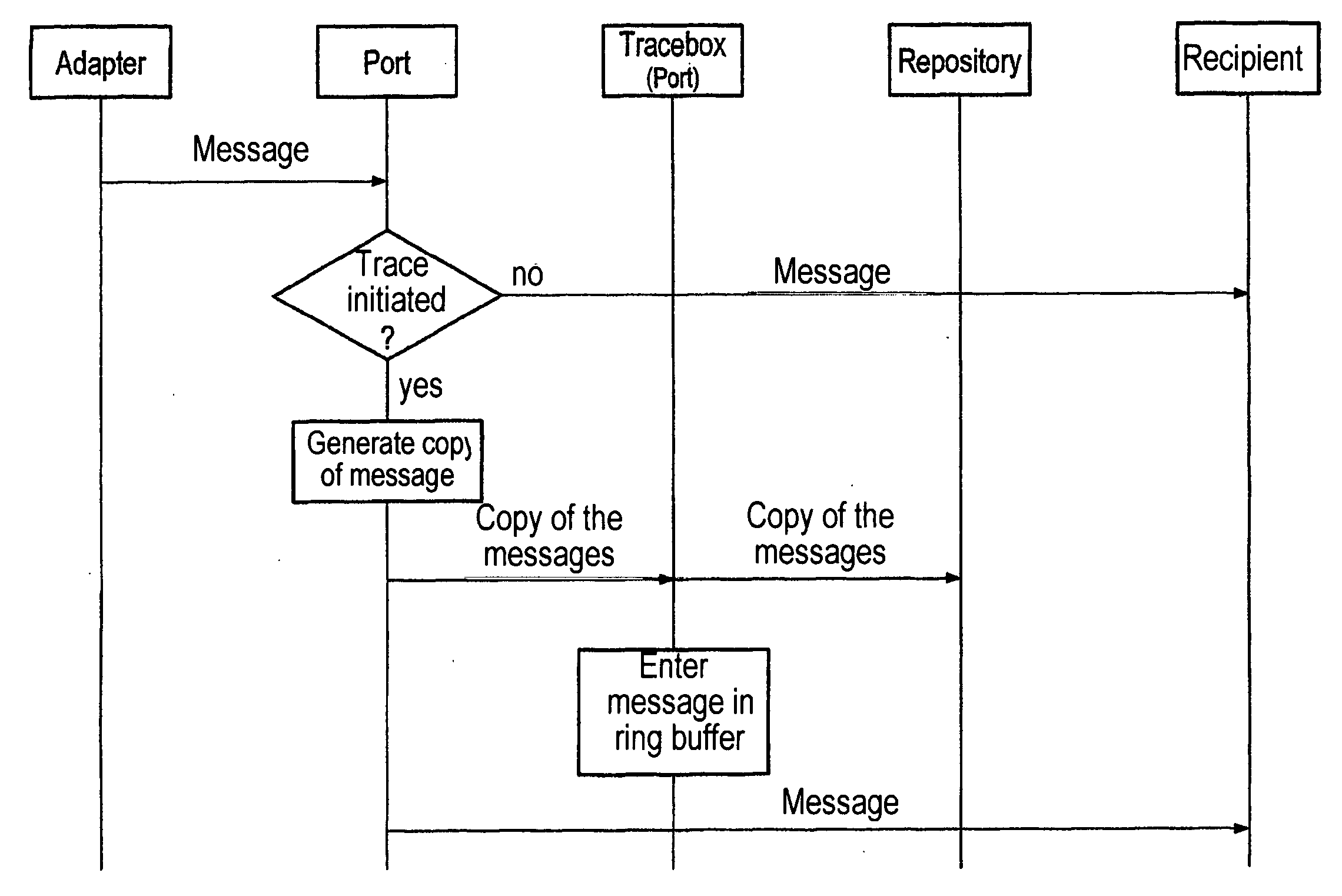
System and method for tracing and/or evaluating the exchange of information
InactiveUS20050015741A1Easily accessProduce quicklyDigital computer detailsSoftware testing/debuggingSoftwareWhole systems
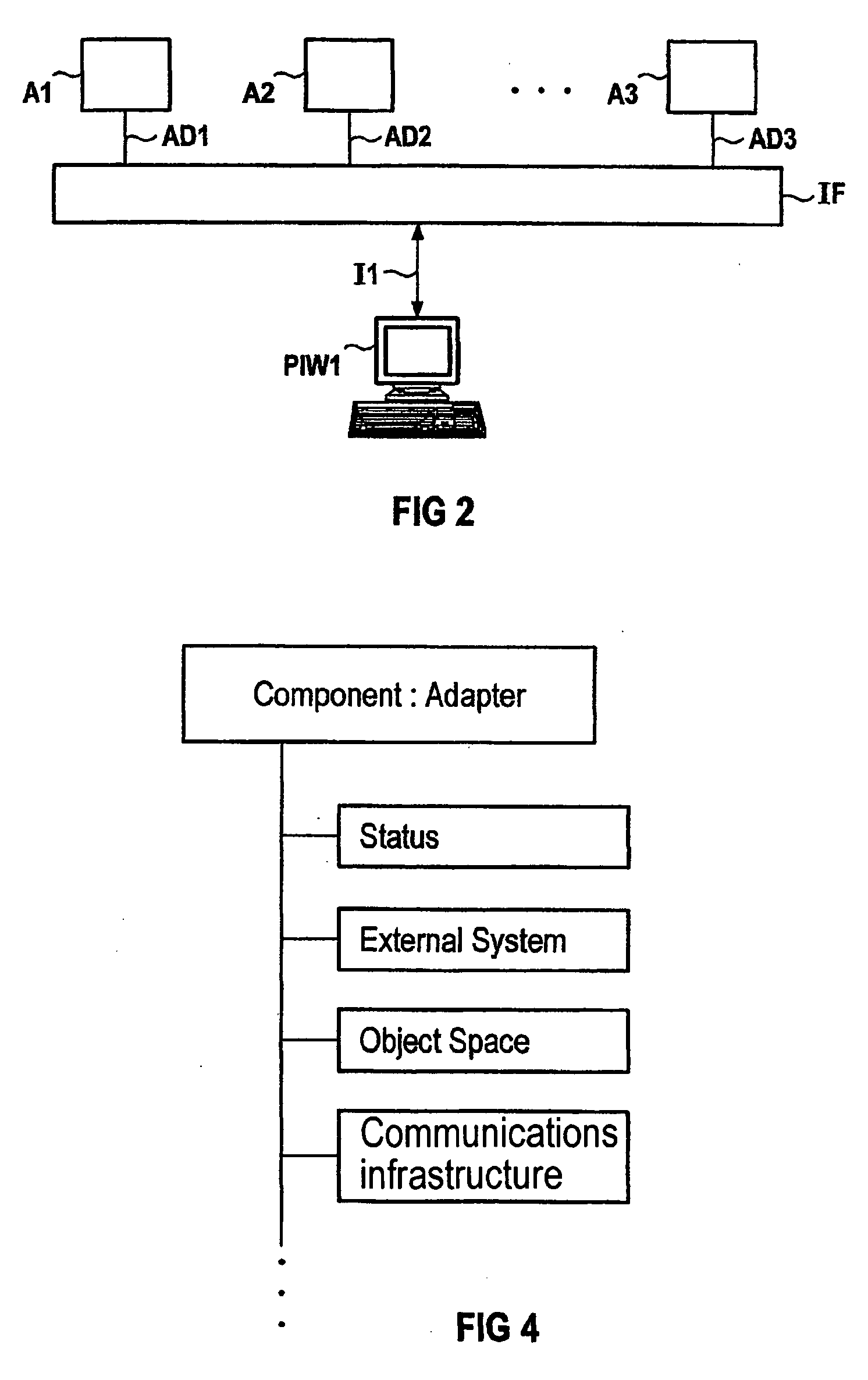
The invention relates to a system and a method for tracing and evaluating the communication of software applications, especially MES applications in an entire system. The tracing and evaluation can be carried out progressively or step-by-step on a project level, an adapter level and a port level, i.e. individual communication connections and individual applications, but the entire project is also traced by (even heterogeneous) application environments. The tracing and evaluation mechanisms enable higher-level services to access online the archived trace and error data at all times. An example of one such service is the generation of a report in the pharmaceutical field, indicating the materials used and sent in production orders.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Method and system for a reliable distributed category-specific do-not-contact list
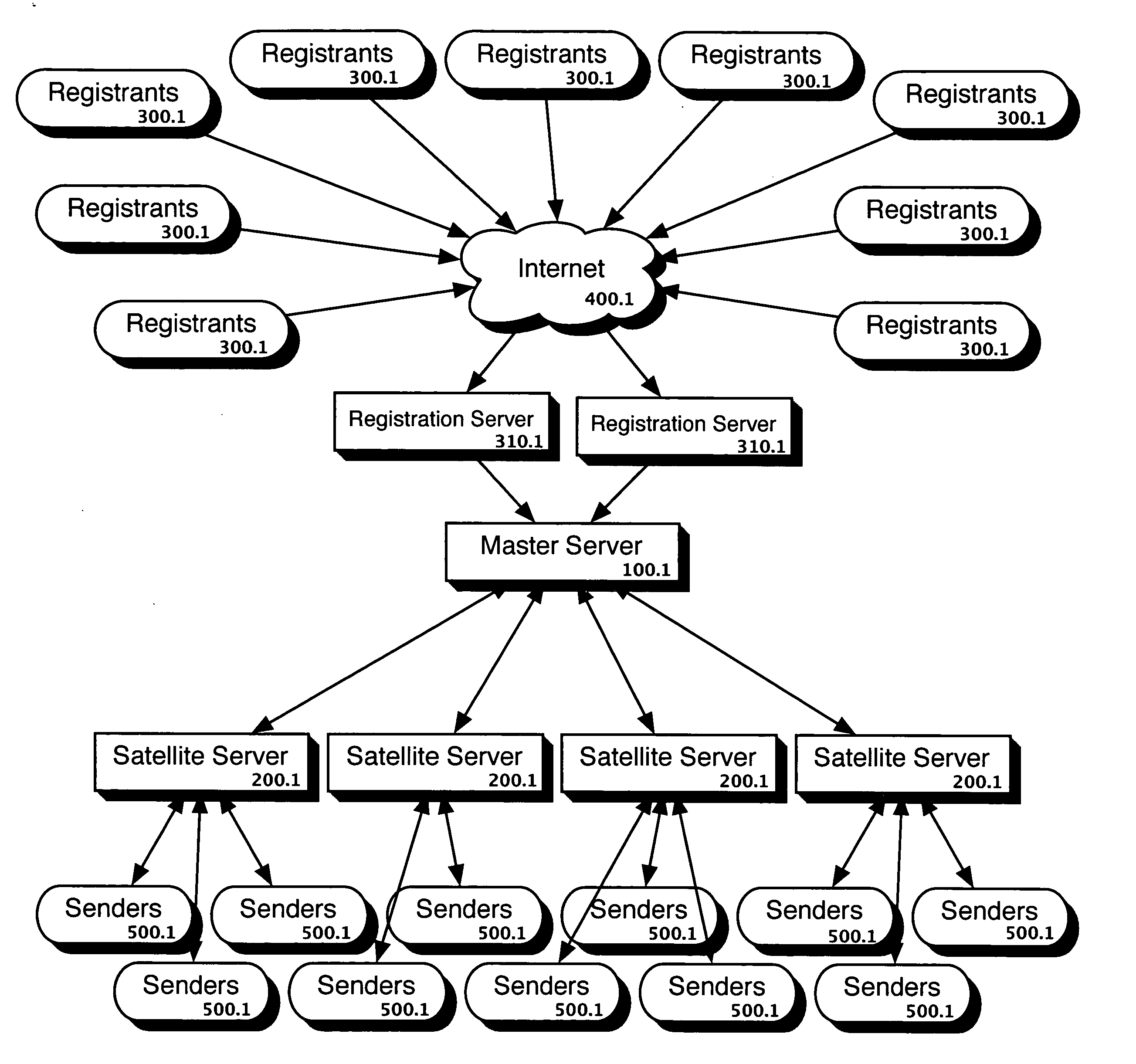
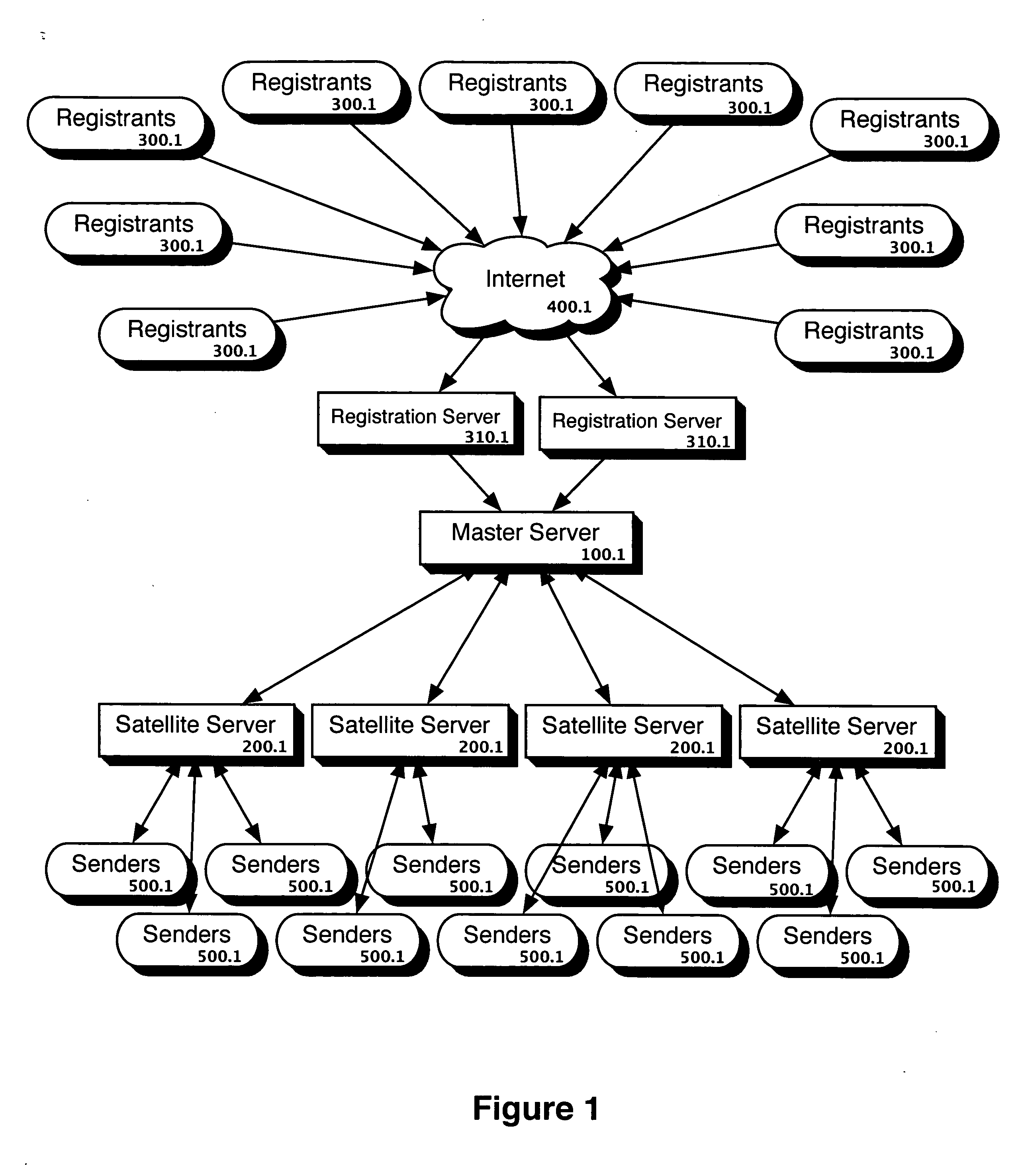
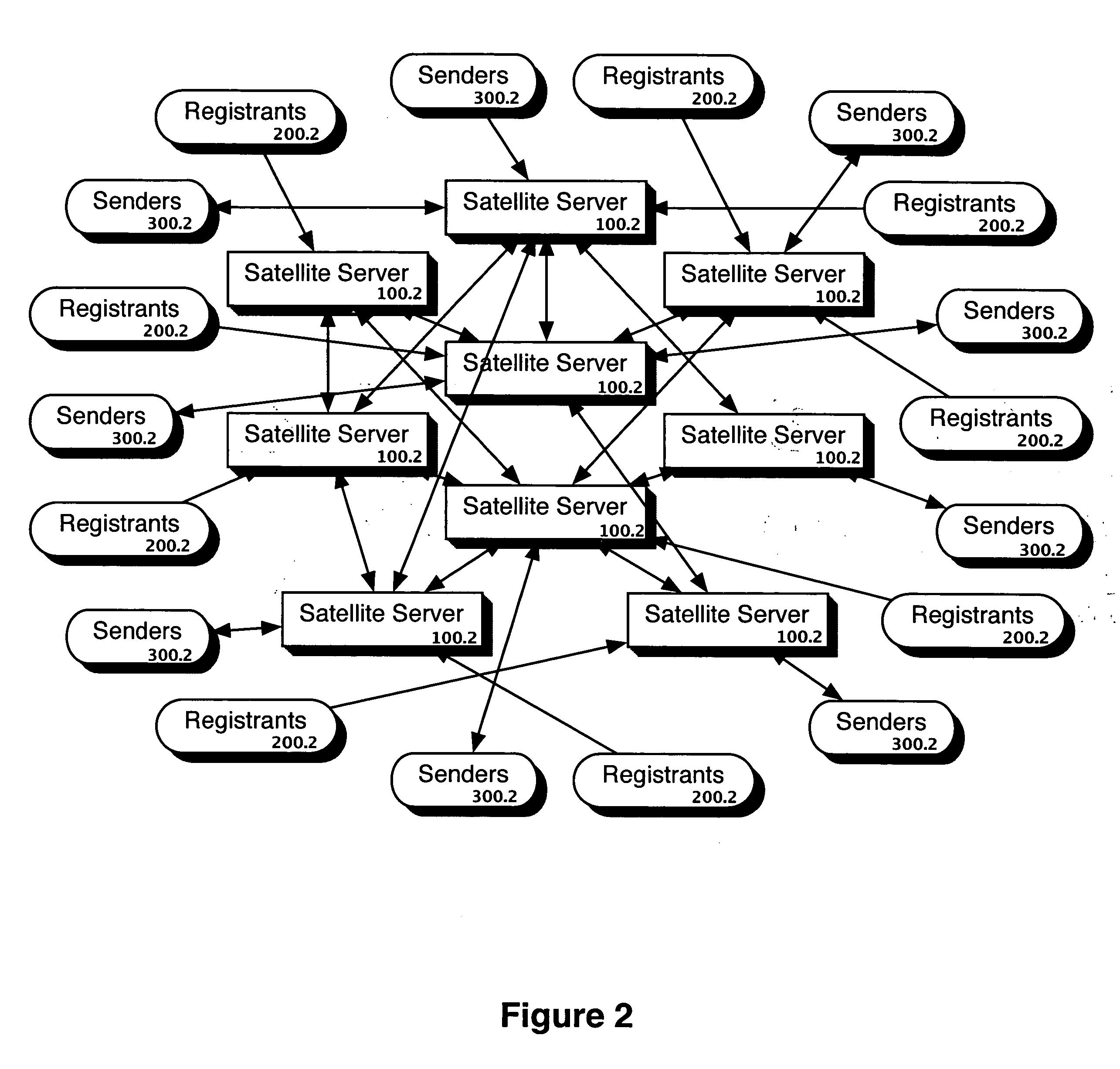
ActiveUS20050246344A1Prevent attackEasily accessMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionSatelliteWindows Registry
A computer implemented method comprising receiving a list of one or more contact points from a sender and comparing the list of one or more contact points to a satellite server's do-not-contact list. Any contact point on the list of one or more contact points that appears on the satellite server's do-not-contact list is reported to the sender. The satellite server's do-not-contact list is generated from a do-not-contact list distributed by a master server. A registrant registers with the master server to provide a registrant contact point to be on the do-not-contact list to be distributed by the master server. The contact points in the registry may be organized in a hierarchy with preferences at one or more levels.
Owner:UNSPAM
Ergonomic Scraper
Owner:JONES GORDON SINCLAIR +2
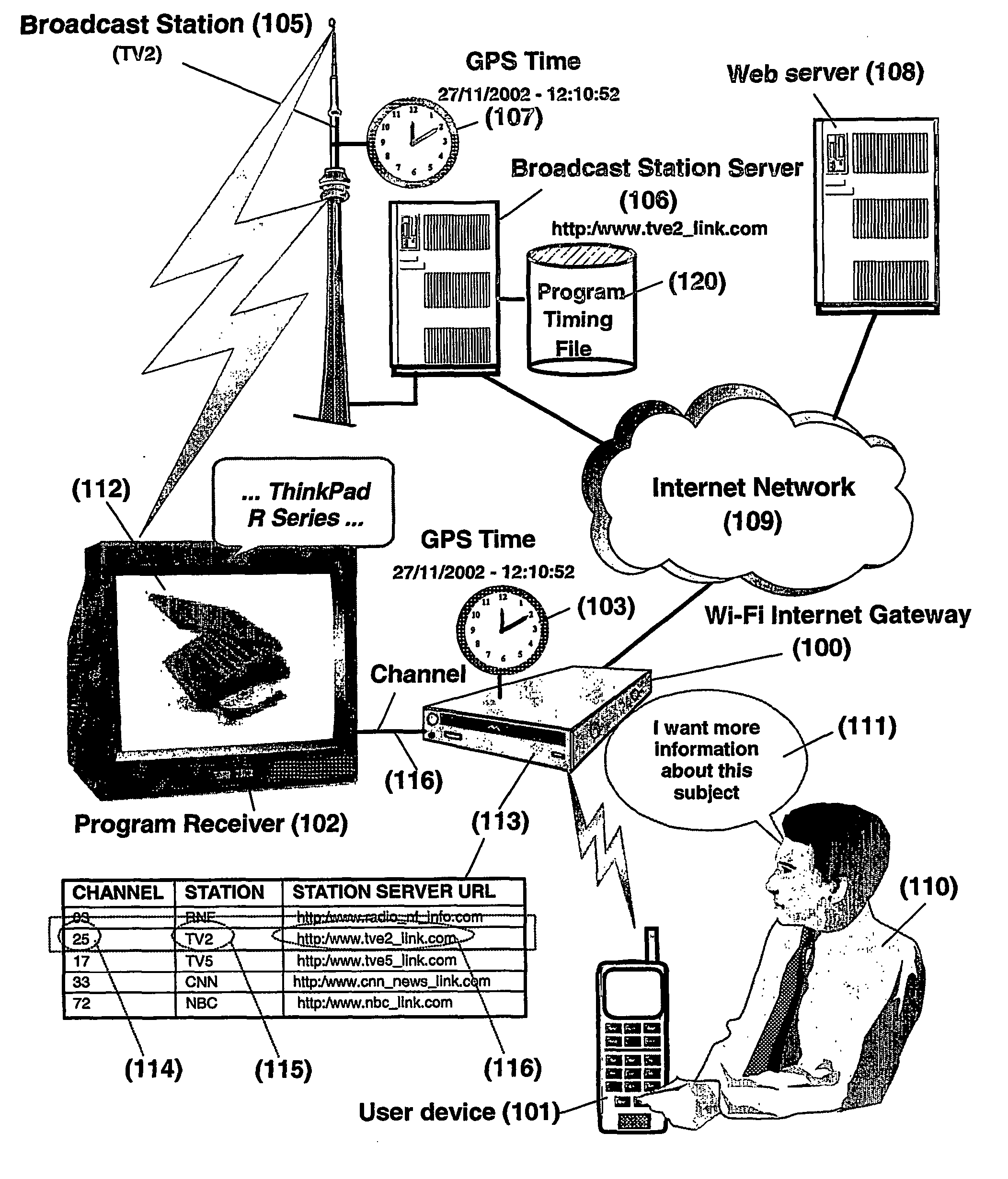
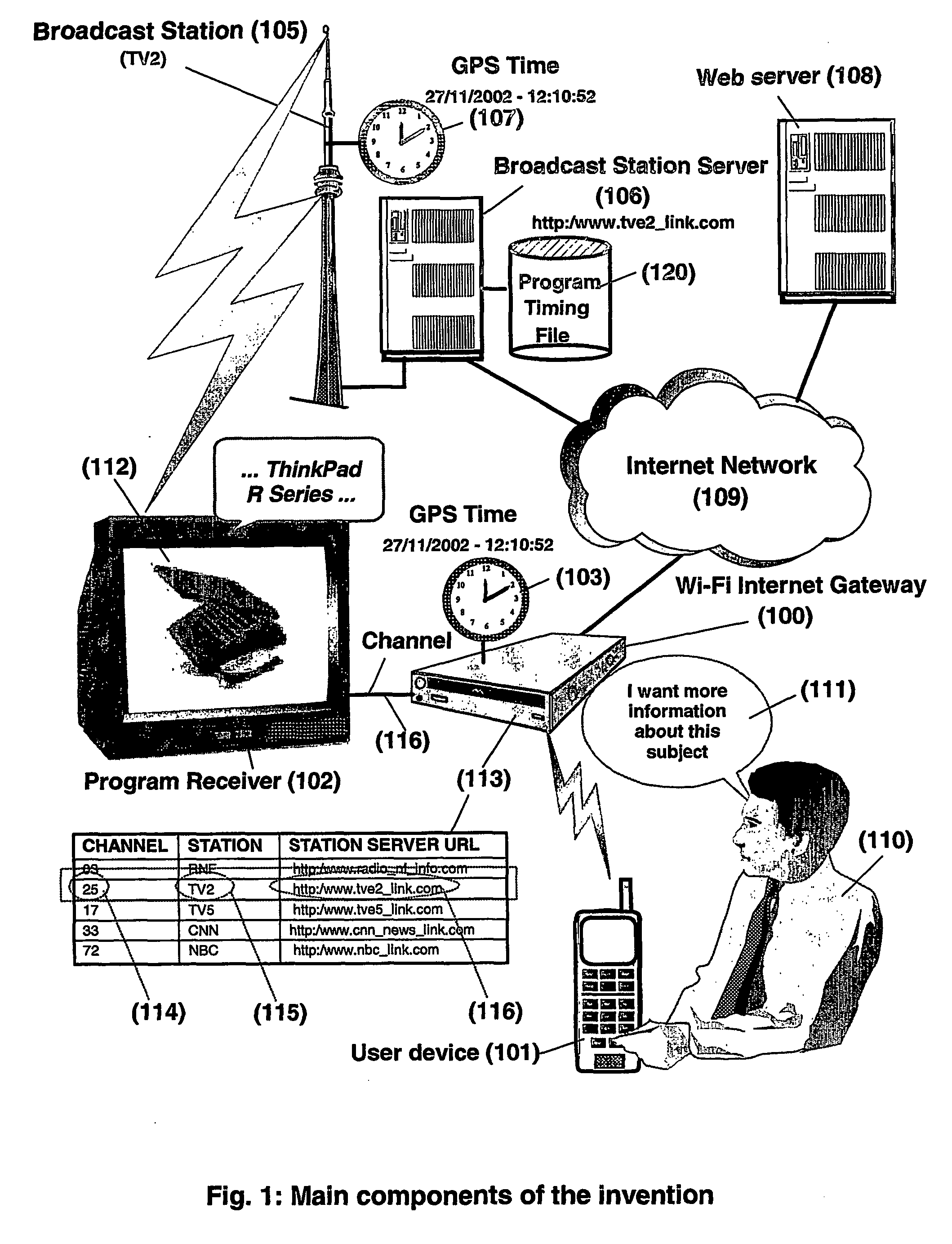
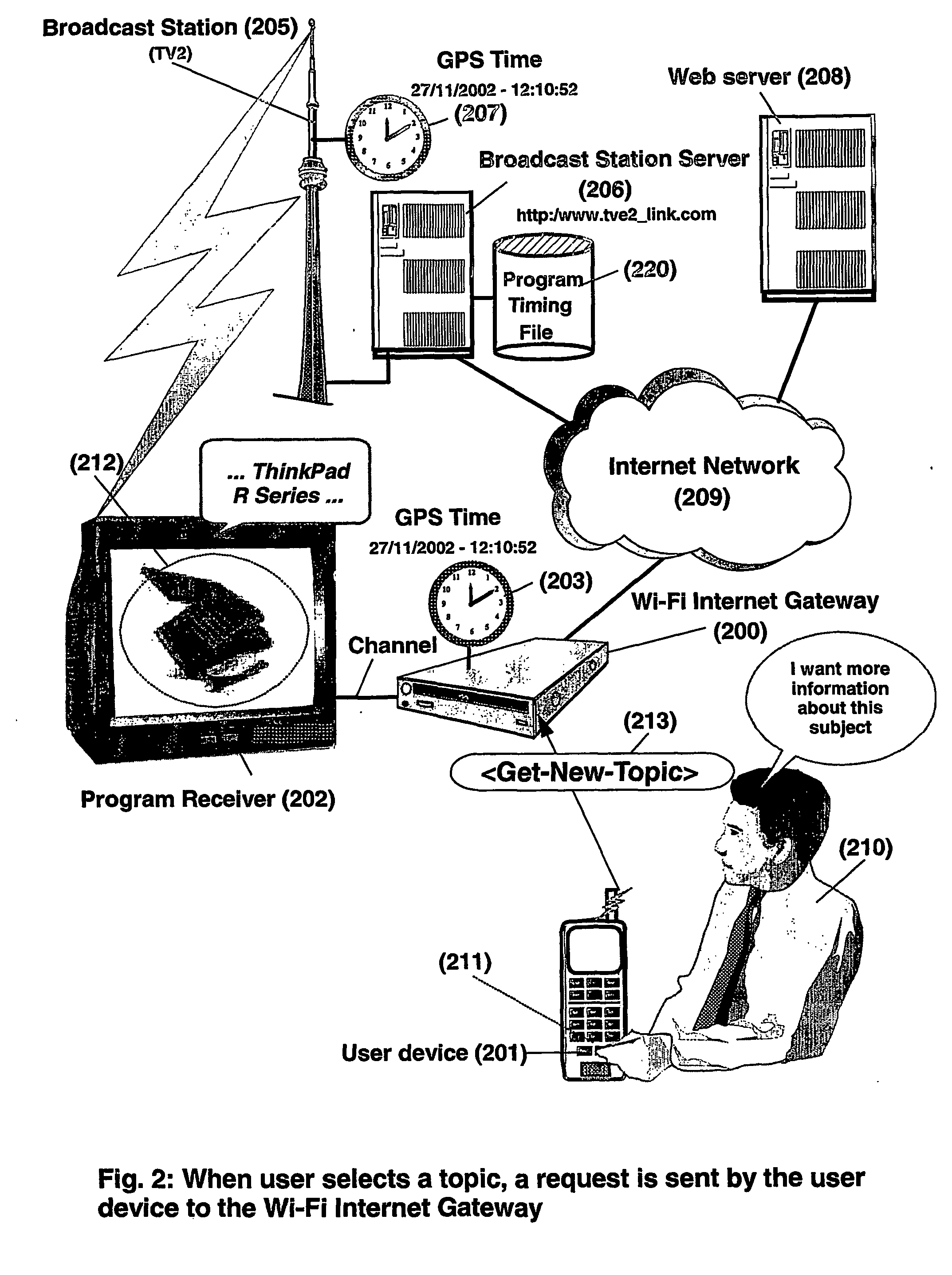
System and method for accessing through wireless internet access points information or services related to broadcast programs
InactiveUS20060136549A1Easily accessConvenient accessBroadcast services for monitoring/identification/recognitionMultiple digital computer combinationsRadio programHyperlink
A method and system for retrieving in real-time a hyperlink related to a topic selected during a broadcast of a program on a channel. A first request to a wireless internet gateway is sent for retrieving a universal-time and an address of a server. The universal-time pertains to when the command was performed. The universal-time and the address of the server is received from the wireless internet gateway in response to the first request. A second request to the server is sent via the wireless internet gateway using the received address of the server, for retrieving the one or a plurality of hyperlinks related to the selected topic, said second request transmitting to the server the received universal-time from which the hyperlink may be determined by the server. The hyperlink is received from the server via the wireless internet gateway and then recorded.
Owner:LENOVO (SINGAPORE) PTE LTD
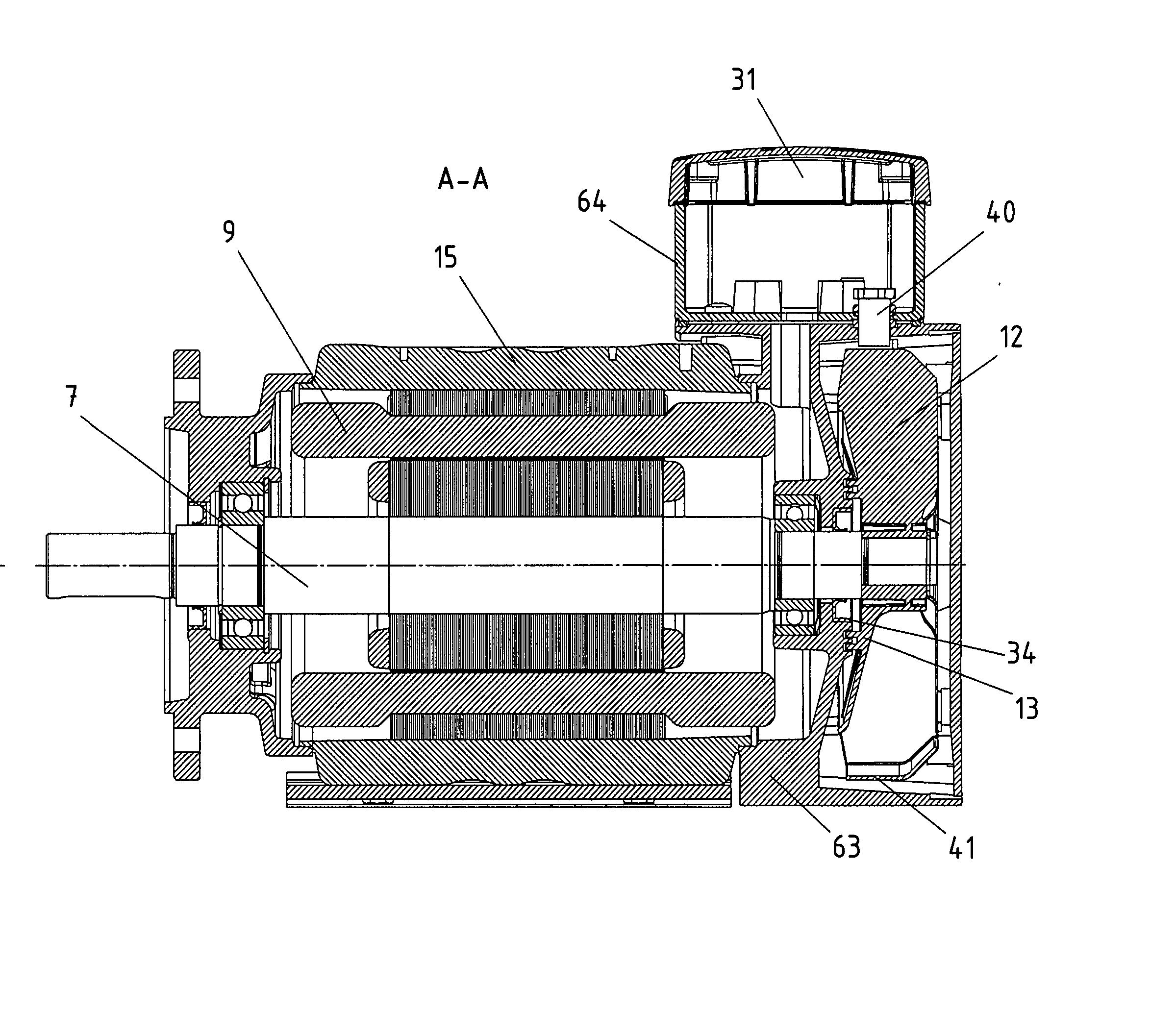
Electric Motor And Series Of Electric Motors
ActiveUS20070210661A1Easily accessEasy accessAssociation with control/drive circuitsMagnetic circuit rotating partsStatorEngineering
An electric motor and modular system of electric motors includes at least a stator, rotor, and a housing, the modular system including several variants of electric motors, e.g., within one size, the housing having a mechanical interface that is arranged for connection to a bearing support, the bearing support including at least a bearing seat for the B-side bearing of the rotor shaft, at least two different bearing supports being alternatively connectible to the housing, a first bearing support including an additional interface for connection to a bottom part of a terminal box, or alternatively to a bottom part for power electronics, and the first bearing support forming a housing for a brake and / or a fan, a second bearing support being constructed in one piece with a bottom part of a terminal box.
Owner:SEW-EURODRIVE GMBH & CO KG
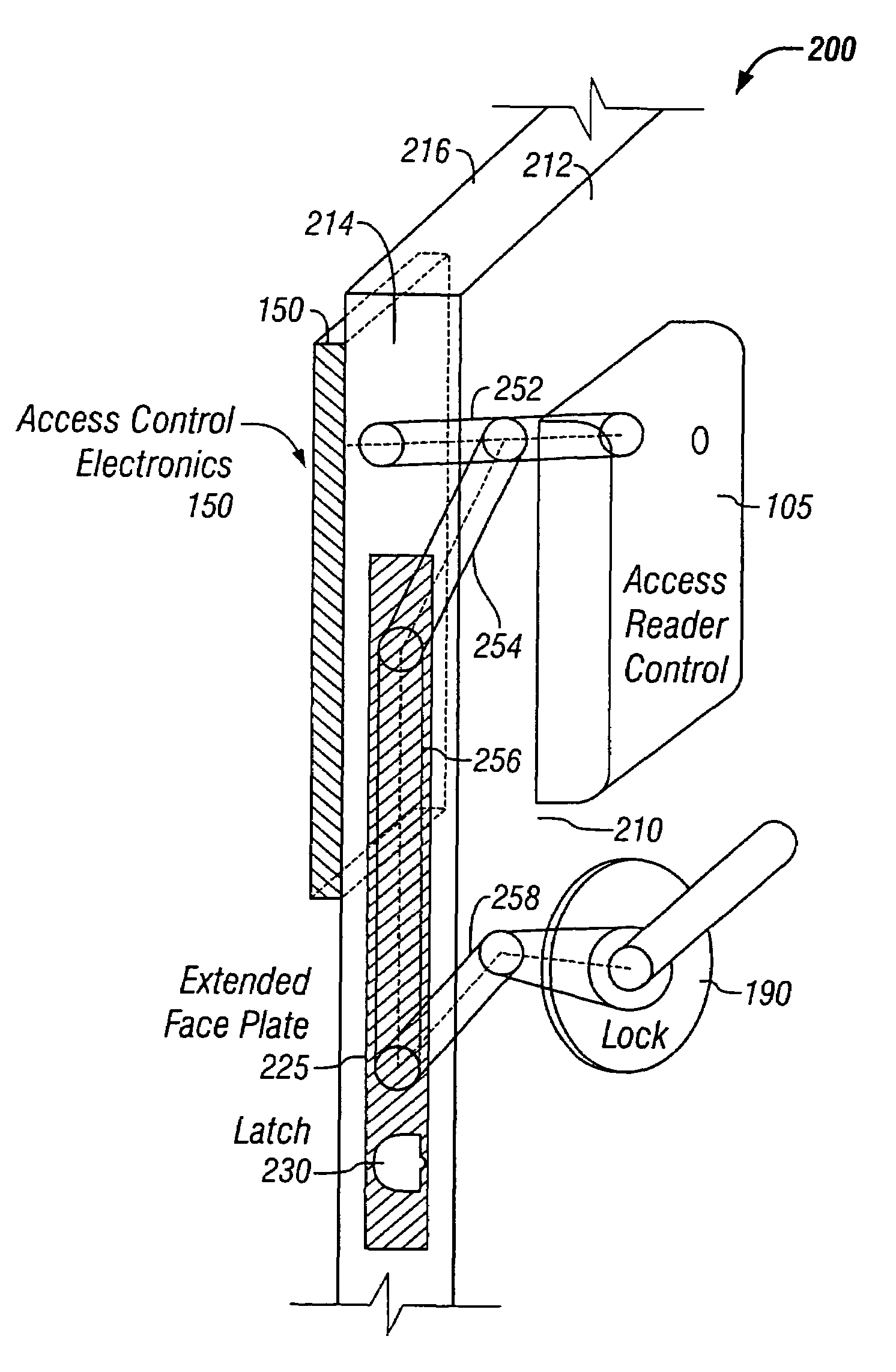
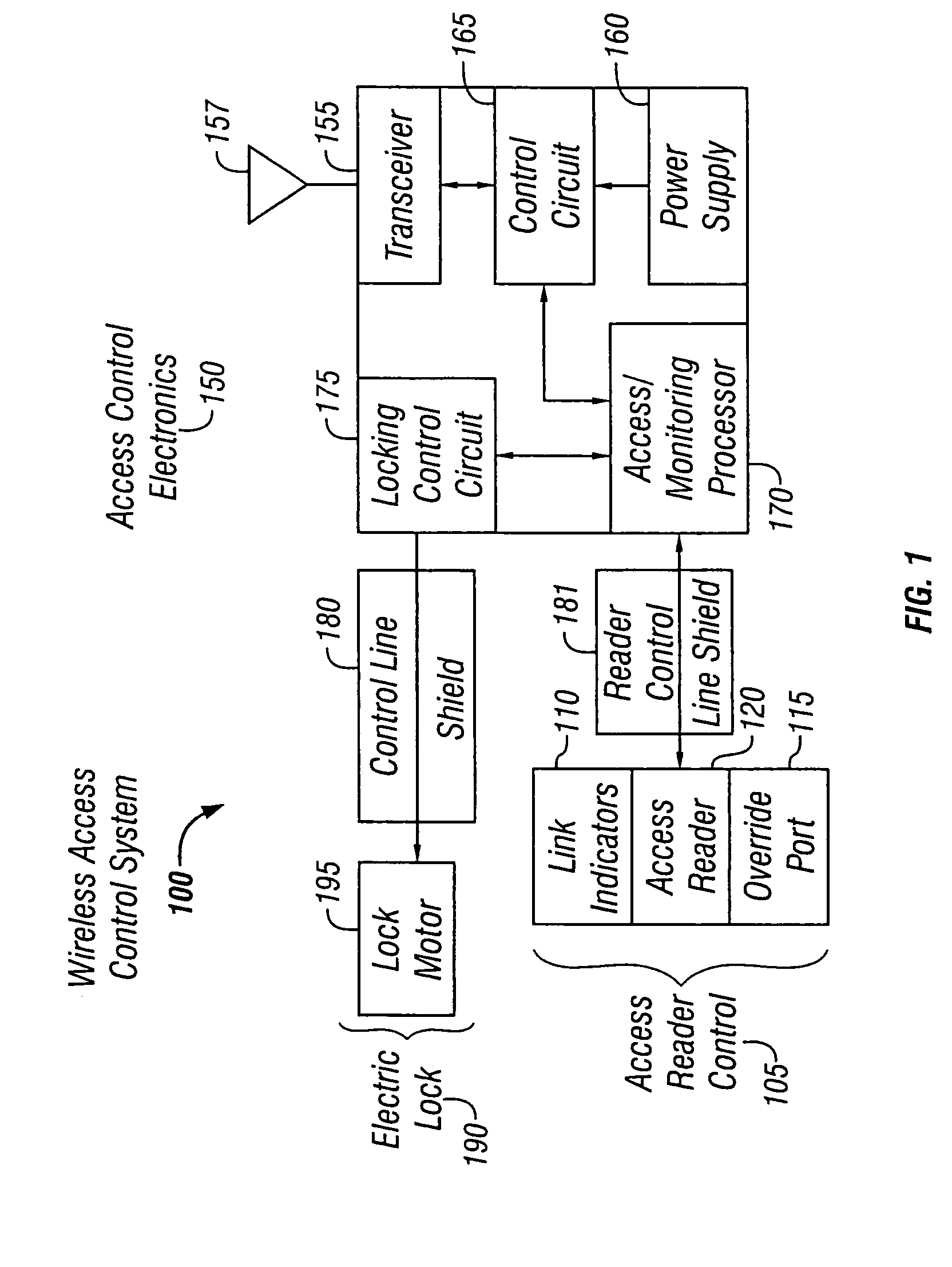
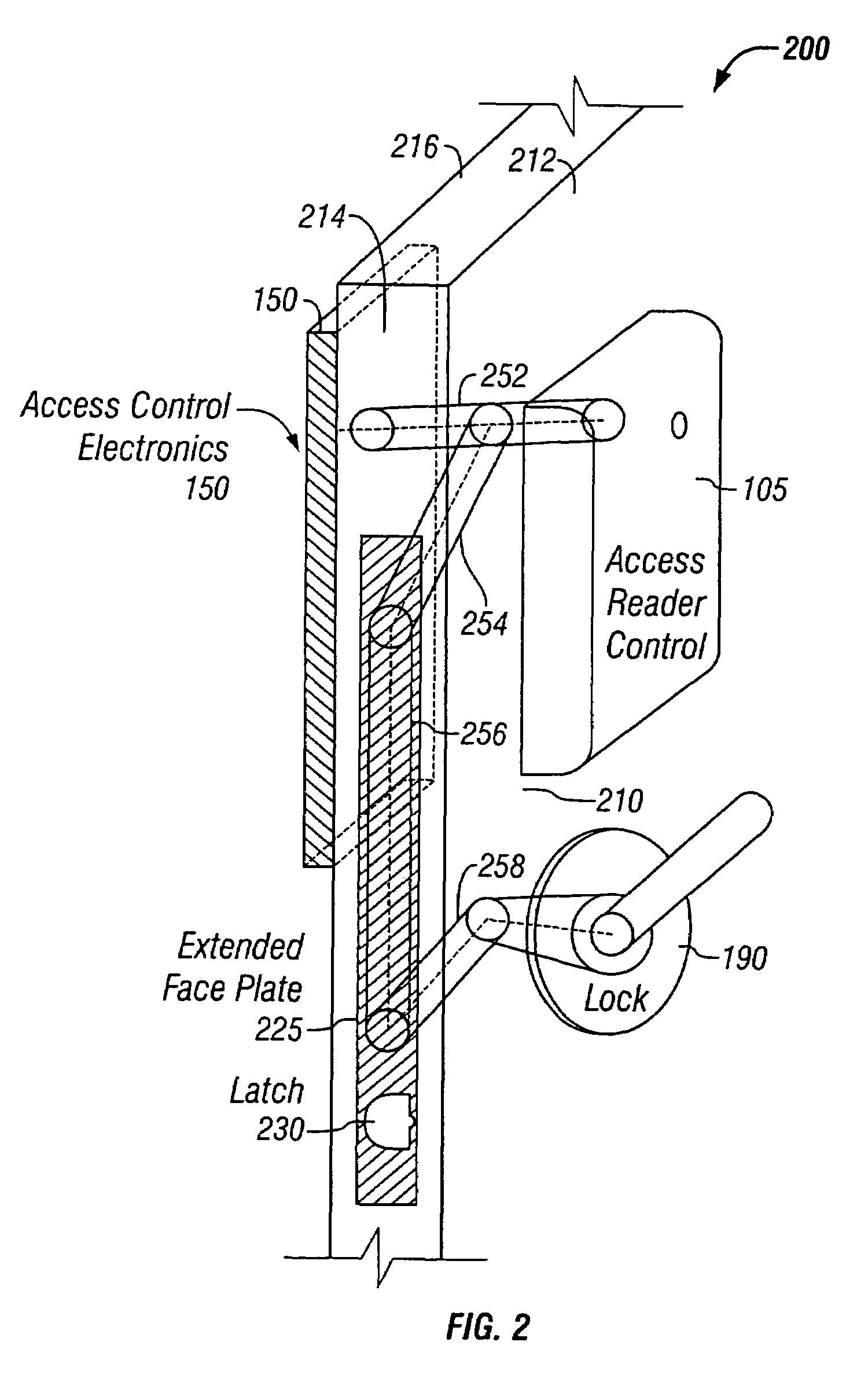
Door wireless access control system including reader, lock, and wireless access control electronics including wireless transceiver
InactiveUS7526934B2Easily accessElectric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsSafe systemTransceiver
The preferred embodiments of the present invention provide an improved access control system that provides additional security for the connection between an existing locking system and an access control system, for example, to prevent tampering. The security system preferably includes a control line shield to protect a control line running from an access reader to an external lock incorporated in a door, for example. The control line shield seals the control line into the interior of the door to prevent easy access for interference and tampering Additionally, the control line shield may be removed as necessary to provide service to the access system.
Owner:HARROW PRODS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com