Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
310 results about "Spanning Tree Protocol" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
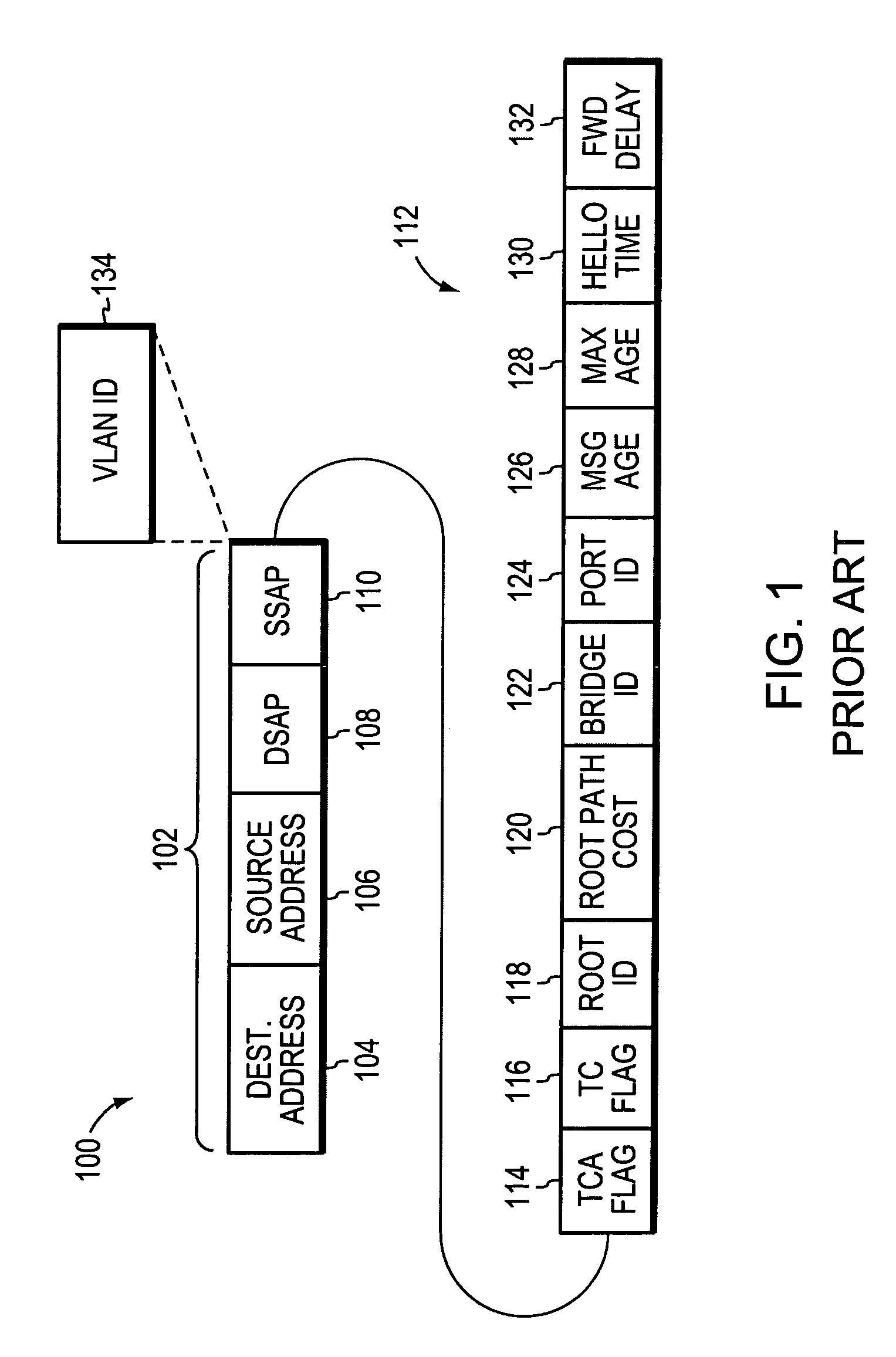
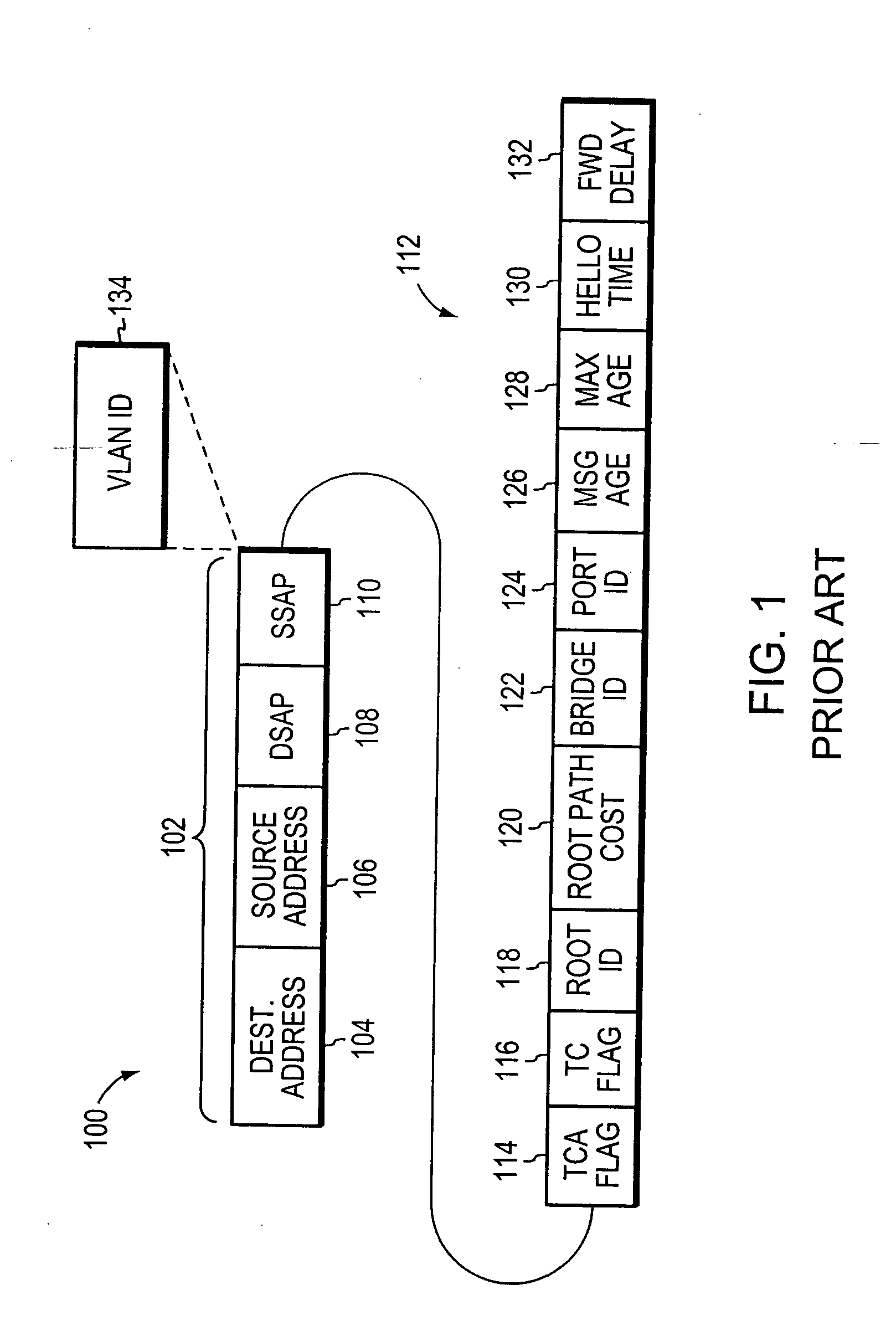
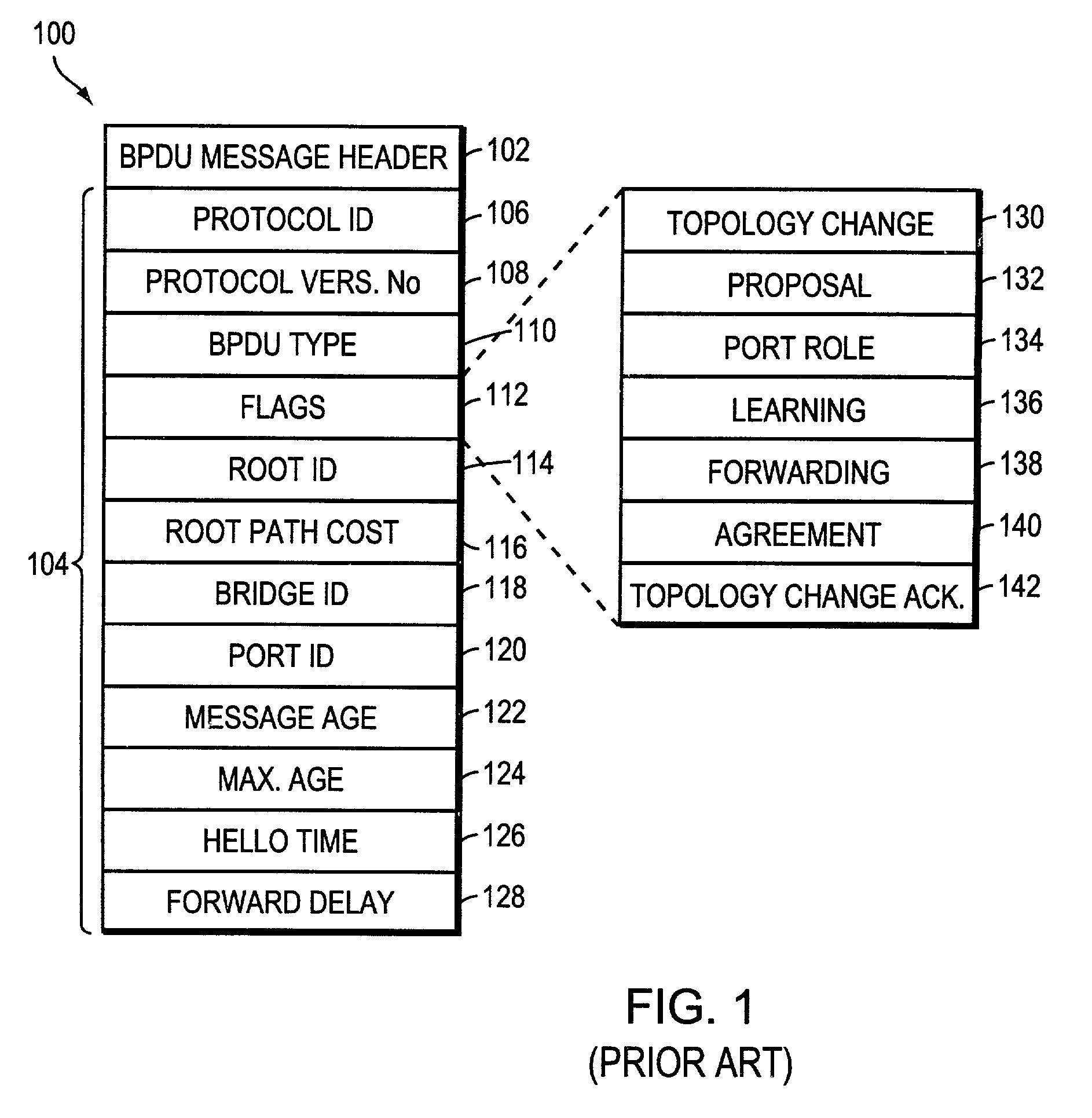
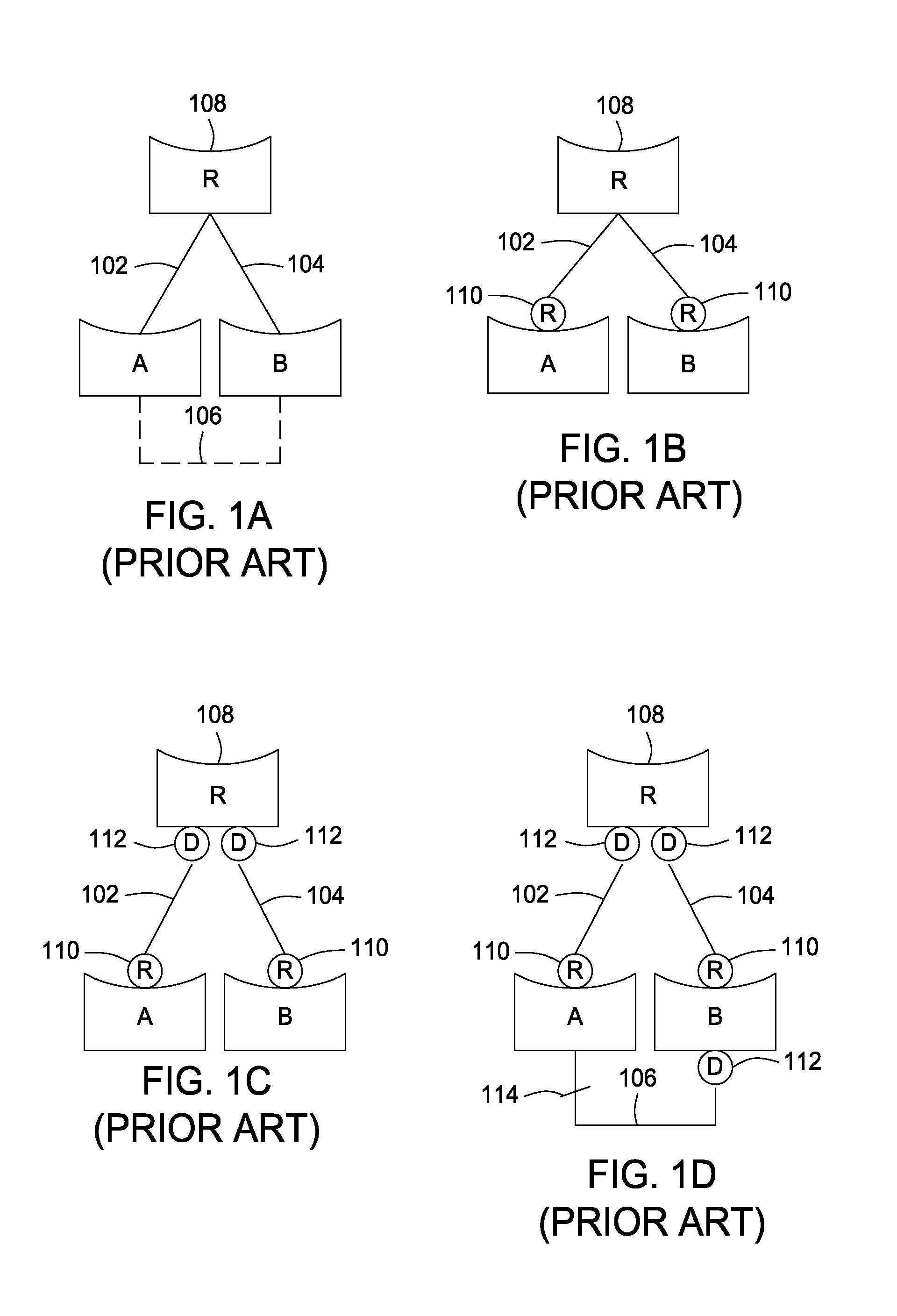
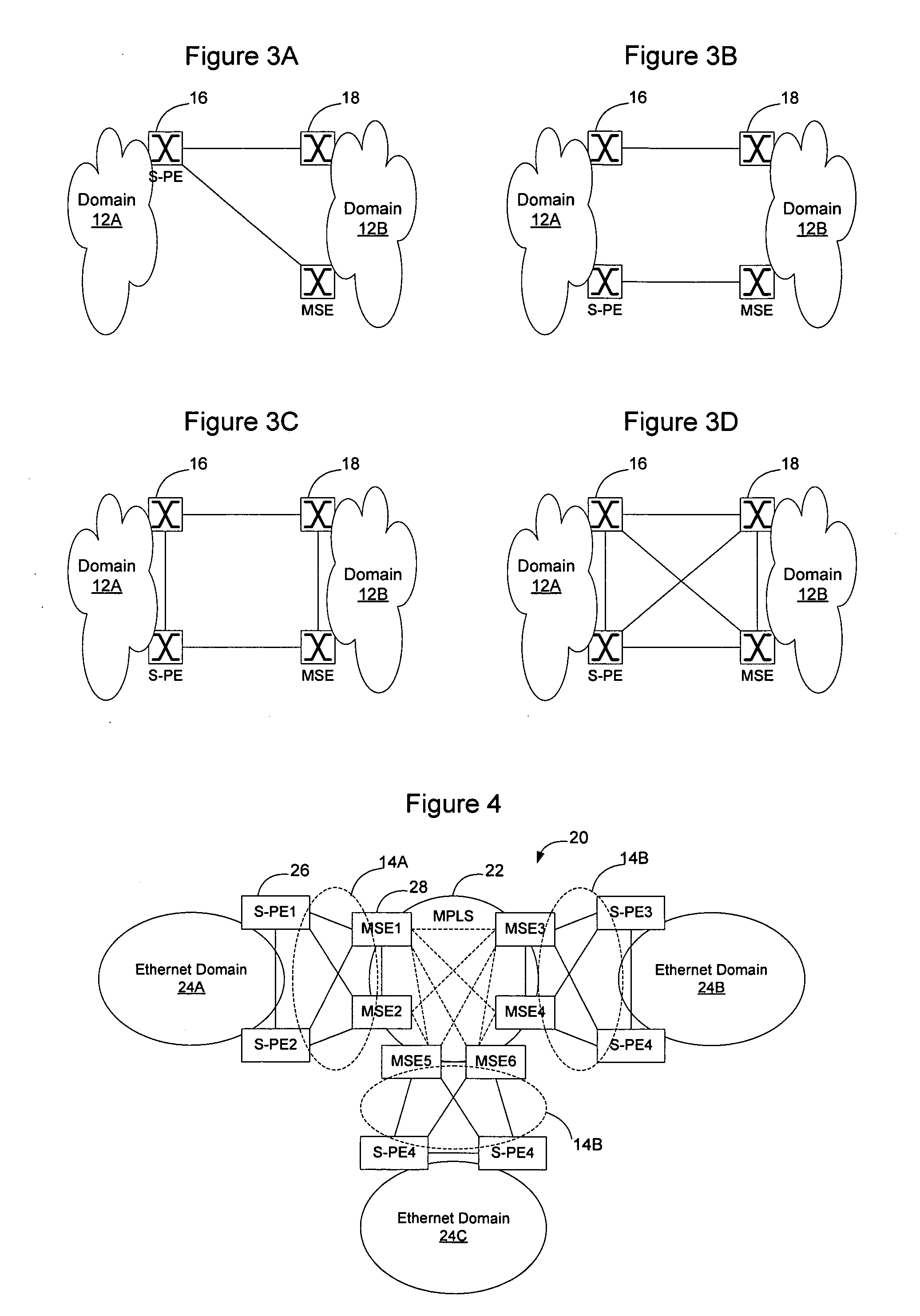
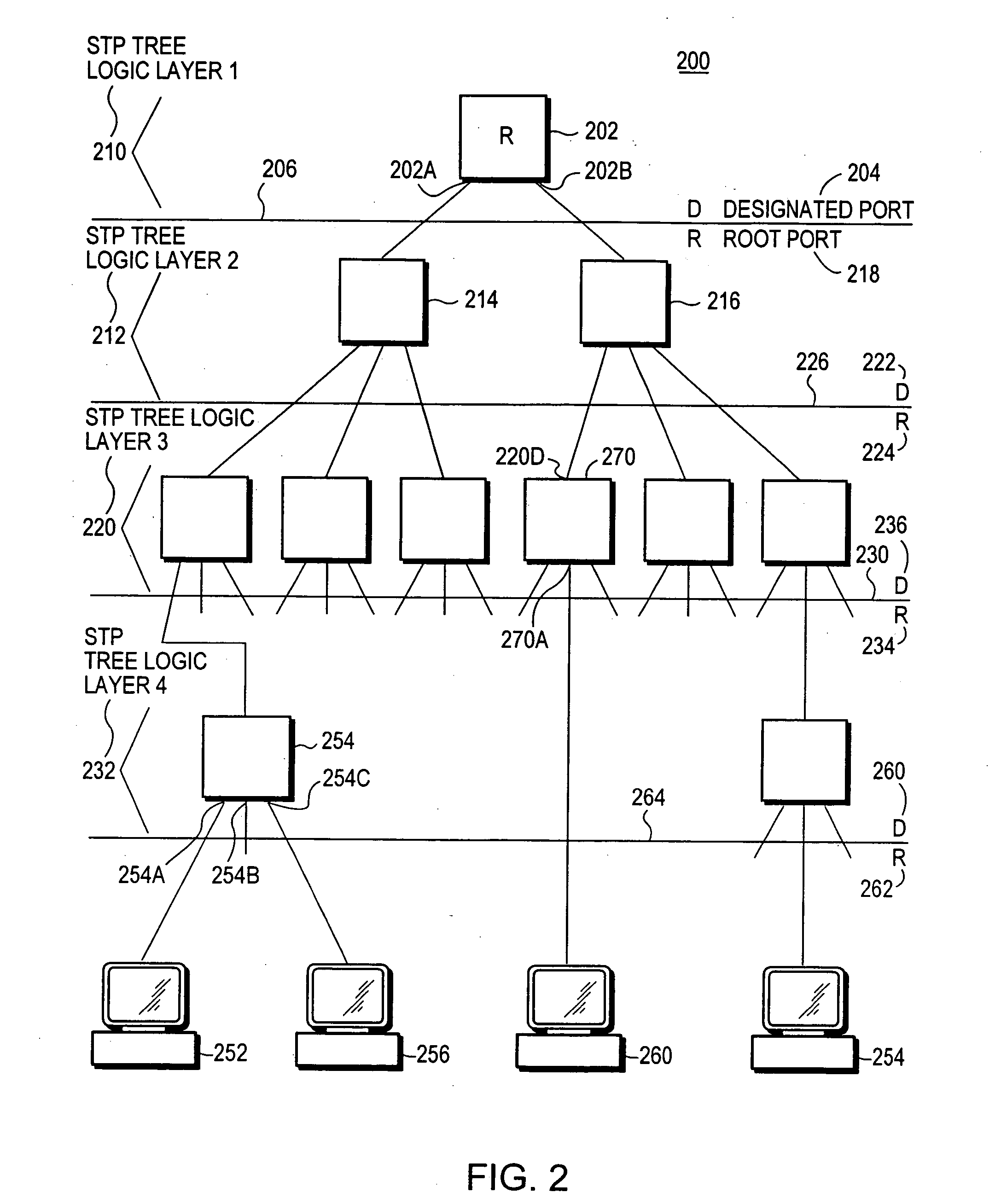
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a network protocol that builds a loop-free logical topology for Ethernet networks. The basic function of STP is to prevent bridge loops and the broadcast radiation that results from them. Spanning tree also allows a network design to include backup links to provide fault tolerance if an active link fails.
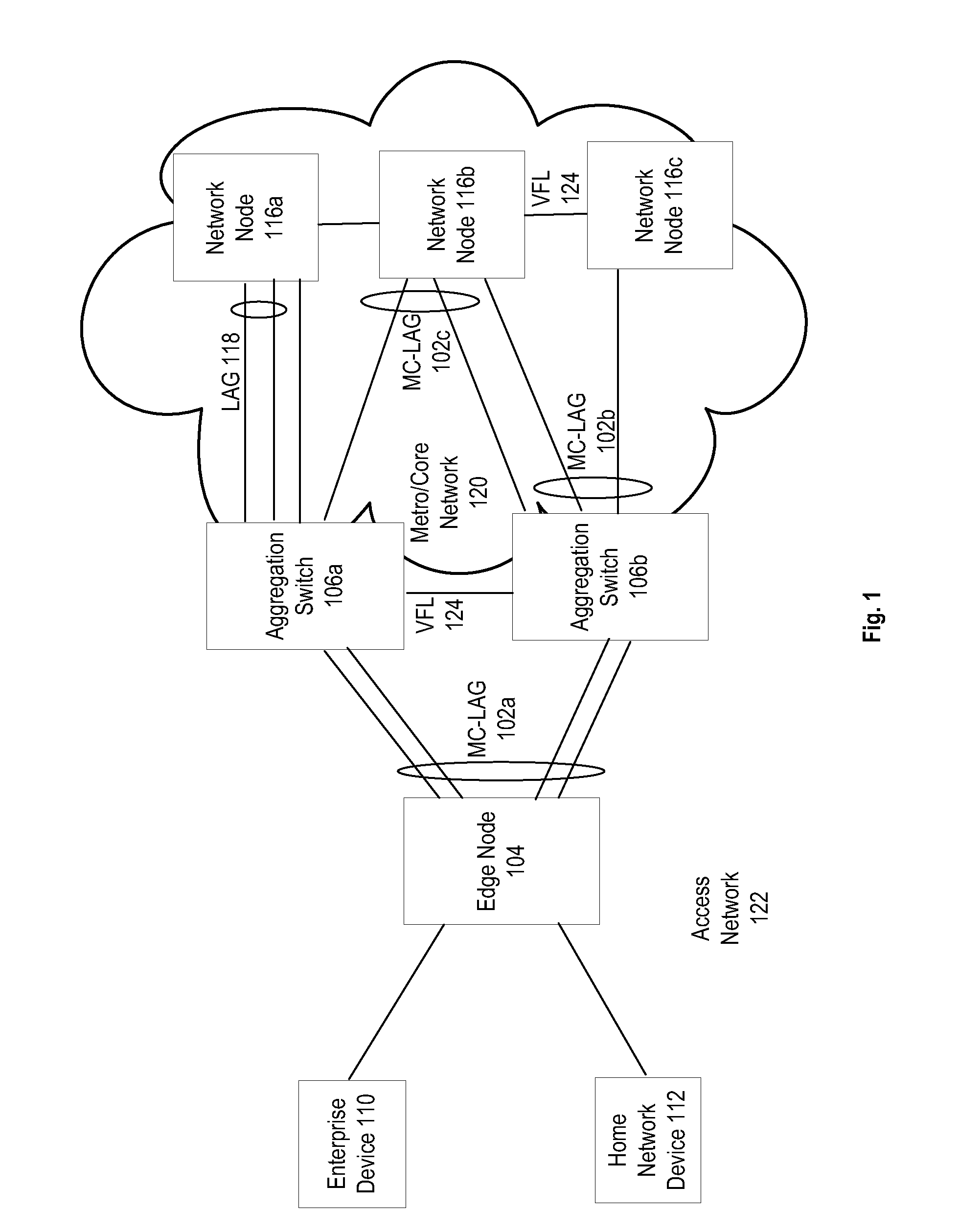
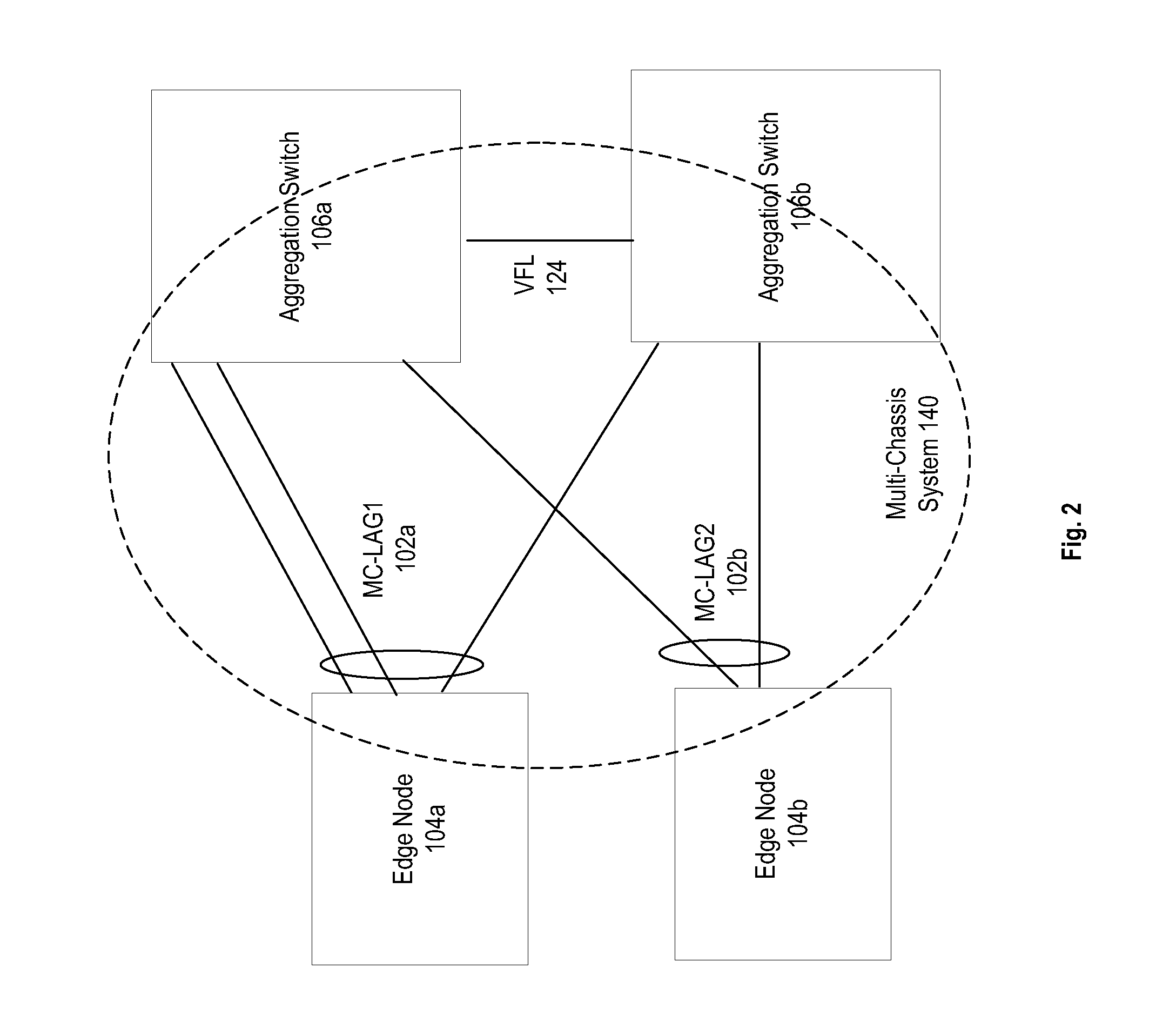
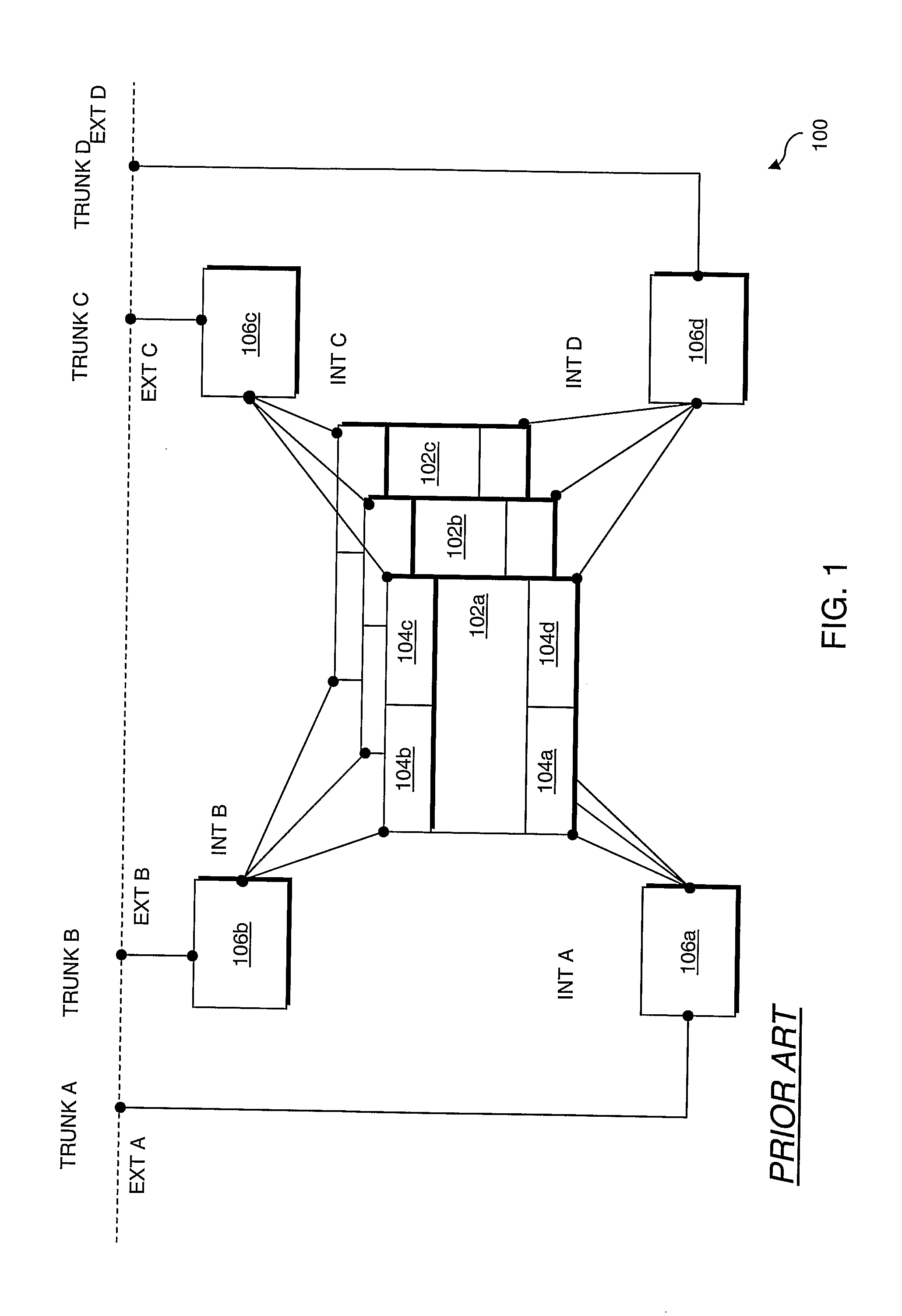
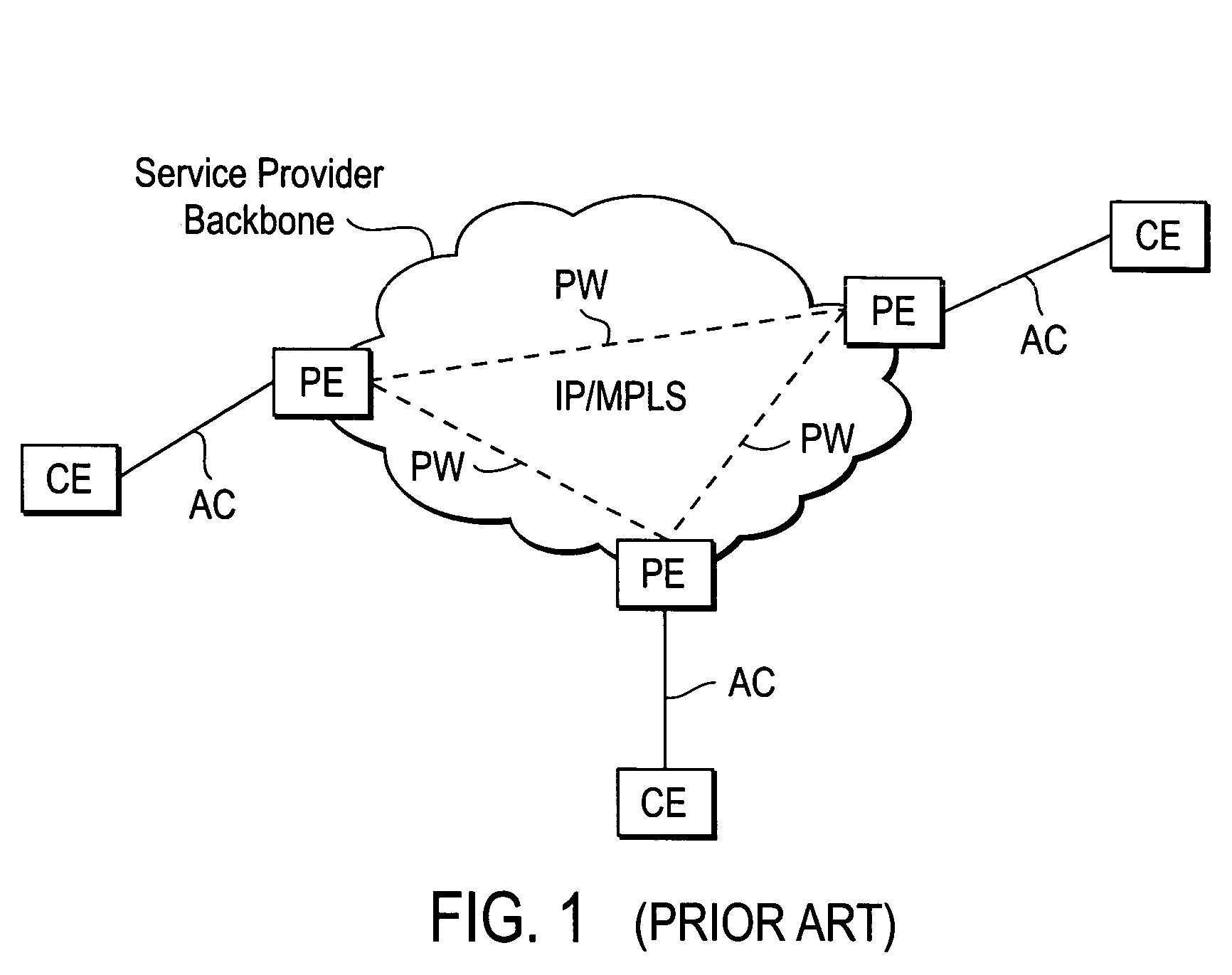
Computer network with point-to-point pseudowire redundancy
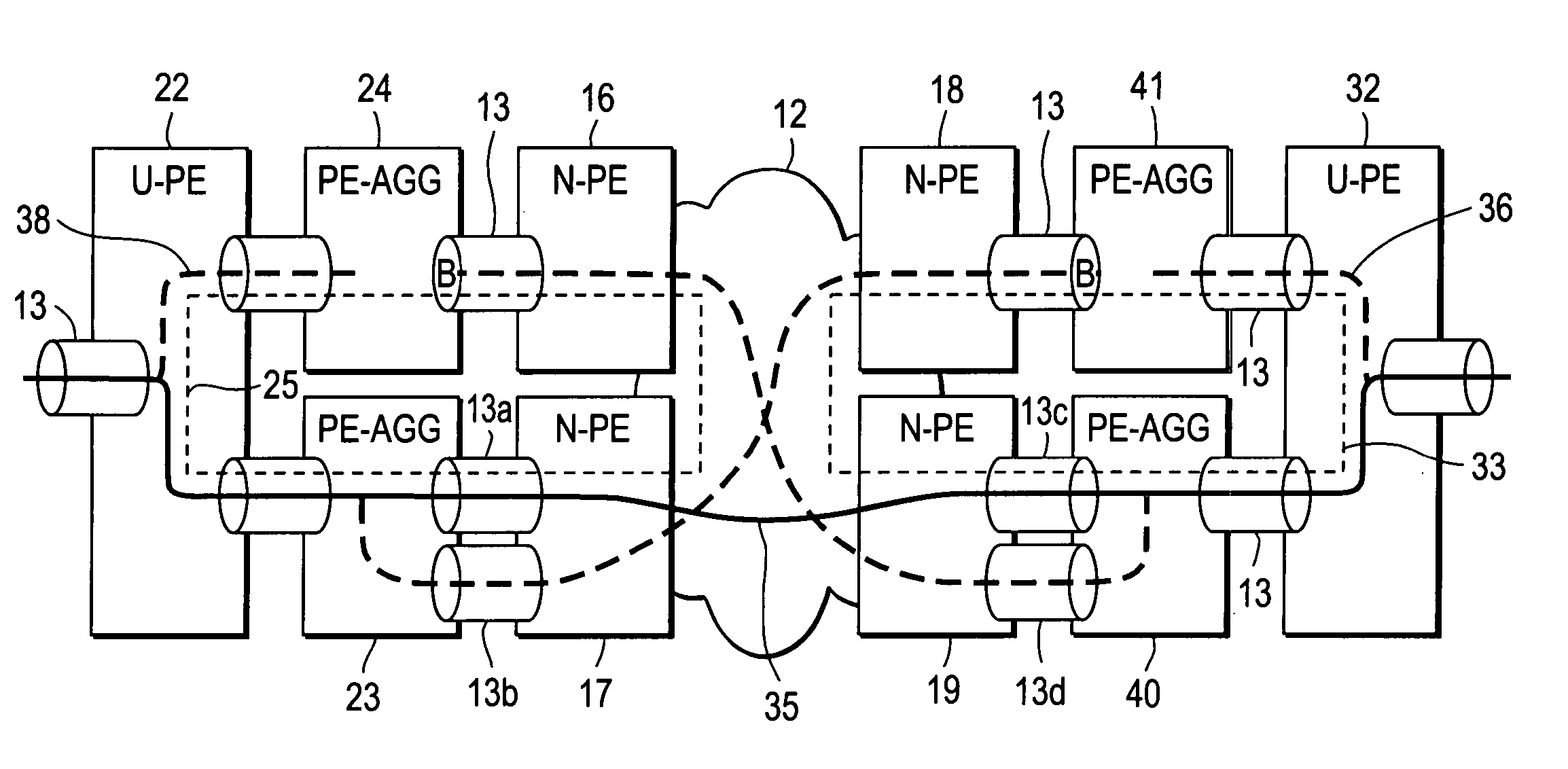
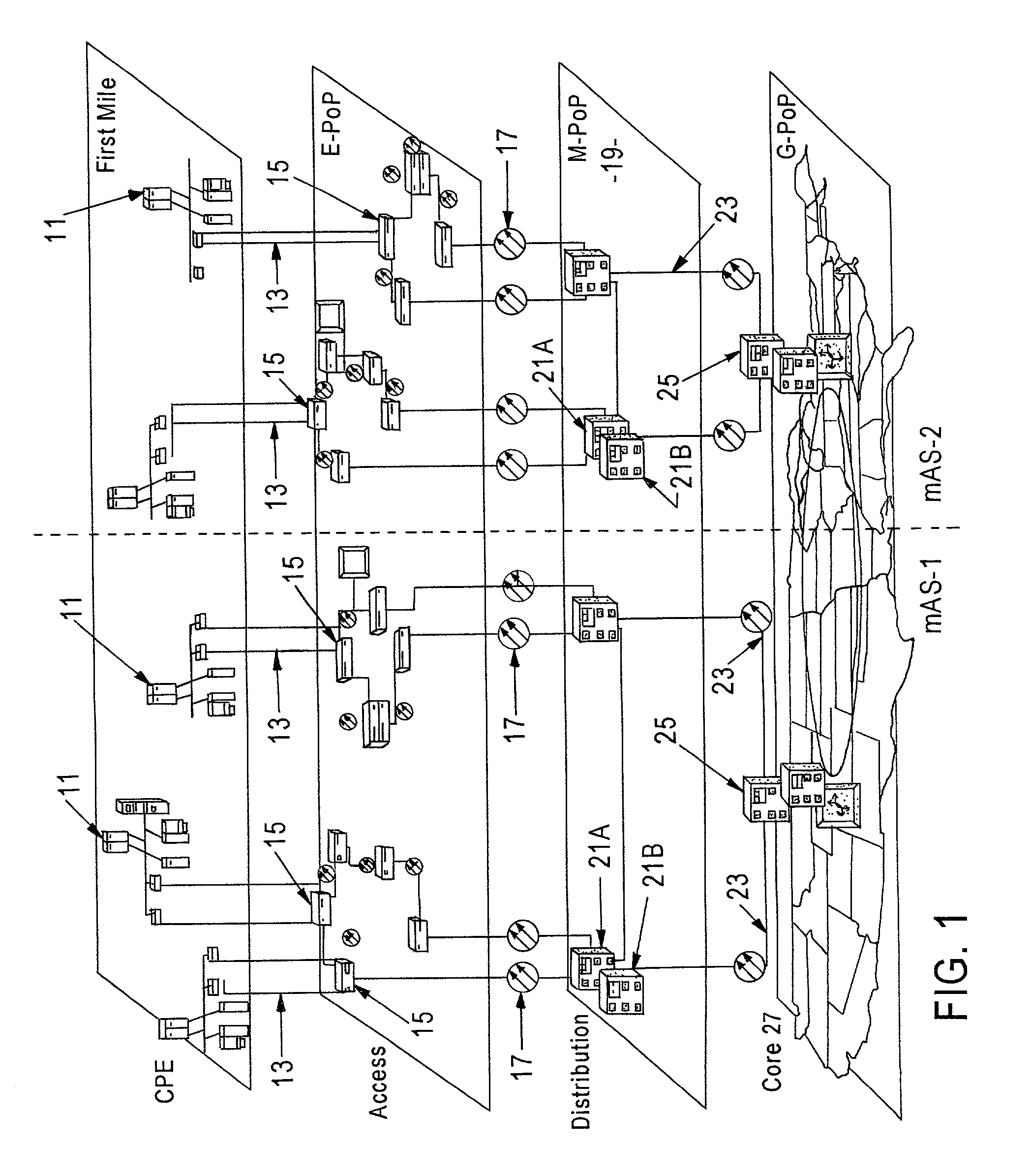
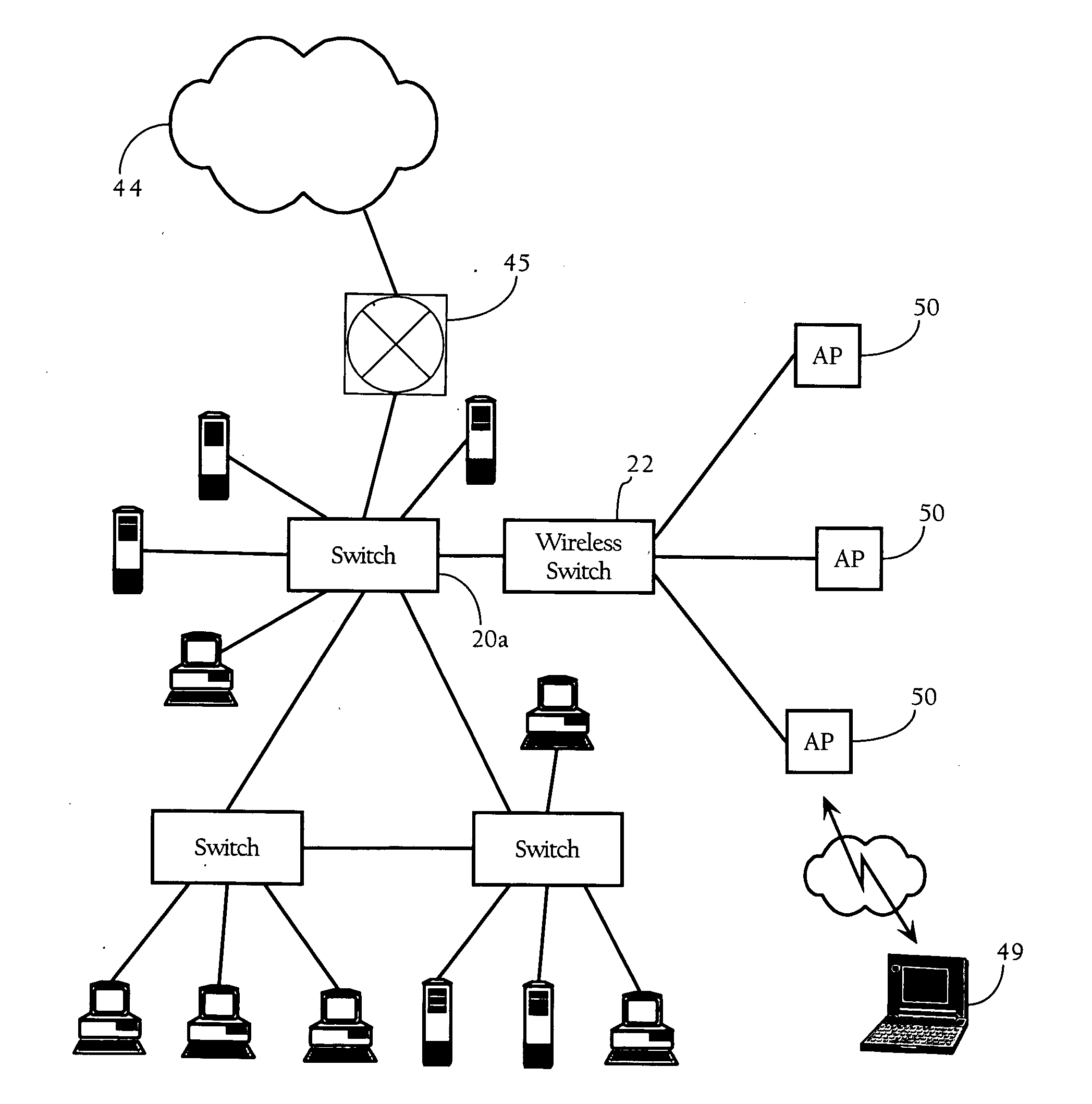
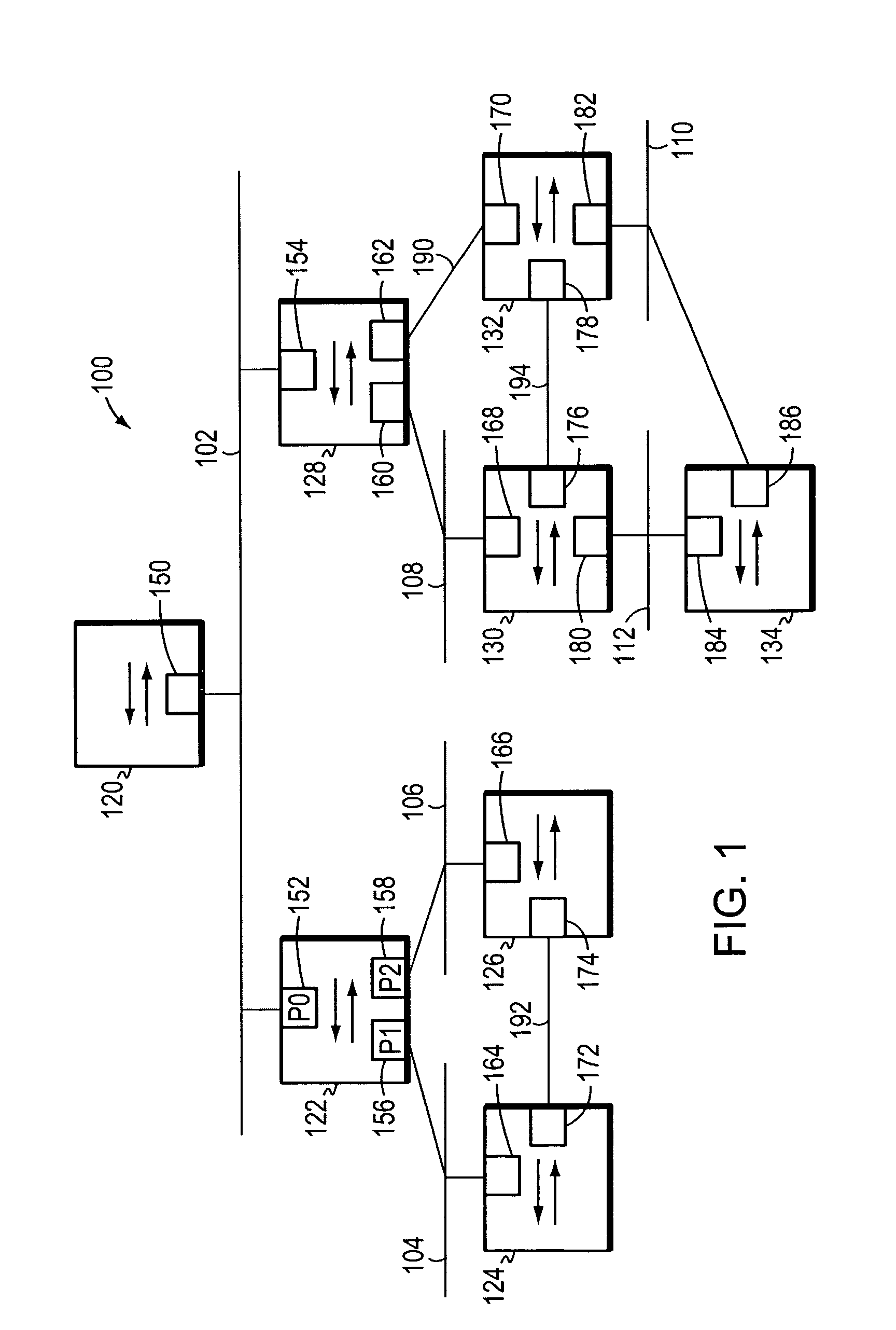
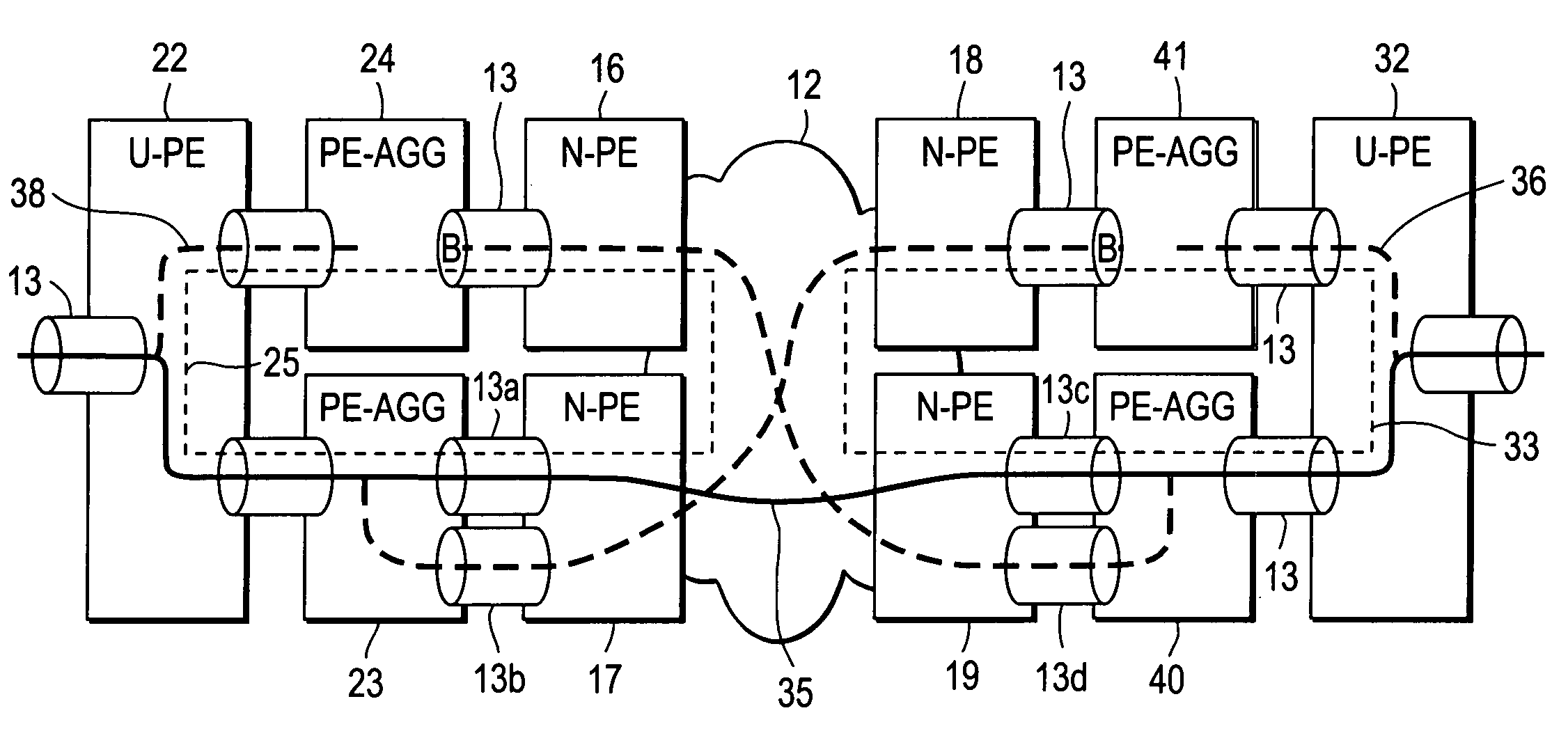
A computer network includes a core network connected with first and second Ethernet access domain networks, each of Ethernet access domain networks including a user-facing provider edge (u-PE) device, a primary network-facing provider edge (n-PE) device, a redundant n-PE device, and a plurality of aggregation provider edge (Agg-PE) devices providing connectivity between to the u-PE device and the primary and redundant n-PE devices, the Agg-PE devices running a spanning-tree protocol (STP) algorithm. A primary data path is provided along with first and second redundant data paths that include first and second redundant pseudowires (PWs), respectively, connected across the core network, the first and second redundant data paths being blocked by the STP algorithm when the primary data path is available, the STP algorithm unblocking either the first or second redundant data path in response to a failure of the primary data path. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract that will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
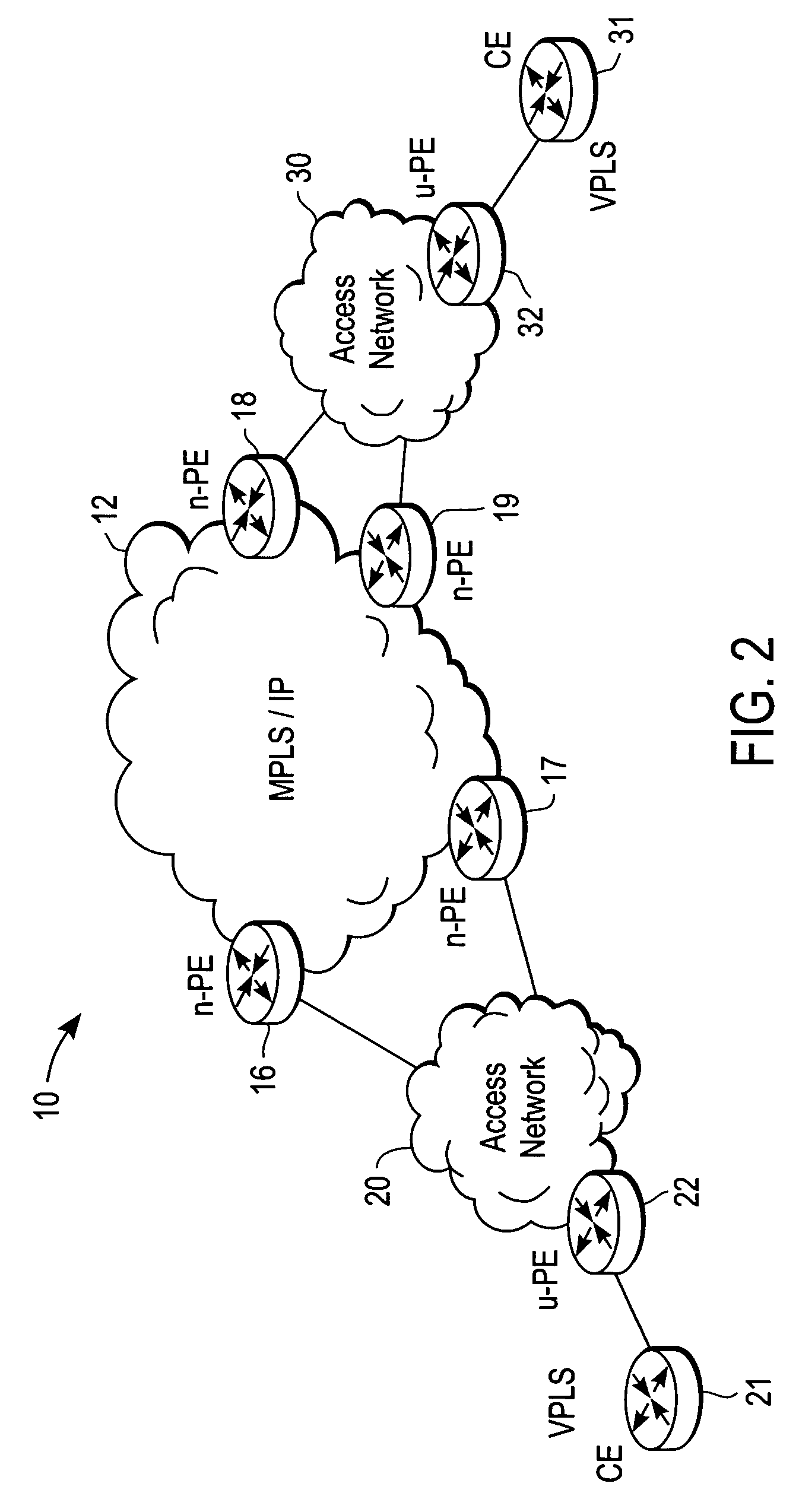
Enhanced data switching/routing for multi-regional IP over fiber network
InactiveUS6963575B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsNetworks interconnectionWide areaBorder Gateway Protocol
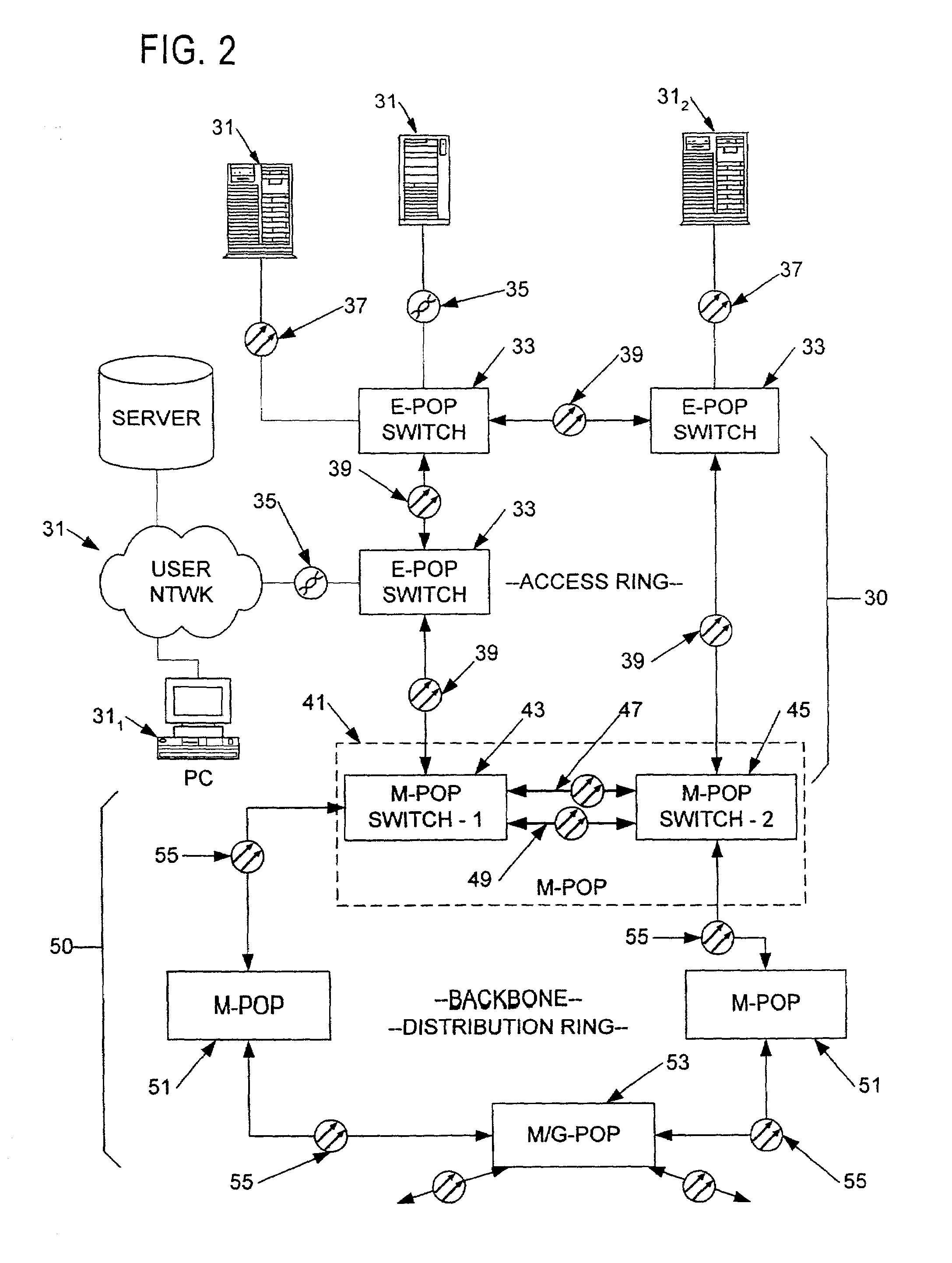
Wide-area data communications utilize regional networks transporting IP-over-Ethernet on fiber. For certain Layer 2 services, a regional implementation of the network makes limited use of spanning tree protocol on a backbone ring. Learning bridge operations in switches on associated access rings involve a short default for an aging timer. For use of Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), the connection of each access ring to the backbone ring uses a pair of routers with dual links therebetween. One of these links is bonded to the backbone (OSPF Area 0), whereas the other link is bonded to the Area of the respective access ring. Also, certain routers within each regional network form a mini-autonomous system, for boundary gateway protocol (BGP). The mini-autonomous systems of the regional networks form a confederation. The network utilizes route reflectors in the mini-autonomous systems. The Internet carries confederation commands to and from a designated hub.
Owner:YIPES ENTERPRISE SERVICES
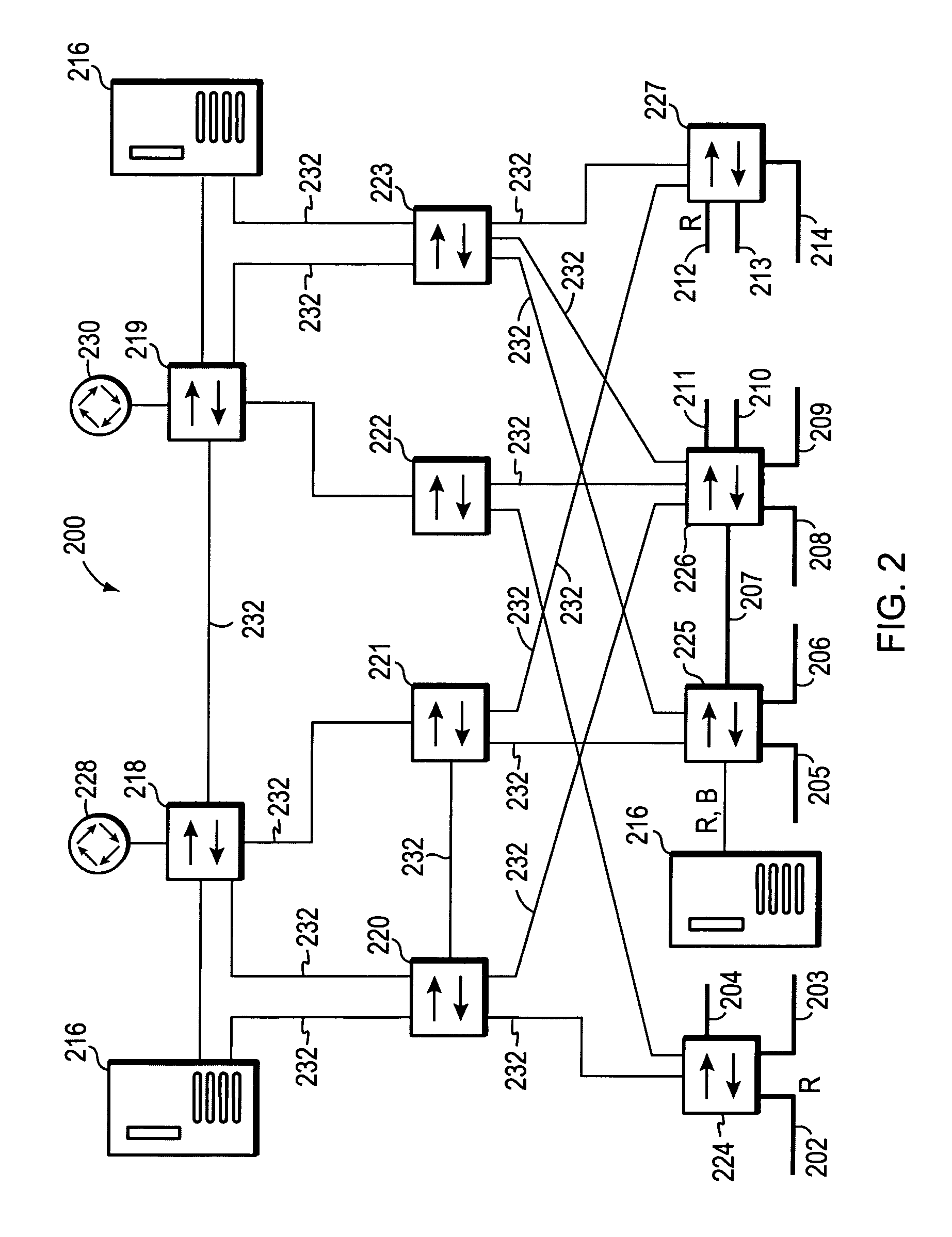
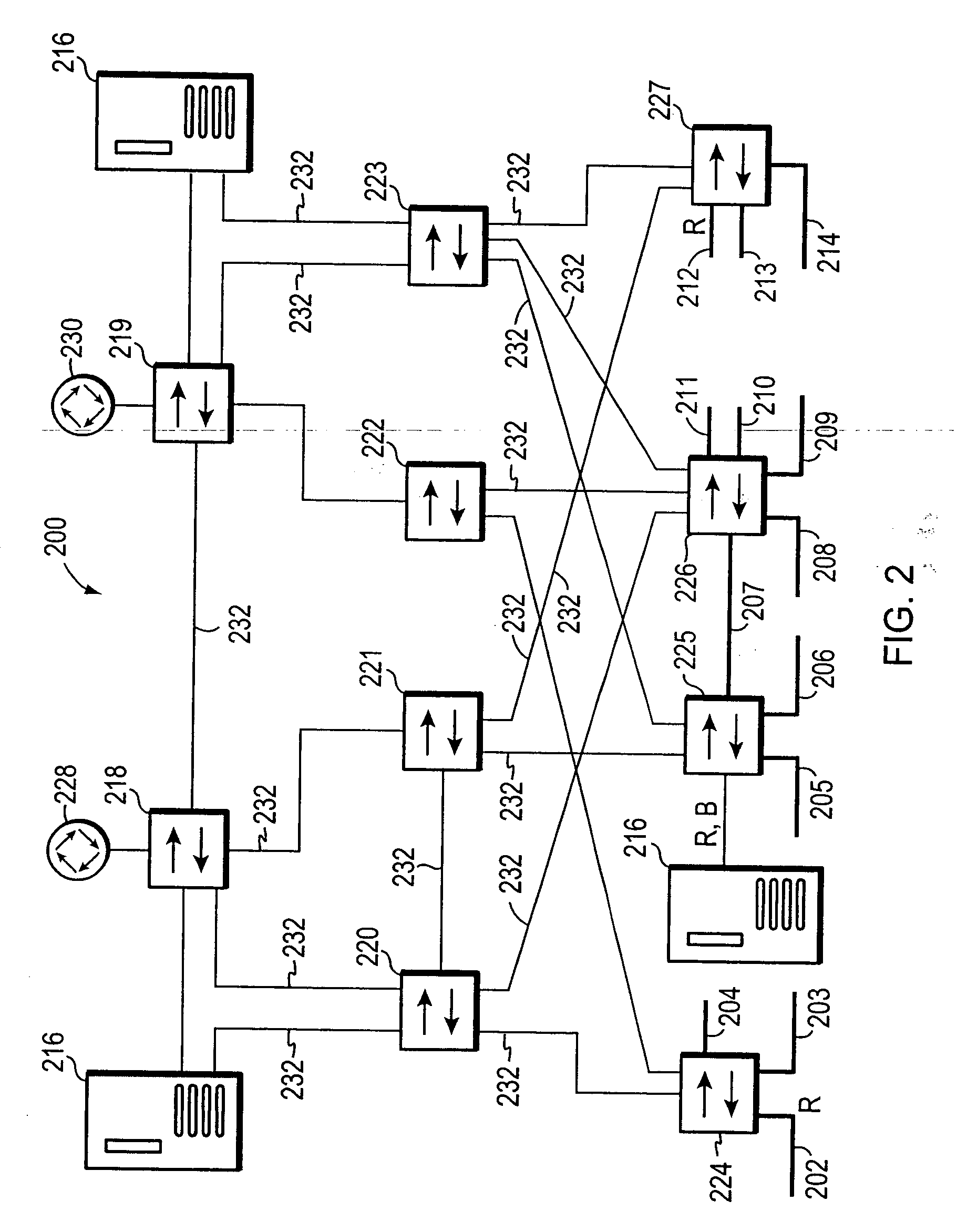
Multiple instance spanning tree protocol
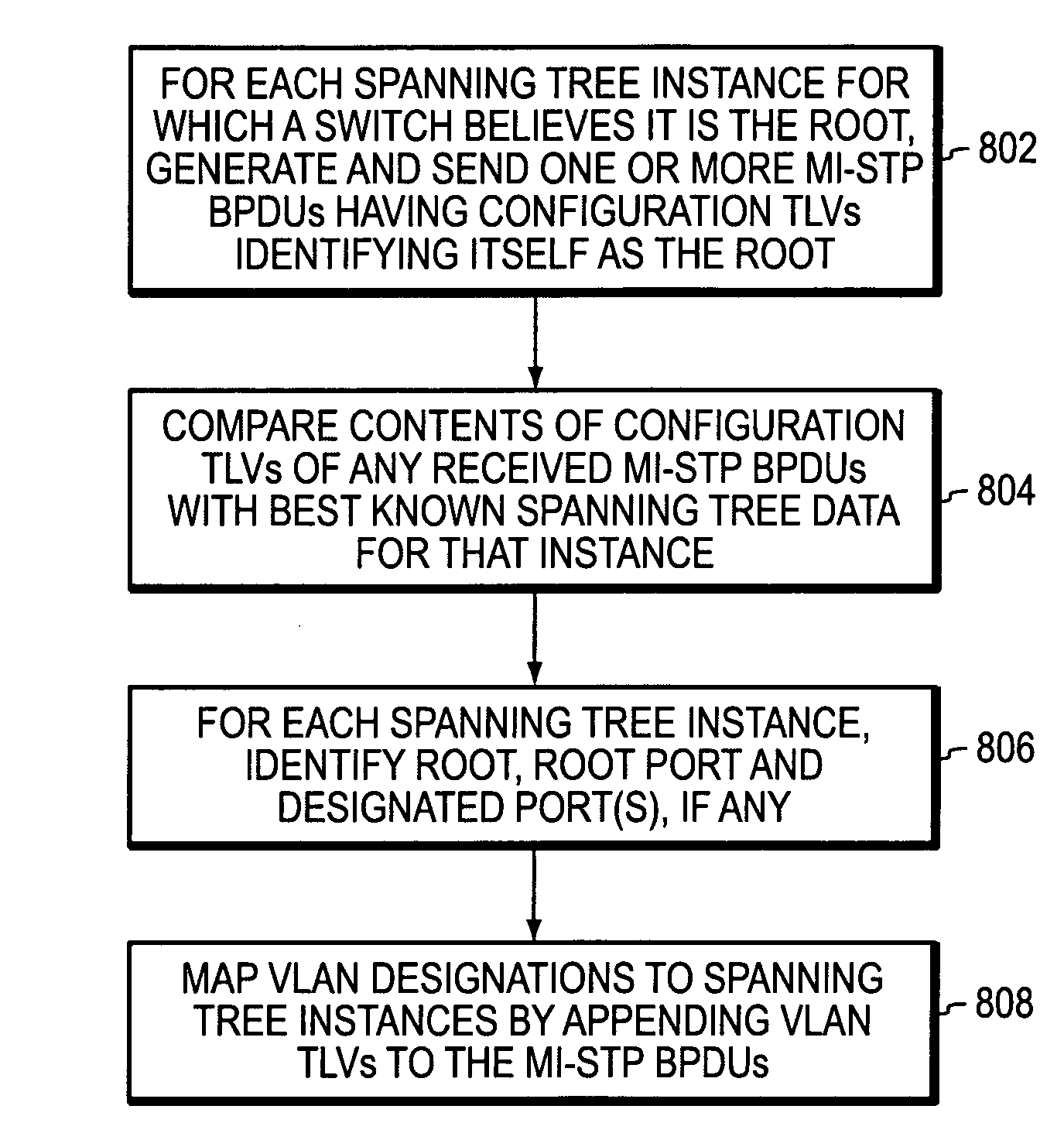
A multiple instance spanning tree protocol (MI-STP) creates a plurality of active topologies (i.e., loop-free paths) within a computer network. These active topologies may be established through the exchange and processing of multiple instance spanning tree bridge protocol data unit messages (MI-STP BPDUs) by the intermediate network devices within the network. The active topologies are preferably created independently of any virtual local area network (VLAN) designations defined within the network. Once the active topologies are defined, each VLAN designation is then mapped to a single active topology, although multiple VLAN designations are preferably mapped to the same active topology to provide load balancing.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Multiple instance spanning tree protocol
A multiple instance spanning tree protocol (MI-STP) creates a plurality of active topologies (i.e., loop-free paths) within a computer network. These active topologies may be established through the exchange and processing of multiple instance spanning tree bridge protocol data unit messages (MI-STP BPDUs) by the intermediate network devices within the network. The active topologies are preferably created independently of any virtual local area network (VLAN) designations defined within the network. Once the active topologies are defined, each VLAN designation is then mapped to a single active topology, although multiple VLAN designations are preferably mapped to the same active topology to provide load balancing.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Cross stack rapid transition protocol
ActiveUS7480258B1Fast rebuildError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic flowComputer science
A cross stack rapid transition protocol is provided for permitting multiple network devices organized as a stack to rapidly transition their ports in response to network changes so as to minimize traffic flow disruptions while avoiding loops. Each switch in the stack has a stack port that connects the switch to another switch in the stack, and a plurality of ports for connecting the switch to other entities of the computer network. Each switch includes a Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) entity that transitions the ports of the switch among a plurality of states including a forwarding state and a blocking state. Each switch also tracks which other switches are members of the switch stack. The stack port of each switch is transitioned to the forwarding state, and a single switch having connectivity to a root is elected to be a Stack Root. One or more other switches may have Alternate Stack Root Ports, that provide alternate paths to the root. If the current Stack Root loses connectivity to the root, the switch whose Alternate Stack Root Port represents the next best path to the root issues one or more proposal messages to the other members of the switch stack. These other members respond with an Acknowledgement, and the former Stack Root transitions its port to the blocking state. Once the proposing switch receives an Acknowledgment from all other active members of the switch stack, it transitions its Alternate Stack Root Port to the forwarding state so that network messages can be forwarded to and from switch stack.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
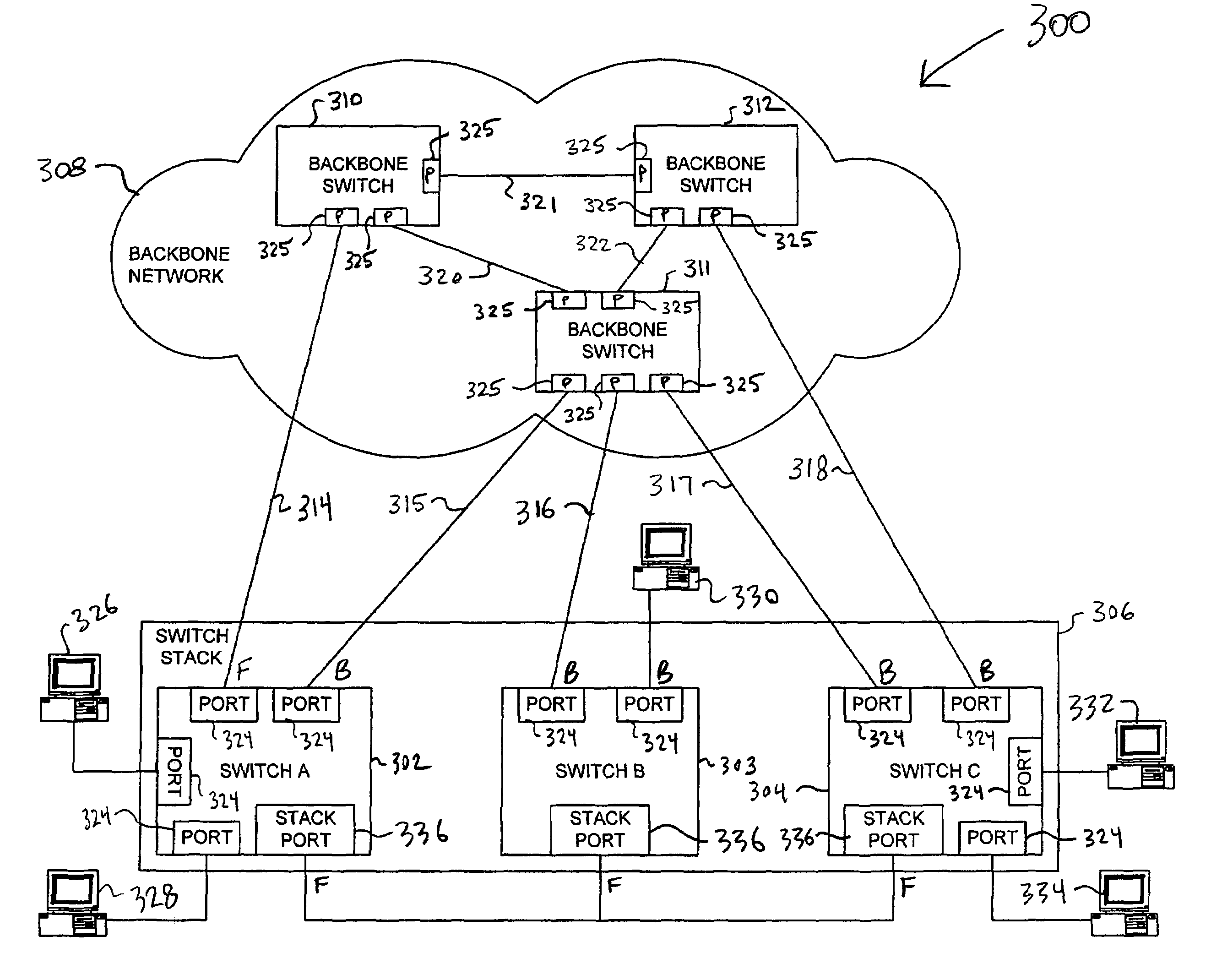
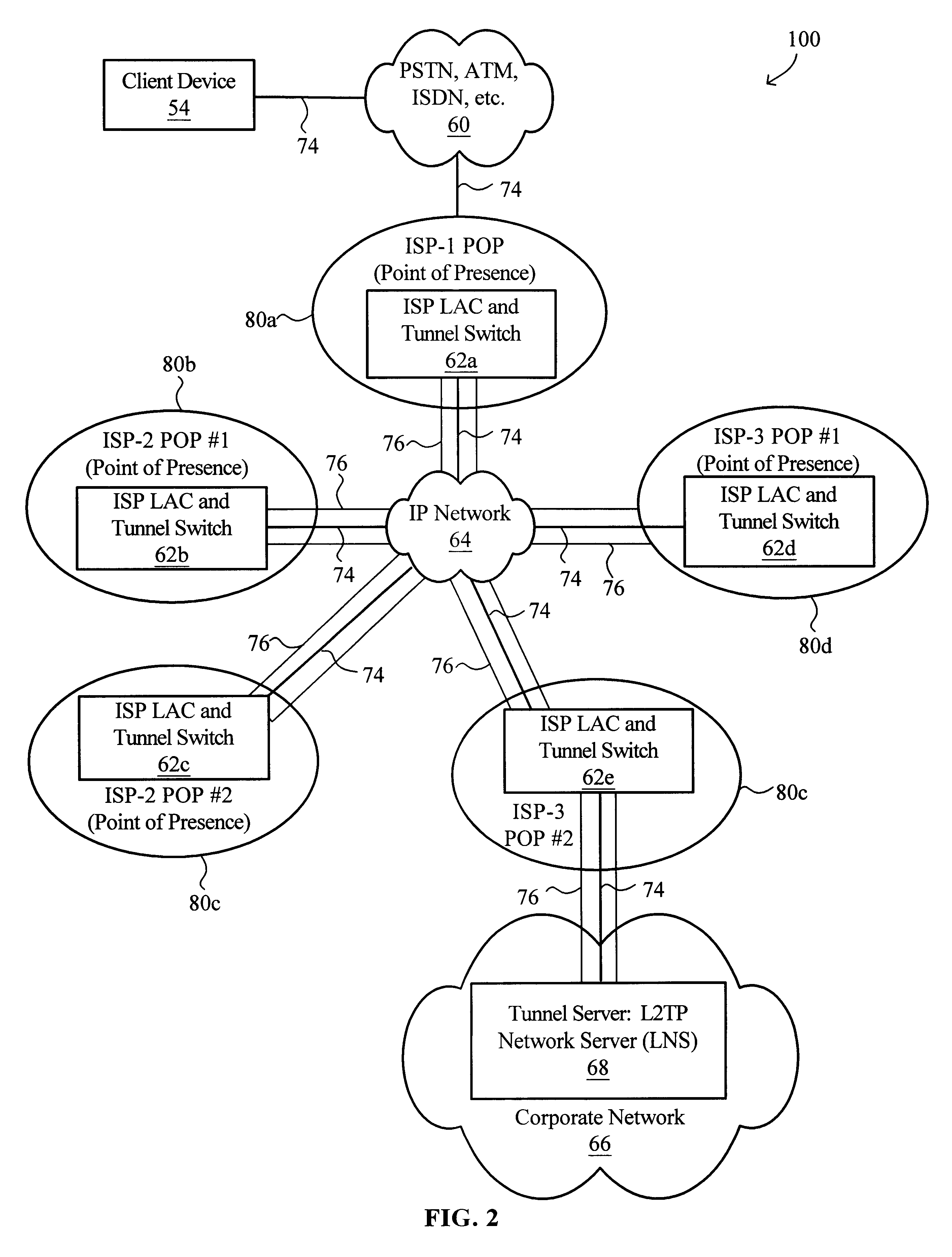
Virtual L2TP/VPN tunnel network and spanning tree-based method for discovery of L2TP/VPN tunnels and other layer-2 services
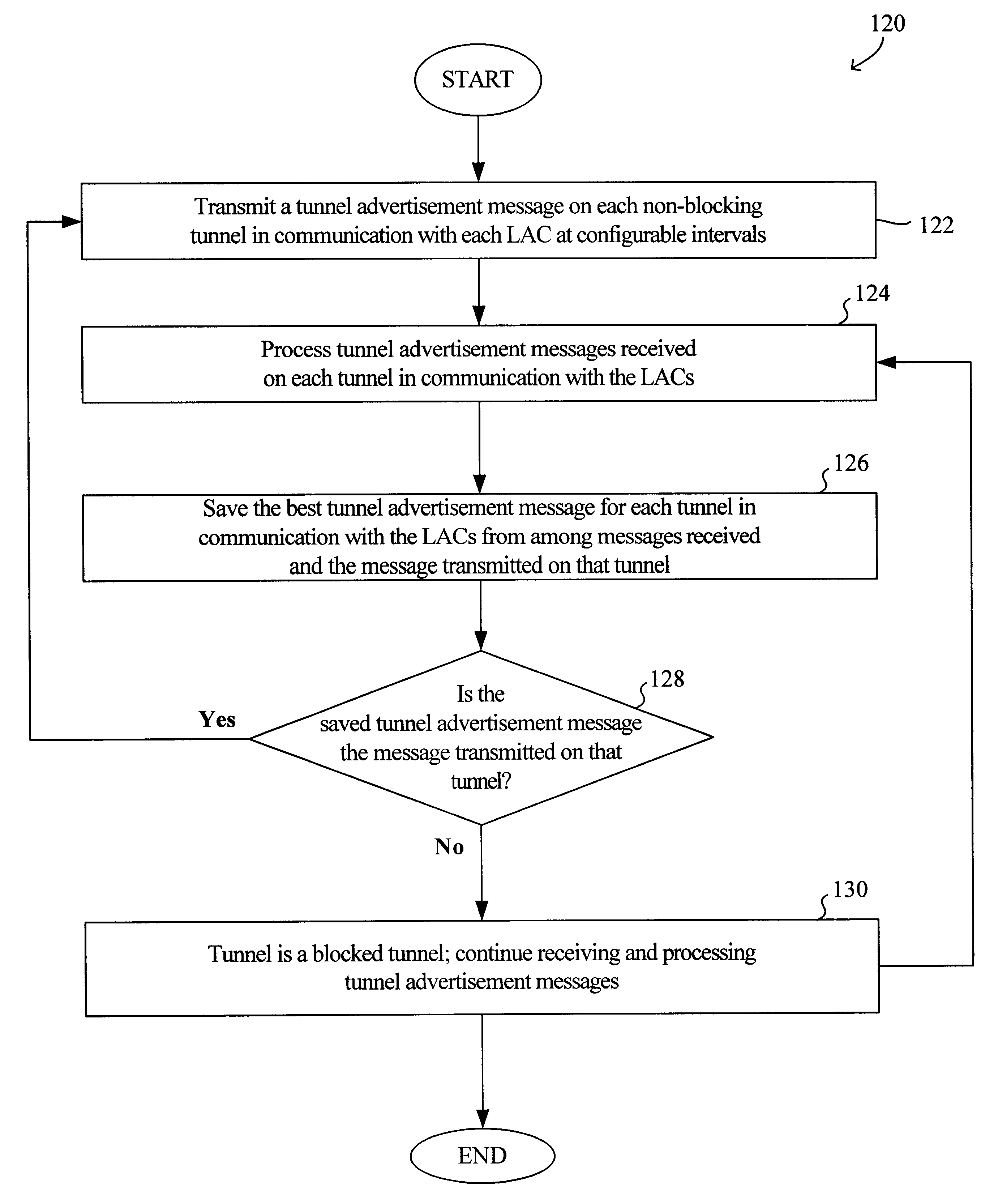
A virtual L2TP / VPN tunnel network as well as a system and method for automatic discovery of VPN tunnels, such as L2TP tunnels, and other layer-2 services using a method such as one based on the spanning tree protocol are disclosed. The method for automatic discovery of layer-2 services across a network of layer-2 devices generally comprises transmitting an advertisement message on each tunnel of each layer-2 device, the advertisement message containing information for generating a spanning tree based on spanning tree algorithm, receiving advertisement message on the tunnels of each layer-2 device, and processing the received advertisement messages to generate a spanning tree topology of the network of layer-2 devices whereby each layer-2 device in the network automatically discovers layer-2 services of other layer-2 devices on the network. The transmitting is preferably repeated at predetermined configurable intervals.
Owner:GC PIVOTAL LLC
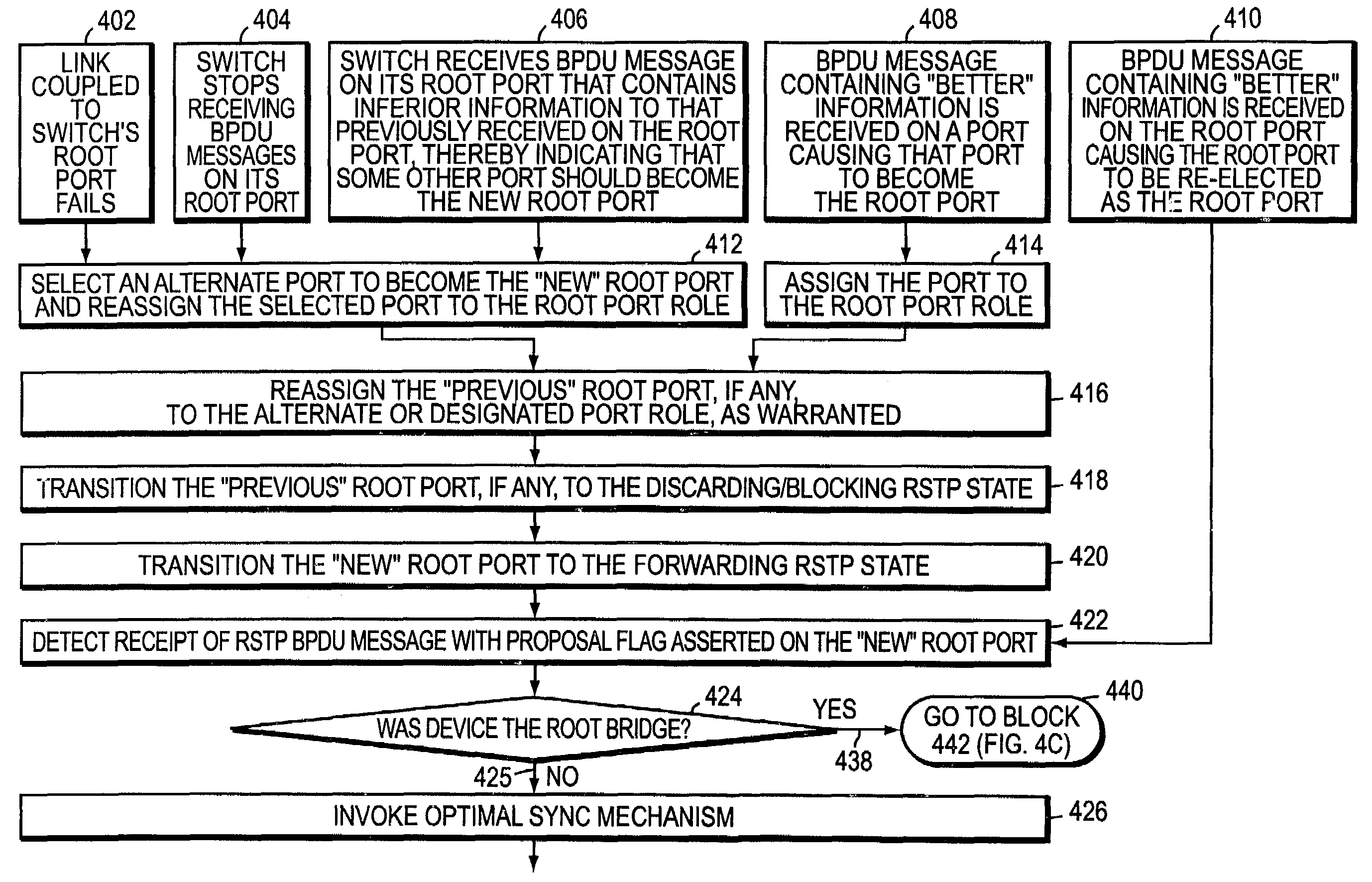
Optimal sync for rapid spanning tree protocol
InactiveUS7177946B1Digital computer detailsData switching by path configurationComputer networkComputer science
An optimization to the rapid spanning tree protocol (RSTP) is presented. An intermediate network device configured in accordance with the present invention preferably includes a plurality of ports for receiving and forwarding messages and a spanning tree protocol (STP) engine which is coupled to the ports. If the device receives a bridge protocol data unit (BPDU) message from a designated port of a neighboring intermediate network device and the BPDU represents a proposal by the neighboring device to rapidly transition its port to the forwarding state, the device first determines whether or not it is the root the bridged network. If the device is not the root, and the BPDU message was received on the device's existing root port or on its newly selected root port, the device preferably invokes an “optimal sync” mechanism. Specifically, the device transitions only its alternate root port(s) and the previous root port, if any, to the blocking state, while leaving all of its designated ports, if any, in the forwarding state. The device then returns an agreement BPDU message to the neighboring device.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
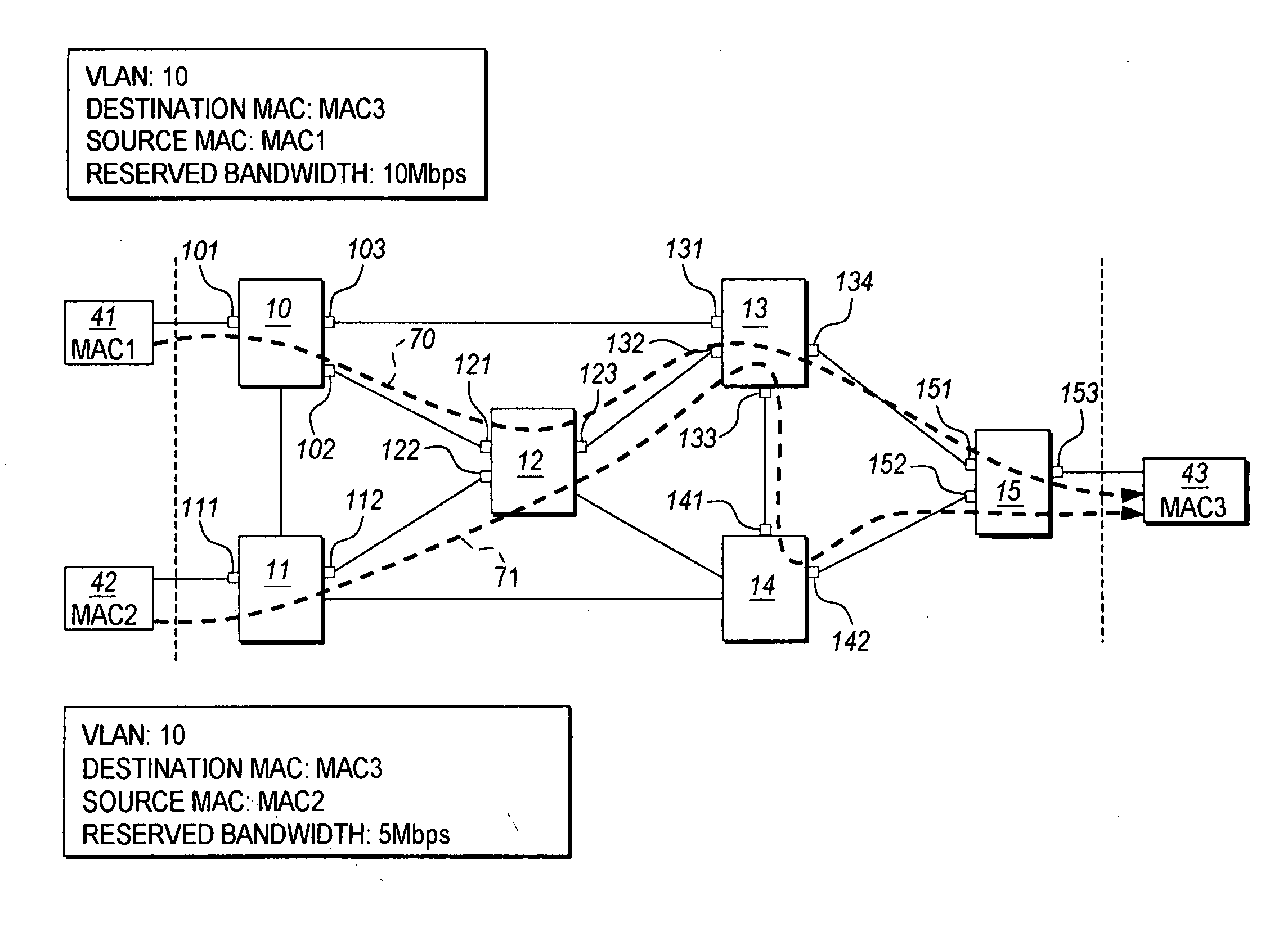
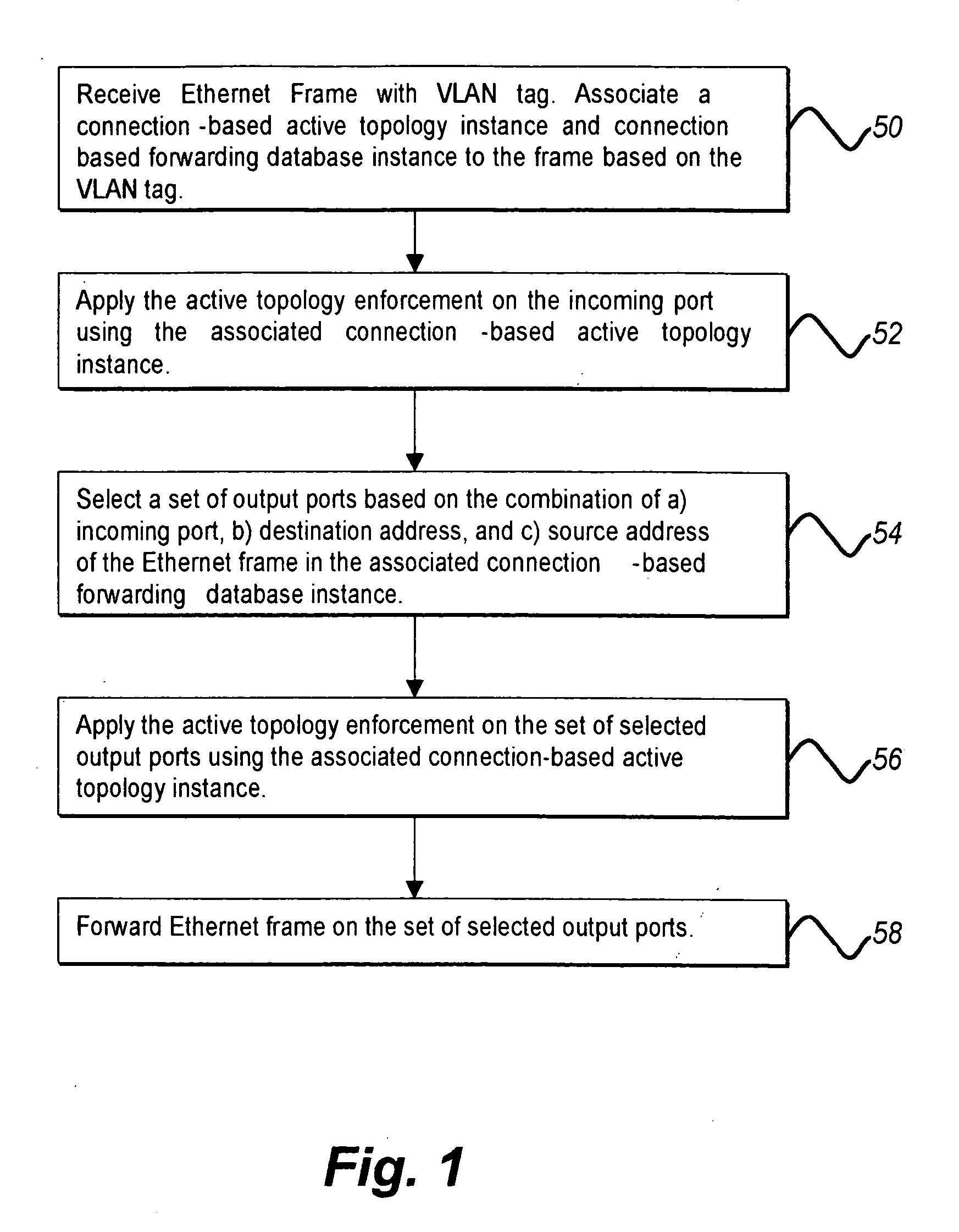
Ethernet connection-based forwarding process
InactiveUS20070177597A1Eliminate requirementsData switching by path configurationSpanning Tree ProtocolMAC address
The Ethernet connection-based forwarding process is a system and method of establishing a pre-determined transmission path before communicating frames of data over an Ethernet connection. The present invention supports reserving resources on each of the Ethernet switches which may be on a desired communications path while setting up the connection based forwarding tables. The present invention can differentiate two connections having the same destination MAC address but different source MAC addresses so that streams of frame data from the different sources can be merged and separated en-route to the destination, thus making it possible to reserve proper resources on the switches for a connection thereby satisfying QoS requirements for the connection. A provisioned connection also eliminates the requirement of a loop free active topology. The present invention also eliminates the requirement of spanning tree protocols so that all bridge ports may be accessed for forwarding of Ethernet frame data.
Owner:JU YU
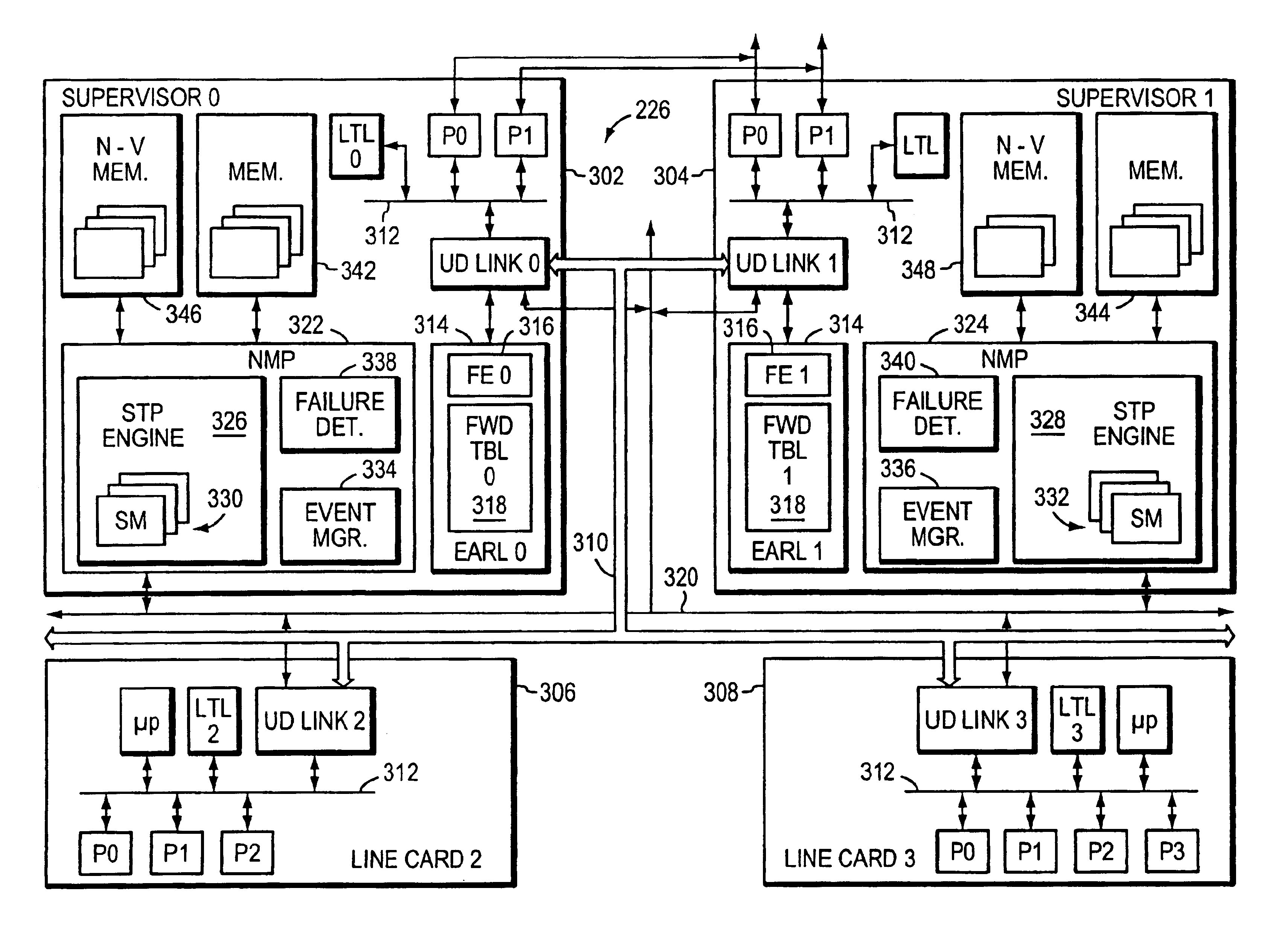
Restartable spanning tree for high availability network systems
InactiveUS6898189B1Avoiding significant network disruptionQuick fixError preventionTransmission systemsHigh availabilitySupervisor review
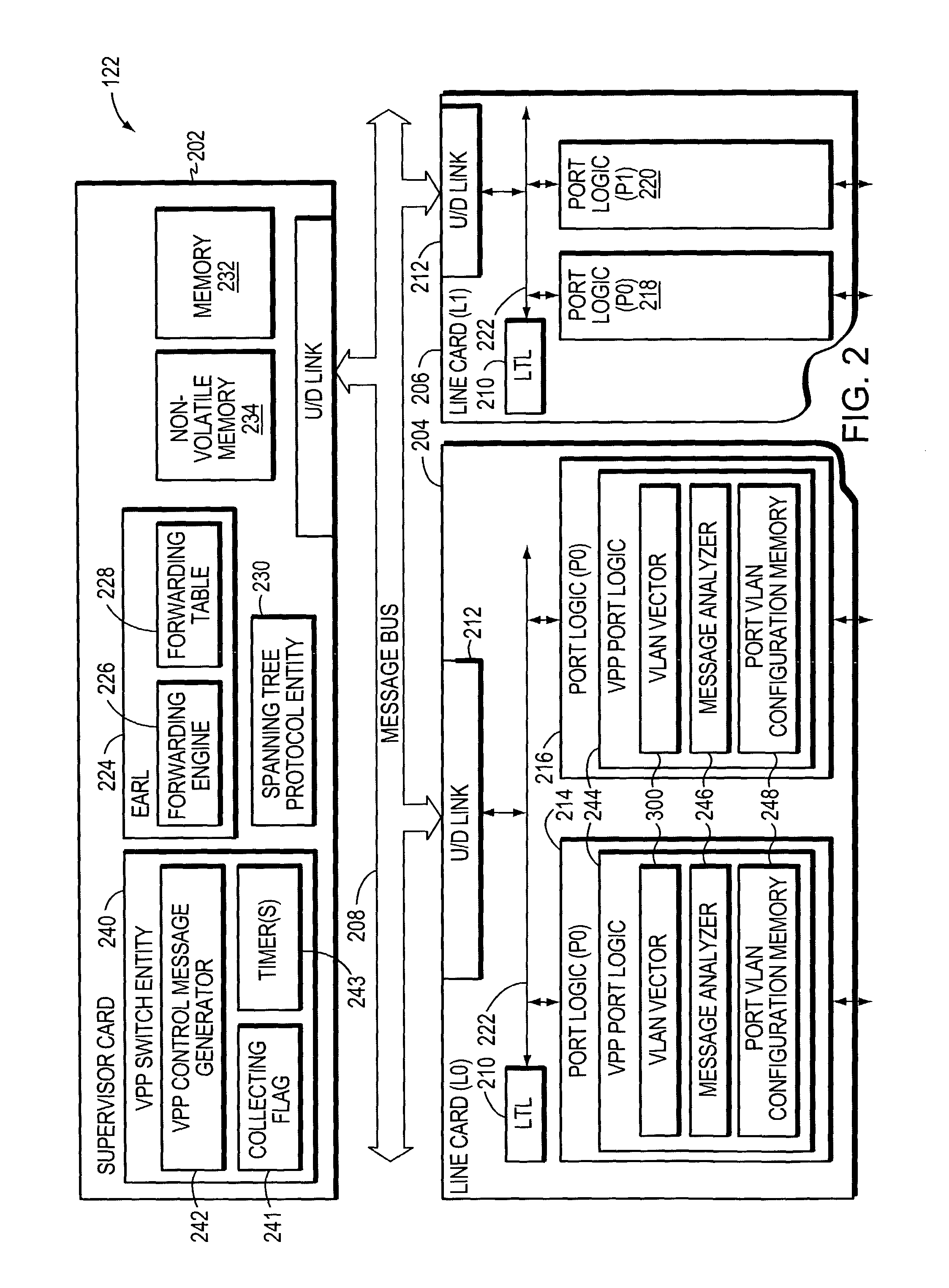
A method and apparatus for continuing the operation of a spanning tree protocol at a network device despite crashes or failures at that device. A supervisor card contained in the network device is designated an active supervisor, while all other supervisor cards are designated standby supervisors. The active supervisor runs the spanning tree protocol, and informs the standby supervisors of the states of ports, but not of the identity of the root or designated bridges. When a crash or failure occurs at the active supervisor, one of the standby supervisors is immediately designated to be the new active supervisor. The newly active supervisor reviews the port state, and queries the line cards to determine whether that port state information is still valid. The newly active supervisor adopts the valid port state information, leaving those ports in their current spanning tree port state.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
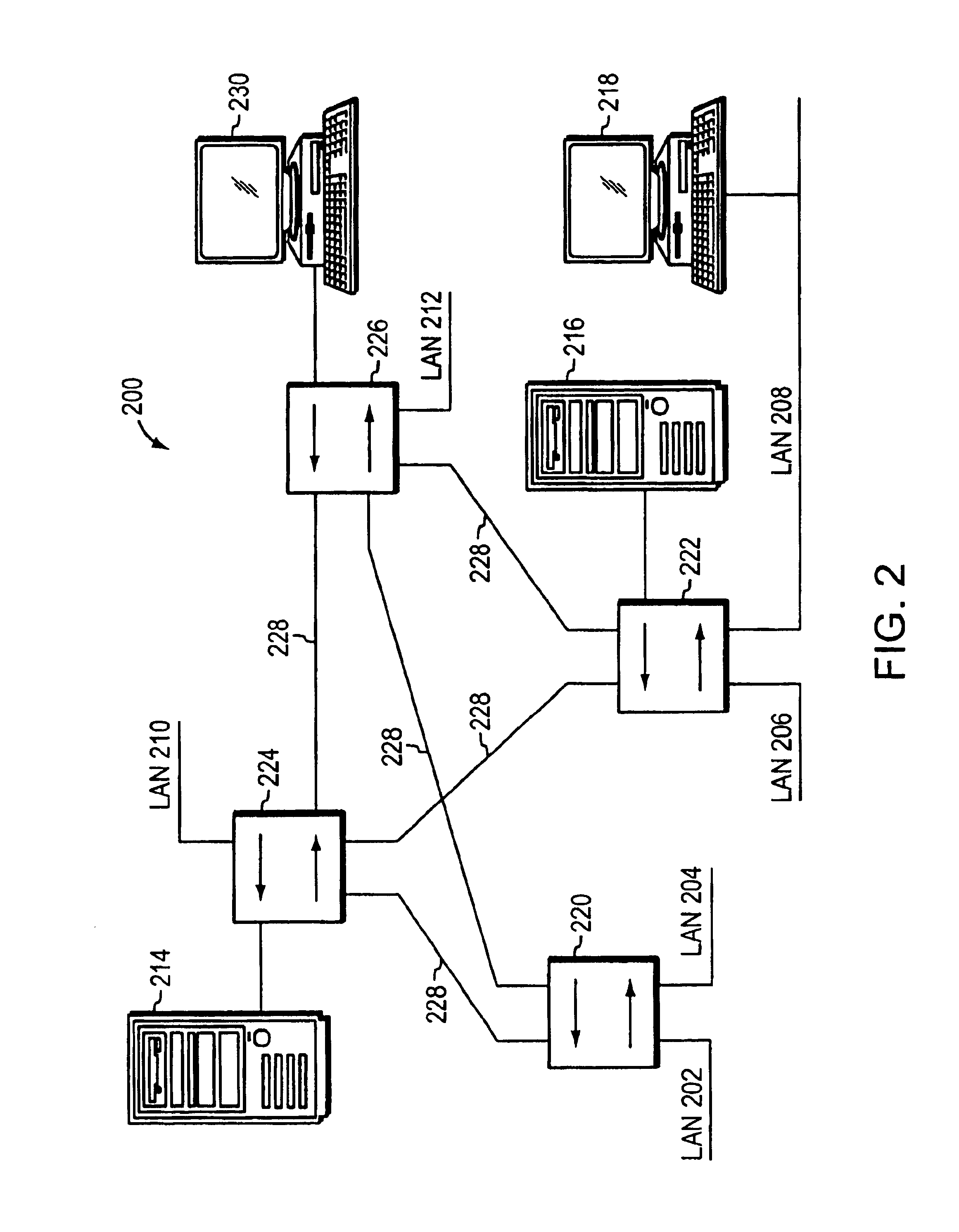
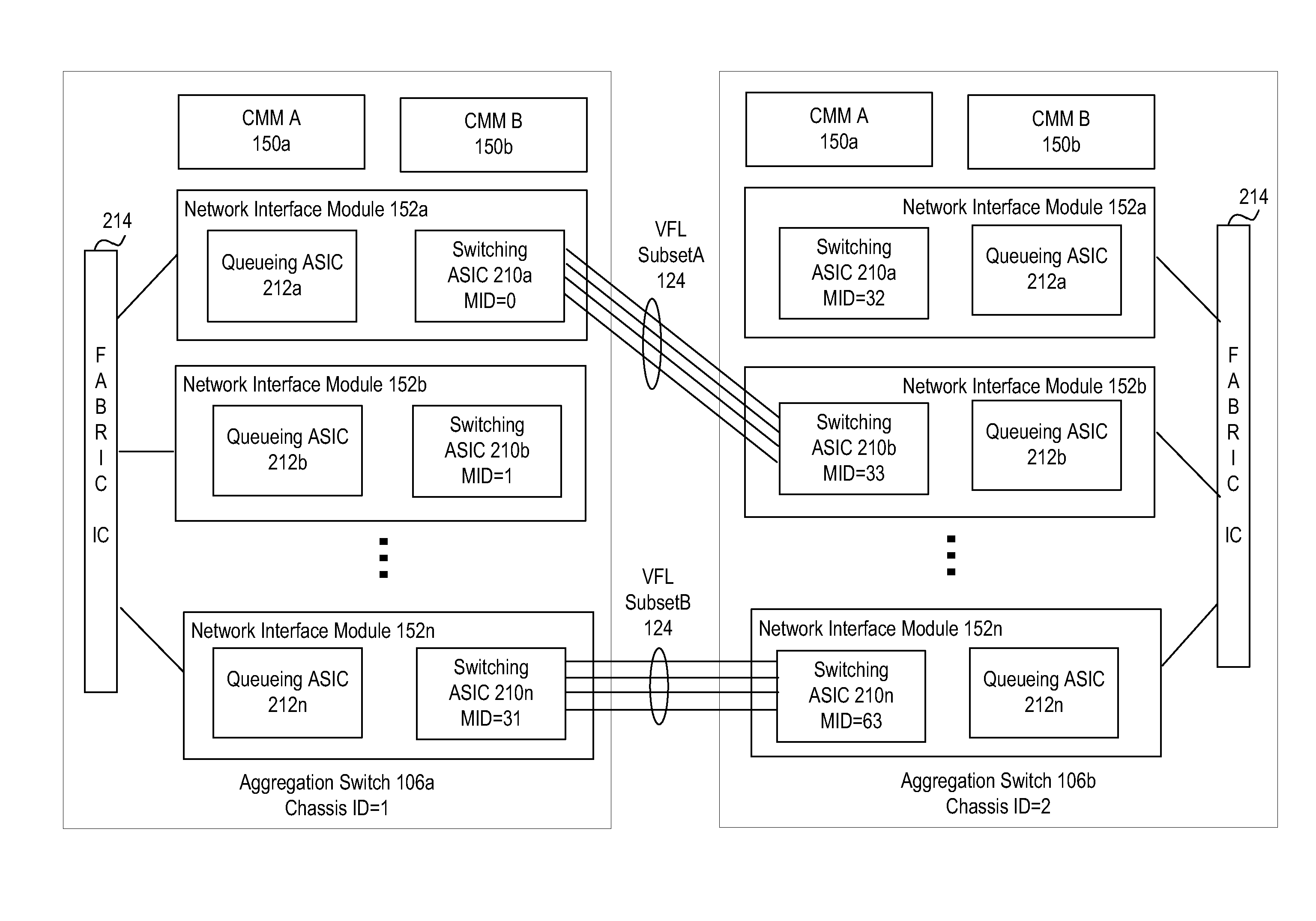
System and method for virtual fabric link failure recovery
Aggregation switches are connected to an edge node by a multi-chassis link aggregation group and a virtual fiber link provides a connection for exchange of information between the aggregation switches regarding MAC addressing to synchronize MAC address tables across the aggregation switches. When failure of the virtual fiber link is detected, the multi-chassis link aggregation group is reconfigured into two or more link aggregates with each link aggregate connecting the edge node to one of the aggregation switches. A spanning tree protocol is initiated over the link aggregates to prevent loops in the network. MAC address tables are flushed and relearned with the two or more link aggregates.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
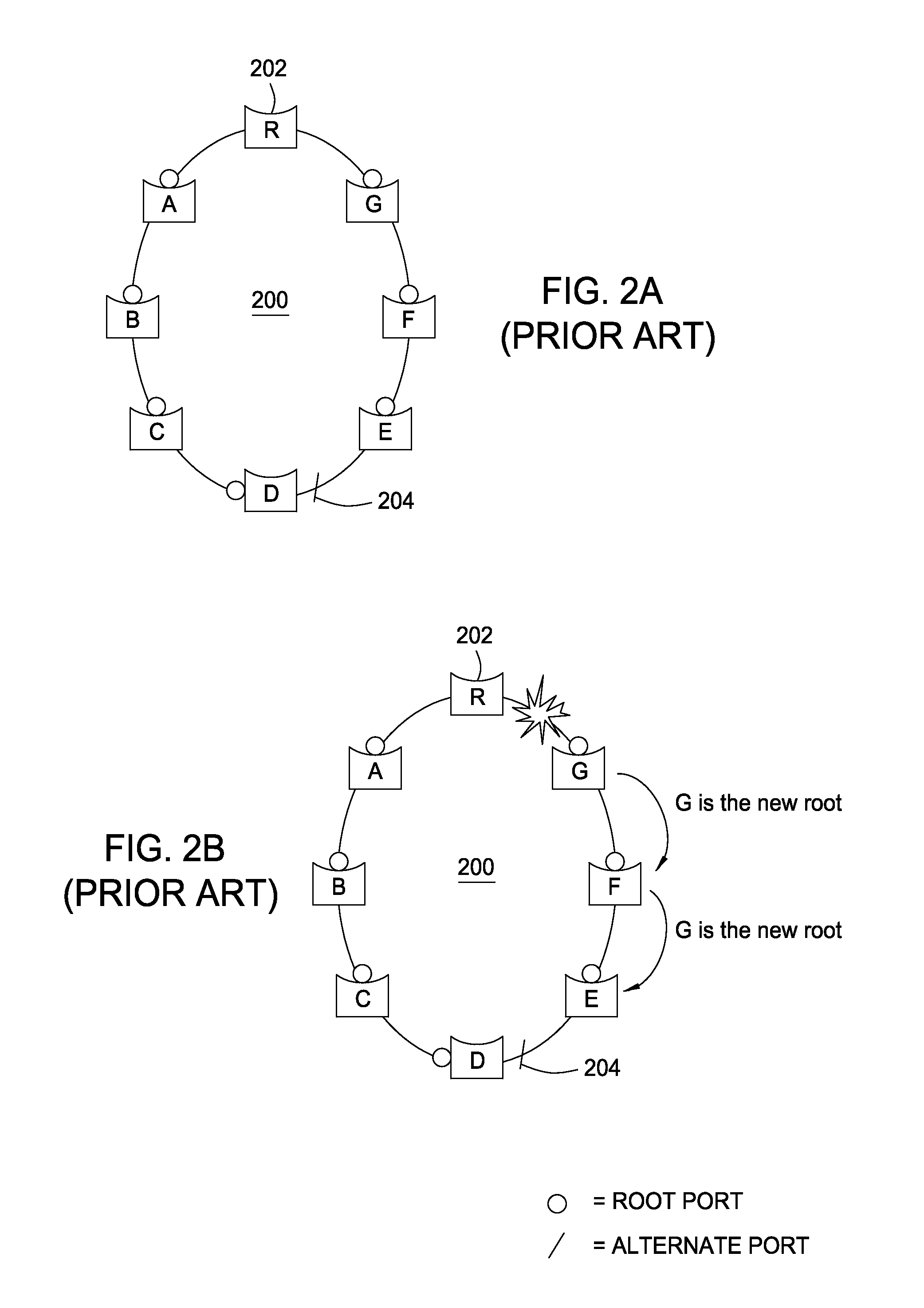
Alternate spanning tree for faster indirect link failure recovery
ActiveUS20080025203A1Restore connectivityError preventionTransmission systemsRecovery methodComputer network
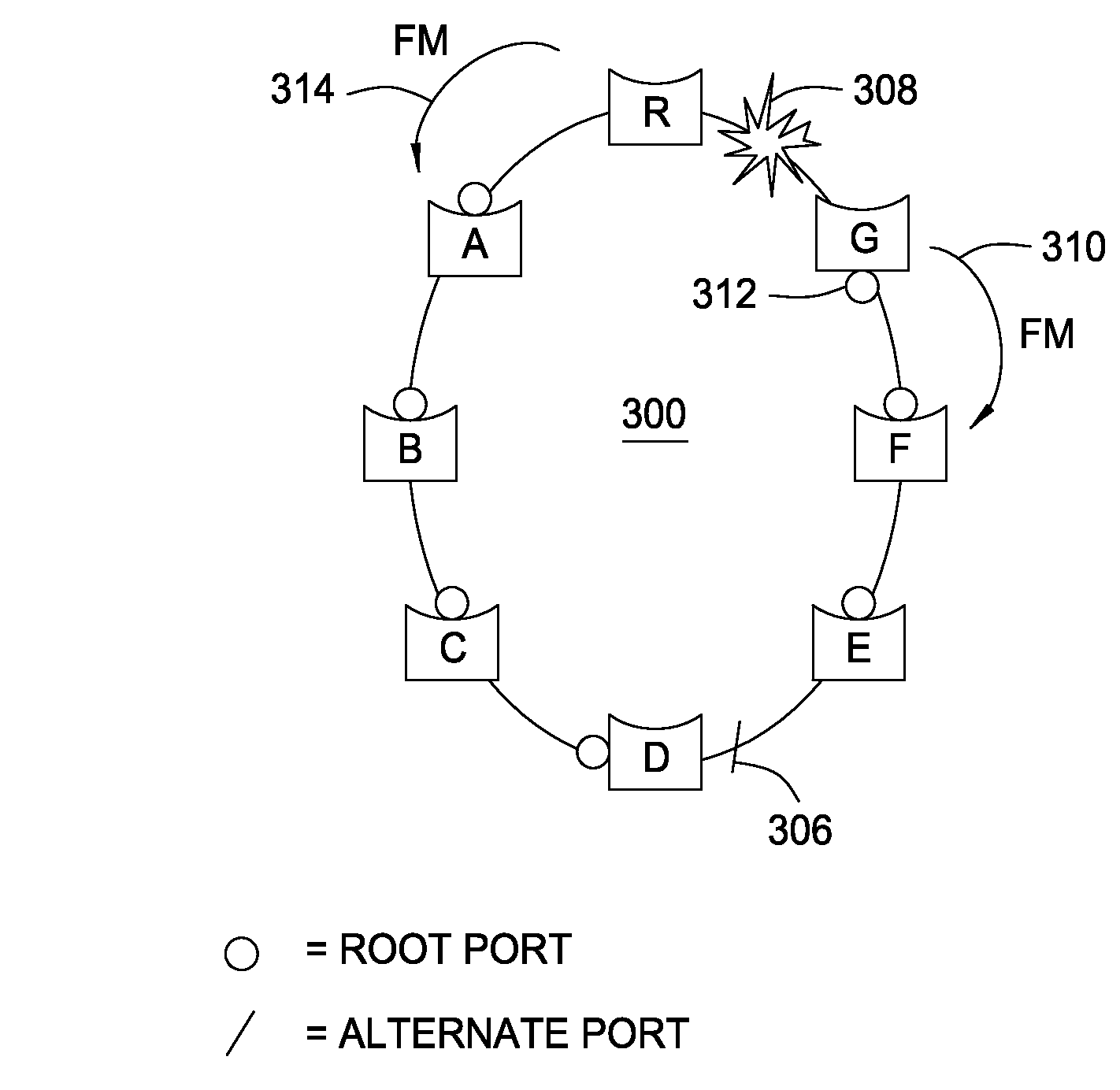
Methods and apparatus that form the basis of an alternate spanning tree protocol that may be used, for example, to identify rings within a properly converged network configured by the spanning tree protocol (STP) or rapid spanning tree protocol (RSTP) are provided. With the knowledge of these rings, the alternate spanning tree has predetermined an alternate port that can restore connectivity without further computation in case of a link failure, thereby providing for extremely fast reconvergence.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
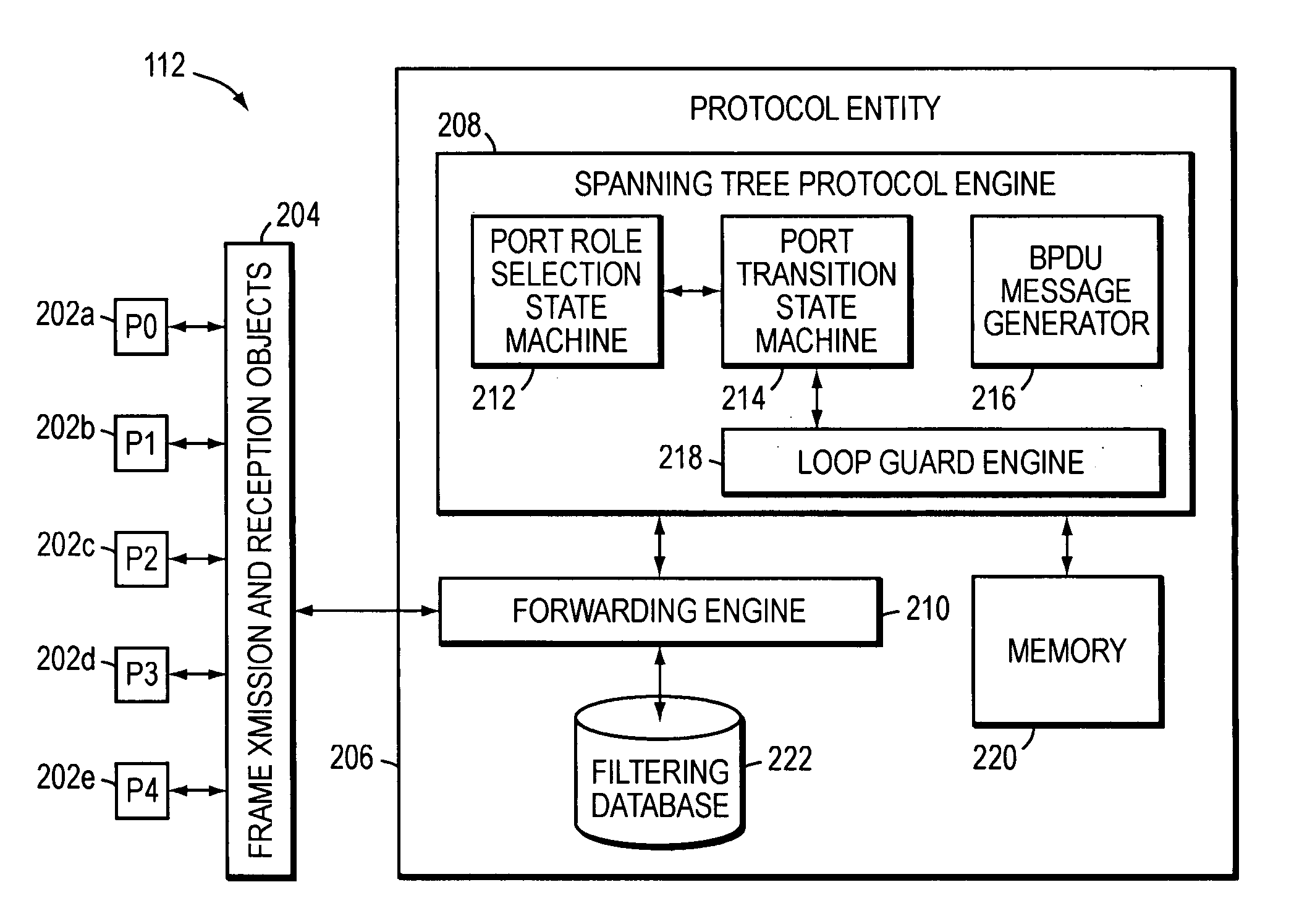
Spanning tree loop guard
ActiveUS7061875B1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationComputer networkEngineering
A system and method prevents the formation of loops that are not detected by the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP). An intermediate network device preferably includes a plurality of ports for receiving and forwarding network messages and a STP engine in communicating relationship with the ports. The STP engine transitions the ports among a plurality of spanning tree port states, including a discarding state, a learning state and a forwarding state. The device further includes a loop guard engine that is in communicating relationship with the STP engine and the ports. The loop guard engine monitors the receipt of configuration bridge protocol data unit (BPDU) messages by the ports. If a given port stops receiving BPDU messages, the loop guard engine prevents the STP engine from transitioning the given port to the forwarding state. Instead, the loop guard engine preferably causes the port to transition to a new state in which networks messages are explicitly blocked from being forwarded or received. If the given port subsequently receives a BPDU message, the loop guard engine releases the port from the new state, thereby allowing it to transition to some other spanning tree port state.
Owner:CISCO SYSTEMS INC
Blocked redundant link-aware spanning tree protocol enhancement
ActiveUS20070242602A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityComputer network
An exemplary embodiment provides for a method for use in a network device of a plurality of network devices configured to implement a link management protocol for blocking ports corresponding to redundant links between individual network devices of the plurality of network devices. The method is used for preventing delivery of selected traffic to and from a port of the network device. Preventing, at the network device, delivery of the selected traffic to the port includes determining that a port corresponding to a remote device is to be placed in a blocked state and transmitting a port blocking notification message to the remote device, wherein the port block notification message is operative to cause the remote device to stop transmitting the selected traffic to the network device on the port. Preventing, at the network device, delivery of the selected traffic from the port includes receiving a bridge protocol data unit (BPDU) and determining if the BPDU is a port block notification message. In turn, transmission of the selected traffic is stopped from the port of the network device that received the BPDU, if the BPDU is the port block notification message.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
High-Availability Networking with Intelligent Failover
InactiveUS20080215910A1Improve usabilityPrevent misidentificationData switching networksRedundant hardware error correctionFailoverOSI model
Methods and systems for maintaining high-availability in a computer network using intelligent failover are presented. In a network switch running an OSI model layer-2 or higher protocol on its external links, the protocol state information is monitored to determine failover status of the link to avoid identifying external link failures due to link flapping. One such protocol is the spanning tree protocol. Additionally, flexibility in failover is provided using configurable triggers to define external failure events. The triggers initiate a link drop of one or more internal links of the network switch in response to an external failure event. The link drops, in turn, initiate failover of an attached computing device to a redundant link through a network interface teaming / failover arrangement whereby the computing device switches to an alternative network interface accessing the network through a redundant path. Failover can be selective depending upon VLAN and trunking configurations.
Owner:AVAYA INC
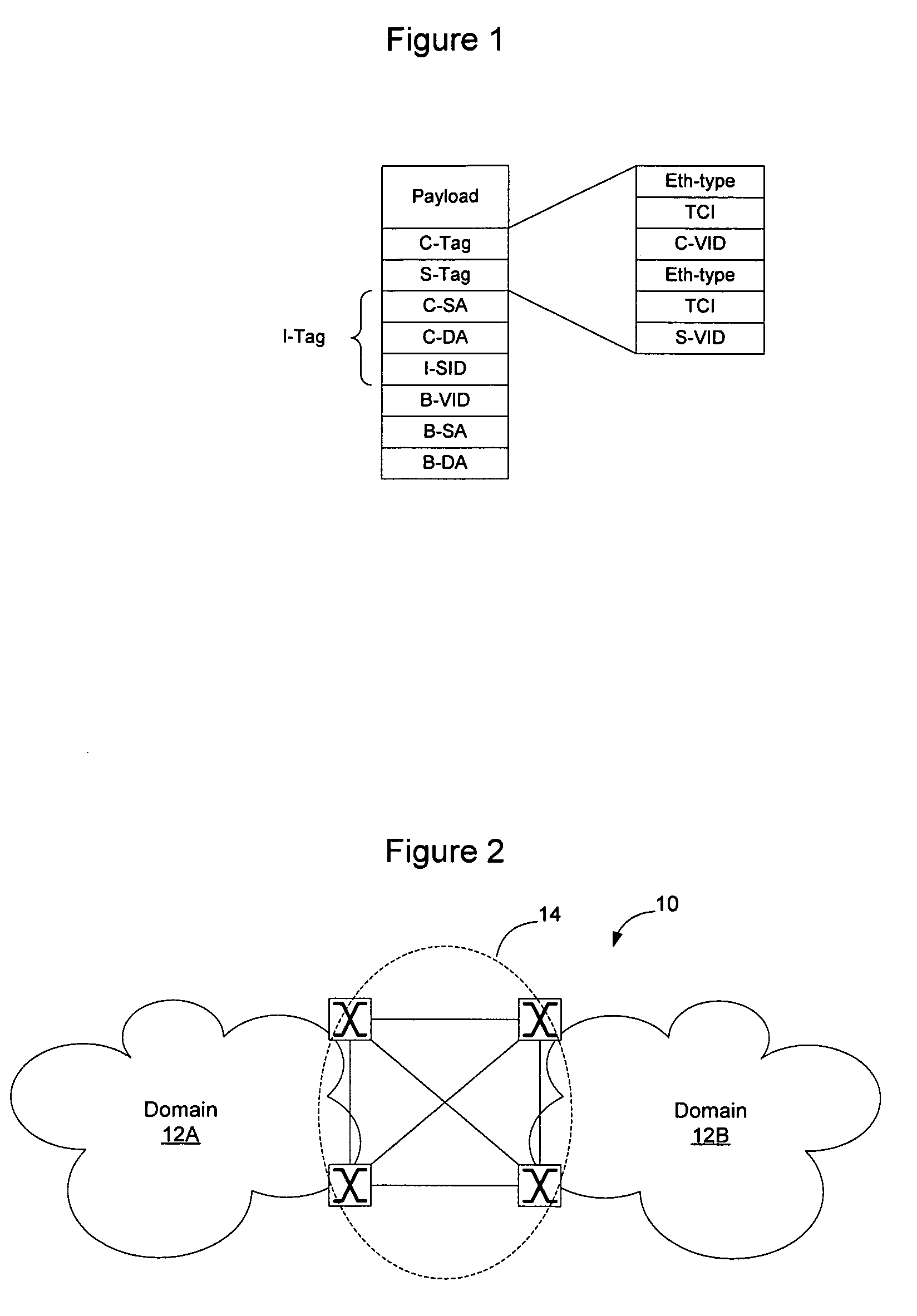
Method and apparatus for managing the interconnection between network domains
A control protocol is run in the interconnect region between network domains so that the interconnect region may be managed using a separate control plane. According to an embodiment of the invention, a spanning tree protocol is used to establish a separate spanning tree within the interconnect region. To avoid loop formation within the interconnect region, links interconnecting adjacent edge nodes that are part of the interconnect region and which belong to a given domain are allowed to pass control frames but not data frames. OAM may be used detect link failure of a link between adjacent nodes on a given domain.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Network failure recovery method with redundancy port
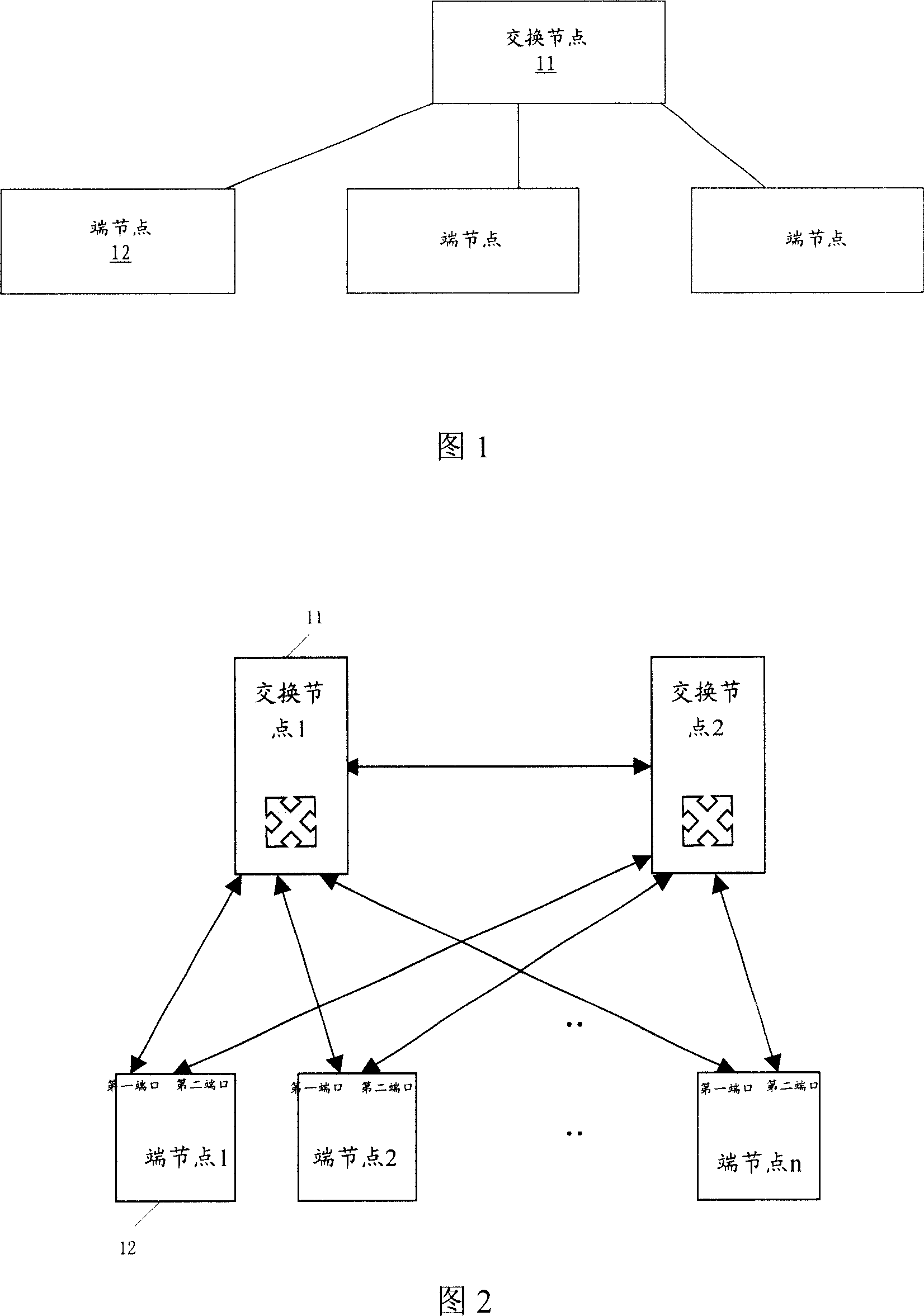
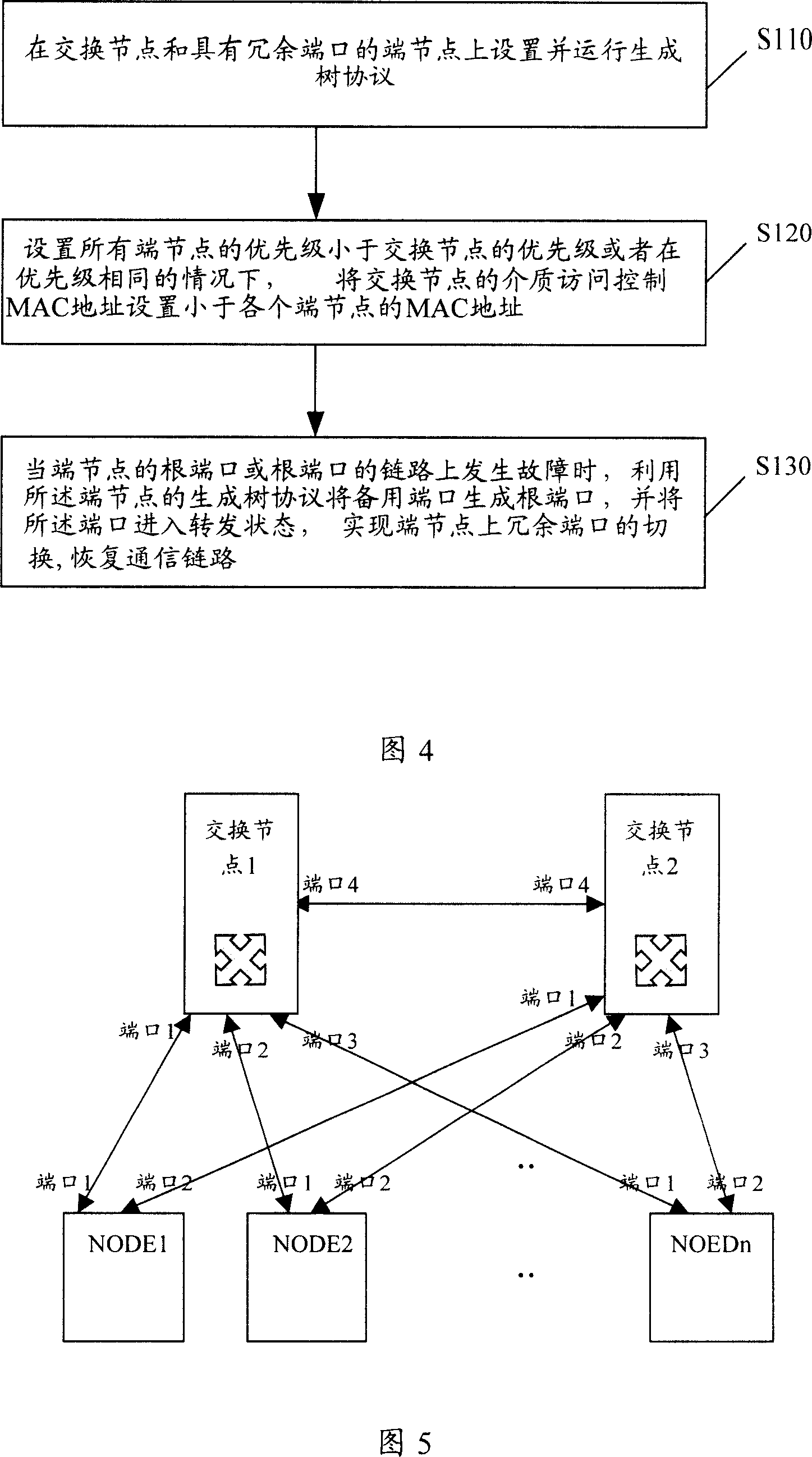
ActiveCN101001165AOvercoming paralyzing deficitsAvoid developmentData switching networksRecovery methodCommunications system
This invention relates to a method for resuming network fault with redundant ports including: 1, operating and setting tree-generation protocol on a switch bridge node and a terminal node with a redundant port, 2, setting that the PRI of all end nodes is smaller than that of the switch bridge node or setting the medium access MAC address of the switch bridge node is smaller than that of the end nodes, 3, when the root port of an end node is faulty, the redundant port is changed to a root port to enter into the transmitting state by computing the generation tree operated on said end node to realize switch of redundant ports on the end nodes, further more, this invention carries out software hierarchy fault detection between end node and switch bridge node by the communication system of the generation tree.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Method for discovering network topology and related equipment
ActiveCN101330405AAvoid the problem of incomplete topology discoveryAccurate discoveryStar/tree networksInformation processingTelecommunications
The invention discloses a network topology discovery method and related equipment thereof. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a spanning tree protocol (STP) result of a switch; processing the STP result of the switch to obtain the topological connection relationships of uplink ports of the switch; judging whether a switch uplink port with an undetermined topological connection relationship exists, and, if yes, obtaining the topological connection relationship of the switch uplink port with the undetermined topological connection relationship according to the MAC address forward table of the switch uplink port with the undetermined topological connection relationship. The invention further discloses a network information processing device with a network topology discovery function. In the method, the link layer topological connection relationship discovered by the STP result and the link layer topological connection relationship discovered by the MAC address forward table are closely related, so that the method can accurately discover and obtain various types of topological connection relationships of the switch uplink ports.
Owner:BEIJING BOCO COMM TECH +1
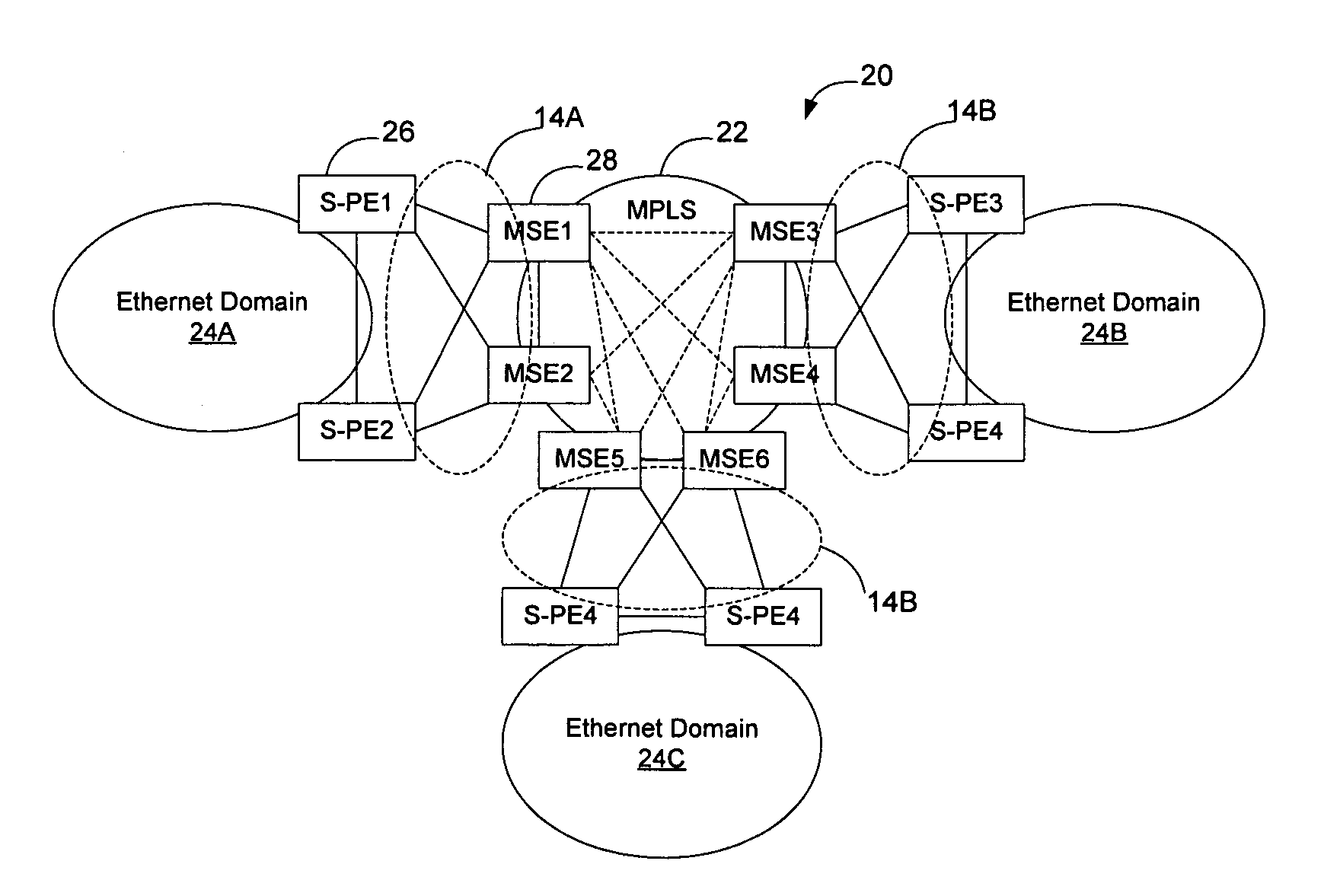
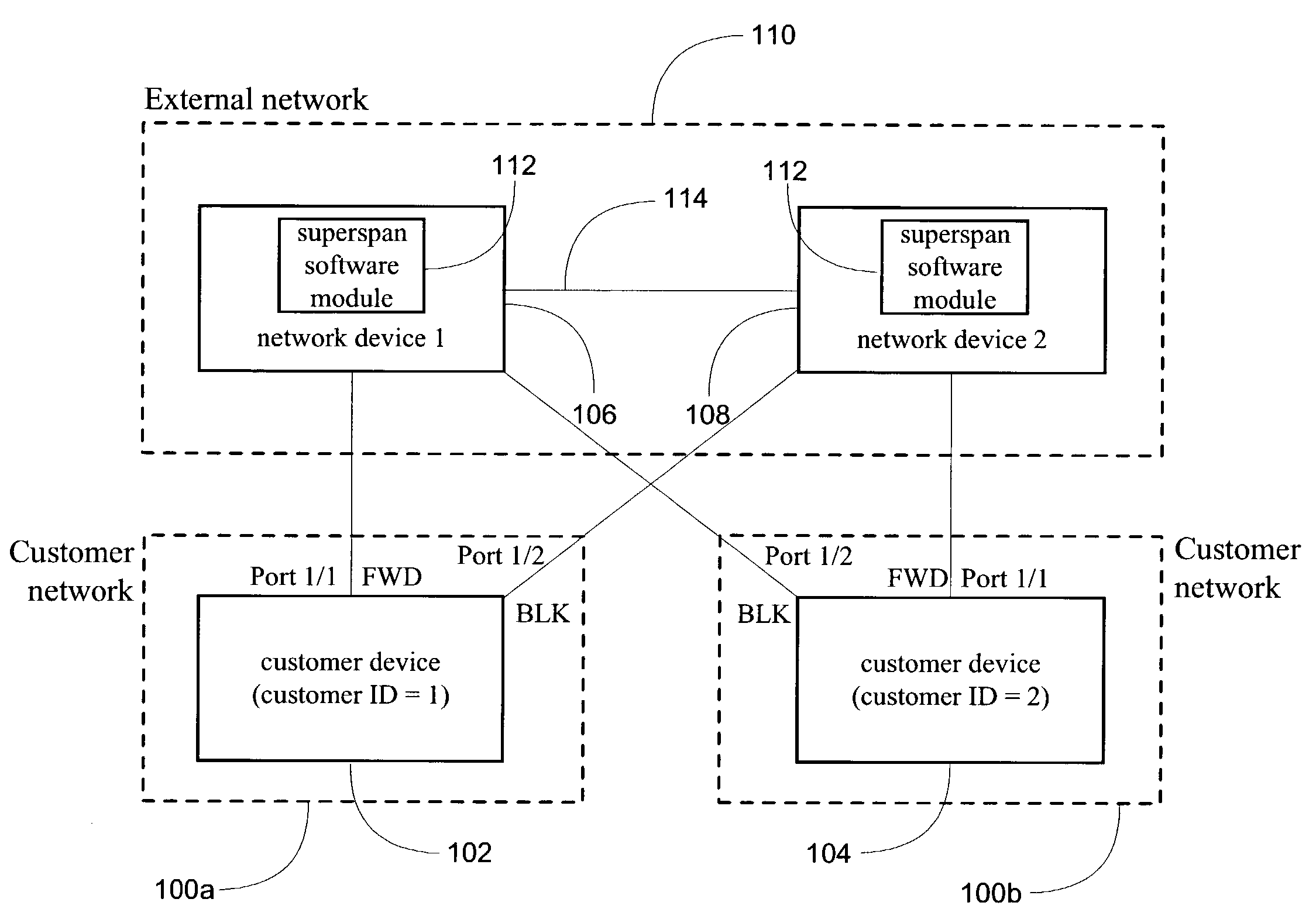
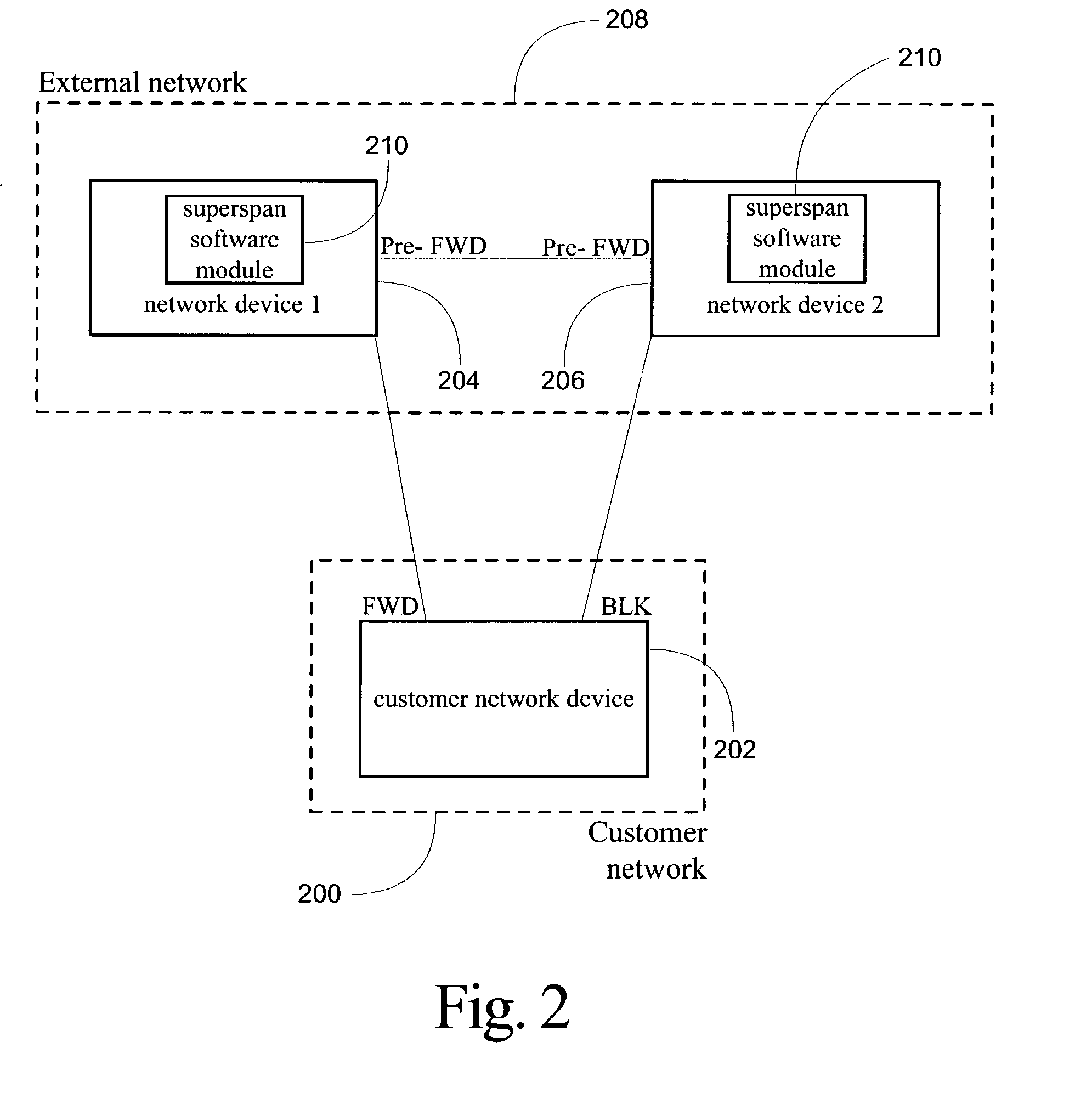
System and method for implementation of layer 2 redundancy protocols across multiple networks
ActiveUS20090274153A1Data switching by path configurationNetwork connectionsComputer networkUnique identifier
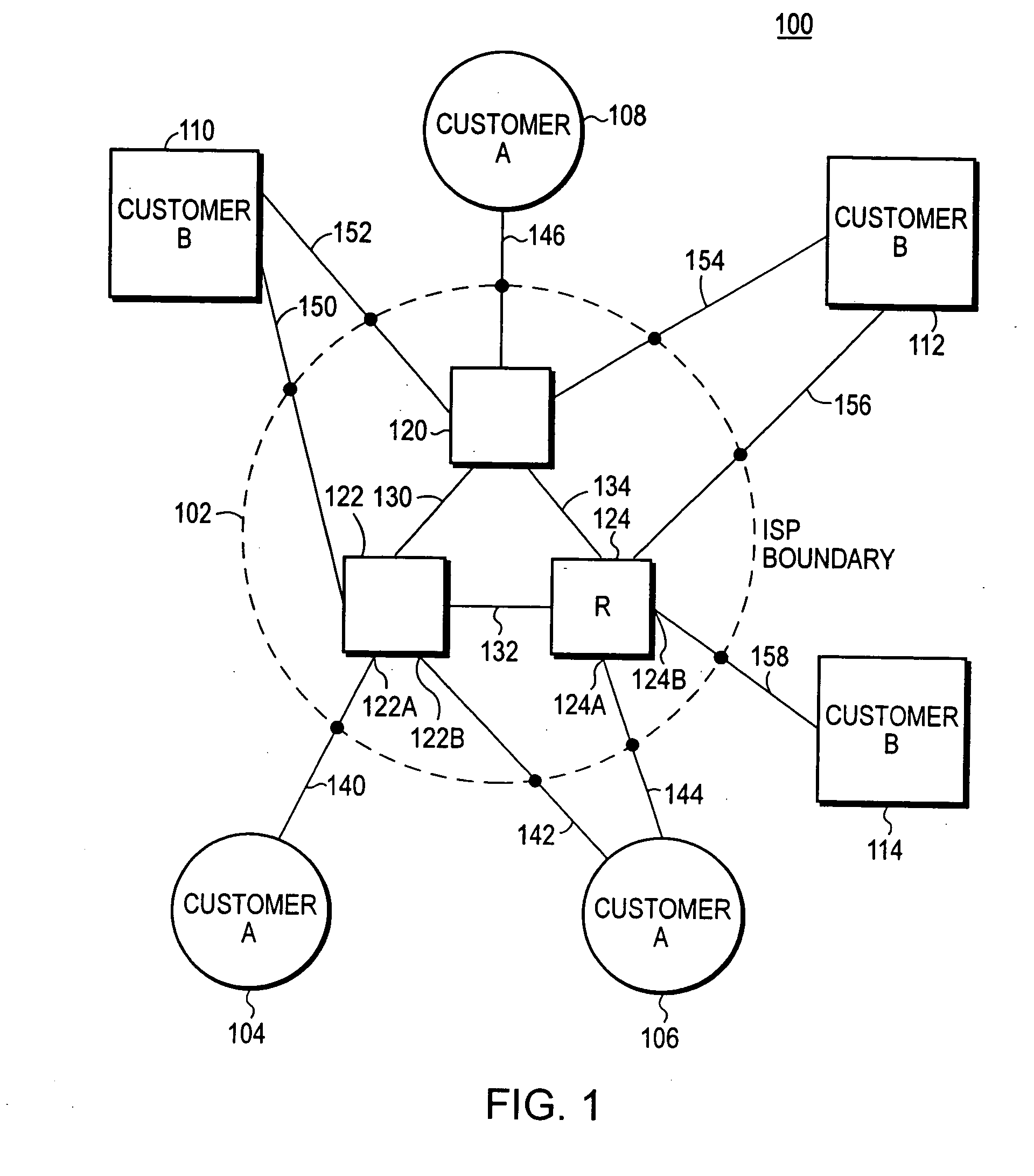
The system, method, and article of manufacture of the present invention allows multiple customers connected to a common external network to each implement a layer 2 redundancy protocol, such as the spanning tree protocol, in order to prevent layer 2 loops. Accordingly, a method is presented for providing an independent loop free layer 2 topology between a external network and a customer network comprising tagging control packets originating on the customer network with a unique identifier and tunneling the control packets received from the customer network between a plurality of boundary interface devices at the external network such that the control packets are routed back to the customer network based on the presence of the unique identifier in the control packet. The layer 2 redundancy protocol on the customer network converges based at least in part on the presence of control packets appearing on more than one port on the customer network.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
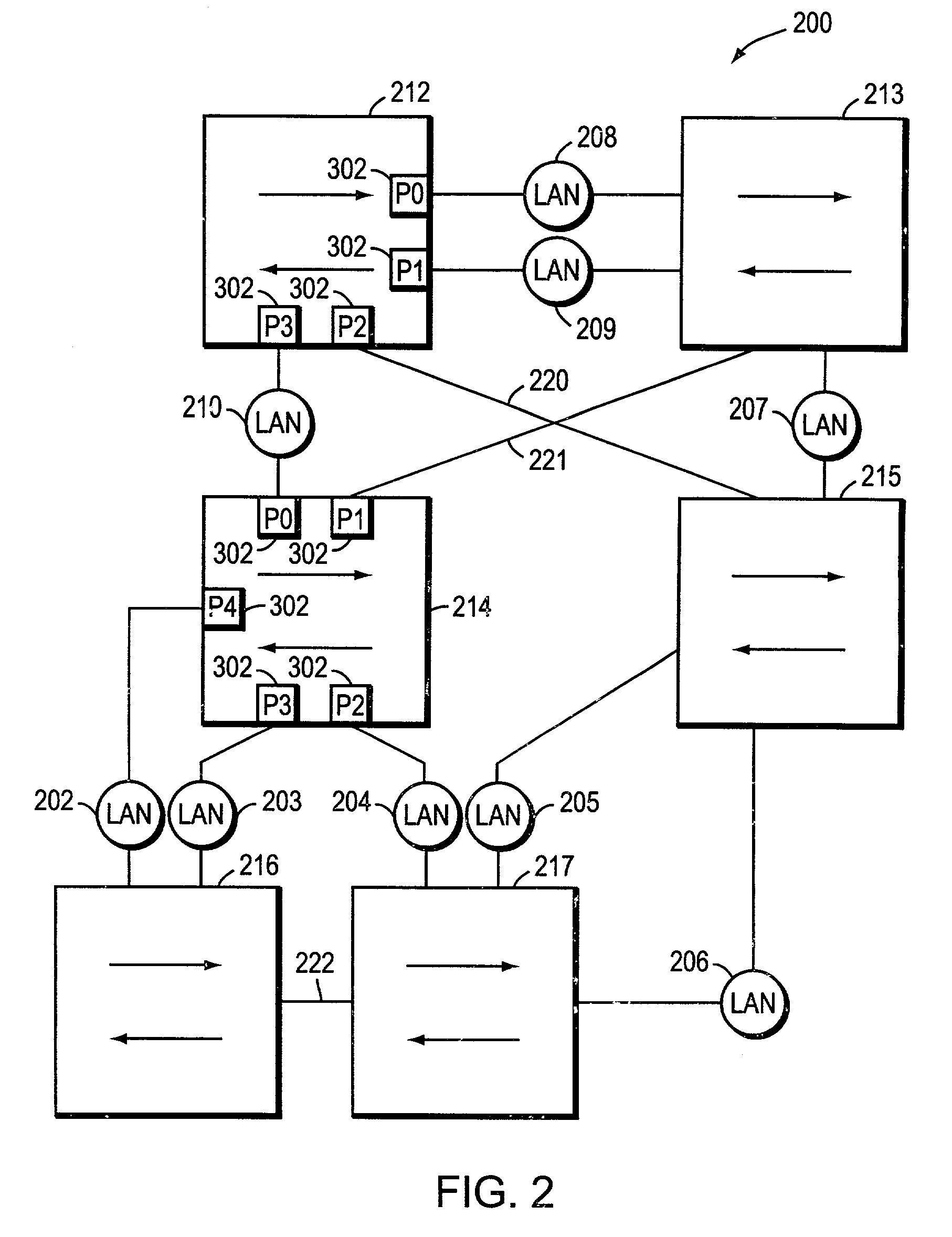
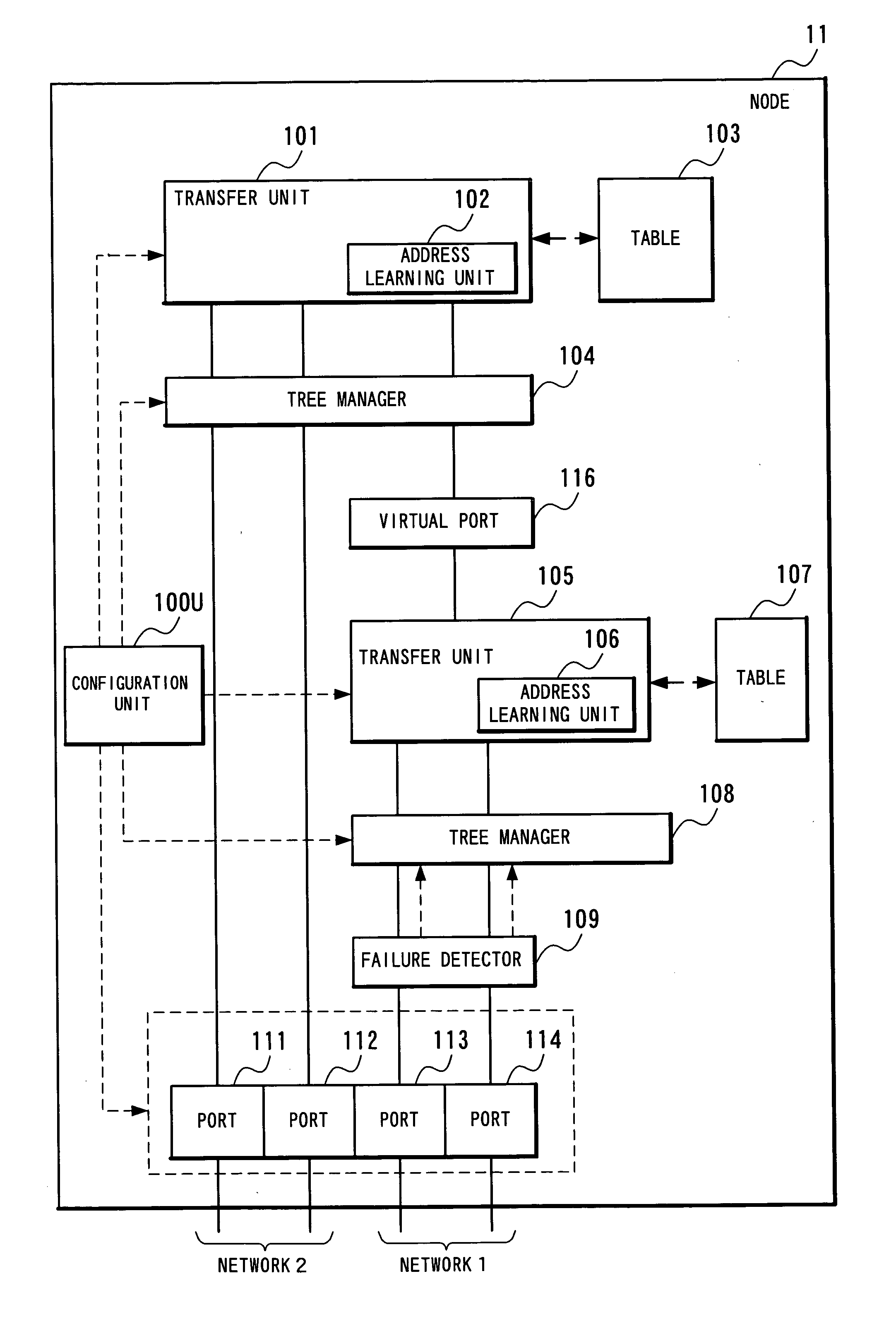
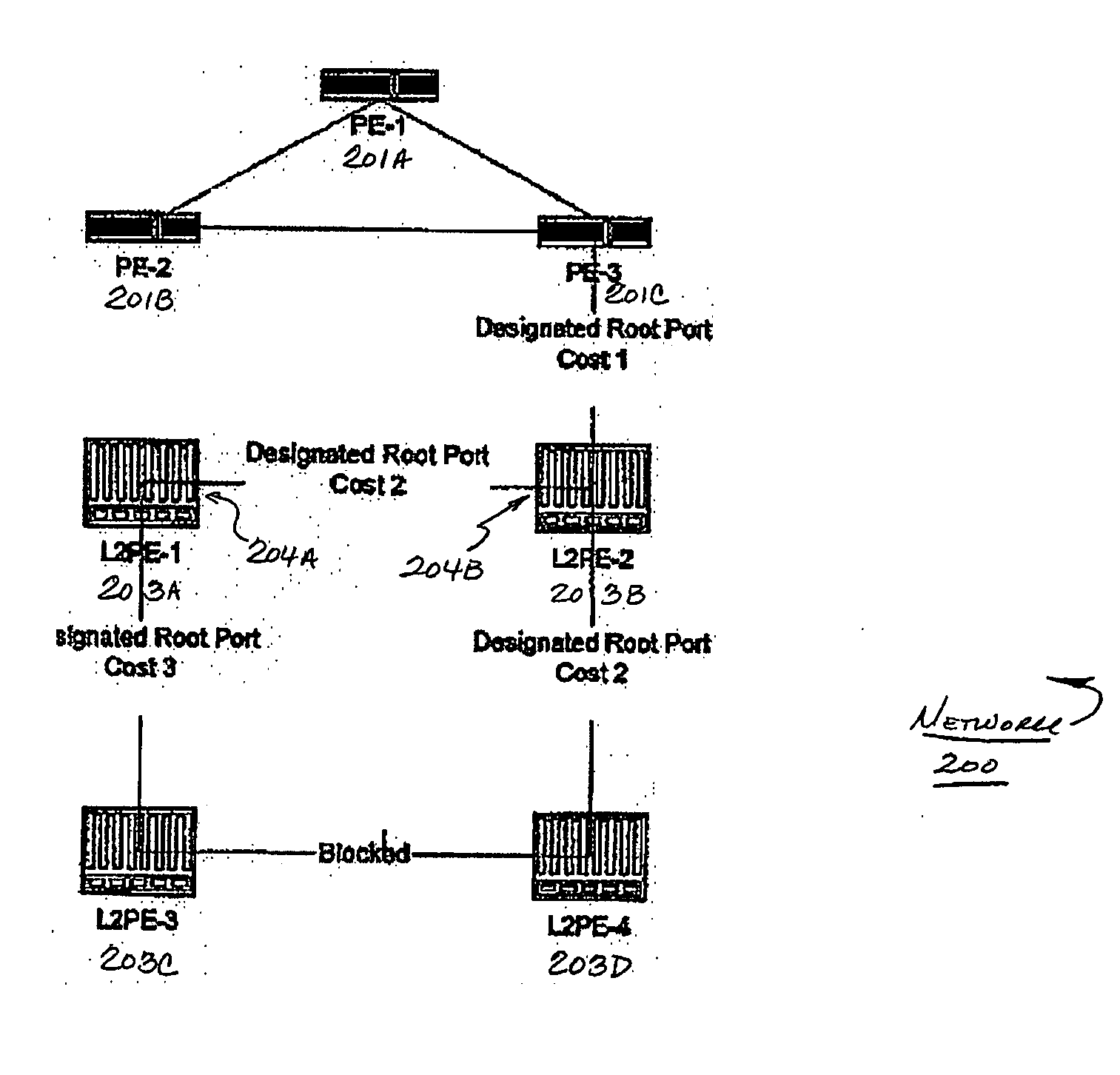
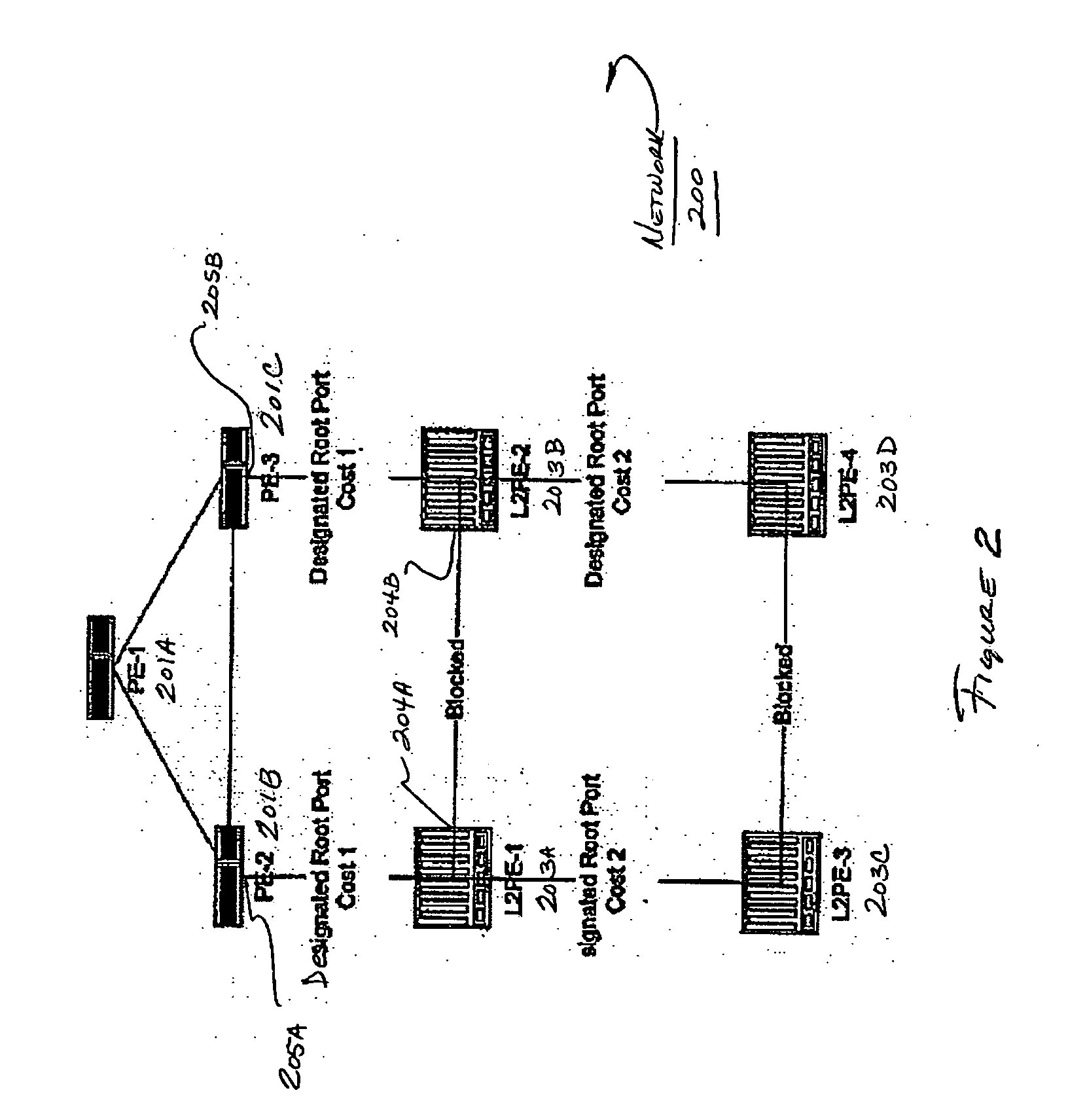
Network system, spanning tree configuration method and configuration program, and spanning tree configuration node
InactiveUS20040160904A1Complex shapeIncrease the number ofStar/tree networksNetworks interconnectionNetworked systemSpanning Tree Protocol
A node of a spanning tree system operating on a network connecting a plurality of nodes, comprises two transfer units which determines an output destination port, based on the destination MAC address of an input frame, two tree managers which configures a spanning tree according to a spanning tree protocol, and a virtual port of connecting the tree manager and the transfer unit.
Owner:NEC CORP
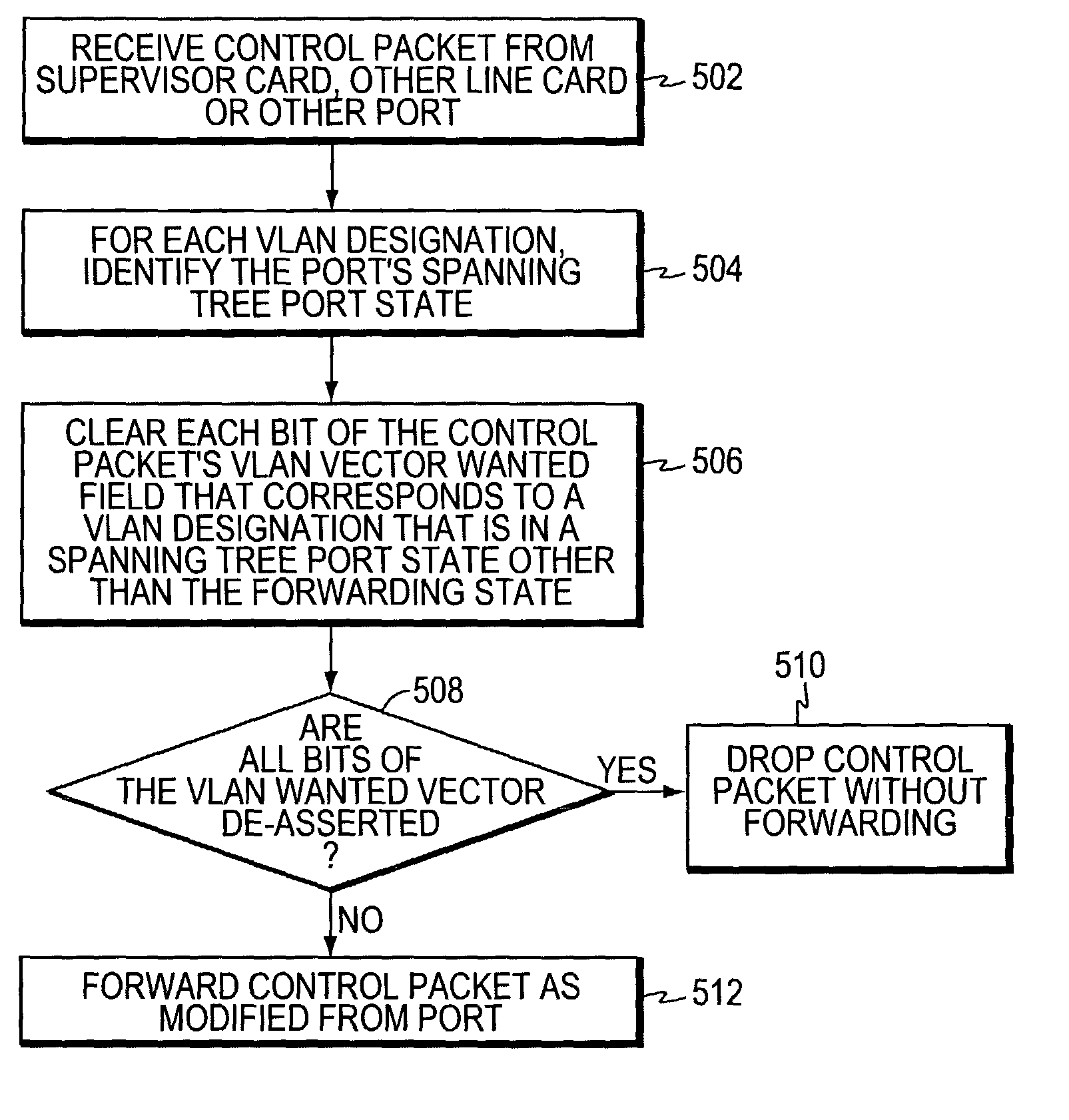
Virtual local area network pruning protocol
ActiveUS7877483B1Blocking in networkData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network AccessSpanning Tree Protocol
In one embodiment, an intermediate network device has a plurality of ports, and at least some of the ports are associated with Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) designations. A spanning tree entity executes a spanning tree protocol to transition the ports among a plurality of spanning tree states. A VLAN port logic circuit is disposed at one or more of the ports and processes control packets advertising VLAN memberships. The VLAN port logic circuit, in response to receiving a control packet broadcast by another intermediate network device, asserts bits in a VLAN wanted vector for which the spanning tree state of the selected port is in the forwarding state, signifying that network messages associated with such VLAN designations are to be forwarded from the respective port. The VLAN wanted vectors may later be transmitted in control messages from the intermediate network device.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
STP root guard
InactiveUS6987740B1Avoid loopsError preventionTransmission systemsNetwork packetSpanning Tree Protocol
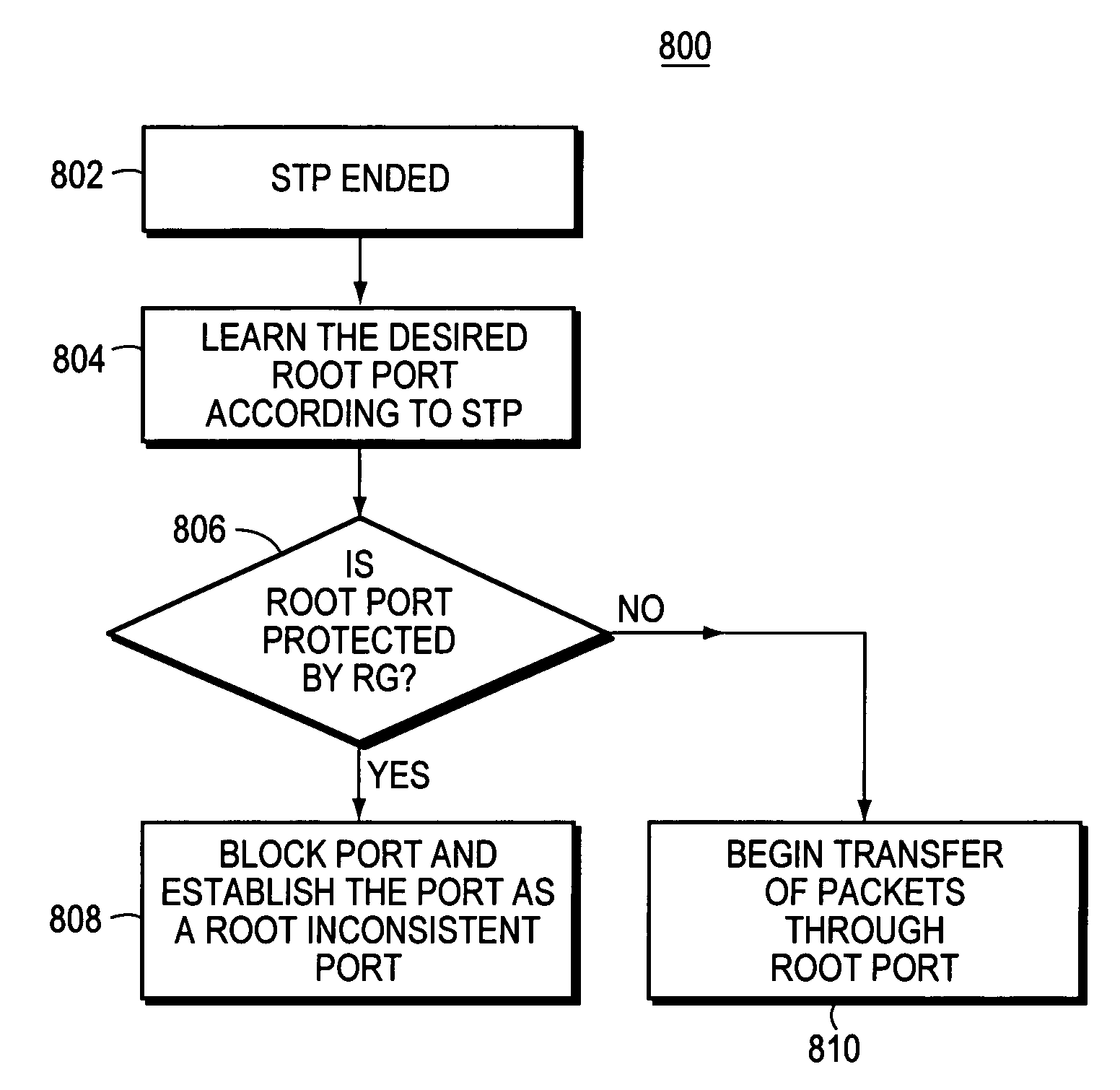
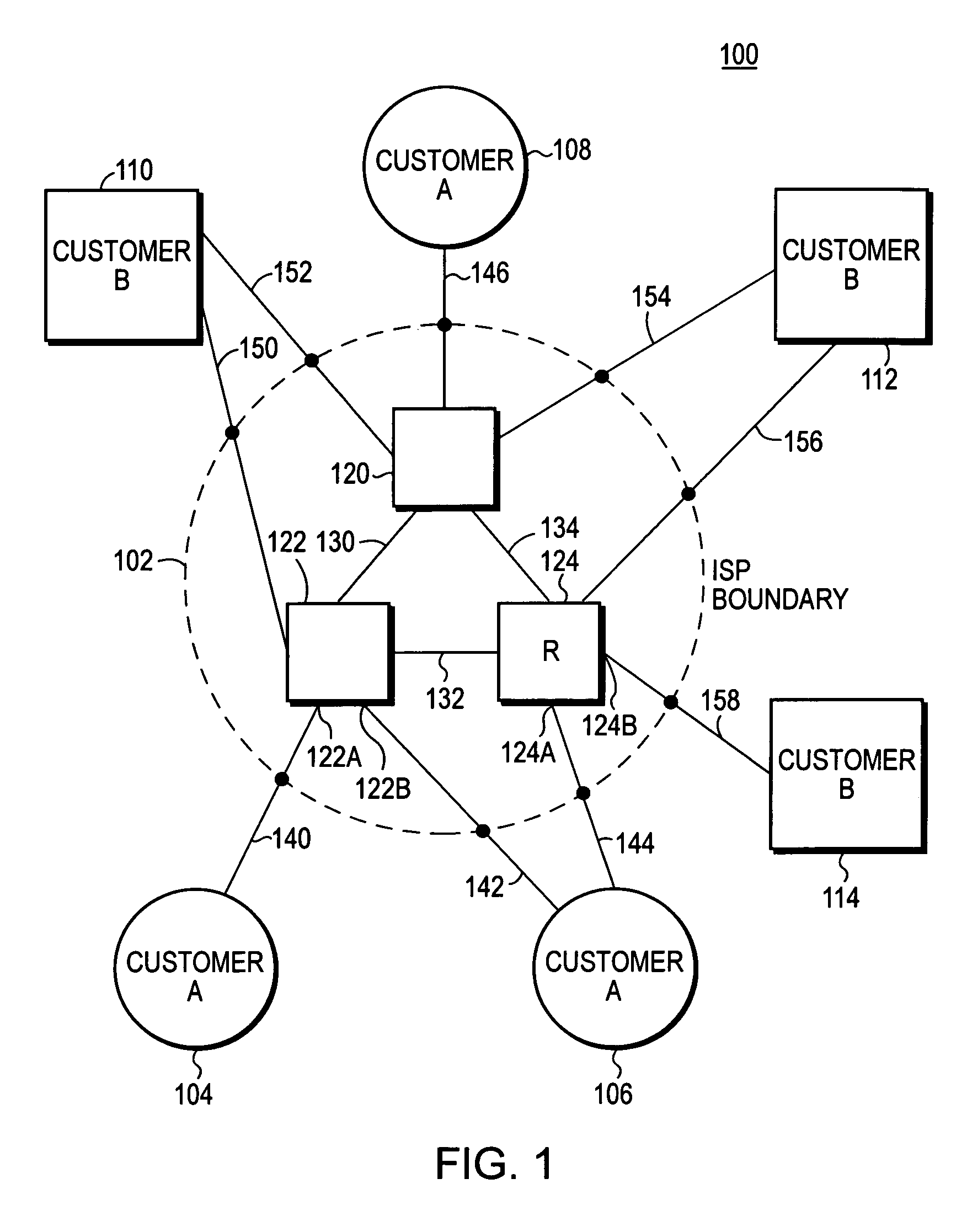
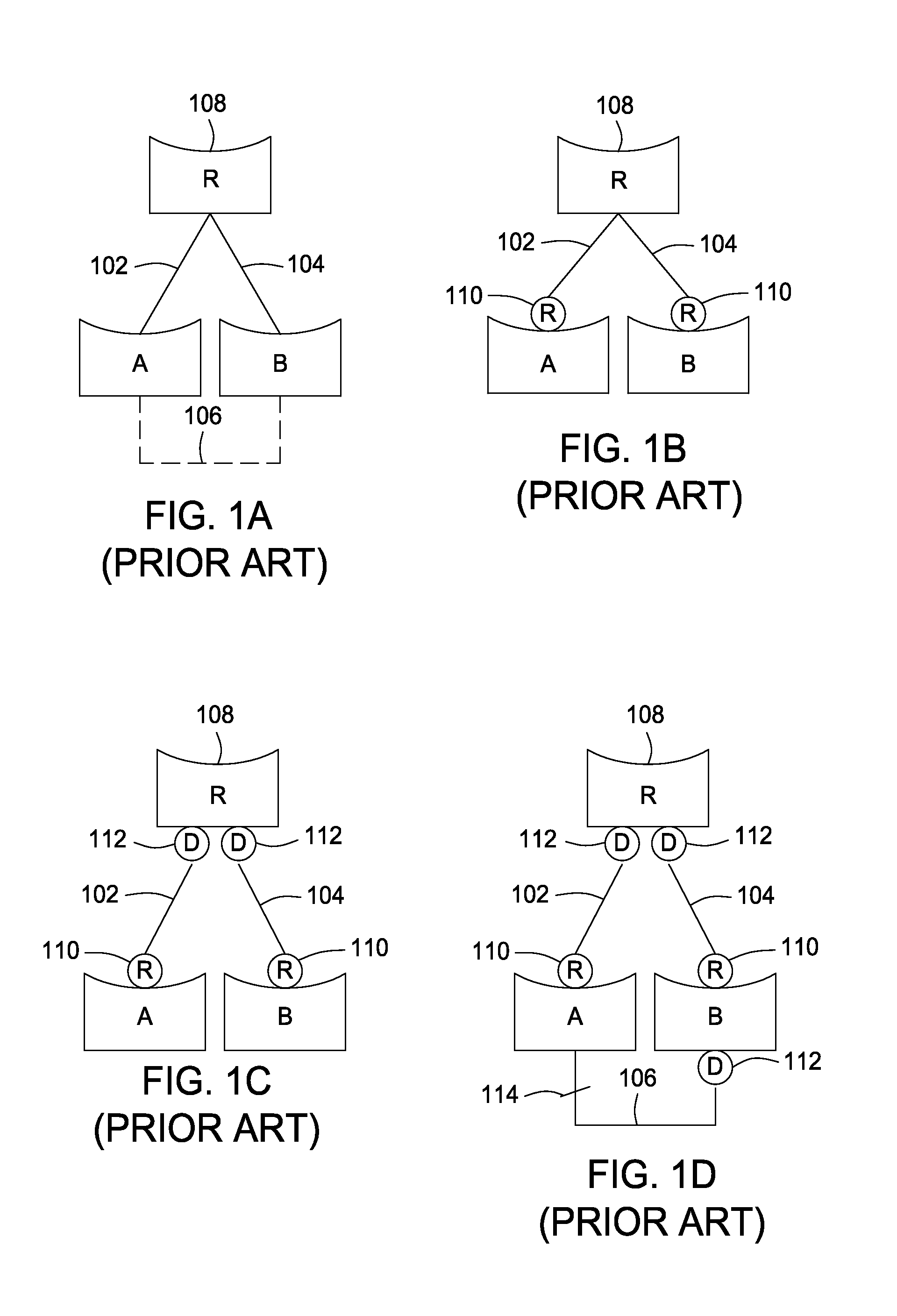
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) chooses a root switch. Each of the other switches has a “root” port and one or more “designated ports(s)” chosen by STP. Packets are transmitted upstream toward the root switch through the root port, and packets designated for downstream switches from the root switch are received by the root port and transmitted through the designated ports. In the invention, an administrator of the core network identifies which switch ports in the core network are boundary ports to customer networks. The administrator designates the boundary ports as “root guard protected” ports (RG ports). The STP then executes as required by the ordinary STP protocol, and if a RG port is selected by the STP to be a root portm then the status of the port is set to “blocked,” and no packets are transmitted through the port.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Ethernet communication method and system and SDN exchanger
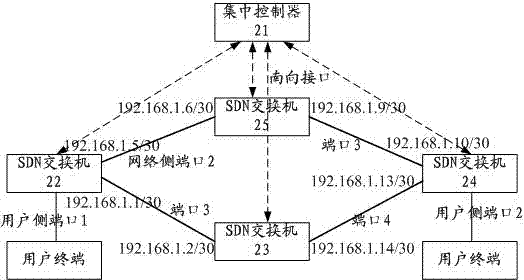
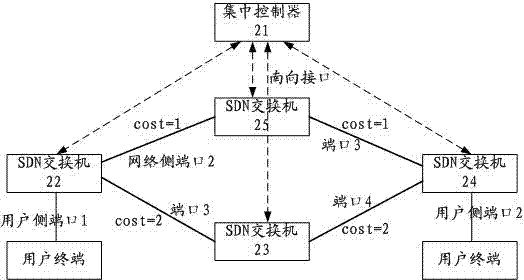
ActiveCN103888369AOvercome limitationsSolve the blockageData switching networksNetwork ConvergenceBroadcast radiation
The invention discloses an Ethernet communication method and system and an SDN exchanger. The method comprises the steps that the SDN exchanger reports the MAC address learned locally to an integrated controller, and the integrated controller issues forwarding tables of forwarding ports corresponding to target MAC addresses to all SDN exchangers under a management domain based on whole network topology automatic finding and route computing based on strategies; and the SDN exchangers achieve Ethernet frame forwarding according to the MAC address forwarding tables learned locally and the MAC address forwarding tables issued by the integrated controller. The integrated controller issues the MAC address forwarding tables to the SCN exchangers in the management domain, the boundedness that a traditional Ethernet exchanger learns whole network MAC addresses through a data forwarding plane is avoided, and the problems that broadcast storm and spanning tree protocols exist in the traditional Ethernet, so that a large amount of redundancy chain blocking is caused, network convergence speed is slow, and traffic engineering cannot be achieved are solved.
Owner:广州市高科通信技术股份有限公司
Spanning tree flooding backbone systems and methods for link state routed networks
ActiveUS20110090787A1Reducing transmitted messageReducing the transmitted messagesError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsComputer networkSpanning Tree Protocol
The present disclosure provides systems and methods for a spanning tree topology used as a “flooding backbone” for control messages on a link state routed network. Specifically, control messages are only broadcast on the flooding backbone thereby significantly reducing message flooding. The present disclosure also provides systems and methods for correctly and efficiently reconfiguring / fixing the spanning tree topology in the event of any spanning tree link failures without re-running the spanning tree protocol.
Owner:CIENA
Layer 2 loop detection system
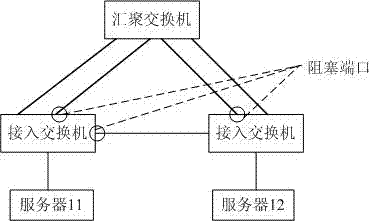
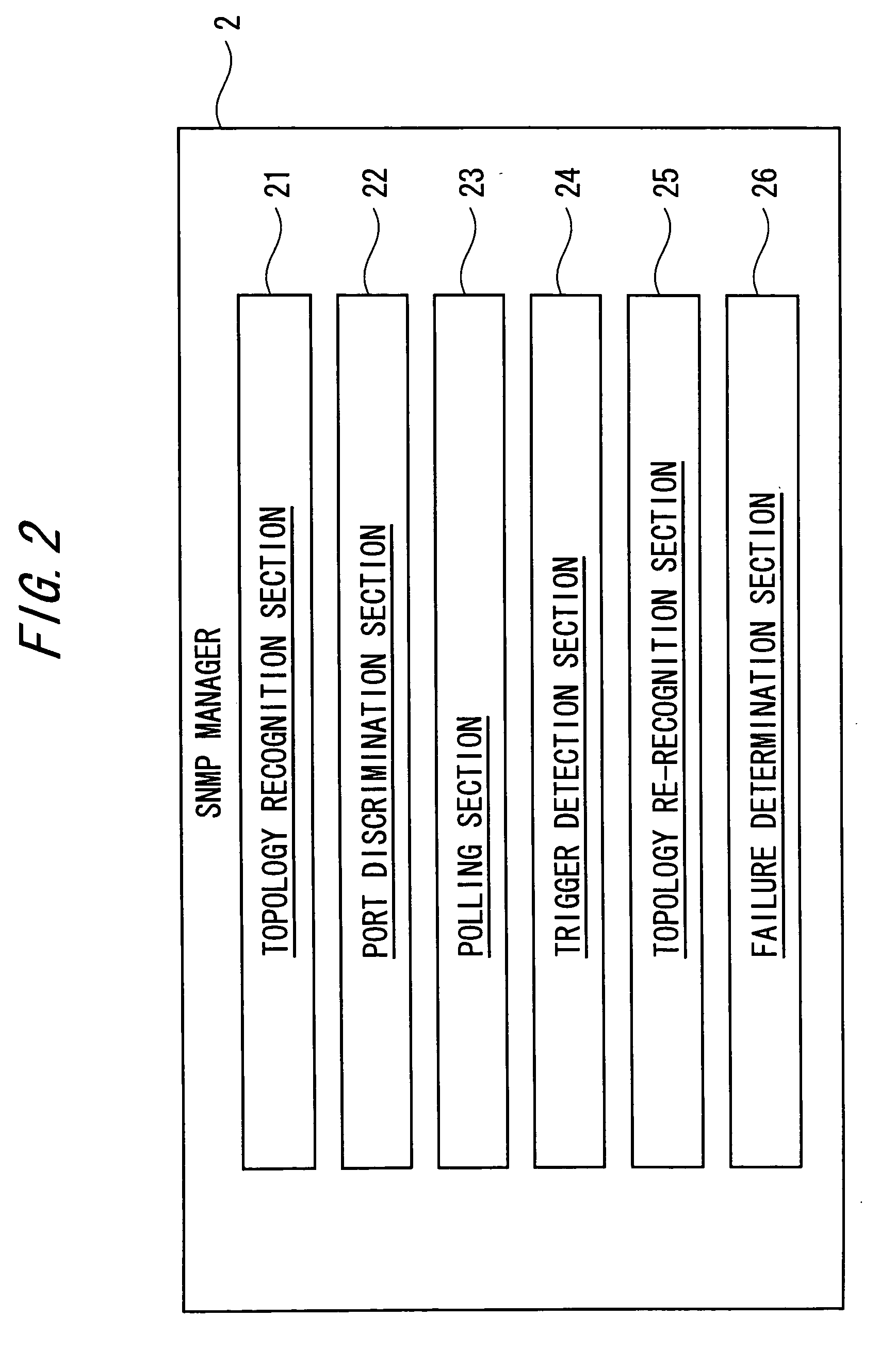
InactiveUS20050220036A1Reliable detectionReduce number of man-hours and labor costError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsComputer networkSpanning Tree Protocol
A layer 2 loop detection apparatus includes a unit recognizing a topology of an L2 network at normal time by collecting MIB information including information concerning ports of a plurality of L2 switches from the plurality of L2 switches through SNMP communication; a unit discriminating, based on a topology recognition processing, a blocking port for traffic blocking and a disable port under a port disable state each set under a Spanning Tree Protocol (STP); a unit setting each of the blocking port and the disable port as a monitoring point and periodically monitoring a state thereof; and a unit performing detection of an L2 loop by re-collecting a part of the MIB information from the plurality of L2 switches through SNMP communication and re-recognizing the topology of the L2 network, the detection of the L2 loop detection being triggered by a change of a state of one of the blocking port and the disable port.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
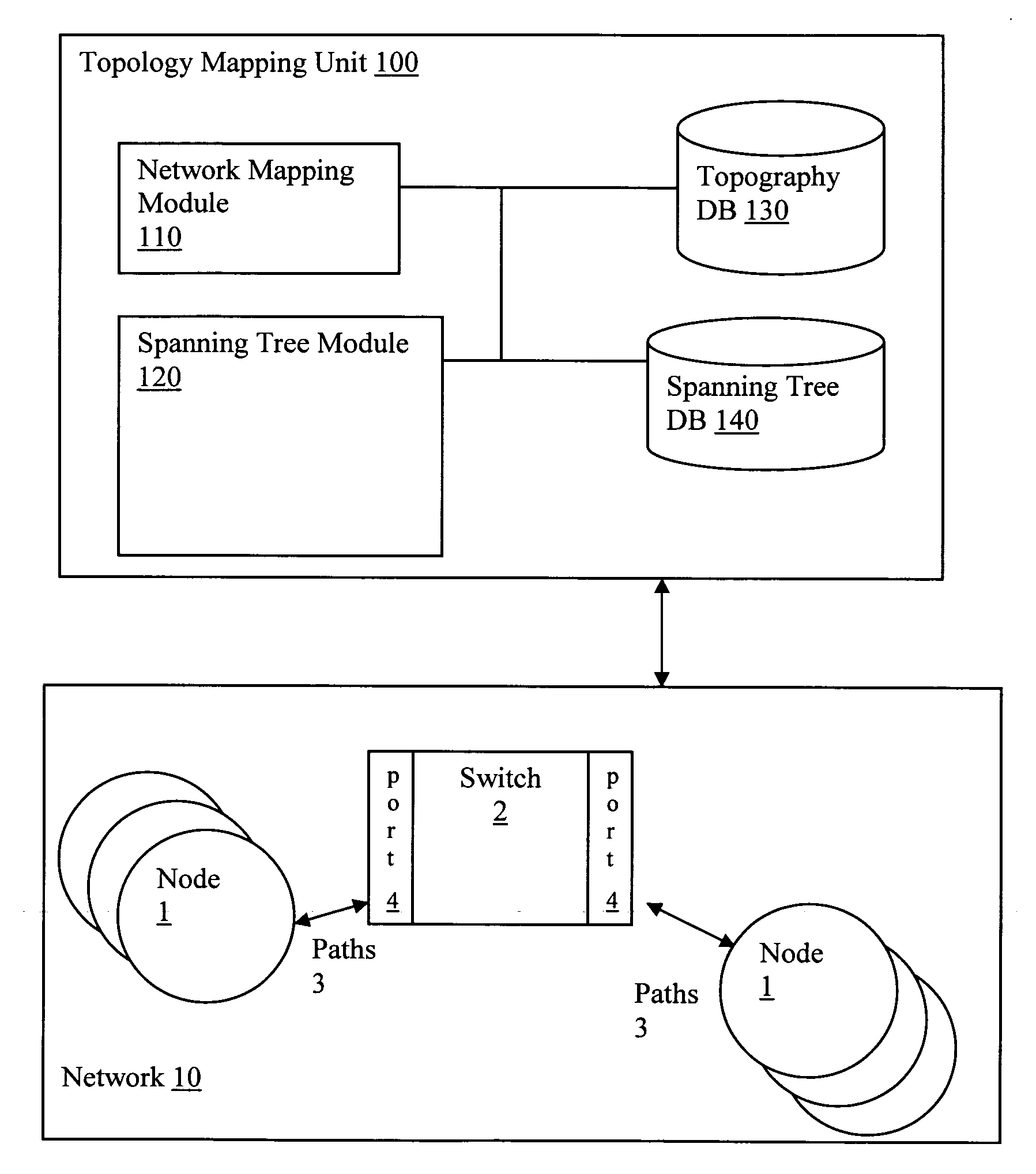
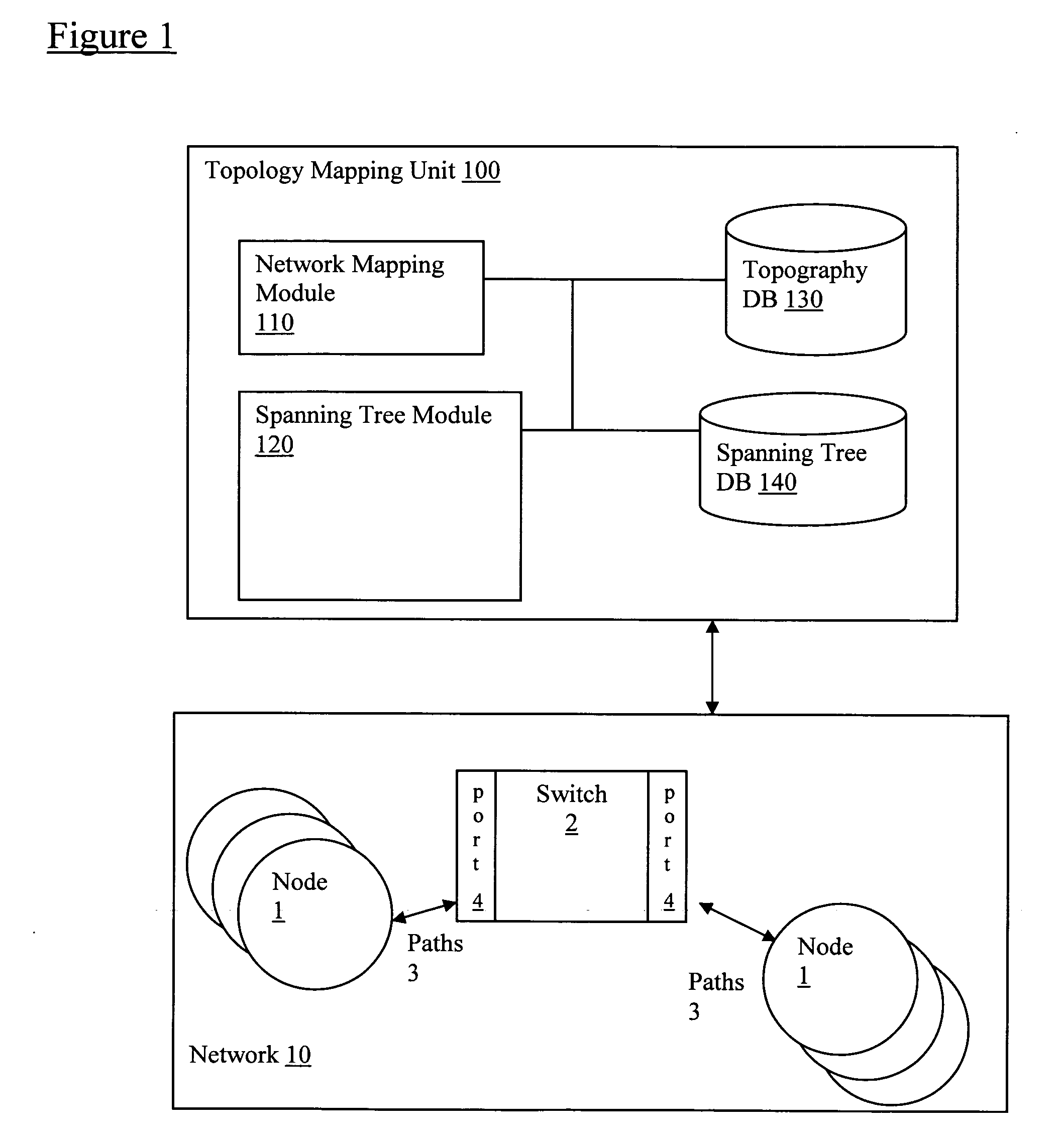
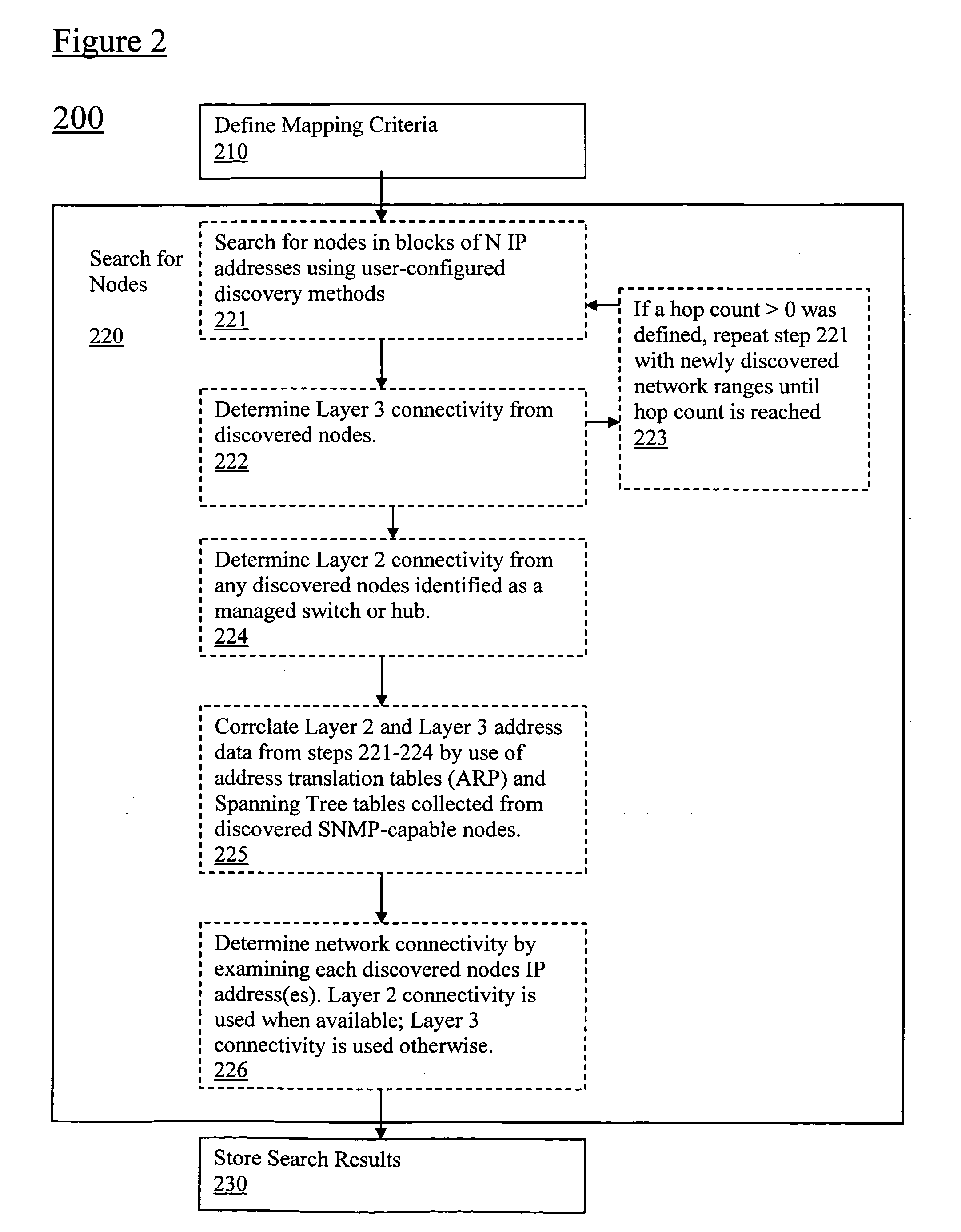
Using spanning tree protocol (STP) to enhance layer-2 network topology maps
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) data is obtained via network switch (SNMP) queries to enhance identification of switch-to-switch links in Layer-2 mapping. In particular, by analyzing the STP data, ambiguity in determining switch uplink ports may be reduced. Specifically, the STP data can be used in conjunction with other topography data to provide Layer-2 connectivity for nodes on a network topology. Layer-2 address mapping tables are collected from a topology mapping, and STP data is collected, along with address translation tables (ARP) tables. Using this information, switches are identified using Layer-2 address tables. The STP data can be correlated by comparing data in switches, identifying switch ports directly connected to other switch ports, and eliminating direct switch-to-switch port connections from consideration for further Layer-2 node mappings.
Owner:SOLARWINDS WORLDWIDE
Alternate spanning tree for faster indirect link failure recovery
Methods and apparatus that form the basis of an alternate spanning tree protocol that may be used, for example, to identify rings within a properly converged network configured by the spanning tree protocol (STP) or rapid spanning tree protocol (RSTP) are provided. With the knowledge of these rings, the alternate spanning tree has predetermined an alternate port that can restore connectivity without further computation in case of a link failure, thereby providing for extremely fast reconvergence.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
STP root guard
A method of managing a computer network switch is disclosed. The method has the steps of: setting a port of the switch to root guard protected status (RG status); selecting by a spanning tree protocol (STP) the port as a designated port; and setting said port into blocked status, in response to said port being both in root guard protected status and selected by STP as a root port. By setting a port to root guard protected, the port is prevented from becoming a designated port, and so then forcing the root port to remain in a desired core network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Computer network with point-to-point pseudowire redundancy
InactiveUS7643409B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork connectionSubject matter
A computer network includes a core network connected with first and second Ethernet access domain networks, each of Ethernet access domain networks including a user-facing provider edge (u-PE) device, a primary network-facing provider edge (n-PE) device, a redundant n-PE device, and a plurality of aggregation provider edge (Agg-PE) devices providing connectivity between to the u-PE device and the primary and redundant n-PE devices, the Agg-PE devices running a spanning-tree protocol (STP) algorithm. A primary data path is provided along with first and second redundant data paths that include first and second redundant pseudowires (PWs), respectively, connected across the core network, the first and second redundant data paths being blocked by the STP algorithm when the primary data path is available, the STP algorithm unblocking either the first or second redundant data path in response to a failure of the primary data path. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract that will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims. 37 CFR 1.72(b).
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
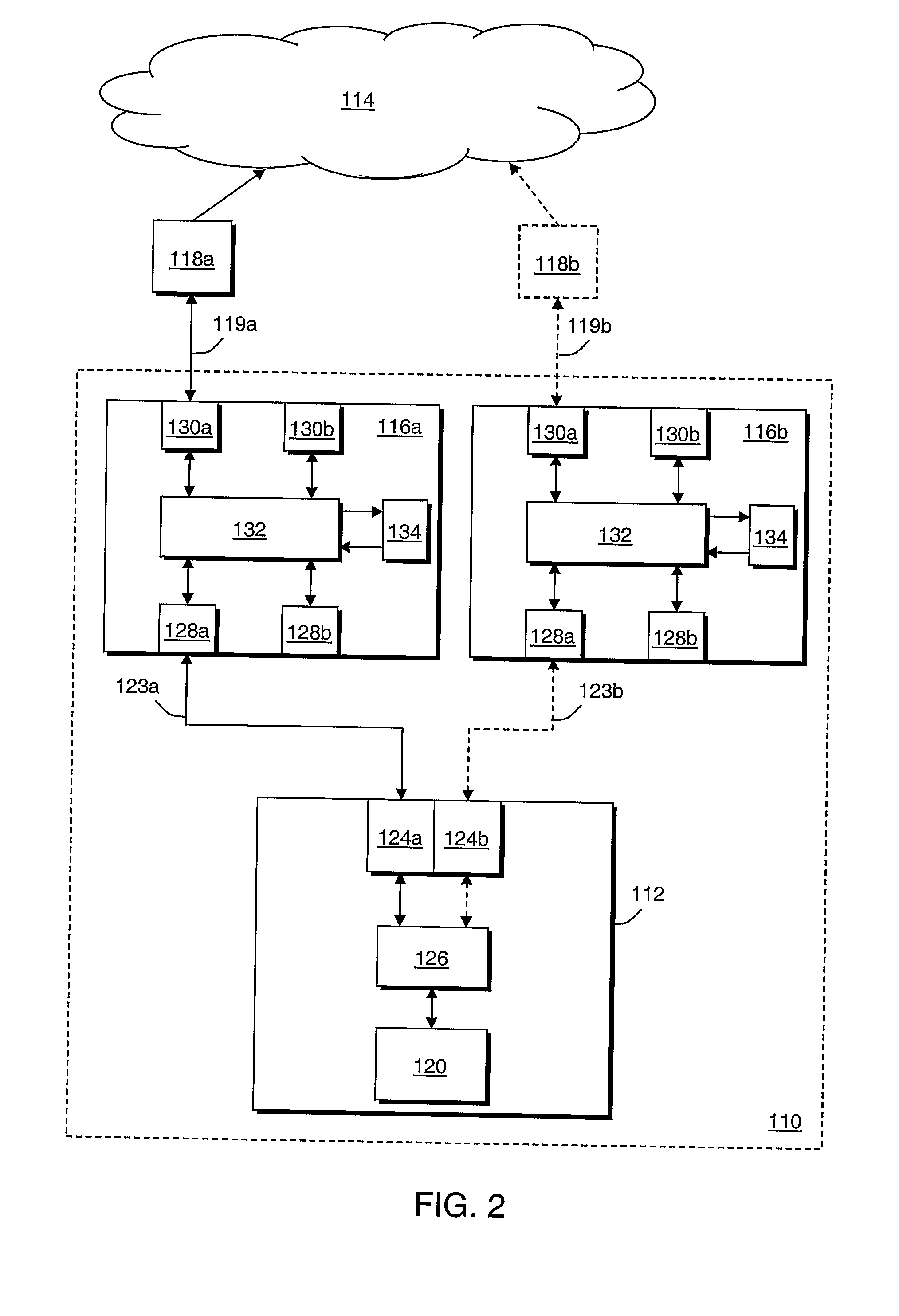
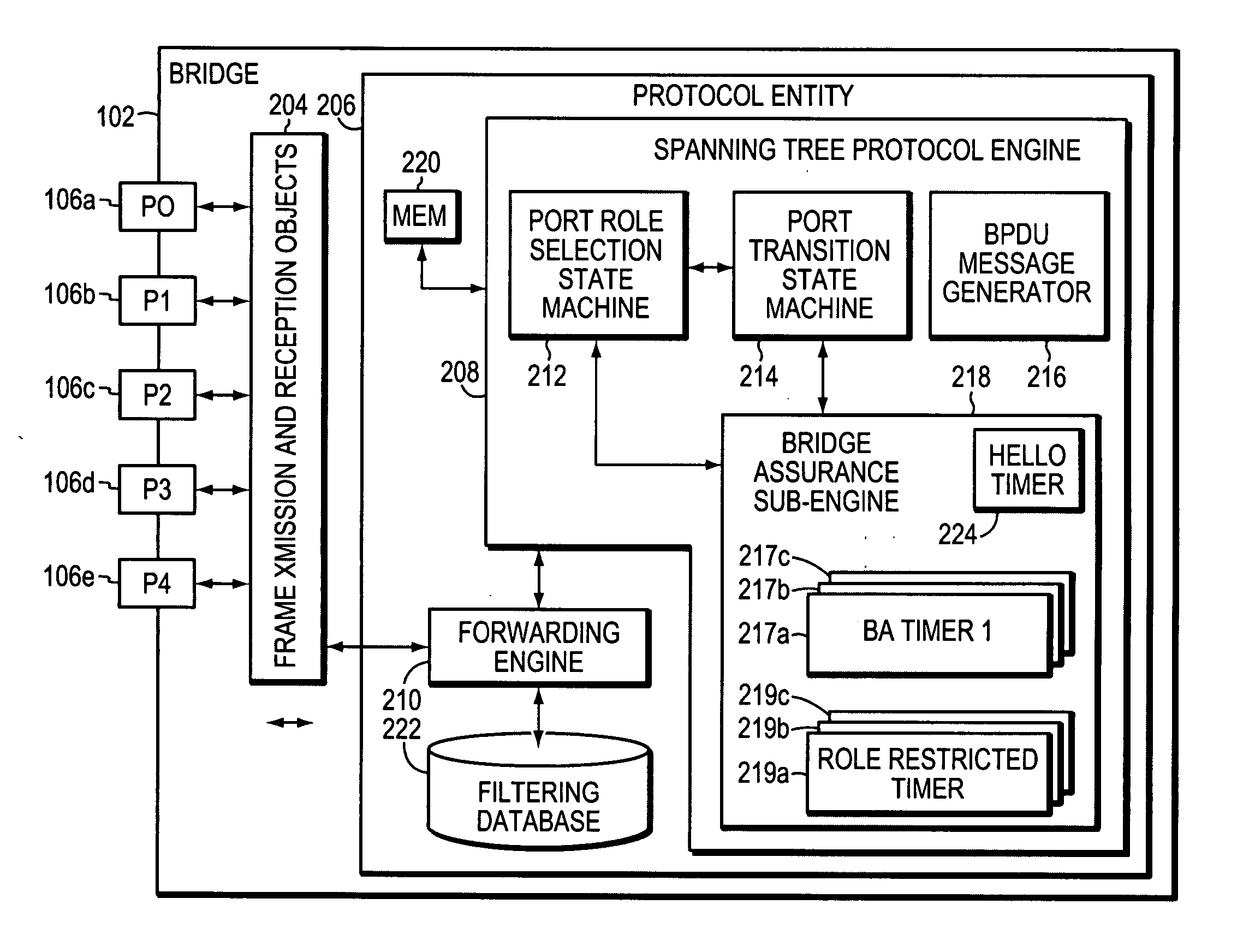
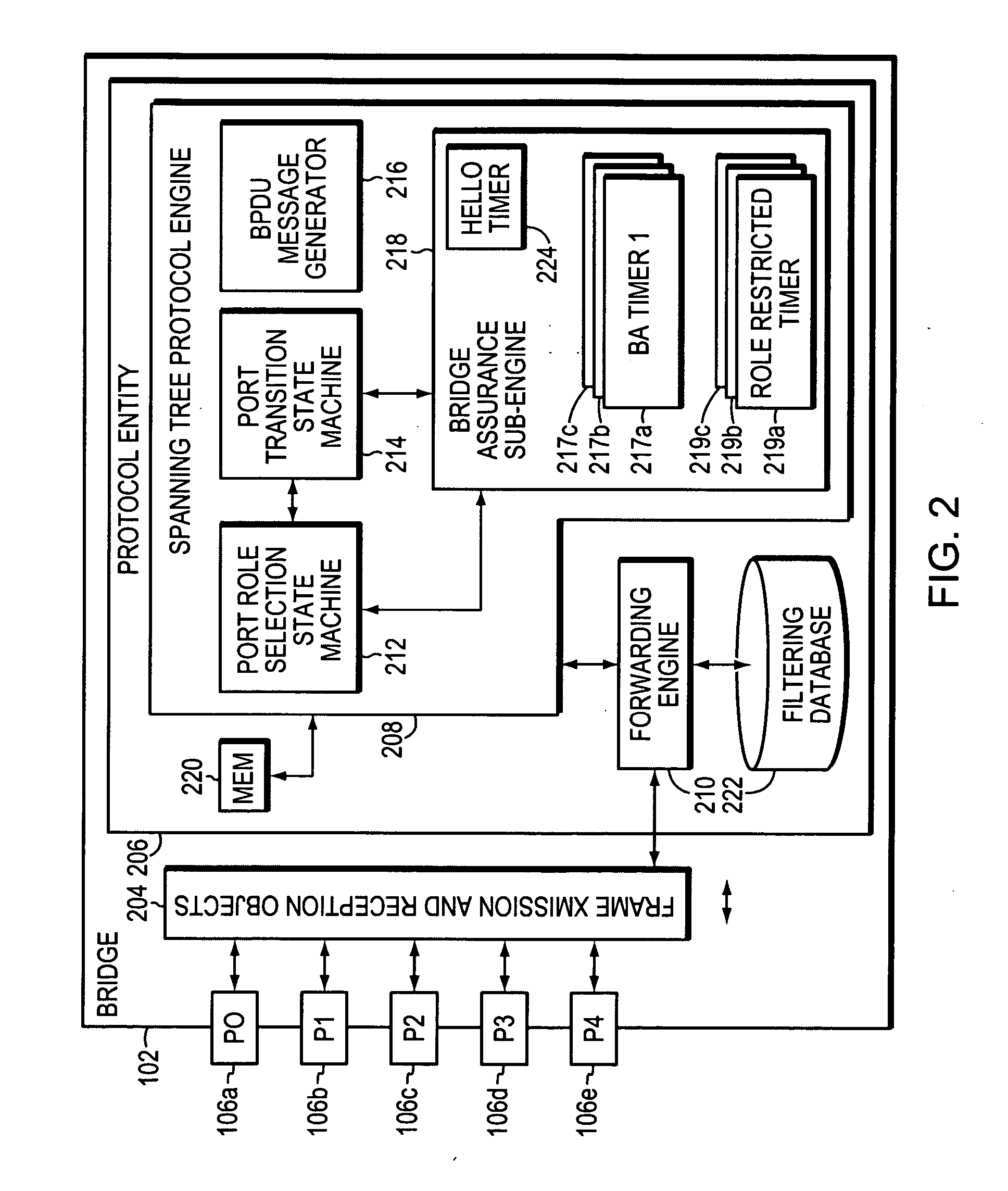
System and method for assuring the operation of network devices in bridged networks
A system and method assures the proper and continued operation of intermediate network devices, such as bridges, in a computer network. The bridge includes a spanning tree protocol (STP) engine, which is configured to have a bridge assurance (BA) sub-engine. The STP engine assigns the bridge's ports to one of a Root, Alternate, Designated or Backup Role. The BA sub-engine directs the STP engine to issue configuration messages from all ports to which neighboring bridges are coupled, including ports assigned to the Root and Alternate roles. The BA sub-engine further looks for the receipt of BPDU messages from neighboring bridges and employs one or more timers to determine whether the neighboring bridges are continuing to operate properly.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for determining a spanning tree
ActiveUS20050138008A1Reduce the amount requiredDigital data processing detailsData switching networksSpanning Tree ProtocolCore network
It is realized that the use of a spanning tree protocol in particular portions of a network may not necessarily be desired due to performance and stability reasons. A method and system is provided for executing a revised spanning tree algorithm that performs more optimally in particular network topologies. In one aspect, a spanning tree protocol is executed over a first and second network connected by a third network, wherein the spanning tree network is disabled in the third network. The third network may be, for example, a core network through which first and second Layer 2 networks are bridged. The first and second networks may be coupled by another network or network connection, and it may be preferable to allow the operation of the spanning tree network between the first and second coupled networks for the purpose of fail over to redundant paths. In network forwarding devices positioned at edges of the core network, the operation of the STP over interfaces where network tunnels of each network forwarding device attached to the core network may be inhibitied (e.g., turned off). A phantom root bridge may be created that does not correspond to an actual network forwarding node, and this phantom root bridge may have a bridge identifier which is used by network forwarding nodes as the root bridge. In this manner, STP protocols may work as intended in peripheral networks, while STP does not need to be executed in the core.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com