Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
82 results about "Peer-to-Peer Protocol" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
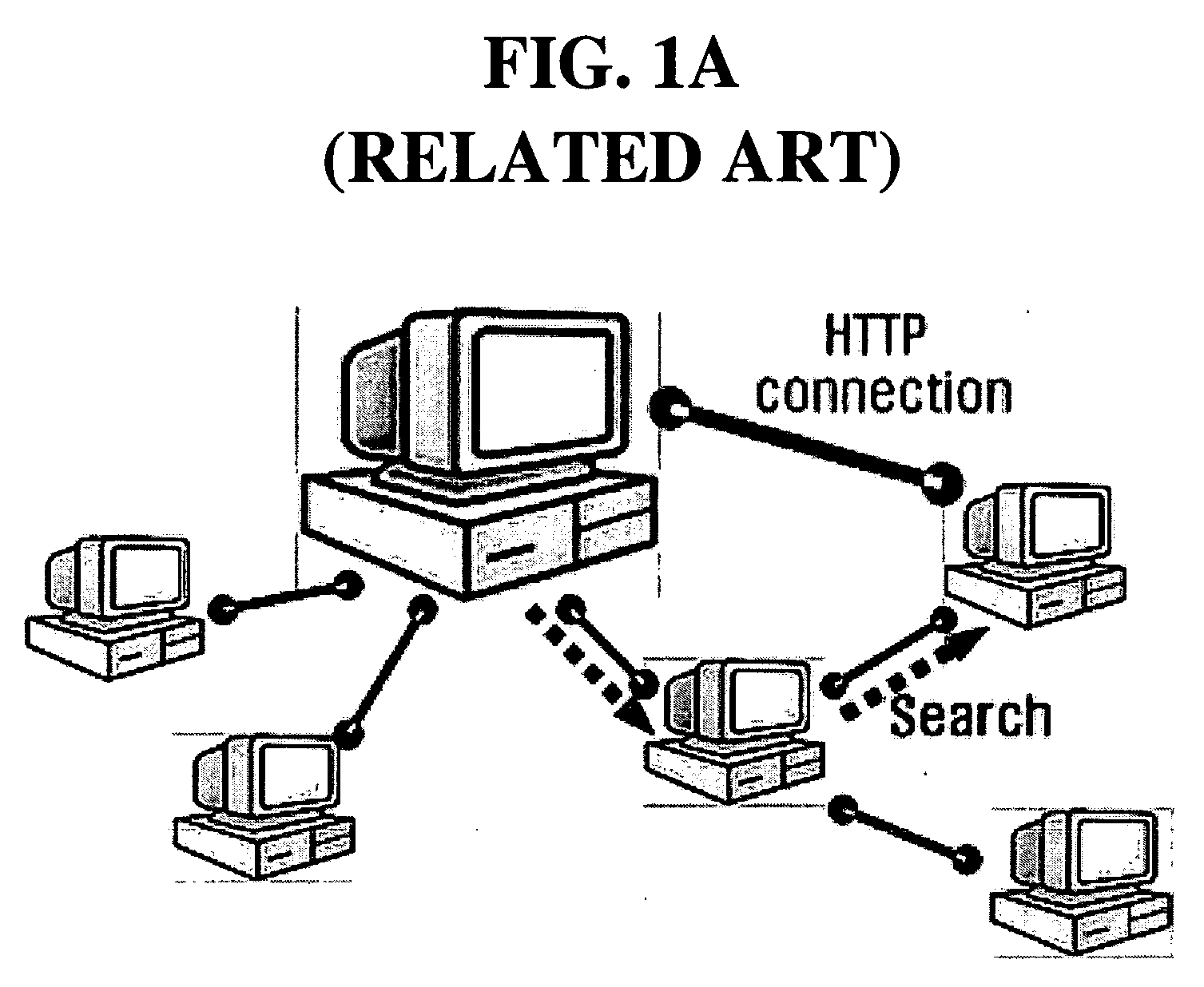
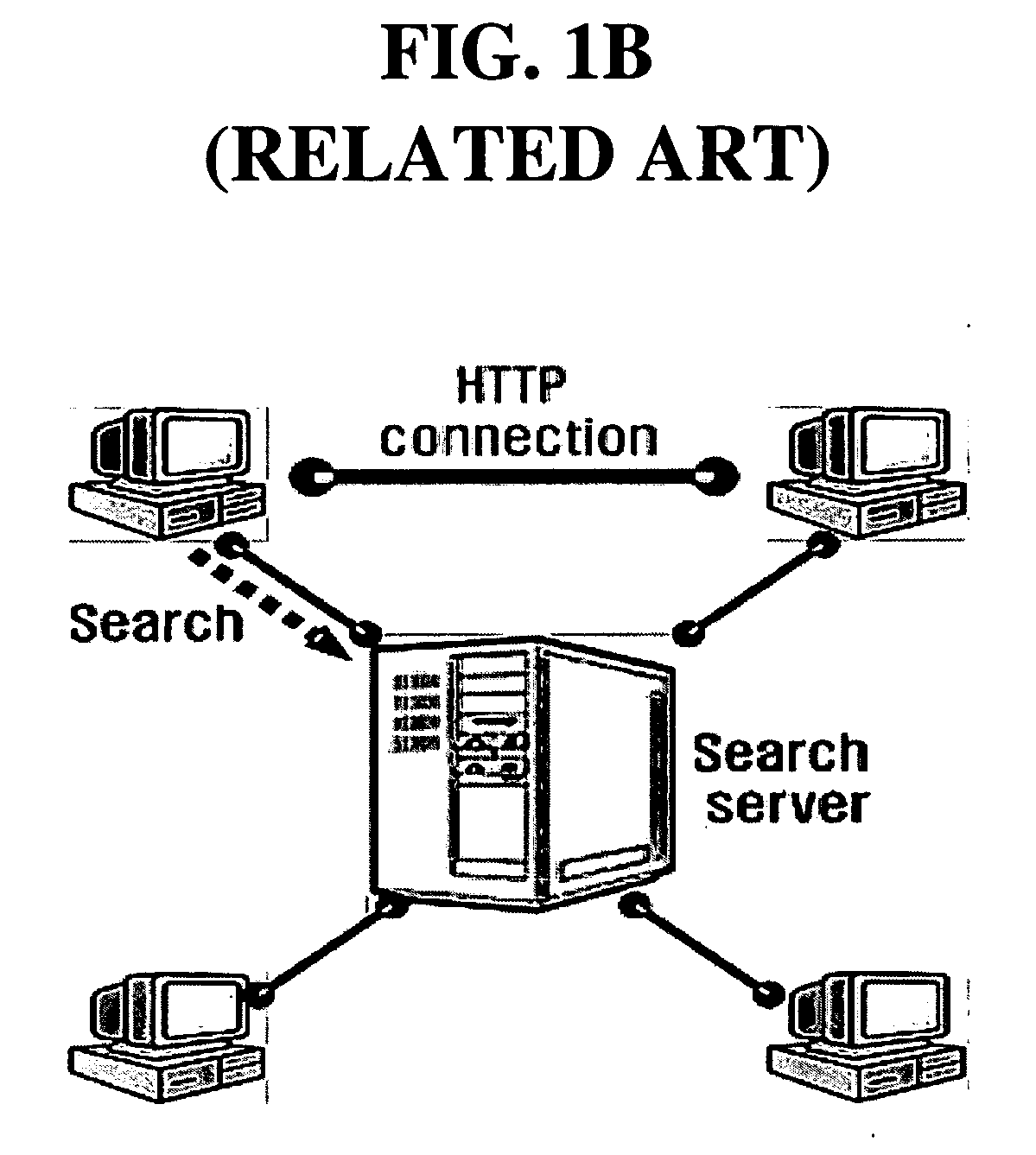
Peer-to-Peer Protocol is an application layer peer-to-peer networking protocol that can be used to form and maintain an overlay network among participant nodes. It was defined in an Internet Draft submitted to the IETF by the P2PSIP Working Group. It provides mechanisms for nodes to join, leave, publish, or search for a resource-object in the overlay. It maintains information about nodes in a routing table. Because of potentially large content, a node's routing table only contains a subset of these nodes. If a node can't accomplish the request, it searches for one who can, by performing a nextHop operation to a destination from the routing table.
Blockchain identity management system based on public identities ledger
ActiveUS9635000B1Effectively prevents unauthorized sharingMultiple keys/algorithms usagePublic key for secure communicationSystems managementIdentity management system
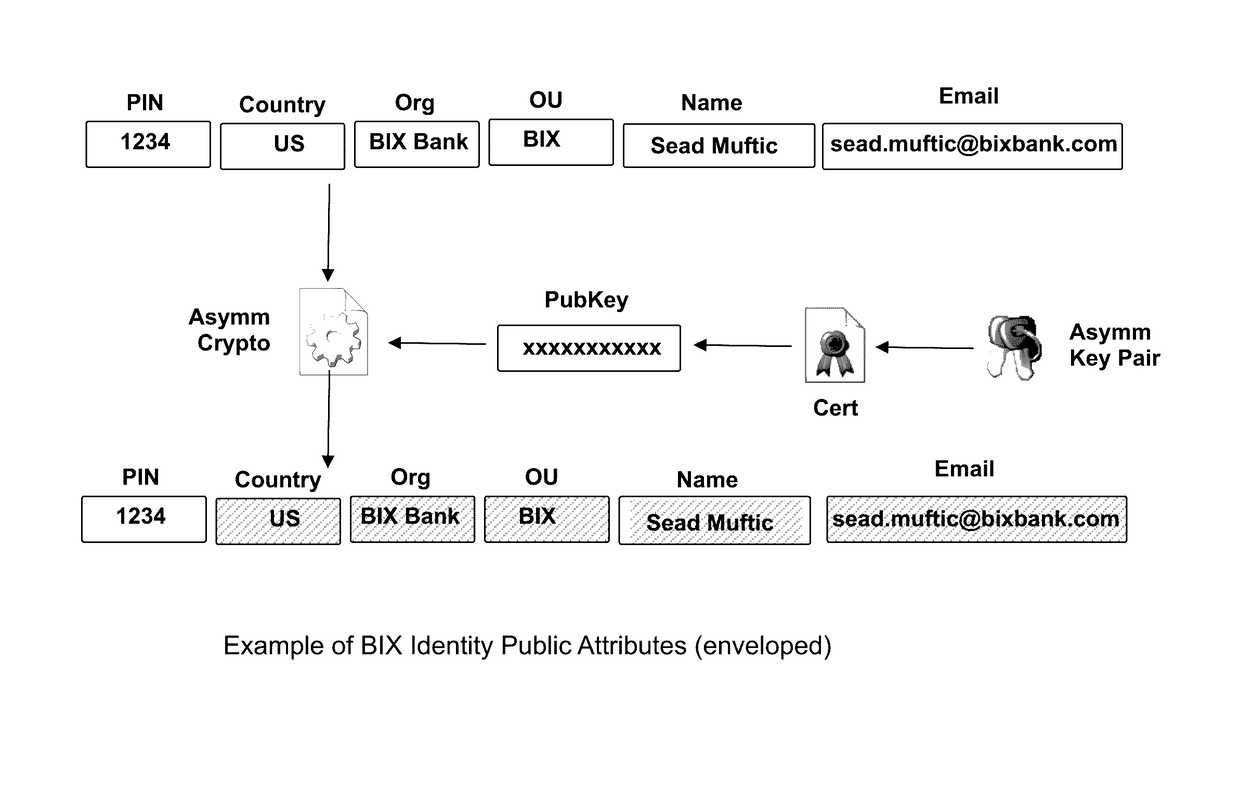
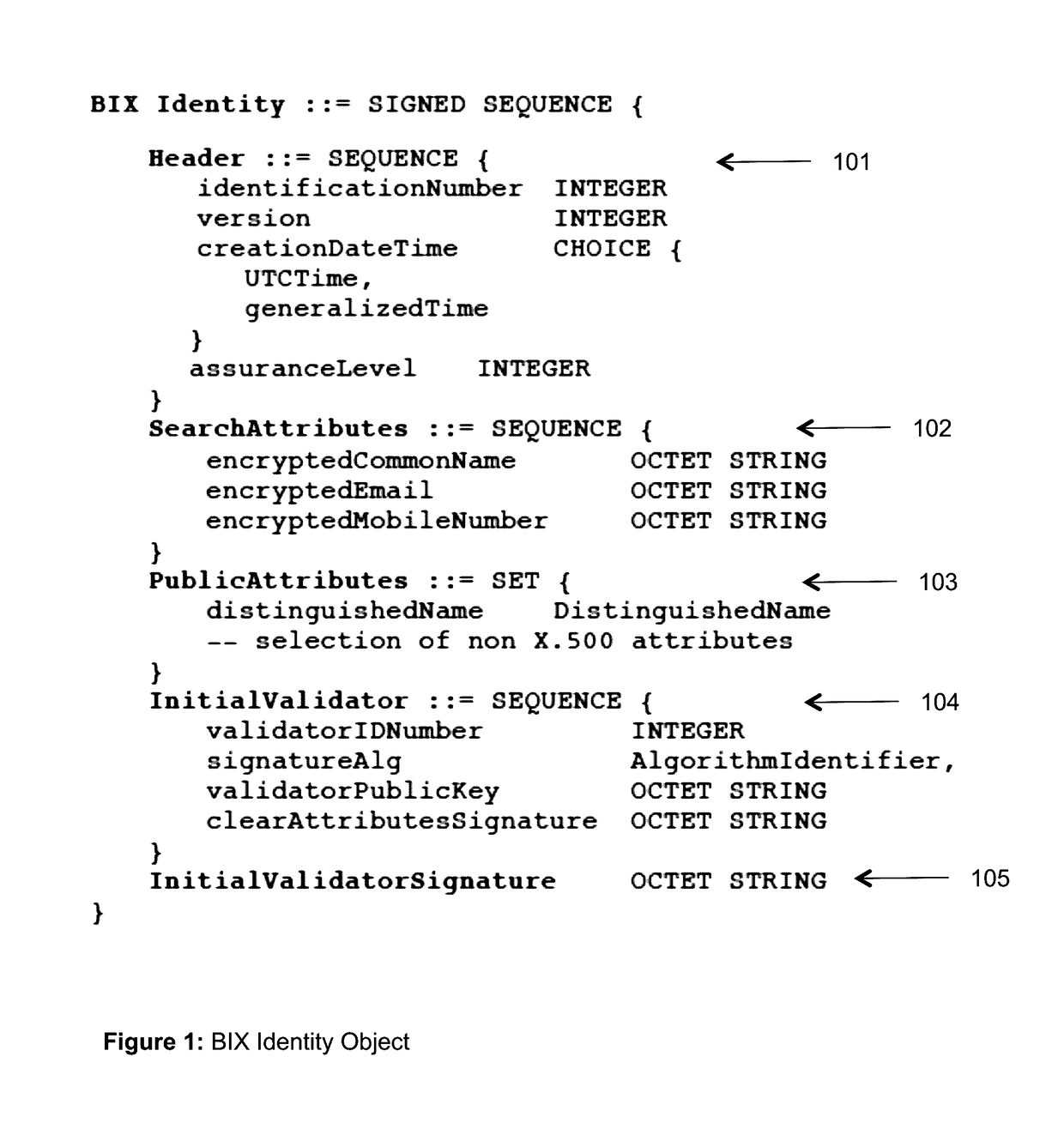
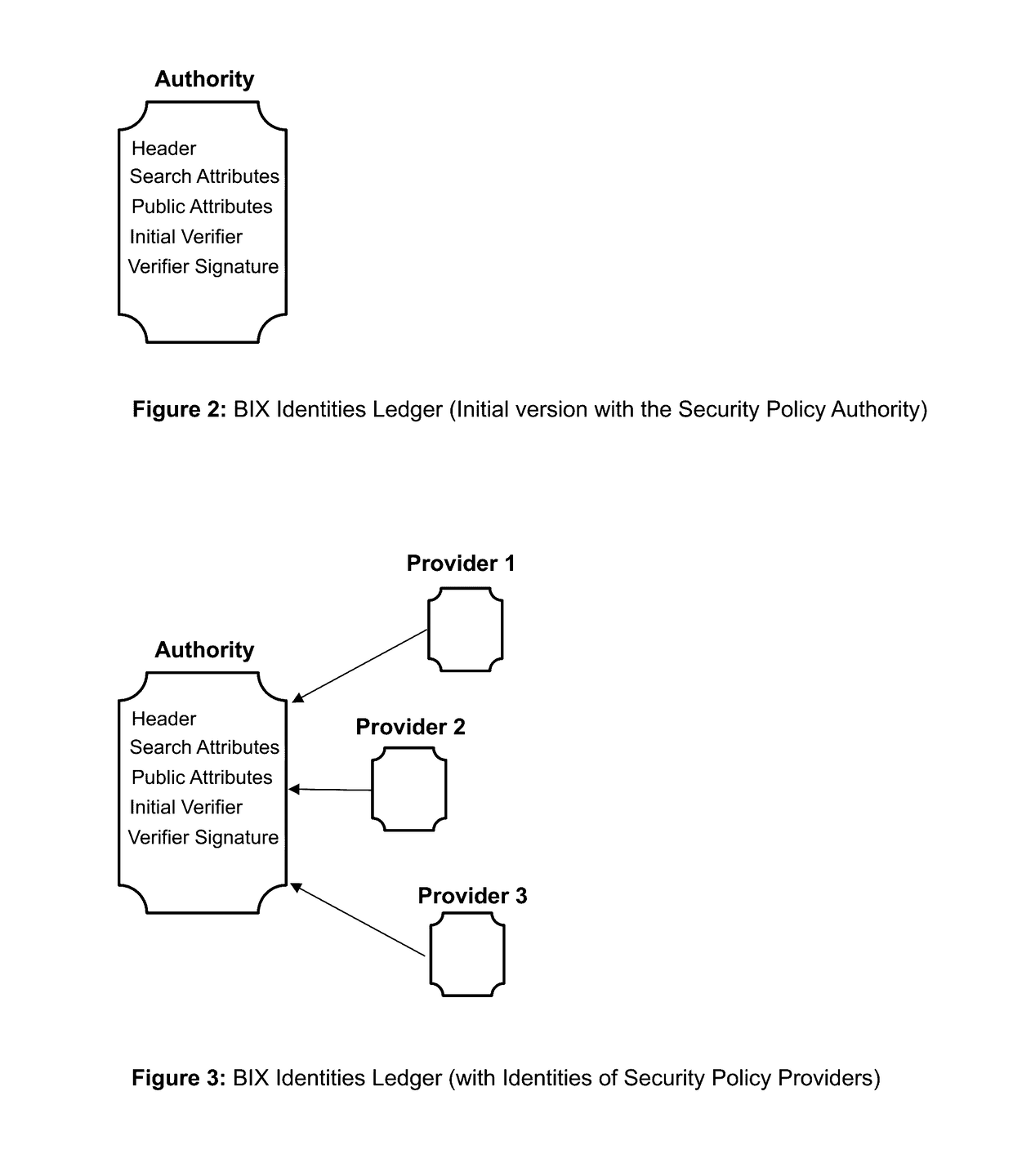
The invention describes an identity management system (IDMS) based on the concept of peer-to-peer protocols and the public identities ledger. The system manages digital identities, which are digital objects that contain attributes used for the identification of persons and other entities in an IT system and for making identity claims. The identity objects are encoded and cryptographically encapsulated. Identity management protocols include the creation of identities, the validation of their binding to real-world entities, and their secure and reliable storage, protection, distribution, verification, updates, and use. The identities are included in a specially constructed global, distributed, append-only public identities ledger. They are forward- and backward-linked using the mechanism of digital signatures. The linking of objects and their chaining in the ledger is based on and reflect their mutual validation relationships. The identities of individual members are organized in the form of linked structures called the personal identities chains. Identities of groups of users that validated identities of other users in a group are organized in community identities chains. The ledger and its chains support accurate and reliable validation of identities by other members of the system and by application services providers without the assistance of third parties. The ledger designed in this invention may be either permissioned or unpermissioned. Permissioned ledgers have special entities, called BIX Security Policy Providers, which validate the binding of digital identities to real-world entities based on the rules of a given security policy. In unpermissioned ledgers, community members mutually validate their identities. The identity management system provides security, privacy, and anonymity for digital identities and satisfies the requirements for decentralized, anonymous identities management systems.
Owner:MUFTIC SEAD
Peer-to-peer computing architecture
ActiveUS20020147771A1Multiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsPhysical addressProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access
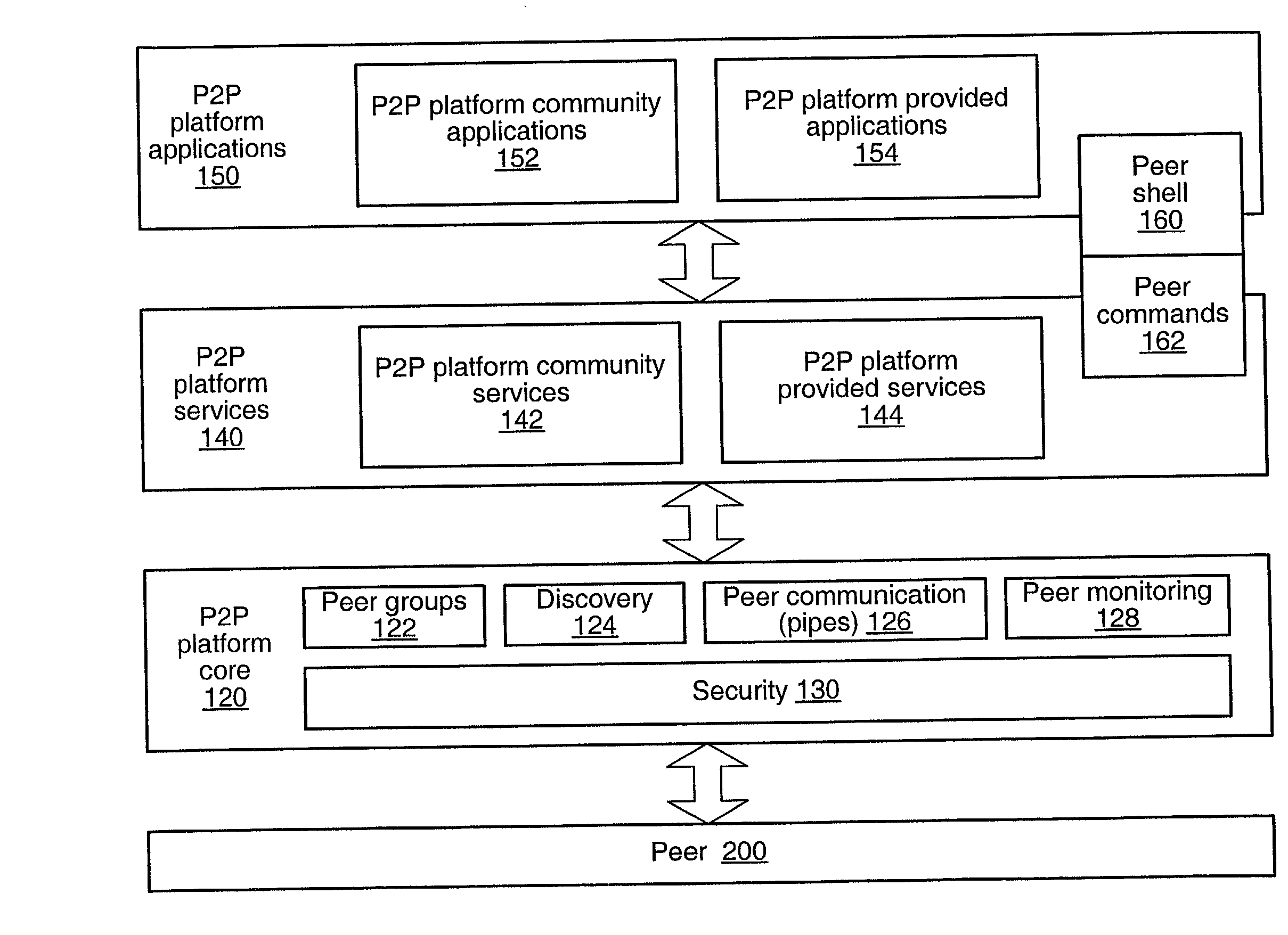
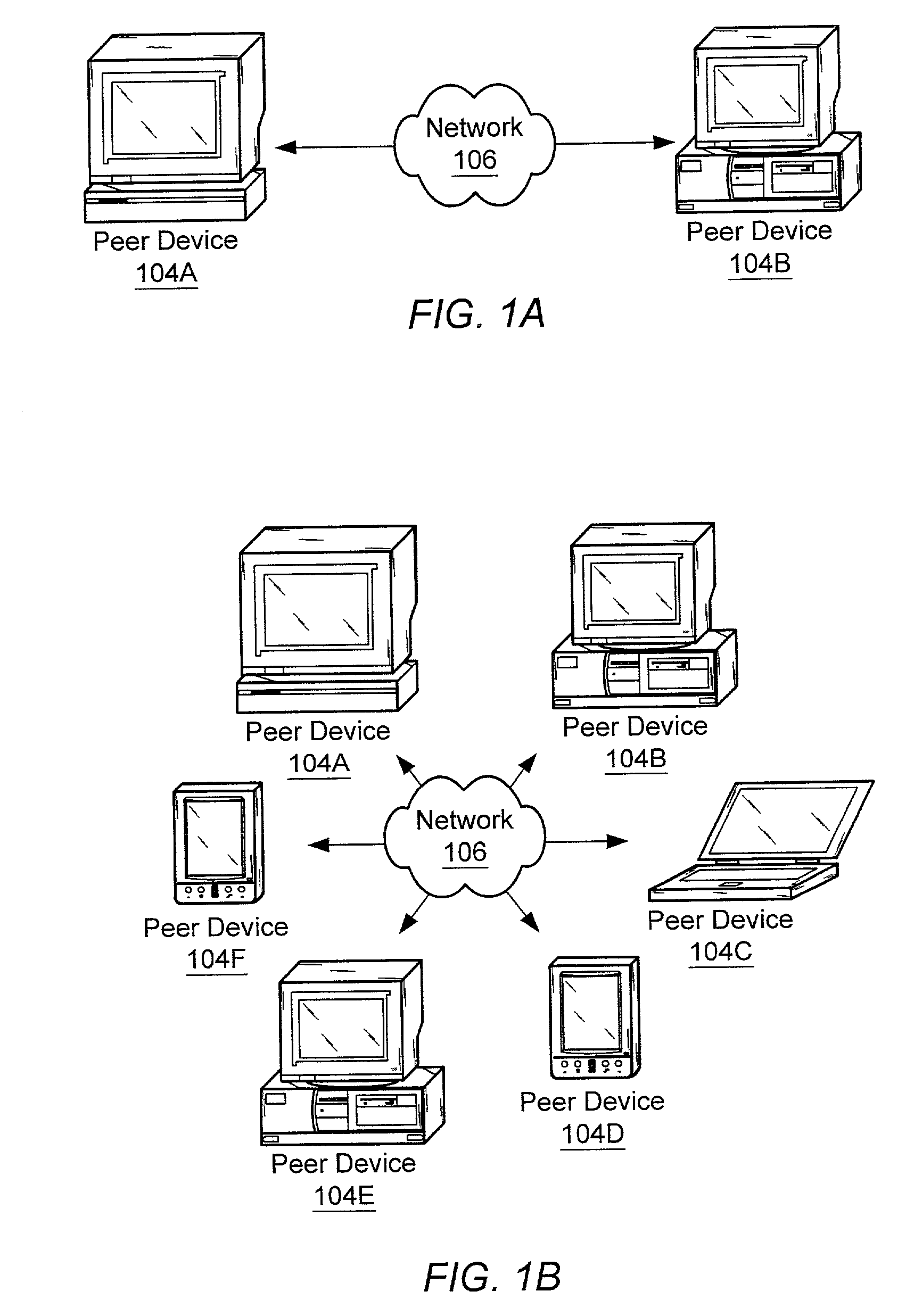
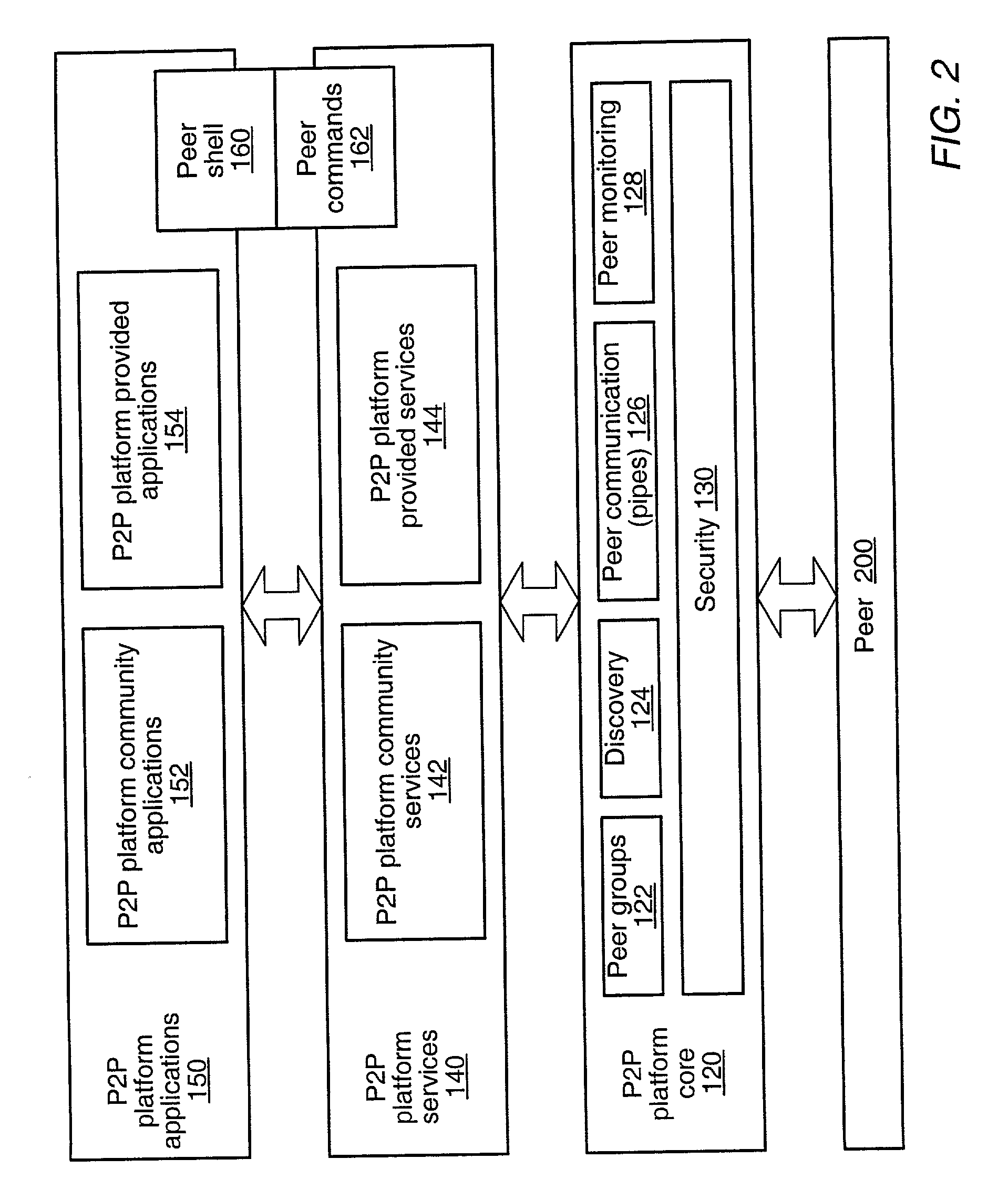
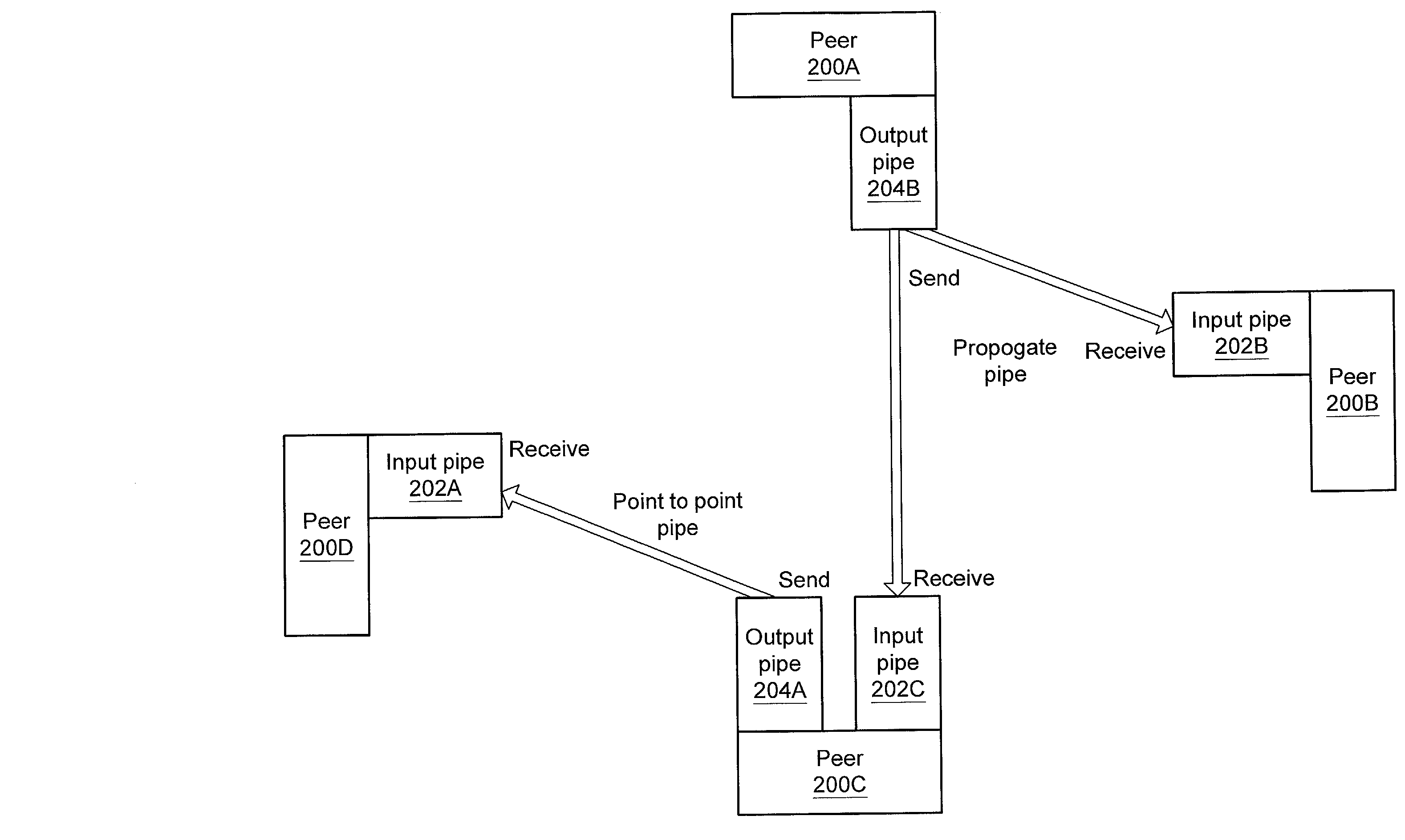
A system and method for providing an open network computing platform designed for peer-to-peer computing. The peer-to-peer platform may provide protocols for peer-to-peer services and applications that allow peers to discover each other, communicate with each other, and cooperate with each other to form peer groups. The protocols may include a peer membership protocol, a peer discovery protocol, a peer resolver protocol, a peer information protocol, a pipe binding protocol, and a peer endpoint protocol. Services and applications that participate in the protocols may be provided to deal with higher-level concepts. Advertisements may be used to publish peer resources. The peer-to-peer platform provides the ability to replicate information toward end users and may enable peers to find content that is closest to them. The peer-to-peer protocols and unique peer identifiers may allow peer nodes to move to different locations and access services and other content independent of network physical addresses.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
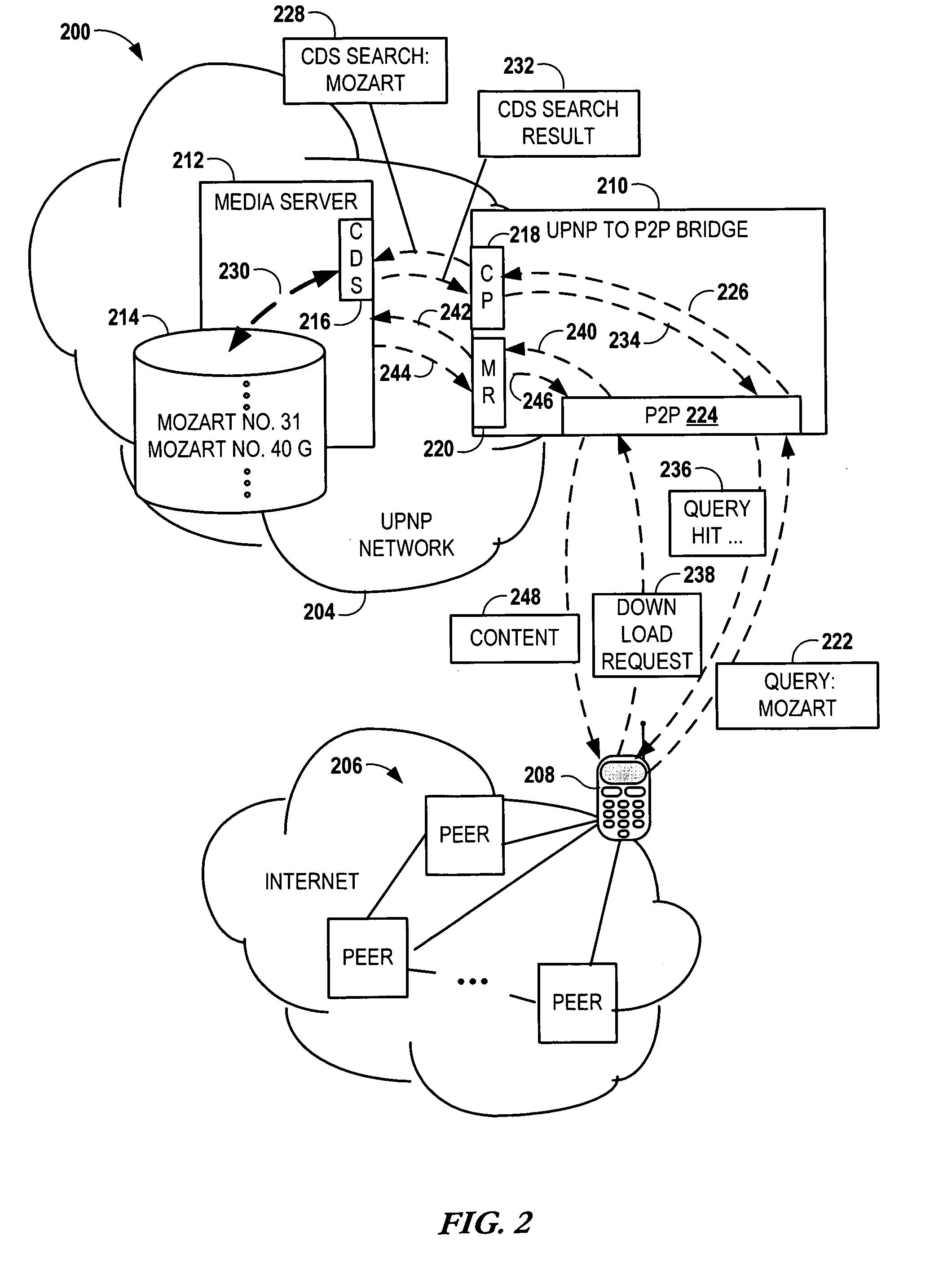
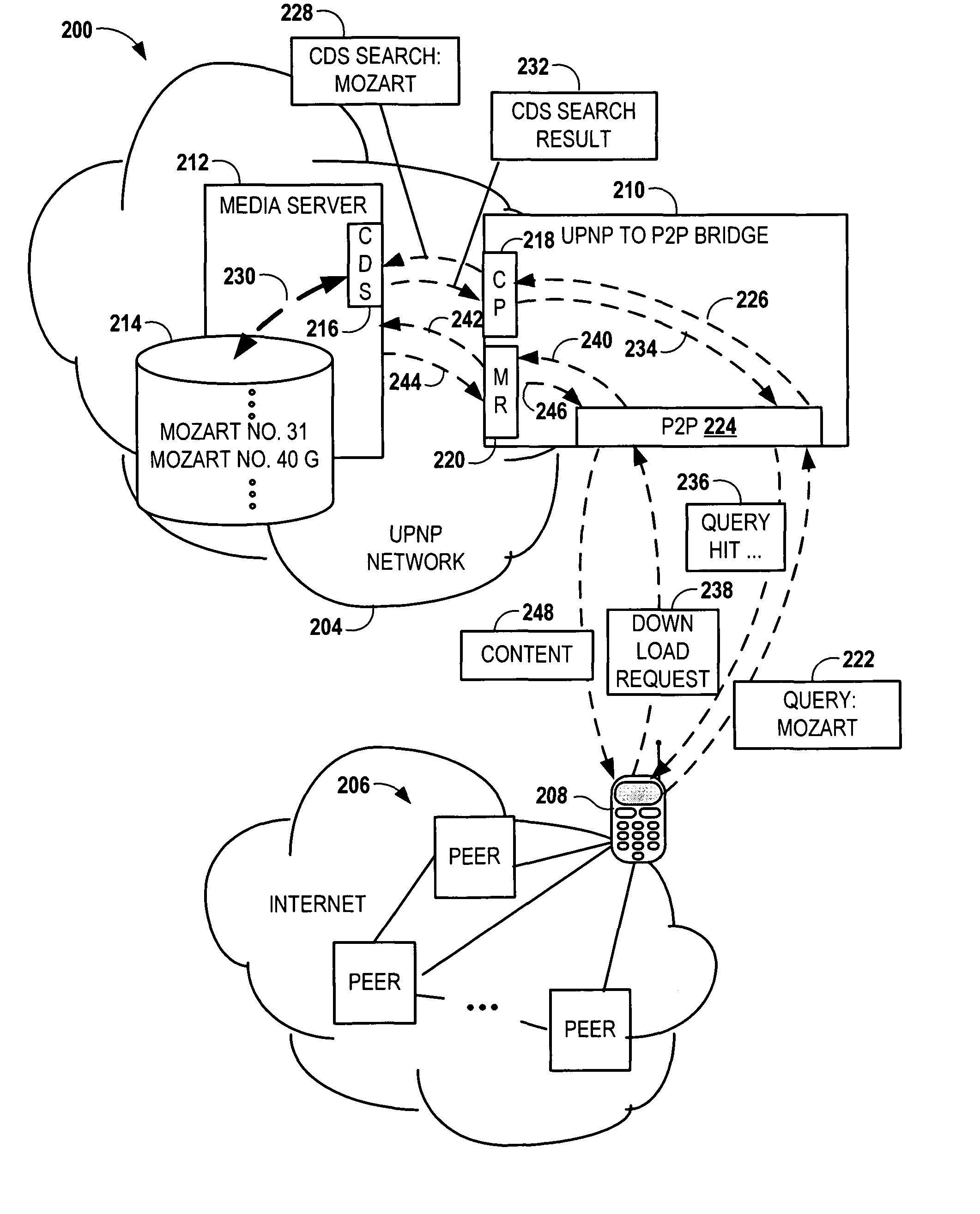
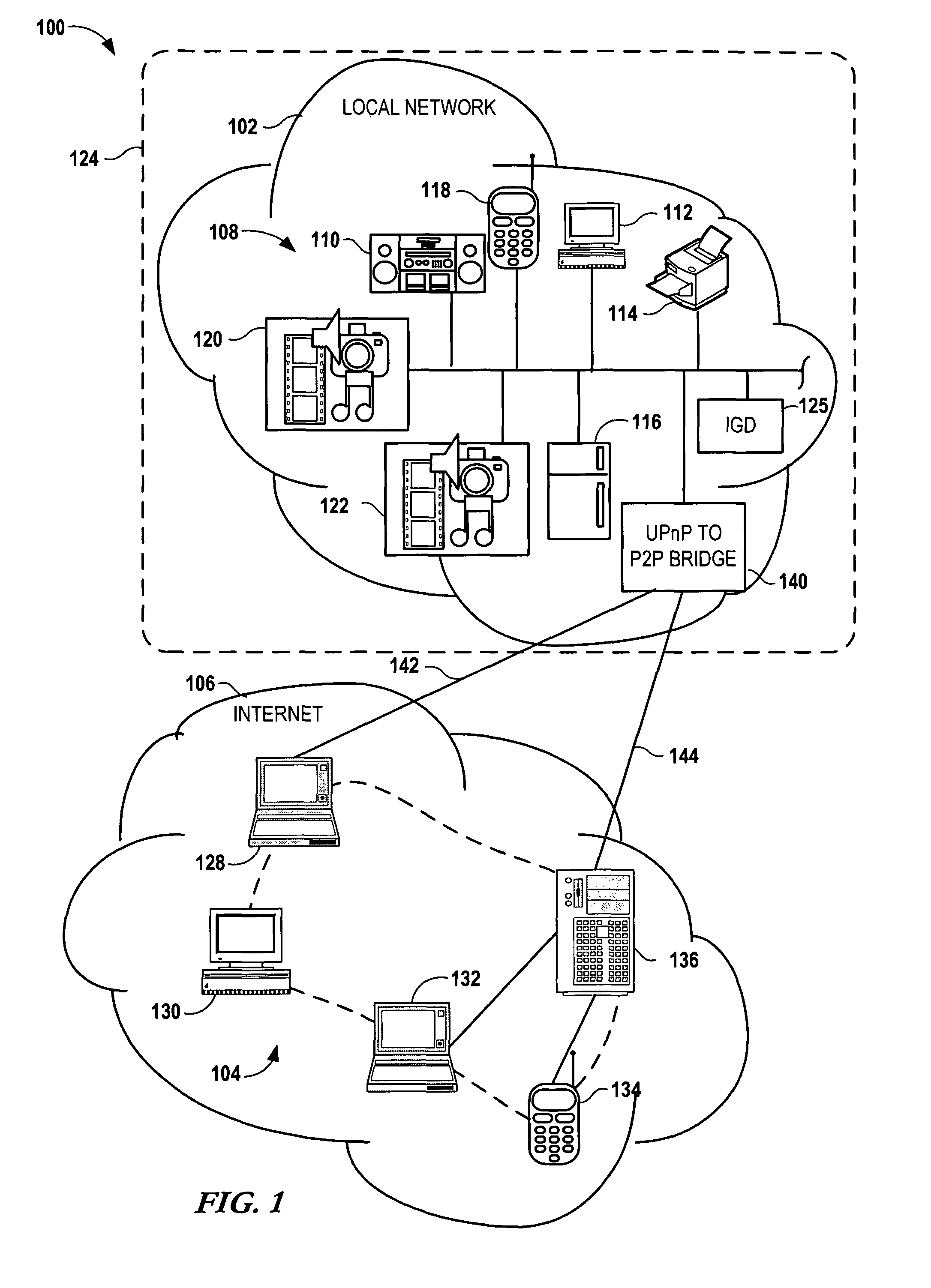
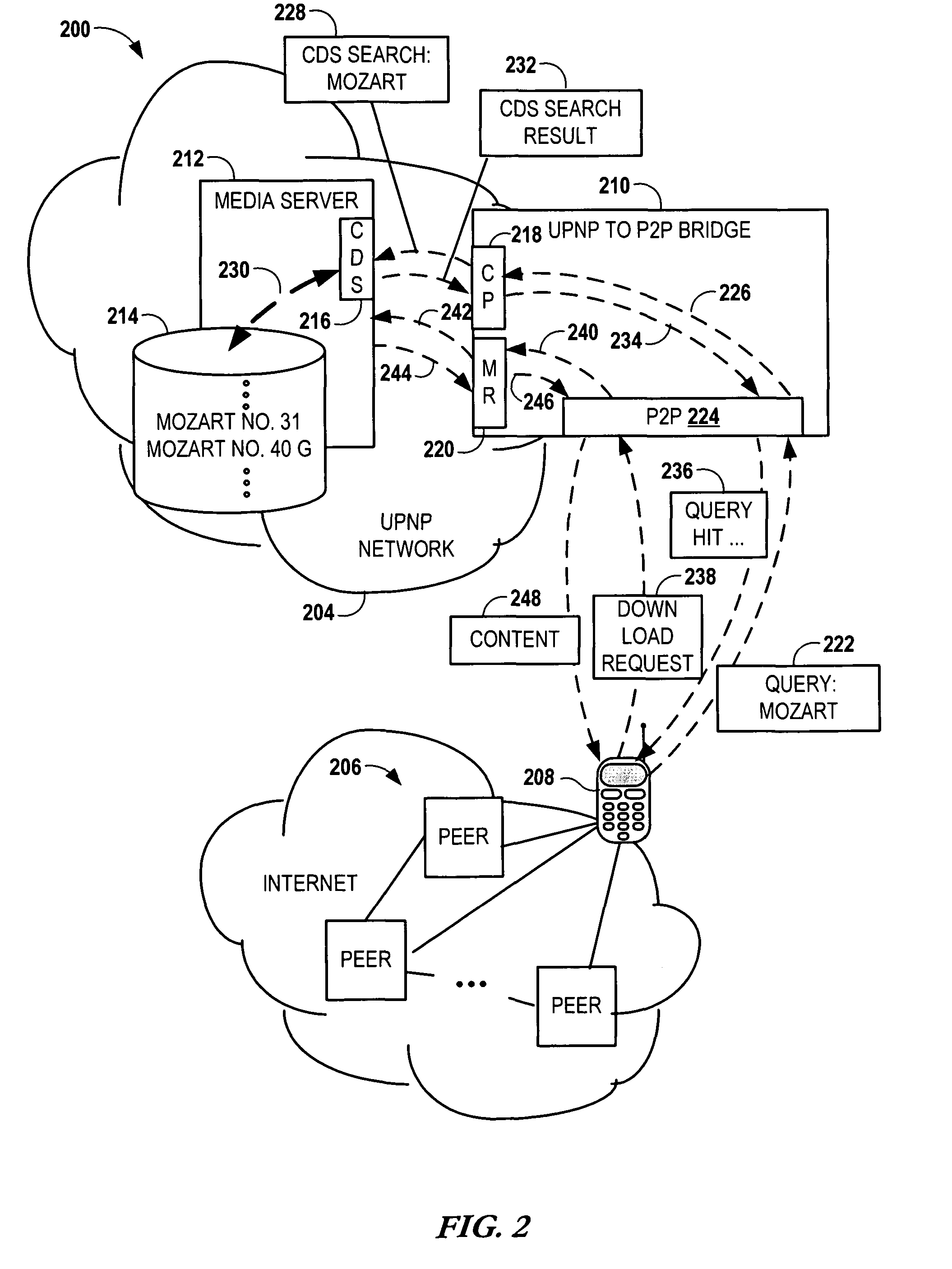
Bridging between AD HOC local networks and internet-based peer-to-peer networks
ActiveUS20070274327A1Easy to downloadFacilitate downloading the mediaData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsNetworking protocolTTEthernet
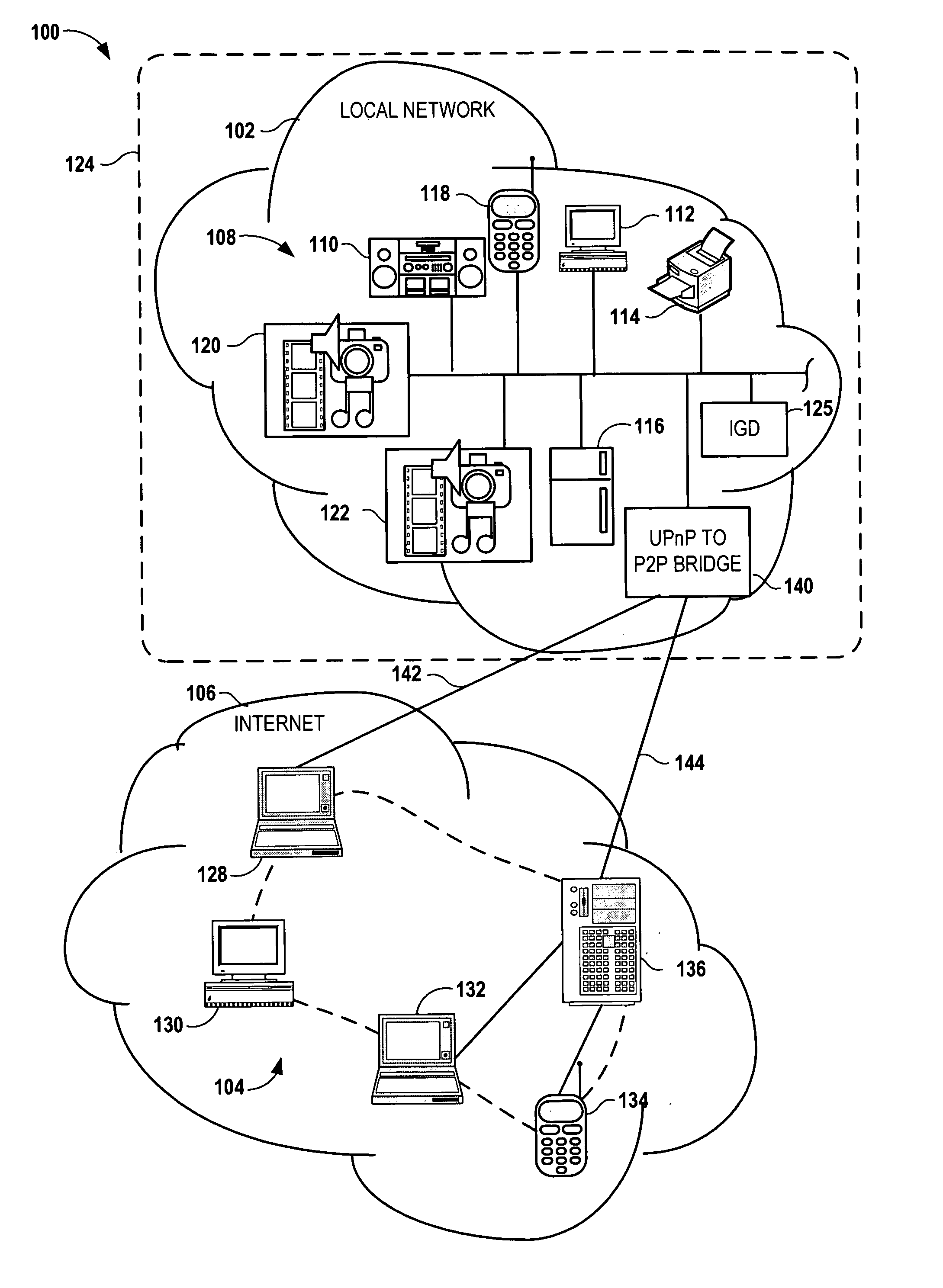
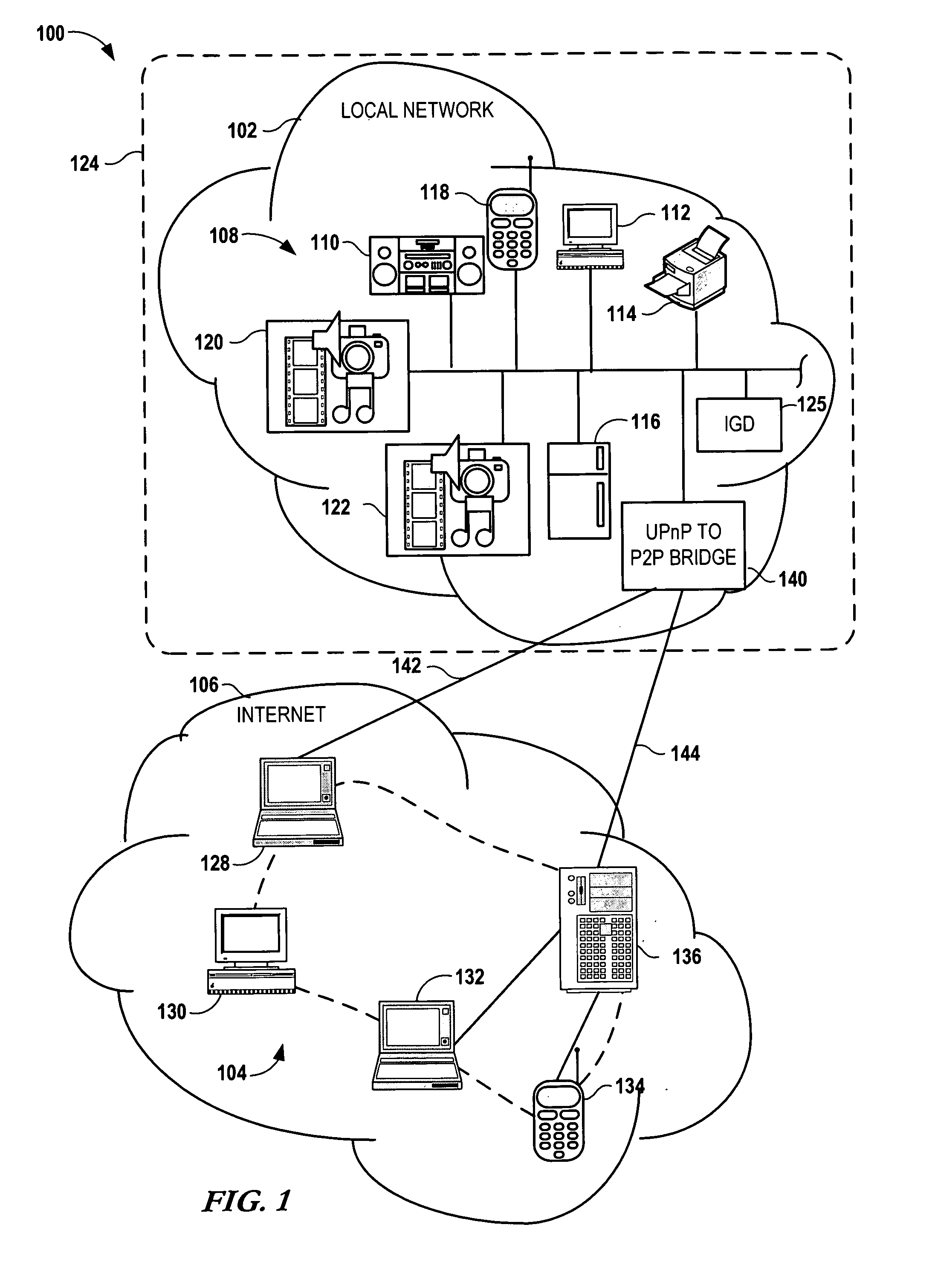
Bridging between ad hoc local networks and Internet based peer-to-peer networks involves coupling a bridge device to a local network using an ad-hoc, peer-to-peer protocol used for exchanging data between consumer electronics devices. The bridge device is coupled to a public network using an Internet-based peer-to-peer networking protocol. In one arrangement, metadata related to media accessible from a media server of the local network is determined via the bridge device, and the metadata is transformed via the bridge device to enable peer-to-peer devices of the public network to discover the media via the bridge device using the Internet-based peer-to-peer networking protocol. In another arrangement, metadata related to media accessible from the public network is determined via the peer-to-peer networking protocol, and the metadata is transformed via the bridge device to enable a device of the local network to discover the media via the bridge device using the ad-hoc, peer-to-peer protocol.
Owner:CONVERSANT WIRELESS LICENSING LTD
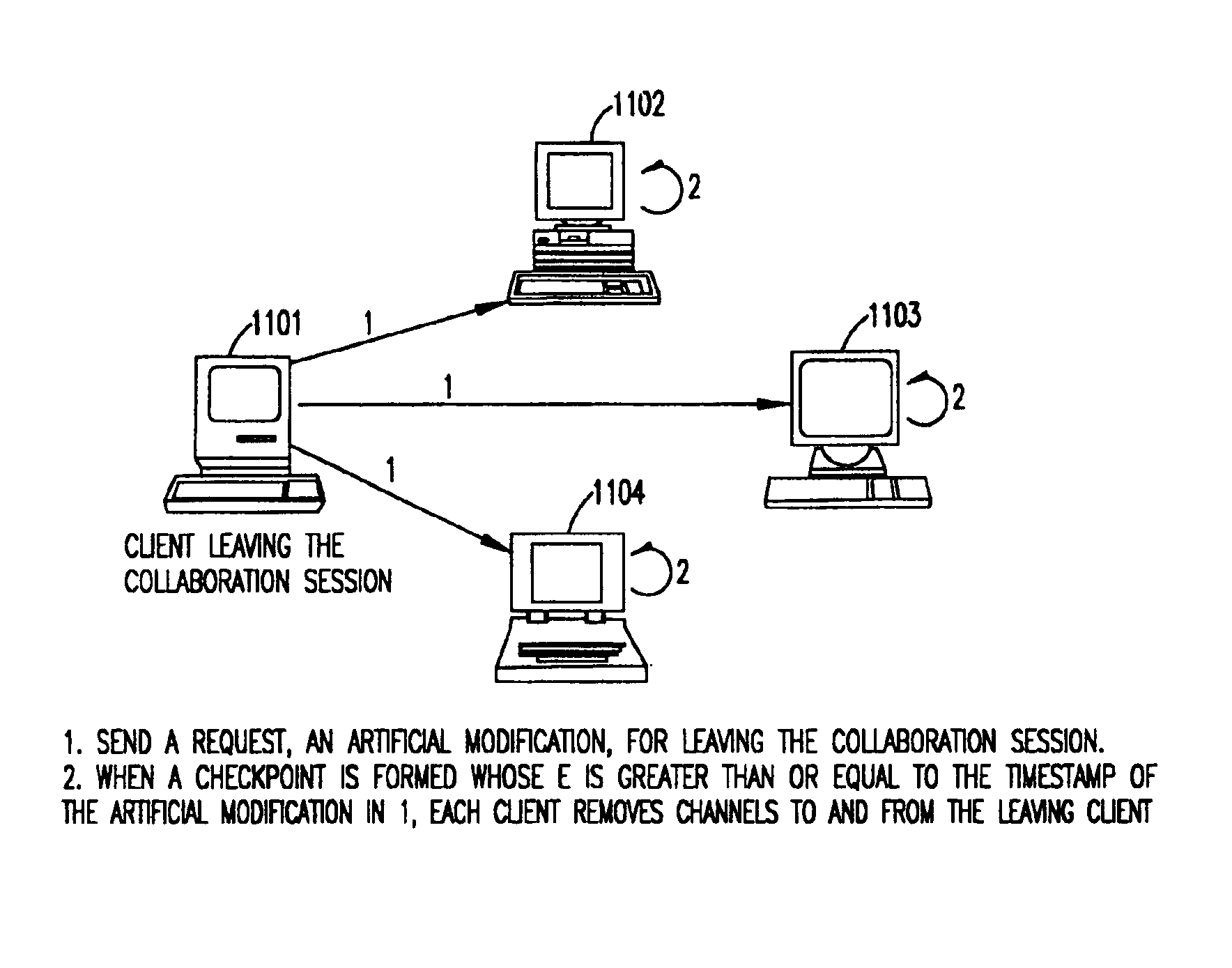
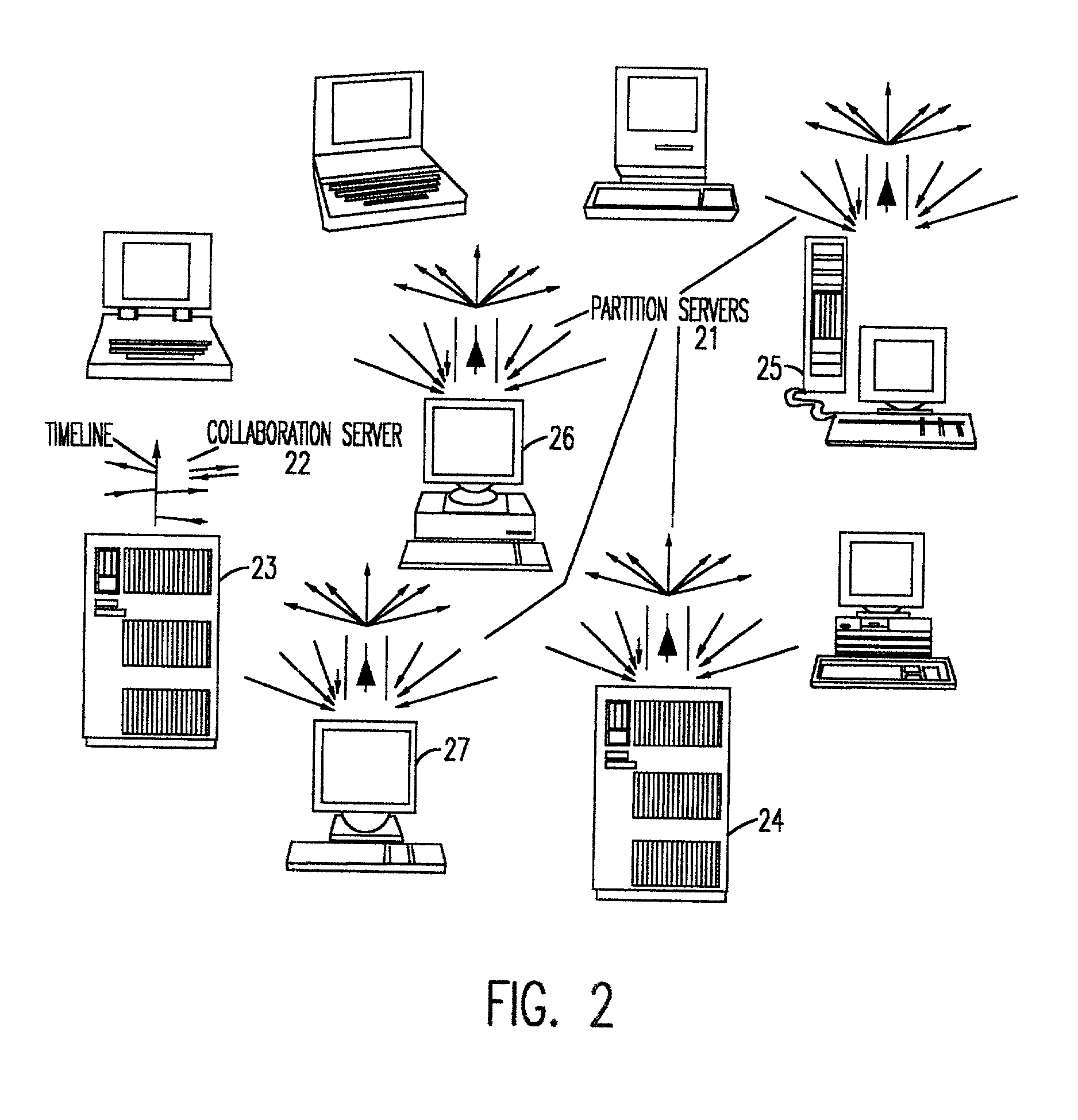
Synchronous collaboration based on peer-to-peer communication
InactiveUS6898642B2Eliminate useFully treatDigital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsTimestampWorkspace
A peer-to-peer protocol is based on the use of global timestamps and client priorities in serializing modifications to a shared workspace of real-time collaboration. The method caters to dynamic clients wherein a client can leave or join an ongoing collaboration session as long as there is always at least one client present / remaining in the collaboration session. The method can support multiple definitions of a modification, including partitioning-based definitions, wherein the method provides full support for locking of partitions, and a full treatment of inter-partition synchronization via a modification definition over multiple partitions. The method is capable of utilizing the many standard methods of creating a global, distributed, synchronized clock for the global timestamps utilized by it. The method is rollback-based for correcting tentative but incorrect serializations, and provides additional backup in terms of checkpoints for additional safety and for the support of lightweight, pervasive clients. The method includes many optimizations for efficiency, and includes a method of switching to and back from distributed server-based serialization for the periods when the network response is better suited to a distributed server than the peer-to-peer protocol.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
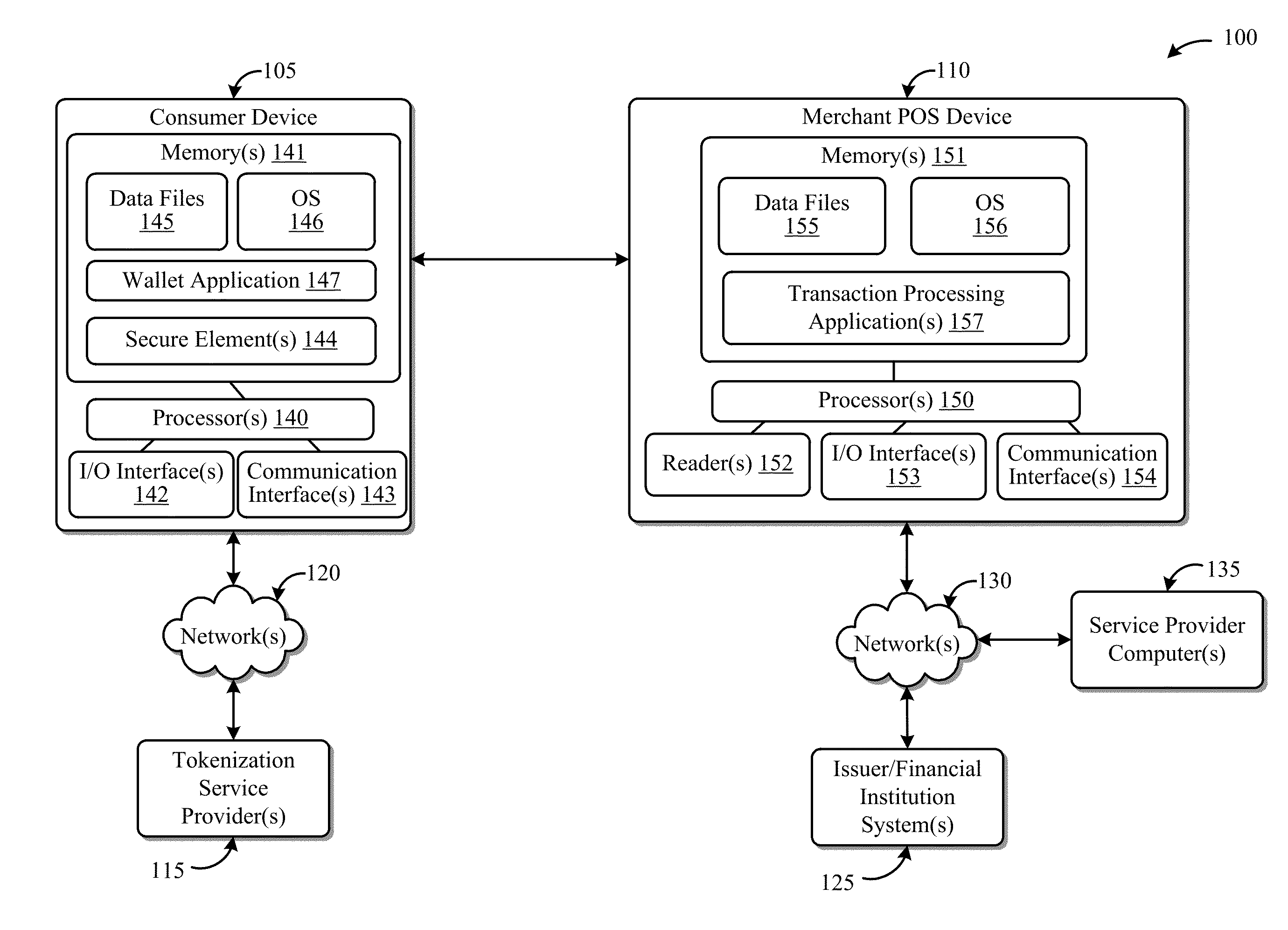
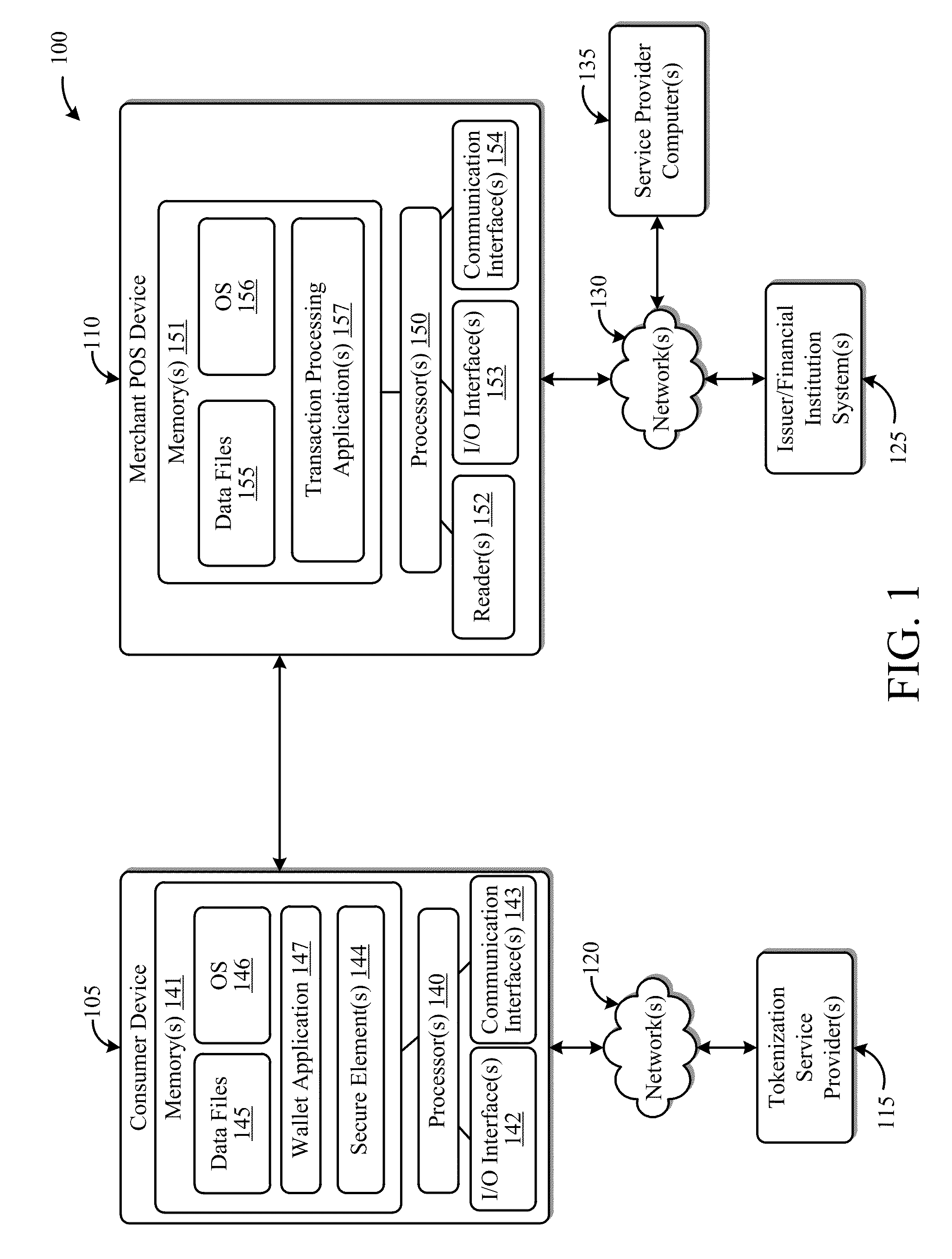
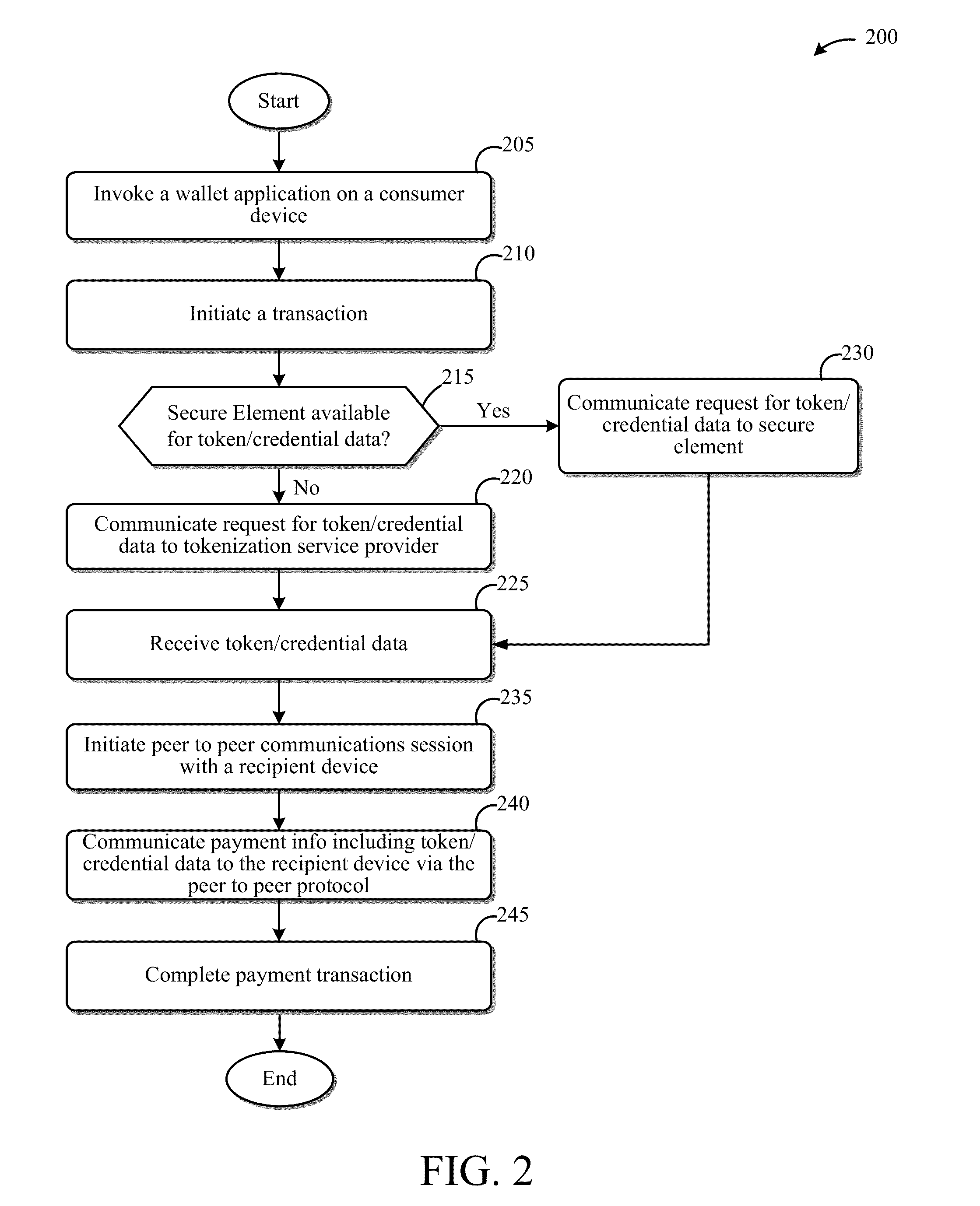
Systems and Methods for Facilitating Payments Via a Peer-to-Peer Protocol
ActiveUS20130254052A1Facilitate peer-to-peer communicationEasy to completeHand manipulated computer devicesFinancePoint-to-Point ProtocolPayment transaction
This disclosure describes systems and methods related to facilitating payments via a peer-to-peer protocol. Tokenized information associated with a payment transaction may be obtained. Establishment of a peer-to-peer communications session with a payment recipient device may be facilitated. The tokenized information to the recipient device via the established peer-to-peer communications session may be communicated in order to facilitate completion of the payment transaction.
Owner:FIRST DATA
Advertisements for peer-to-peer computing resources
A system and method for providing advertisements in a peer-to-peer networking environment is described. In one embodiment, the peer-to-peer protocols may use advertisements to describe and publish the existence of peer resources. An advertisement may be defined as a structured, language neutral metadata structure that names, describes, and publishes the existence of a peer-to-peer platform resource, such as a peer, a peer group, a pipe, or a service. In one embodiment, user-defined advertisement subtypes (for example, using XML schemas) may be formed from these basic types. A peer in a peer-to-peer network may publish a resource advertisement to make the resource corresponding to the advertisement available to other peers on the network. Peers may discover published advertisements by broadcasting discovery query messages. Other peers may respond to discovery query messages by sending response messages that may include advertisements.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Peer-to-peer email messaging
ActiveUS20040064511A1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksClient-sideDistributed computing
System and method for facilitating communications between peers in a peer-to-peer environment and network email clients. In one embodiment, network nodes including peer nodes may host mail transfer agents. The mail transfer agents may act as bridges between peer-to-peer protocols and email communication protocols. The mail transfer agents may communicate with peers according to peer-to-peer protocols and with email clients according to email communications protocols. Peers may communicate with mail transfer agents to send peer-to-peer messages to email clients. Email clients may communicate with the mail transfer agents to send email messages to and receive email messages from other email clients via the peer-to-peer network and to obtain peer-to-peer messages from peers.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
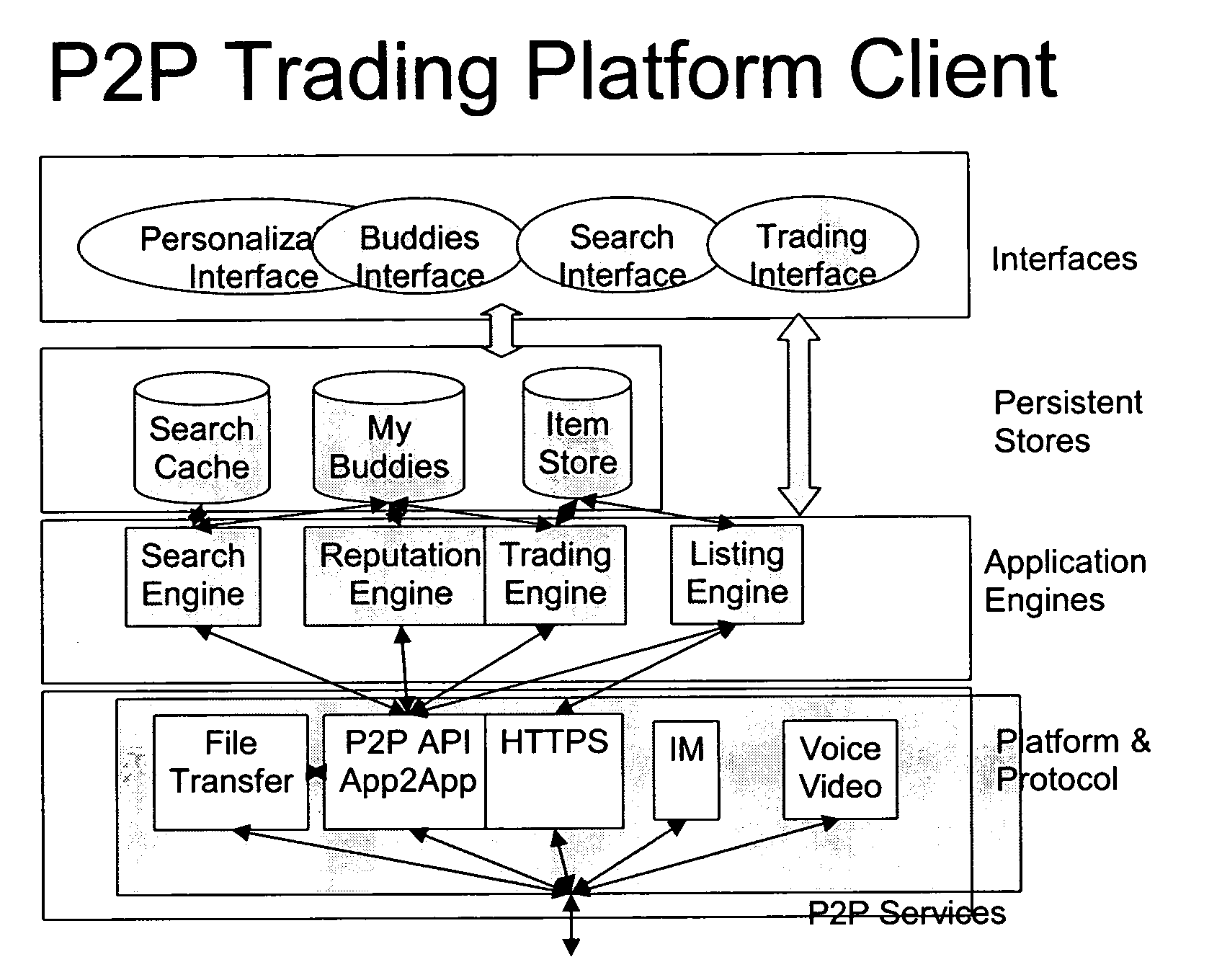
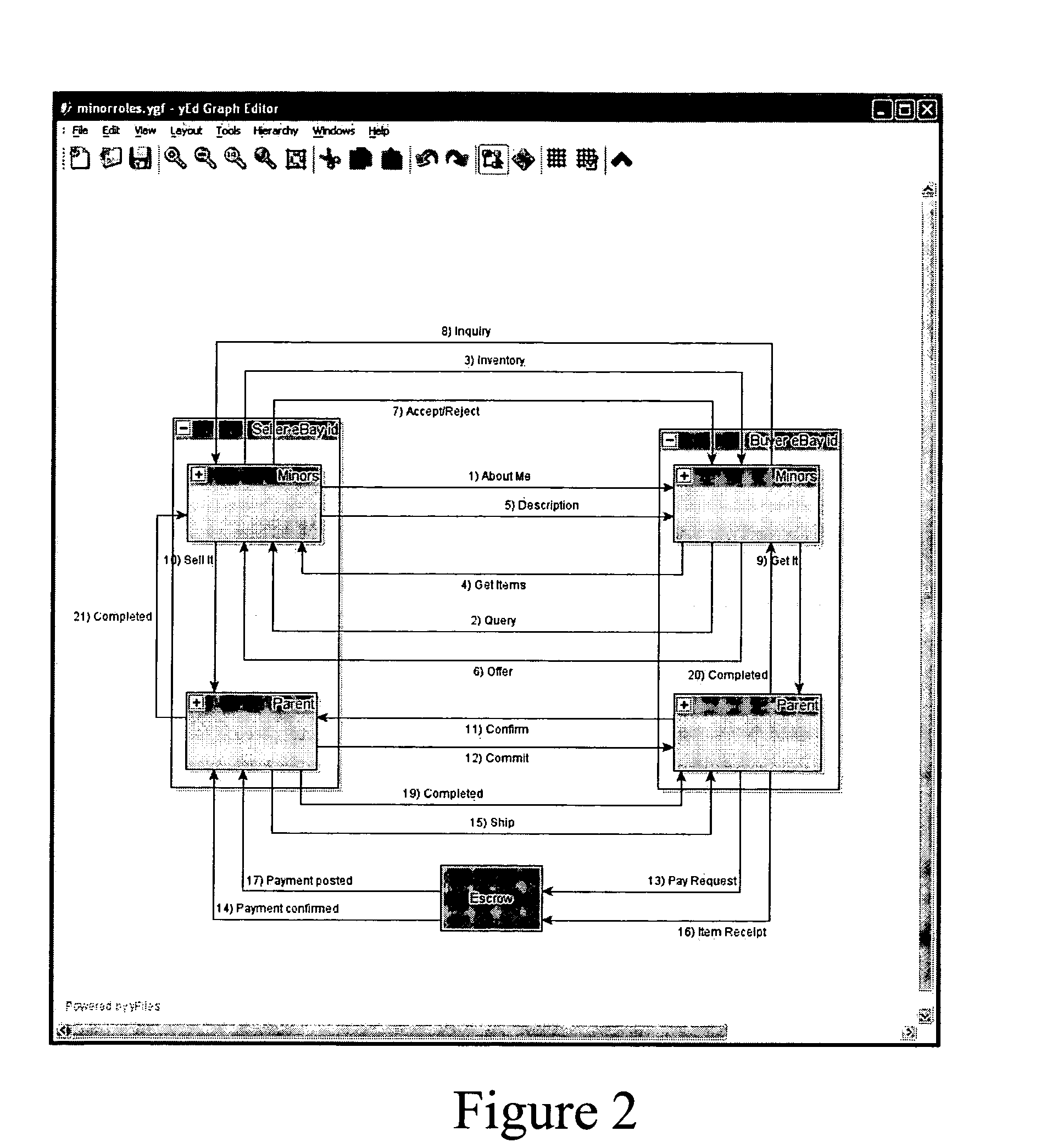
Peer-to-peer trading platform with relative reputation-based item search and buddy rating
ActiveUS20070214259A1Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsApplication softwareClient-side
Owner:EBAY INC
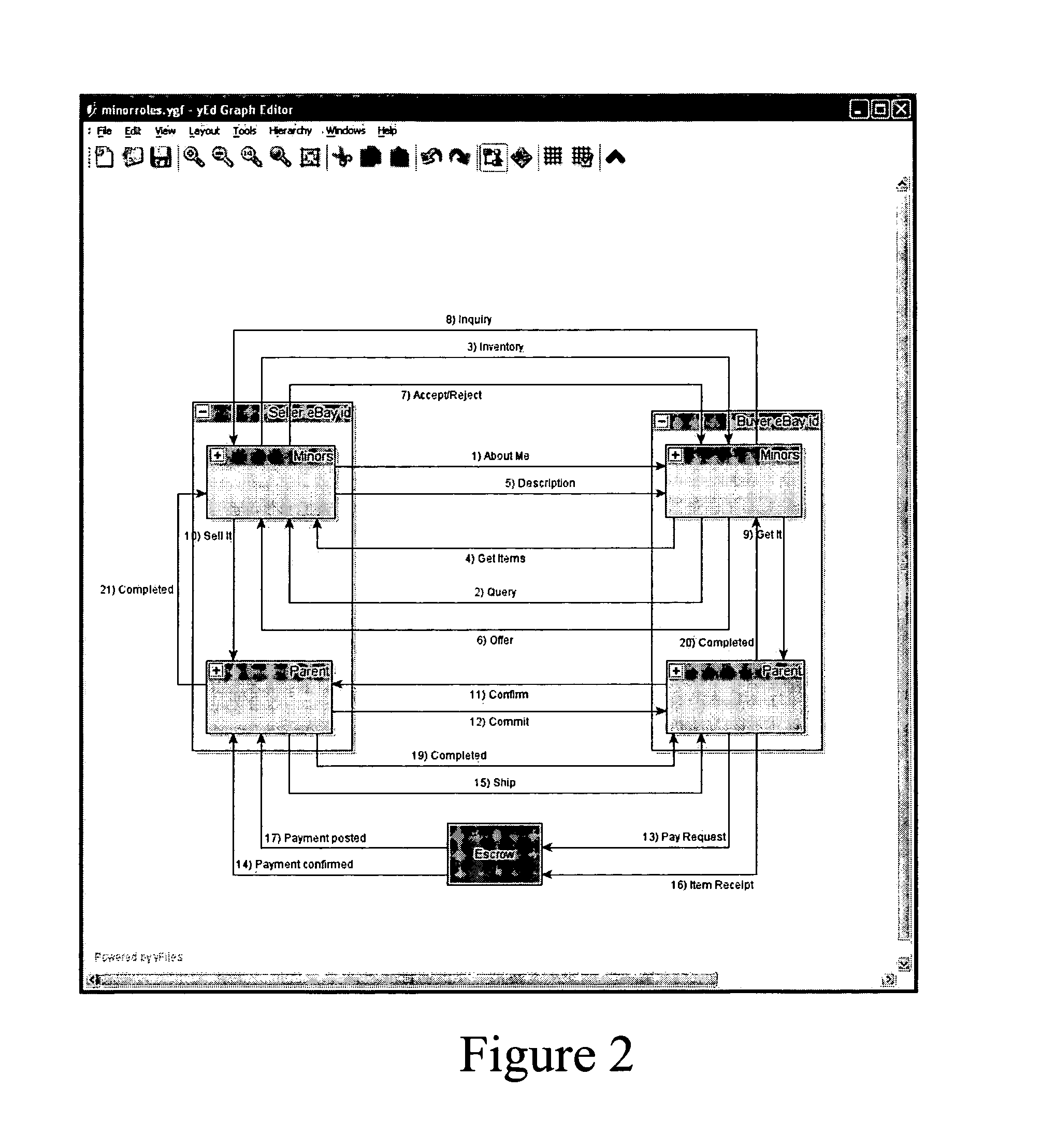
Peer-to-peer trading platform with roles-based transactions
A computer-implemented method and system is disclosed in which a network-based interaction environment includes a plurality of peer-to-peer nodes being able to communicate directly with each other using a peer-to-peer protocol and a peer-to-peer client application, and a first peer-to-peer client application running on a first peer-to-peer client of the plurality of peer-to-peer nodes, the first peer-to-peer client application to maintain persistent user account information on the first peer-to-peer client, the persistent information being related to a plurality of user accounts for conducting e-commerce interactions on the network-based interaction environment, the plurality of user accounts including at least one user account based on a plurality of roles of a corresponding user.
Owner:EBAY INC
Method and apparatus for sharing applications using P2P protocol
InactiveUS20050120073A1Efficient sharingData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsClient-sidePeer-to-Peer Protocol
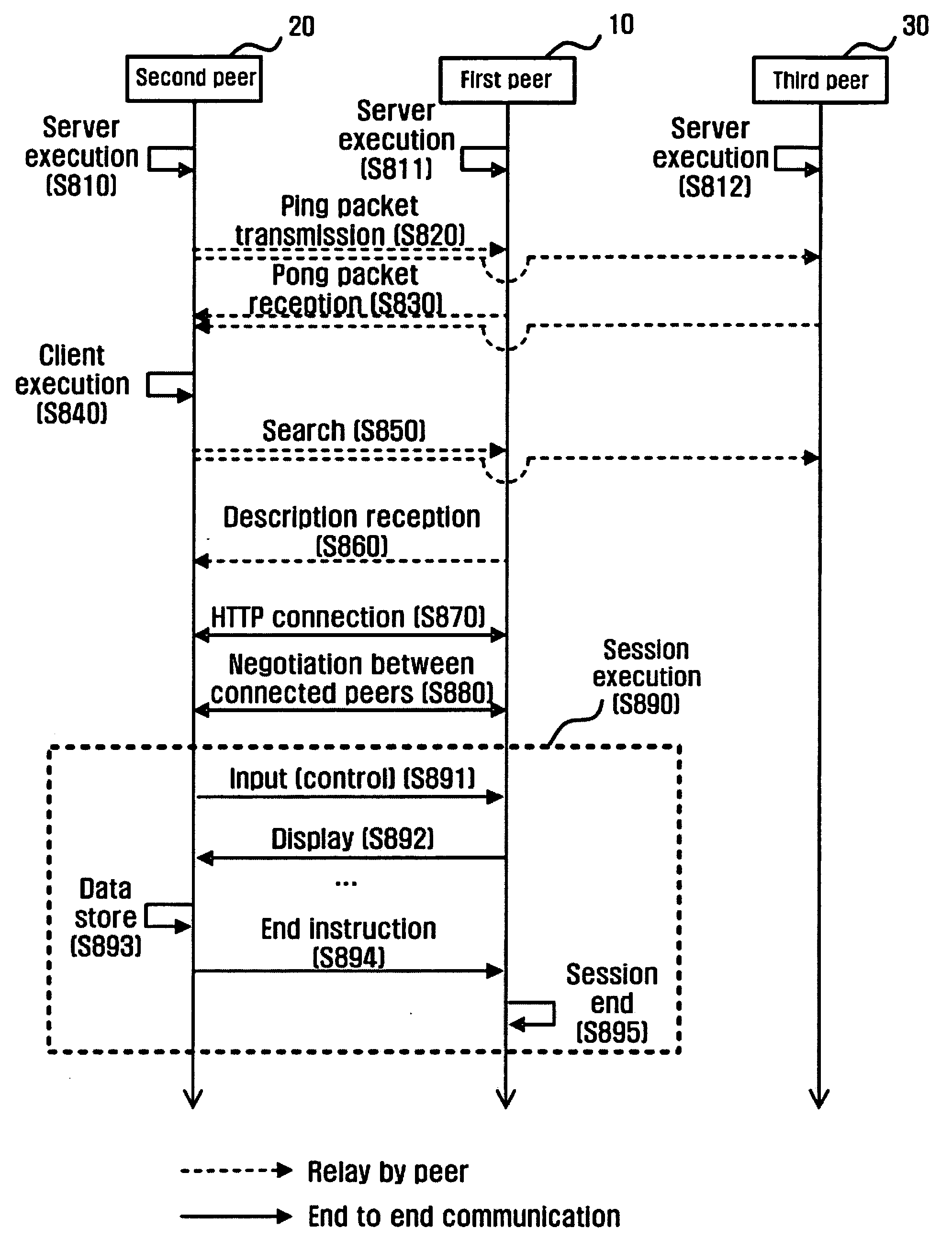
A method of sharing applications using a peer-to-peer protocol includes registering, by a first peer, applications to be shared; determining whether the registered application files meet a search condition included in an application search instruction that is received from a second peer, and transmitting a description file to the second peer in response to the determination results; making a connection to the second peer through a predetermined protocol to perform a service pertaining to an application meeting the search condition; and executing a session for providing a remote display service pertaining to the application for the second peer, such that client peers can share idle resources in server peers, and can use applications that cannot be executed with their current resources or in their current environments.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
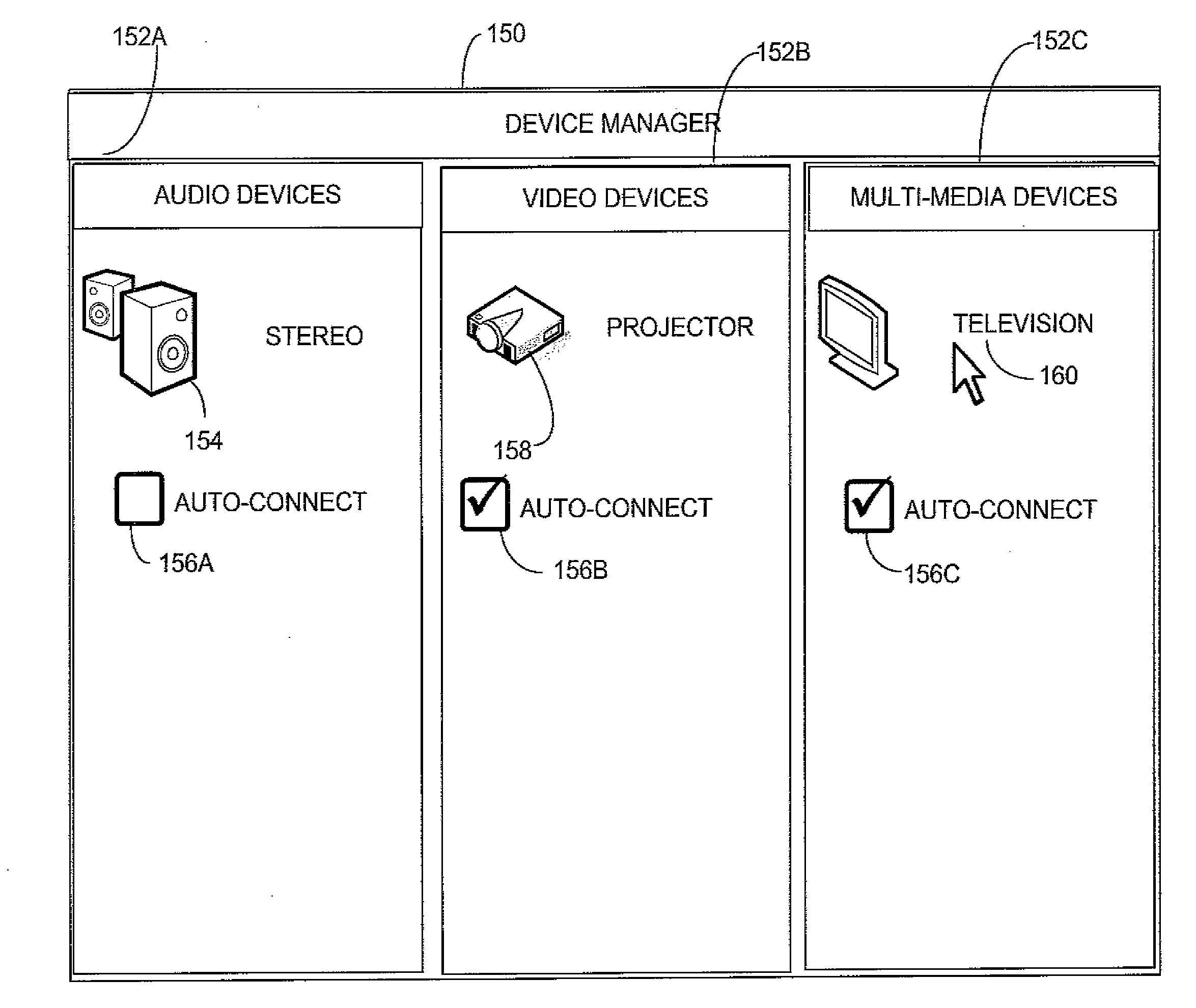
Auto-connect in a peer-to-peer network
ActiveUS20120297229A1Quick identificationDrain controlHardware monitoringConnection managementUser inputPeer-to-Peer Protocol
A wireless device that automatically forms a connection to a remote device in accordance with a peer-to-peer protocol. The remote device may be designated as an auto-connect device for the wireless device such that, when the wireless device determines that it is in the vicinity of the auto-connect device, it can re-form a connection to the remote device based on stored information for re-establishing connections among a persistent group of devices, but without any express user input. When a user requests that the wireless device perform a function that involves interaction with an auto-connect device, that function may be performed with the delay associated with forming a connection. Any of multiple techniques may be employed for identifying devices designated as auto-connect devices and for determining when the wireless device and a remote, auto-connect devices are in close proximity.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Apparatuses and methods for facilitating communication of devices
InactiveUS20090023476A1Facilitate communicationSubstation equipmentSensing record carriersSmart cardPeer-to-Peer Protocol
A system for facilitating communication between an initiator and a target is provided. The initiator transmits a signal to the target including an indication of the communication capability of the initiator. For example, the indication may specify that the initiator is a peer-to-peer capable device. In this way, if the target is configured to communicate according to multiple techniques, such as peer-to-peer protocols and proximity card techniques, the target may be able to determine the appropriate communication method to use. Furthermore, the target may be able to change from a smart card emulation to a peer-to-peer configuration based on the indication received. Corresponding methods, apparatuses, and computer program products are also provided.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Peer-to-peer trading platform with search caching
ActiveUS20070214250A1Digital computer detailsCommerceClient-sideProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access
A computer-implemented method and system is disclosed in which a network-based interaction environment includes a plurality of peer-to-peer nodes being able to communicate directly with each other using a peer-to-peer protocol and a peer-to-peer client application, the plurality of peer-to-peer nodes including a first peer-to-peer client, a second peer-to-peer client, and a third peer-to-peer client, a first peer-to-peer client application running on the first peer-to-peer client to process persistent item information on the first peer-to-peer client, the persistent item information being related to an item being offered by a first user of the first peer-to-peer client application, a second peer-to-peer client application running on the second peer-to-peer client to cache the persistent item information on the second peer-to-peer client; and a third peer-to-peer client application running on the third peer-to-peer client to search a cache of the second peer-to-peer client for the persistent item information related to the item being offered by the first user.
Owner:EBAY INC
Synchronous collaboration based on peer-to-peer communication
InactiveUS20020152271A1Fully treatImprove interoperabilityDigital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsTimestampWorkspace
A peer-to-peer protocol is based on the use of global timestamps and client priorities in serializing modifications to a shared workspace of real-time collaboration. The method caters to dynamic clients wherein a client can leave or join an ongoing collaboration session as long as there is always at least one client present / remaining in the collaboration session. The method can support multiple definitions of a modification, including partitioning-based definitions, wherein the method provides full support for locking of partitions, and a full treatment of inter-partition synchronisation via a modification definition over multiple partitions. The method is capable of utilizing the many standard methods of creating a global, distributed, synchronized clock for the global timestamps utilized by it. The method is rollback-based for correcting tentative but incorrect serializations, and provides additional backup in terms of checkpoints for additional safety and for the support of lightweight, pervasive clients. The method includes many optimizations for efficiency, and includes a method of switching to and back from distributed server-based serialization for the periods when the network response is better suited to a distributed server than the peer-to-peer protocol.
Owner:IBM CORP
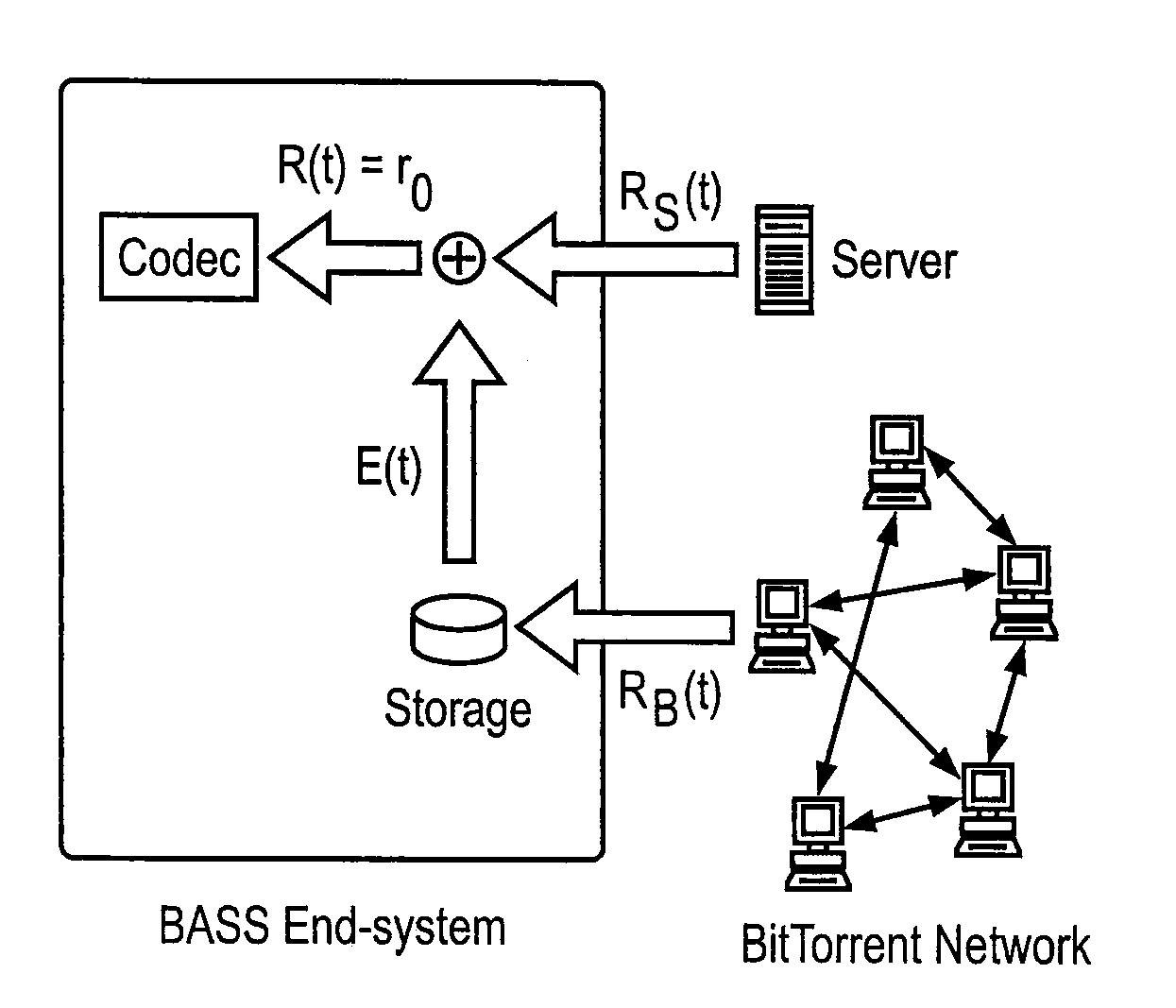
Peer-to-Peer Streaming Of Non-Live Content
ActiveUS20080140853A1Minimal impactEasy to scaleMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionPoint-to-Point ProtocolEnd system
A Peer-to-Peer protocol such as BitTorrent is used to assist streaming. Peers download streaming content from the P2P network while simultaneously playing the downloaded content. As the stream plays, an end system downloads any missing pieces directly from a server or other infrastructure node. This method roughly squares server capacity and can be refined to require on average 0(1) servers regardless of the number of concurrent users. Thus BitTorrent assisted streaming scales better than traditional server-client and other infrastructure-only solutions, each of which requires a number of infrastructure nodes that scale linearly as a function of the number of users. Unlike End-System-Multicast, BitTorrent assisted streaming does not subject users to the vagaries of intermediate unreliable, potentially bandwidth-constrained end-systems; the departure of any single end-system has minimal impact on overall performance; and BitTorrent has a well-crafted incentive mechanism for encouraging users to contribute their upstream capacity.
Owner:BITTORRENT
Peer-to-peer trading platform with search caching
A computer-implemented method and system is disclosed in which a network-based interaction environment includes a plurality of peer-to-peer nodes being able to communicate directly with each other using a peer-to-peer protocol and a peer-to-peer client application, the plurality of peer-to-peer nodes including a first peer-to-peer client, a second peer-to-peer client, and a third peer-to-peer client, a first peer-to-peer client application running on the first peer-to-peer client to process persistent item information on the first peer-to-peer client, the persistent item information being related to an item being offered by a first user of the first peer-to-peer client application, a second peer-to-peer client application running on the second peer-to-peer client to cache the persistent item information on the second peer-to-peer client; and a third peer-to-peer client application running on the third peer-to-peer client to search a cache of the second peer-to-peer client for the persistent item information related to the item being offered by the first user.
Owner:EBAY INC
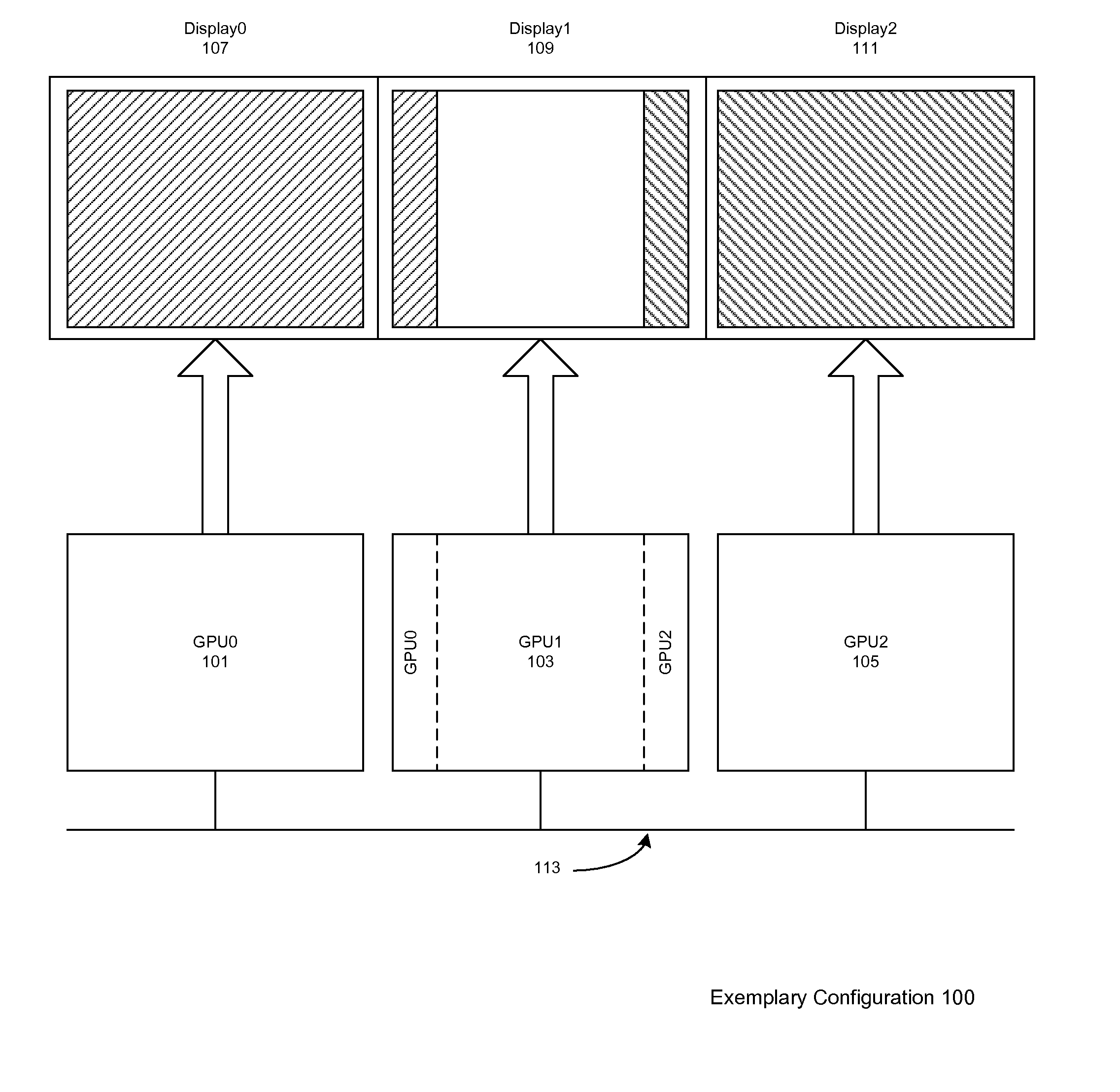
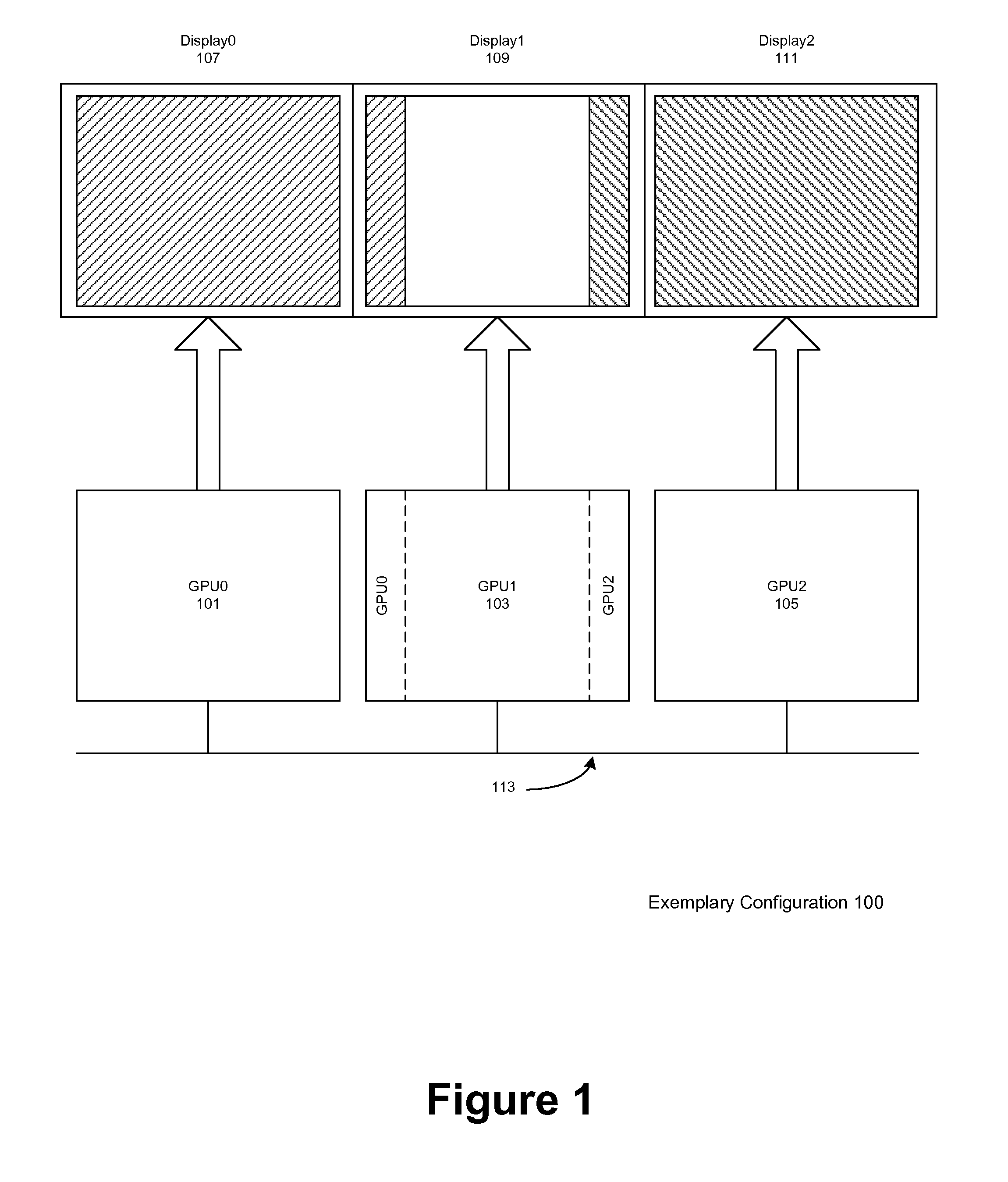
Load balancing in a system with multi-graphics processors and multi-display systems
ActiveUS20110157193A1Optimize allocationLow efficiencyCathode-ray tube indicatorsProcessor architectures/configurationGraphicsSplit lines
In typical embodiments a three GPU configuration is provided comprising three discrete video cards, each connected to a standard monitor placed horizontally for a 3× horizontal resolution. In this configuration, depending on the load on each GPU, the vertical split lines are dynamically adjusted. To adjust the load balancing according to these virtual split lines, the rendering clip rectangle of each GPU is adjusted, in order to reduce the number of pixels rendered by the heavily loaded GPU. These split lines define the boundary of the scene to be rendered by each GPU, and, according to some embodiments, may be moved horizontally. Thus for example if a GPU has a more complex rendering clip polygon to render than the other GPUs, the neighboring GPUs may render the rendering clip polygon it displays plus a portion of the rendering clip polygon to be displayed by heavily loaded GPU. The assisting GPUs transmit to the heavily loaded GPU the portion of the rendering clip polygon to be displayed by GPU via the chipset with a peer-to-peer protocol or through a communication bus. The split line is dynamically adjusted after each scene.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Peer-to-peer email messaging
ActiveUS7849140B2Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksClient-sideDistributed computing
System and method for facilitating communications between peers in a peer-to-peer environment and network email clients. In one embodiment, network nodes including peer nodes may host mail transfer agents. The mail transfer agents may act as bridges between peer-to-peer protocols and email communication protocols. The mail transfer agents may communicate with peers according to peer-to-peer protocols and with email clients according to email communications protocols. Peers may communicate with mail transfer agents to send peer-to-peer messages to email clients. Email clients may communicate with the mail transfer agents to send email messages to and receive email messages from other email clients via the peer-to-peer network and to obtain peer-to-peer messages from peers.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Auto connect in peer-to-peer network
ActiveUS20120296986A1Quick identificationDrain controlConnection managementMultiple digital computer combinationsUser inputComputer science
A wireless device that automatically forms a connection to a remote device in accordance with a peer-to-peer protocol. The remote device may be designated as an auto-connect device for the wireless device such that, when the wireless device determines that it is in the vicinity of the auto-connect device, it can re-form a connection to the remote device based on stored information for re-establishing connections among a persistent group of devices, but without any express user input. When a user requests that the wireless device perform a function that involves interaction with an auto-connect device, that function may be performed with the delay associated with forming a connection. Any of multiple techniques may be employed for identifying devices designated as auto-connect devices and for determining when the wireless device and a remote, auto-connect devices are in close proximity.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Advanced switching peer-to-peer protocol
InactiveUS20060004837A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network AccessDistributed computing
A peer-to-peer connection protocol for establishing and managing peer-to-peer connections between endpoints coupled via a serial-based interconnect fabric. A requesting endpoint generates and sends a query to a fabric manager requesting connection information for at least one target endpoint having attributes matching attributes specified in the query. The fabric manager returns a query reply containing connection information to connect the requesting endpoint to a target endpoint or multiple target endpoints having matching attributes. In the case of multiple target endpoints, one target endpoint is selected for the connection. The requesting and target endpoints then negotiate and establish the connection by passing connection information and parameters between themselves directly. Upon establishing the connection, the fabric manager is apprised of the new connection and updates its connection list. The method is facilitated by software components running on various devices coupled to the serial-based interconnect fabric. Such devices include server blades and ATCA boards. In one embodiment, the serial-based interconnect fabric comprises an Advanced Switching (AS) fabric.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Peer-to-peer communication optimization
InactiveUS20100293294A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionApplication softwareClient-side
A peer-to-peer communication optimizer uses both peer locality and content diversity in a peer group to reduce network usage cost associated with using remote peers in a peer-to-peer system while reducing impact on the download time relative to peer-to-peer protocols operating with locality optimization alone or no localization of peers. The optimizer intercepts control messages in the peer-to-peer system and substitutes peer lists that meet both diversity indicator and network usage cost thresholds. Transparent embodiments operate without requirement to change peer or tracker implementations. Such embodiments include control message redirection, interception, and modification transparent to the client and tracker applications. Other embodiments include proxy designation. Still other embodiments include the use of gateway peers selected as function of diversity of content and network topology. Still other embodiments involve modification to one or more of client and / or tracker software and potentially the use of a standard interface for network topology determination.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
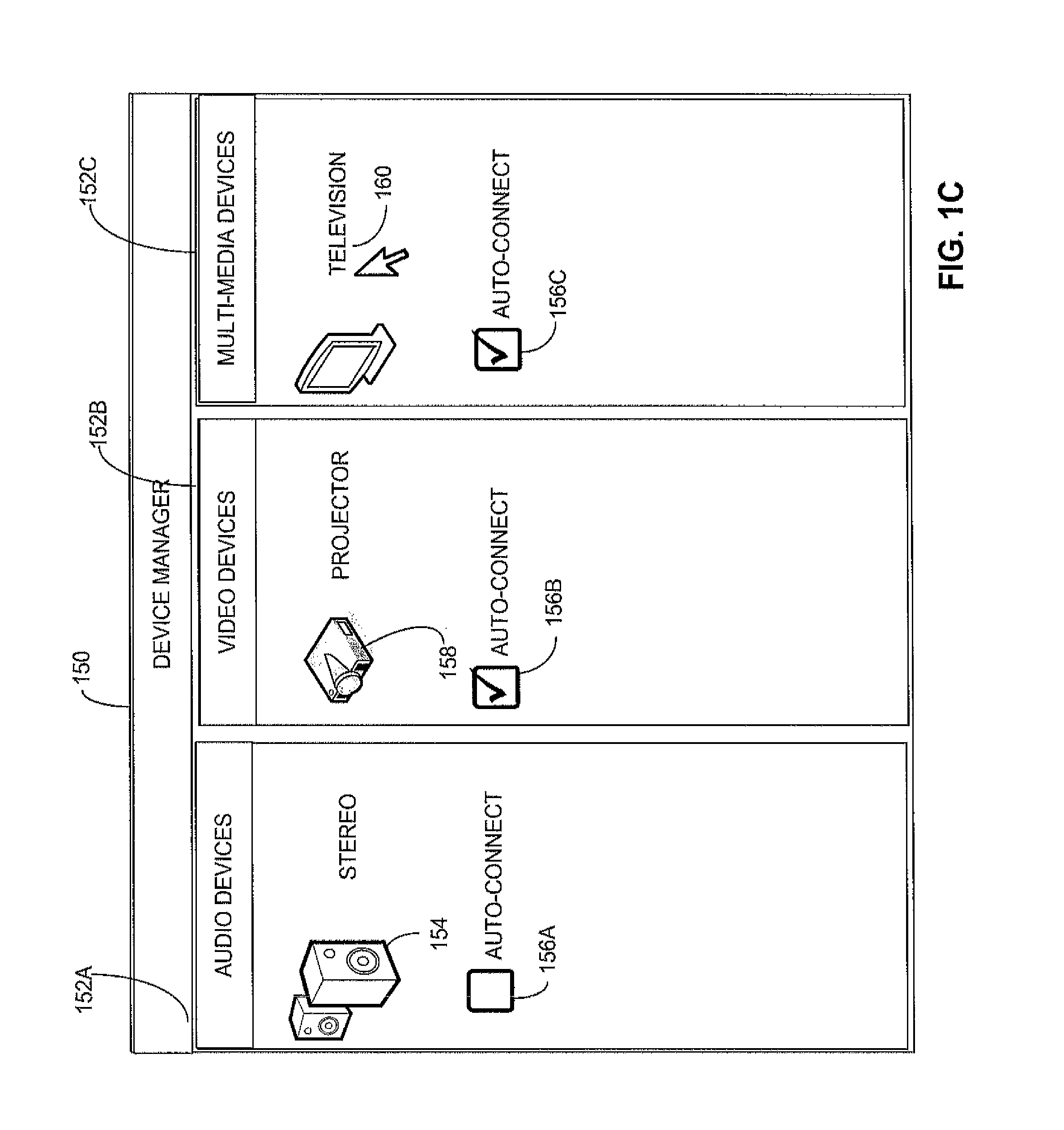
Mass re-formation of groups in a peer-to-peer network
ActiveUS20120290730A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionFrequency spectrumDevice form
A system in which wireless devices form a group in accordance with a peer-to-peer protocol and, at a later time, a device may send an invitation request to trigger the devices tore-form the peer-to-peer group. The invitation request may contain an identifier that is associated with a set of a plurality of devices. Those devices may be related such that they perform a function for which a user would want to use those devices together. The group of devices, for example, may be multimedia devices that receive and present streaming multimedia content or may be human interface devices that collectively act as an interface for a work station incorporating a wireless computing device operated by a user. Requesting that remote devices concurrently re-form a group reduces the time and spectral congestion associated with re-forming the group, particularly when the remote devices may periodically enter a low power state.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Social networking on a website with topic-based data sharing
ActiveUS20090164475A1Guaranteed continuous availabilityDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsPersonalizationNetizen
A method and system for constructing a social network using advanced content-based indexing, data and index sharing, and a peer-to-peer network in conjunction with a web site interface. The system uses novel indexing techniques to identify and share common interests among users of the network, and integrated peer-to-peer software facilitates data sharing based on these interests.Users who wish to join the social network download client software from the network's web site. When installed, the software indexes data on the user's local storage devices by considering possible high- and low-order links between data elements, mimicking human intuition. The indexing software generates an index of user data that is partitioned or into separate topic indexes. This index represents a cross-section of the user's interests. The user is then able to join various “friend” groups on the network, and to select by topic which portions of the index are shared with which friend groups.The client software implements a novel mesh-based, self-healing peer-to-peer protocol for sharing both topic indexes and the indexed data, according to the user's selections. The social network's servers use the index to automatically generate an attractively individualized user profile page. The interface of the social network's website works in conjunction with the indexing and sharing software installed on the user's computing device. Updates to the user's index may cause notifications to be displayed on the web pages of friends who share the same topic. Users may use the web site to select to share data, which is then carried out transparently by the peer-to-peer software installed on the users' devices. This system provides users greater convenience and utility in using the functions of a social networking web site to share data, without having to upload data manually to a server. Versions of the software running both on personal computers and on smaller mobile devices are described.
Owner:INTUIDEX
Peer-to-peer trading platform
ActiveUS20070214249A1Digital computer detailsBuying/selling/leasing transactionsClient-sideApplication software
A computer-implemented method and system is disclosed in which a network-based interaction environment includes a plurality of peer-to-peer nodes being able to communicate directly with each other using a peer-to-peer protocol and a peer-to-peer client application, and a first peer-to-peer client application to maintain persistent item information on at least one peer-to-peer node of the plurality of peer-to-peer nodes, the persistent information being related to an item being offered by a first user of the first peer-to-peer client application.
Owner:EBAY INC
Auto-connect in a peer-to-peer network
ActiveUS20120297306A1Quick identificationDrain controlInput/output for user-computer interactionNetwork topologiesUser inputPeer-to-Peer Protocol
A wireless device that automatically forms a connection to a remote device in accordance with a peer-to-peer protocol. The remote device may be designated as an auto-connect device for the wireless device such that, when the wireless device determines that it is in the vicinity of the auto-connect device, it can re-form a connection to the remote device based on stored information for re-establishing connections among a persistent group of devices, but without any express user input. When a user requests that the wireless device perform a function that involves interaction with an auto-connect device, that function may be performed with the delay associated with forming a connection. Any of multiple techniques may be employed for identifying devices designated as auto-connect devices and for determining when the wireless device and a remote, auto-connect devices are in close proximity.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Use of nodes to monitor or manage peer to peer networks
InactiveUS20050052999A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsApplication softwareDistributed computing
A method for controlling a computer entity to participate in a peer to peer network of a plurality of computer entities comprises, for each computer entity, operating a peer to peer protocol for enabling the computer entity to utilise resources of at least one other computer entity of the network, and for enabling at least one other computer entity of the network to utilise resources of the computer entity. Whenever the resources of a computer entity are not being used by a service application at a higher level layer than the peer to peer protocol, that computer entity is arranged to operate a process for managing at least one other computer entity in the network.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
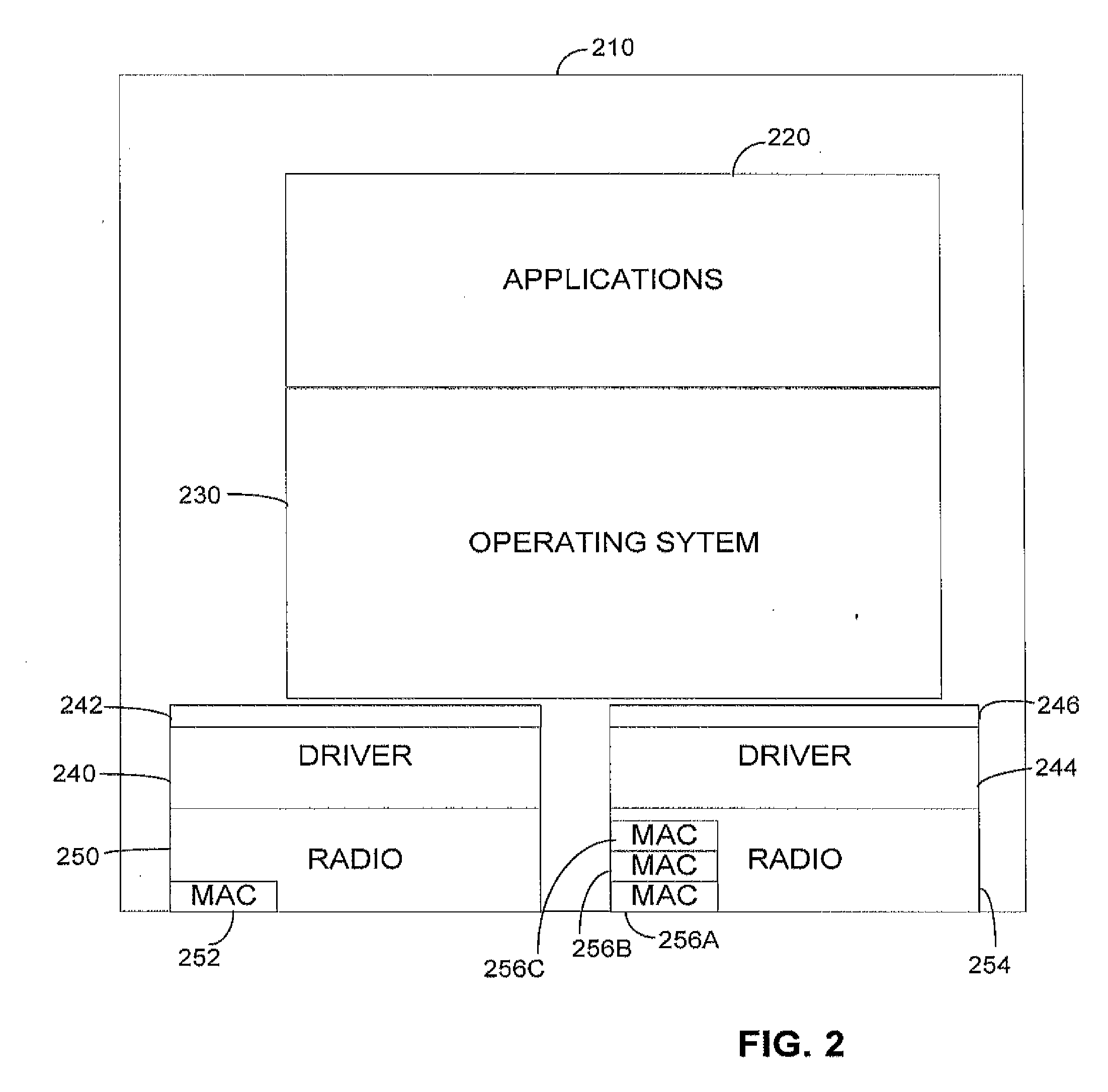
Bridging between AD HOC local networks and internet-based peer-to-peer networks
ActiveUS8194681B2Easy to downloadFacilitate downloading the mediaData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsNetworking protocolMedia server
Bridging between ad hoc local networks and Internet based peer-to-peer networks involves coupling a bridge device to a local network using an ad-hoc, peer-to-peer protocol used for exchanging data between consumer electronics devices. The bridge device is coupled to a public network using an Internet-based peer-to-peer networking protocol. In one arrangement, metadata related to media accessible from a media server of the local network is determined via the bridge device, and the metadata is transformed via the bridge device to enable peer-to-peer devices of the public network to discover the media via the bridge device using the Internet-based peer-to-peer networking protocol. In another arrangement, metadata related to media accessible from the public network is determined via the peer-to-peer networking protocol, and the metadata is transformed via the bridge device to enable a device of the local network to discover the media via the bridge device using the ad-hoc, peer-to-peer protocol.
Owner:CONVERSANT WIRELESS LICENSING LTD
Peer-to-peer trading platform with roles-based transactions
A computer-implemented method and system is disclosed in which a network-based interaction environment includes a plurality of peer-to-peer nodes being able to communicate directly with each other using a peer-to-peer protocol and a peer-to-peer client application, and a first peer-to-peer client application running on a first peer-to-peer client of the plurality of peer-to-peer nodes, the first peer-to-peer client application to maintain persistent user account information on the first peer-to-peer client, the persistent information being related to a plurality of user accounts for conducting e-commerce interactions on the network-based interaction environment, the plurality of user accounts including at least one user account based on a plurality of roles of a corresponding user.
Owner:EBAY INC
Auto connect in peer-to-peer network
ActiveUS8775533B2Quick identificationDrain controlConnection managementMultiple digital computer combinationsUser inputProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access
A wireless device that automatically forms a connection to a remote device in accordance with a peer-to-peer protocol. The remote device may be designated as an auto-connect device for the wireless device such that, when the wireless device determines that it is in the vicinity of the auto-connect device, it can re-form a connection to the remote device based on stored information for re-establishing connections among a persistent group of devices, but without any express user input. When a user requests that the wireless device perform a function that involves interaction with an auto-connect device, that function may be performed with the delay associated with forming a connection. Any of multiple techniques may be employed for identifying devices designated as auto-connect devices and for determining when the wireless device and a remote, auto-connect devices are in close proximity.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Peer-to-peer trading platform with relative reputation-based item search and buddy rating
ActiveUS7877353B2Digital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsClient-sidePeer-to-Peer Protocol
A computer-implemented method and system is disclosed in which a network-based interaction environment includes a plurality of peer-to-peer nodes being able to communicate directly with each other using a peer-to-peer protocol and a peer-to-peer client application, the plurality of peer-to-peer nodes including a first peer-to-peer client and a second peer-to-peer client, a first peer-to-peer client application running on the first peer-to-peer client to maintain persistent buddy information on the first peer-to-peer client, the persistent buddy information including a buddy list identifying trusted peer-to-peer nodes of the plurality of peer-to-peer nodes, and a second peer-to-peer client application running on the second peer-to-peer client to maintain persistent reputation information on the second peer-to-peer client, the persistent reputation information including information related to the reputation of the first peer-to-peer client in the network-based interaction environment.
Owner:EBAY INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com