Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
64 results about "Cannula insertion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
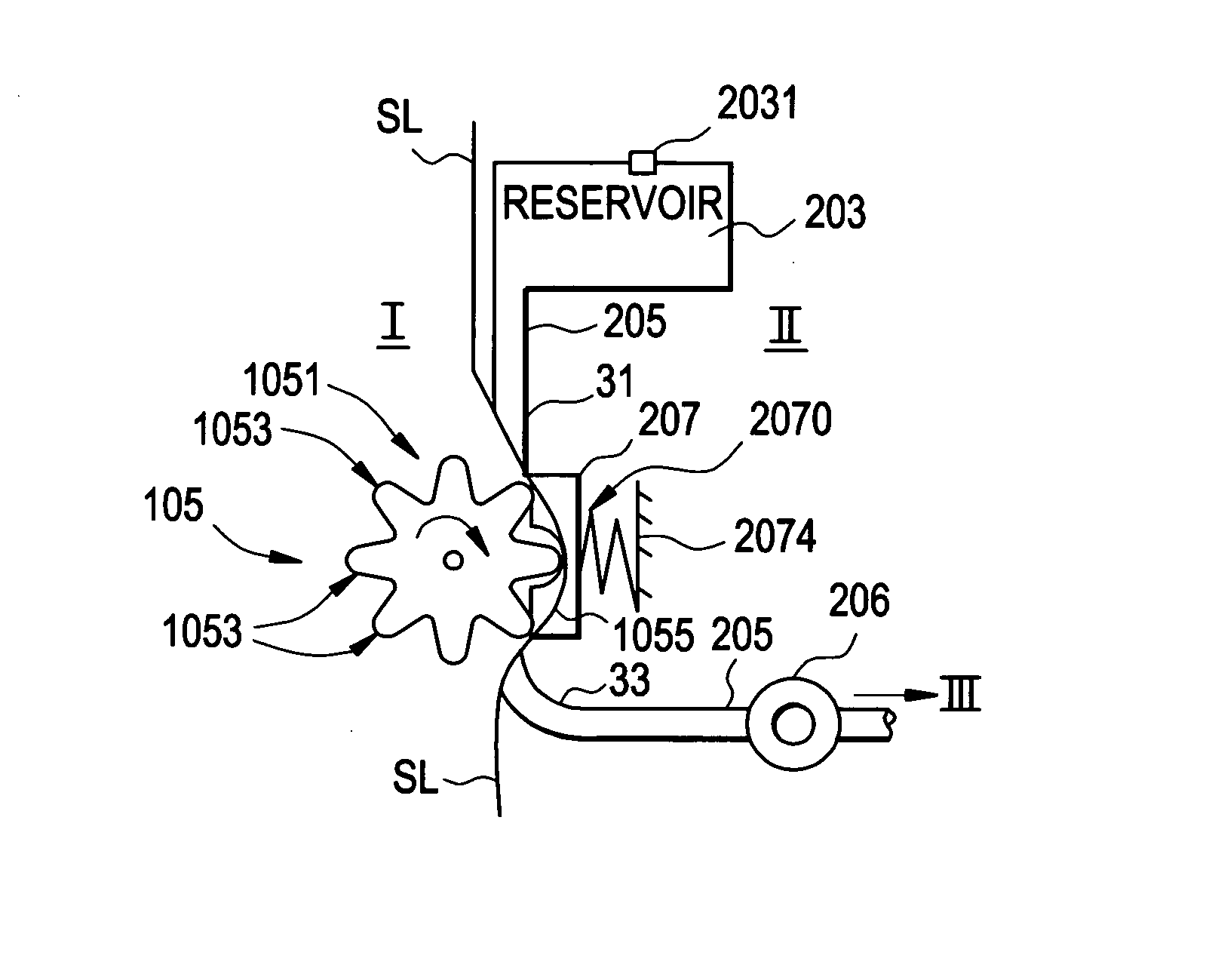
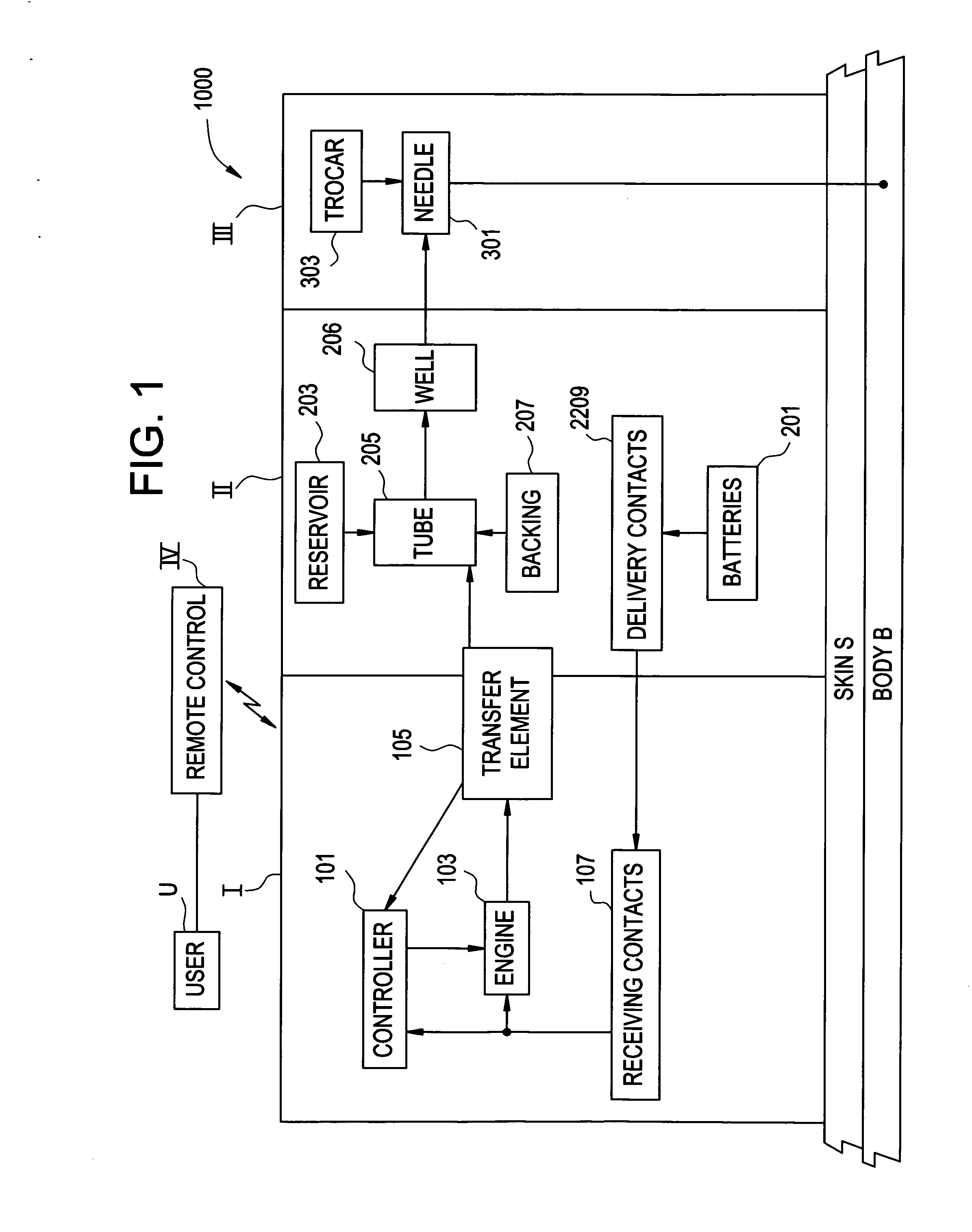
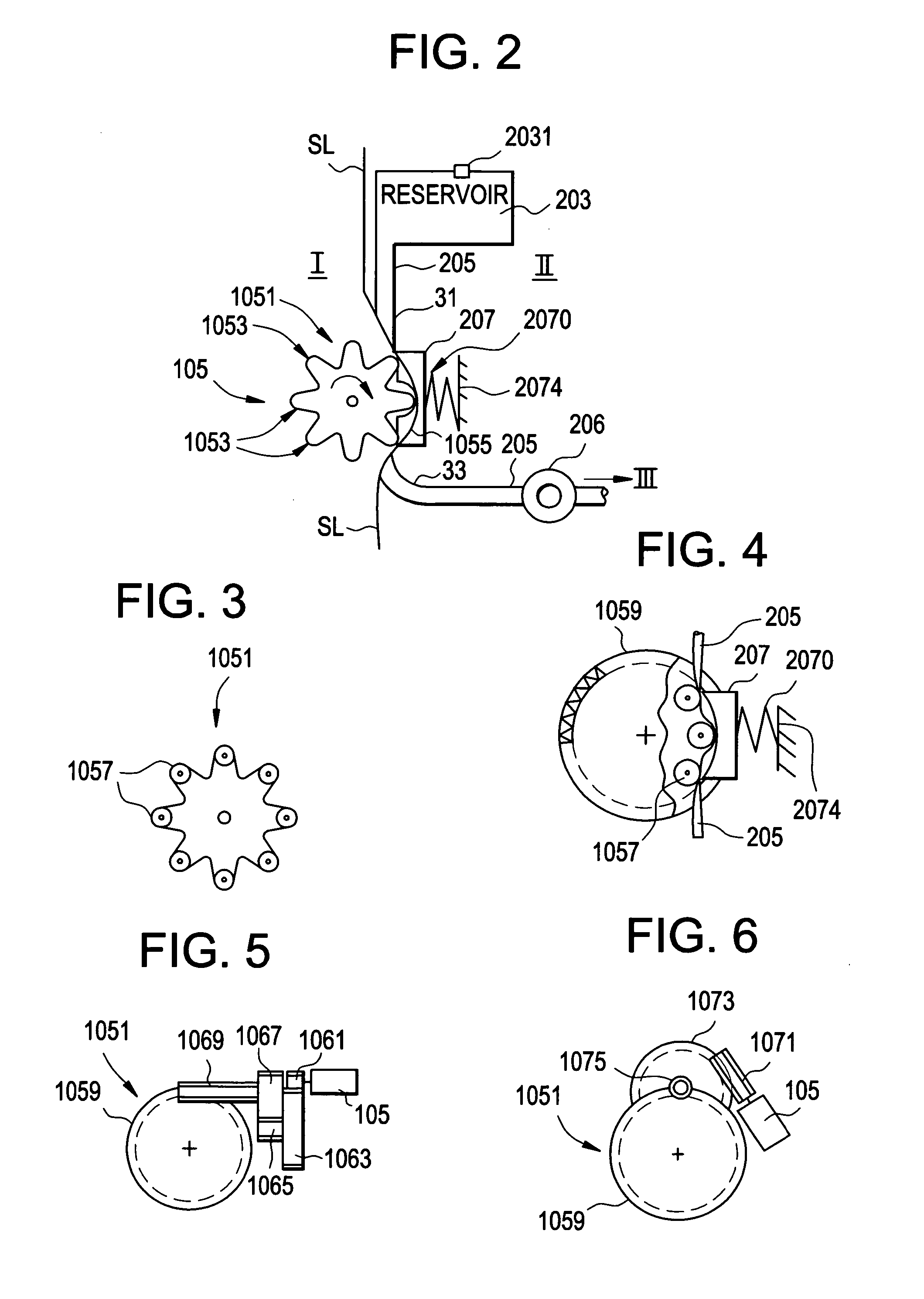
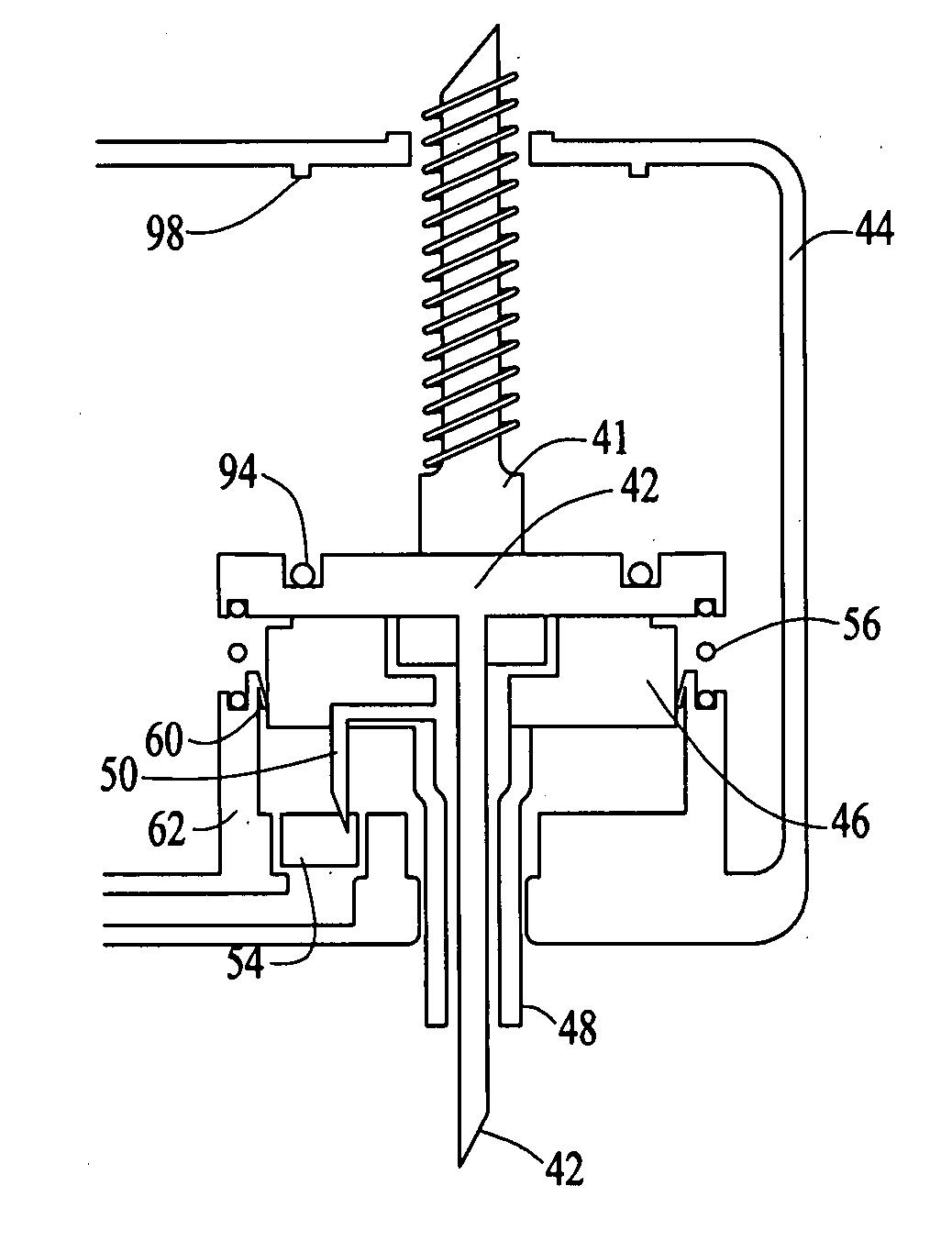
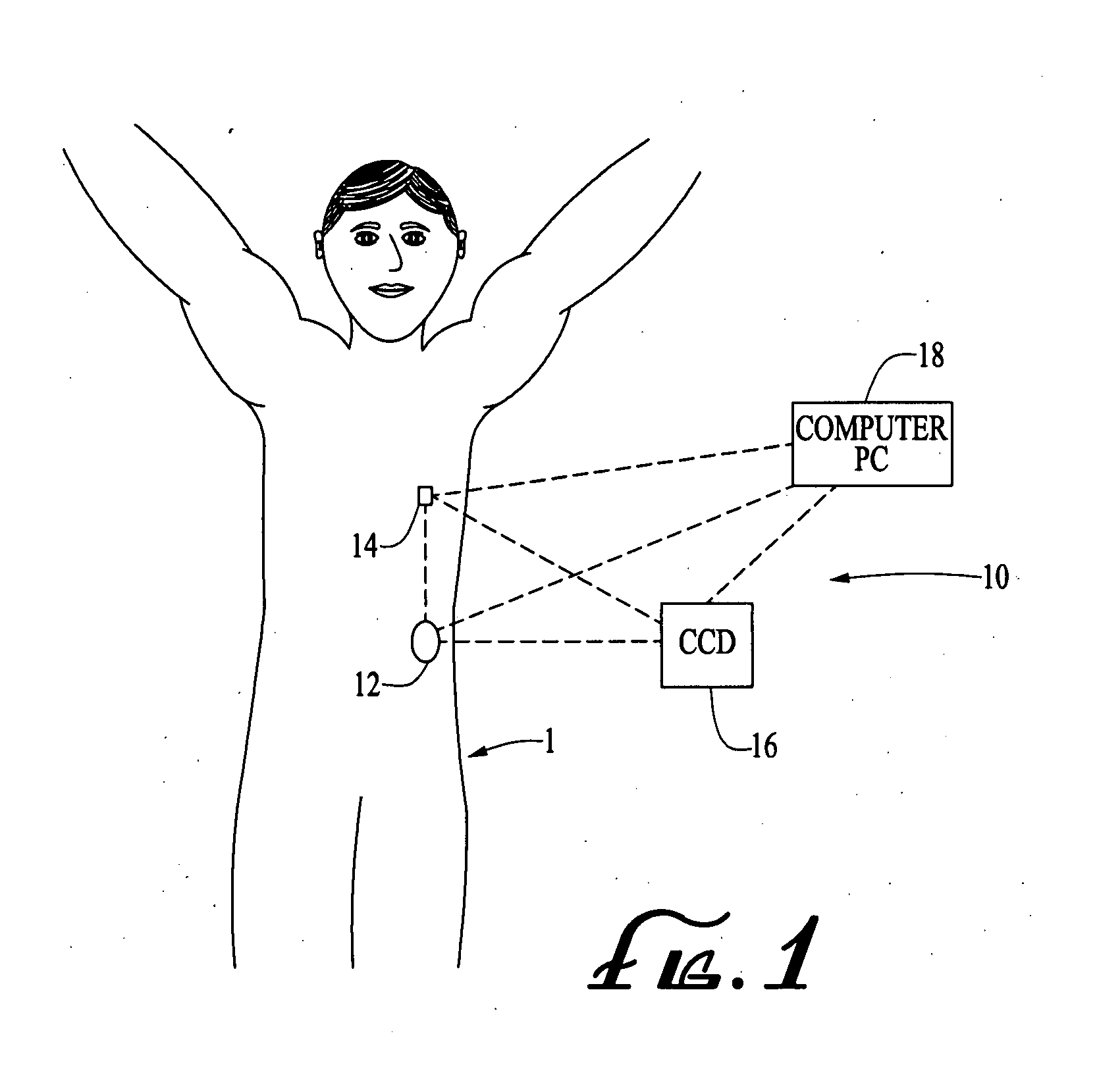
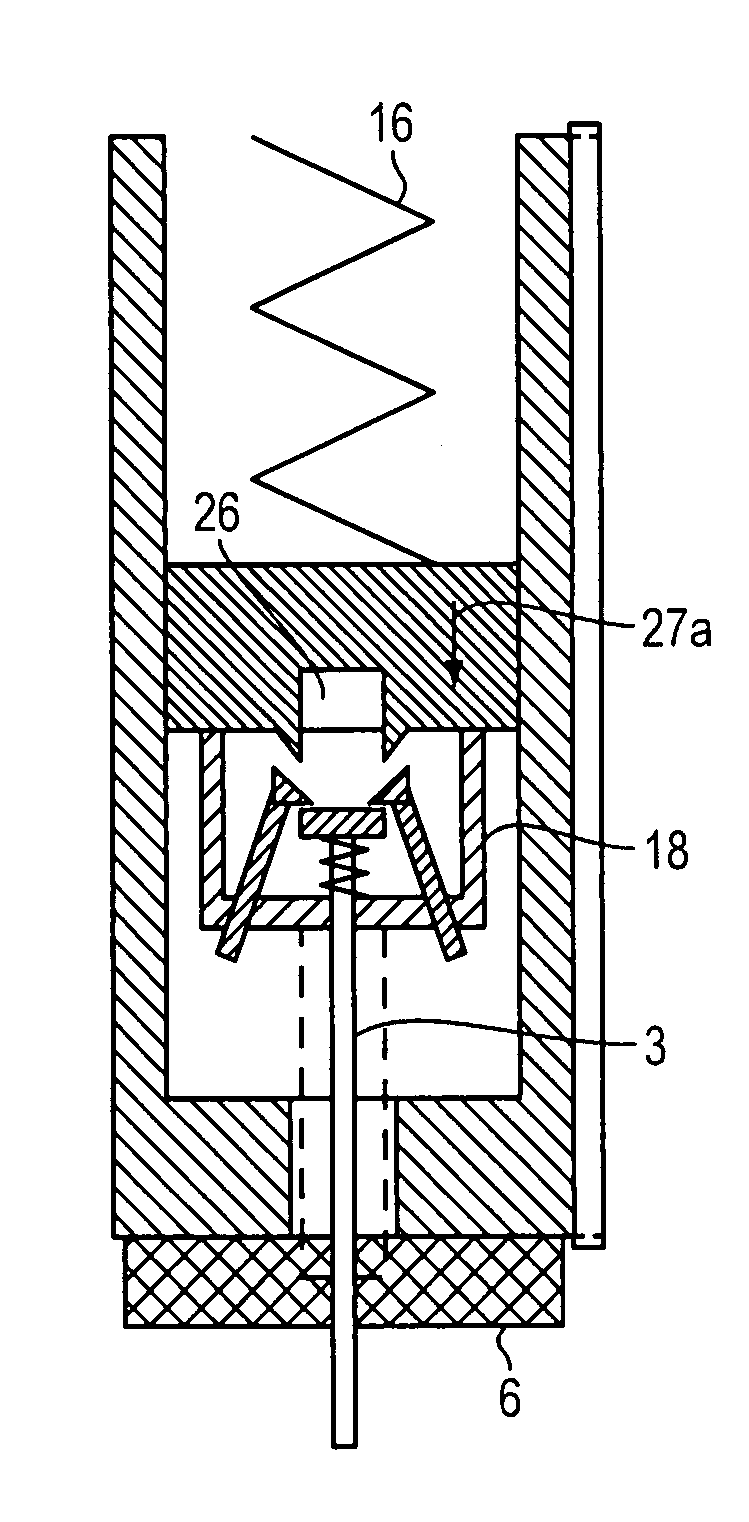
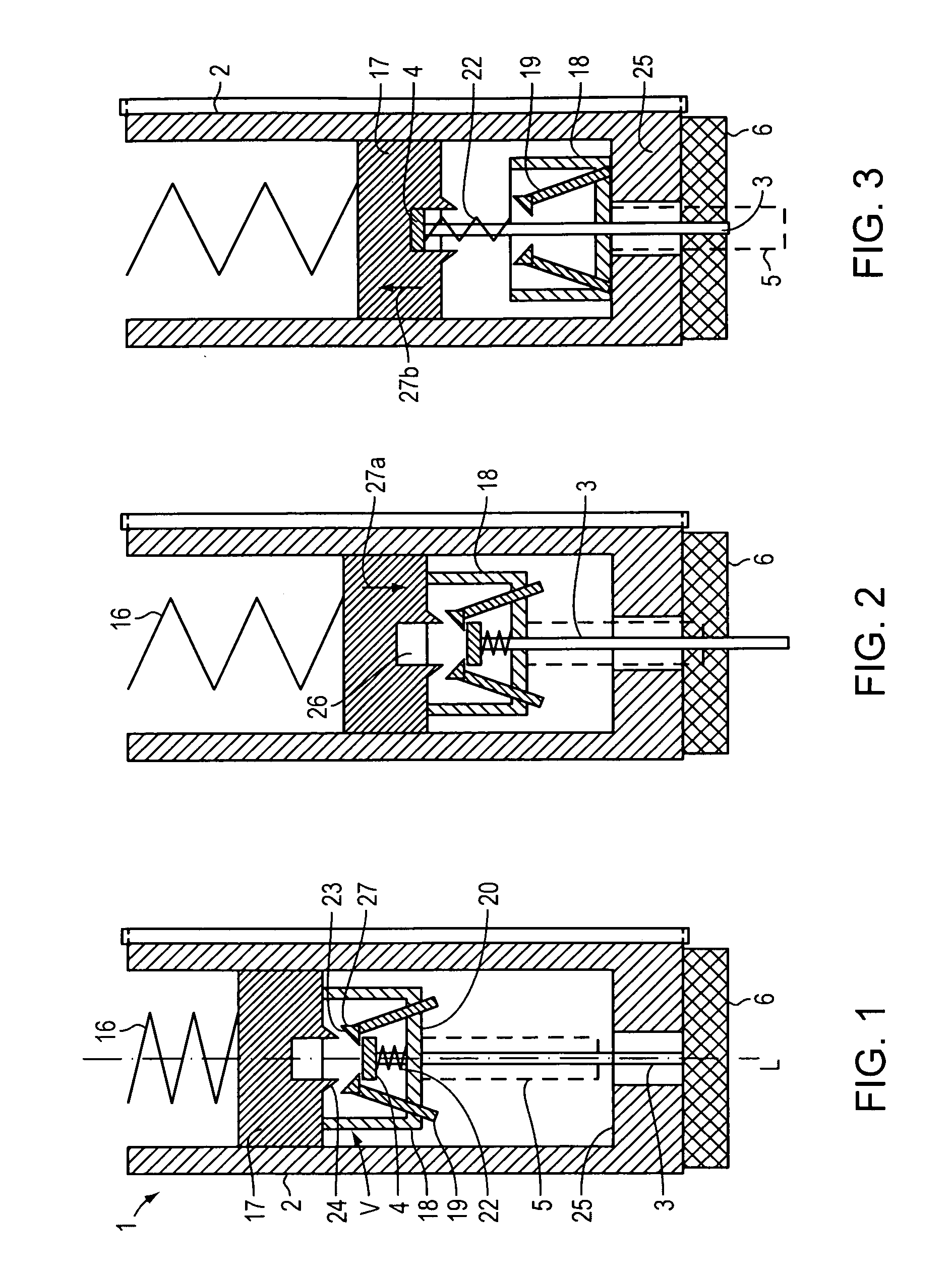
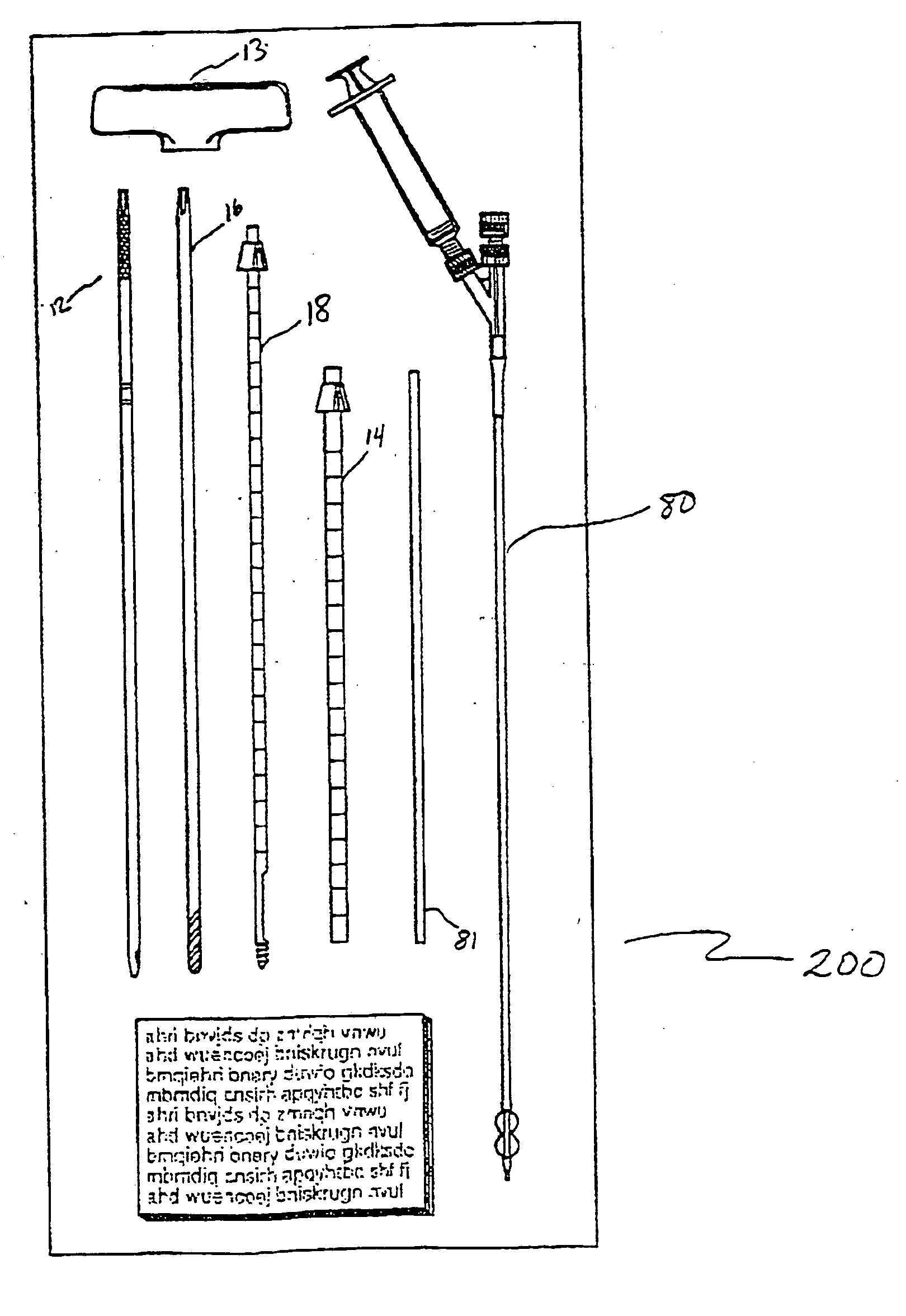
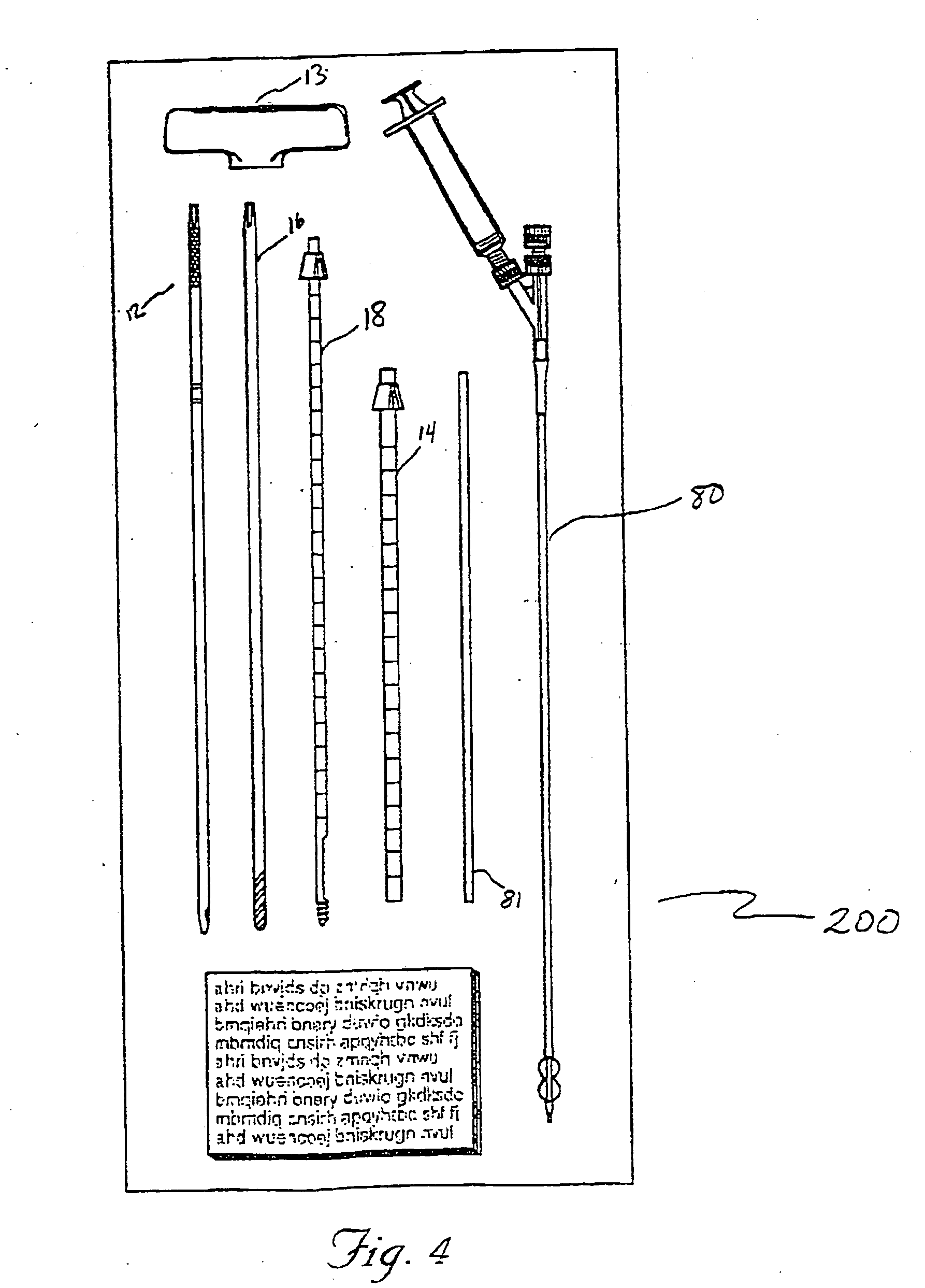
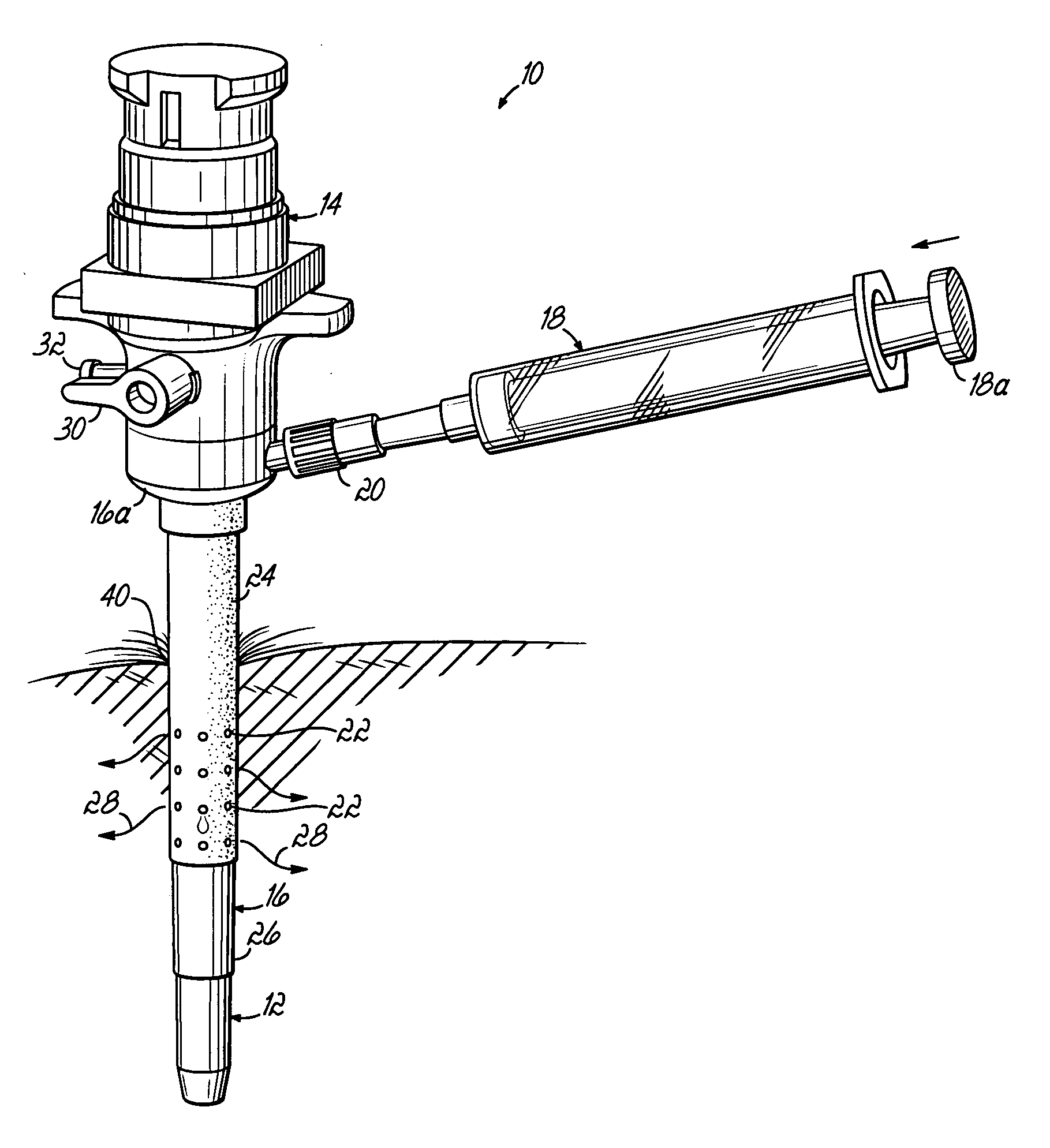
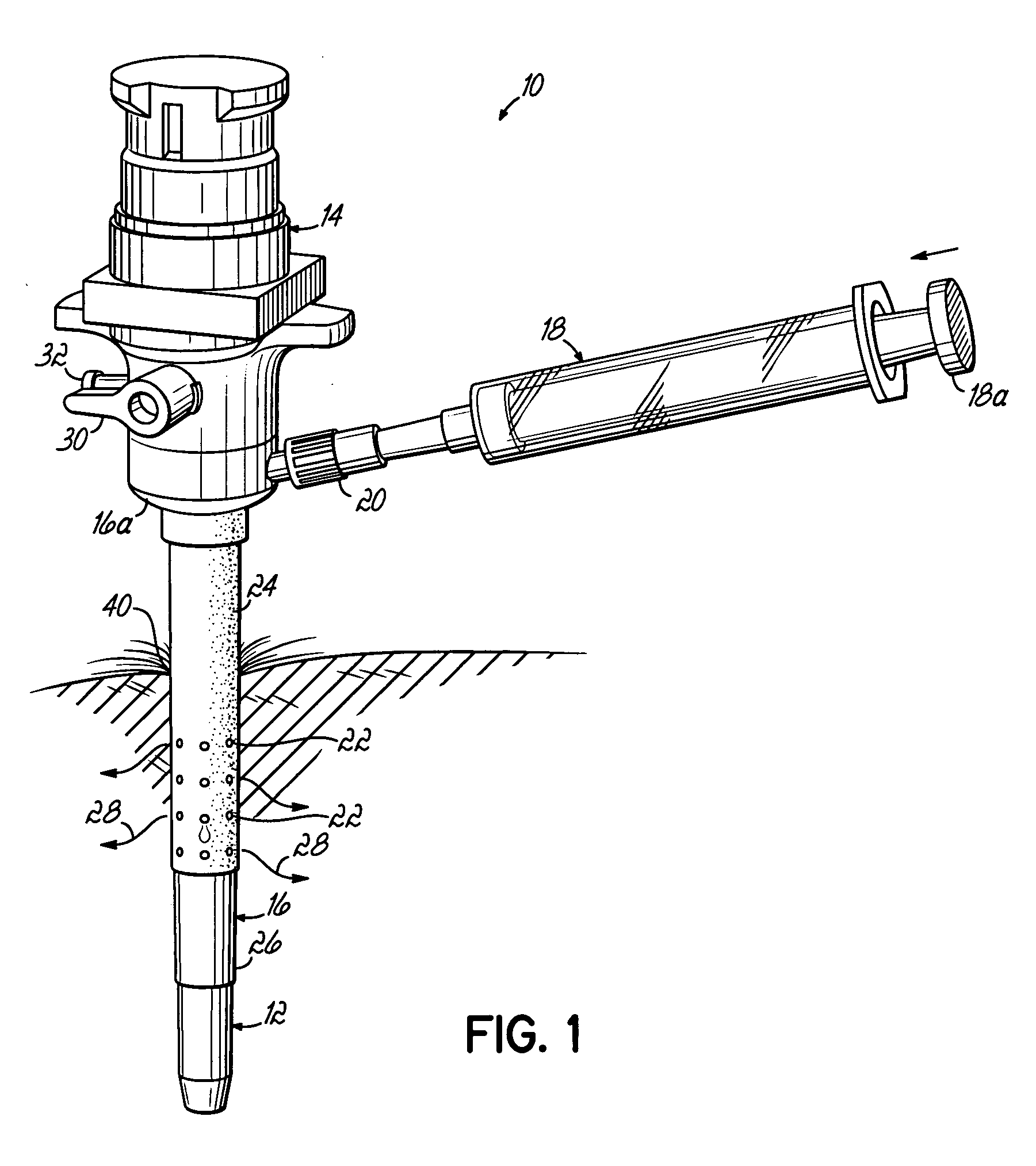
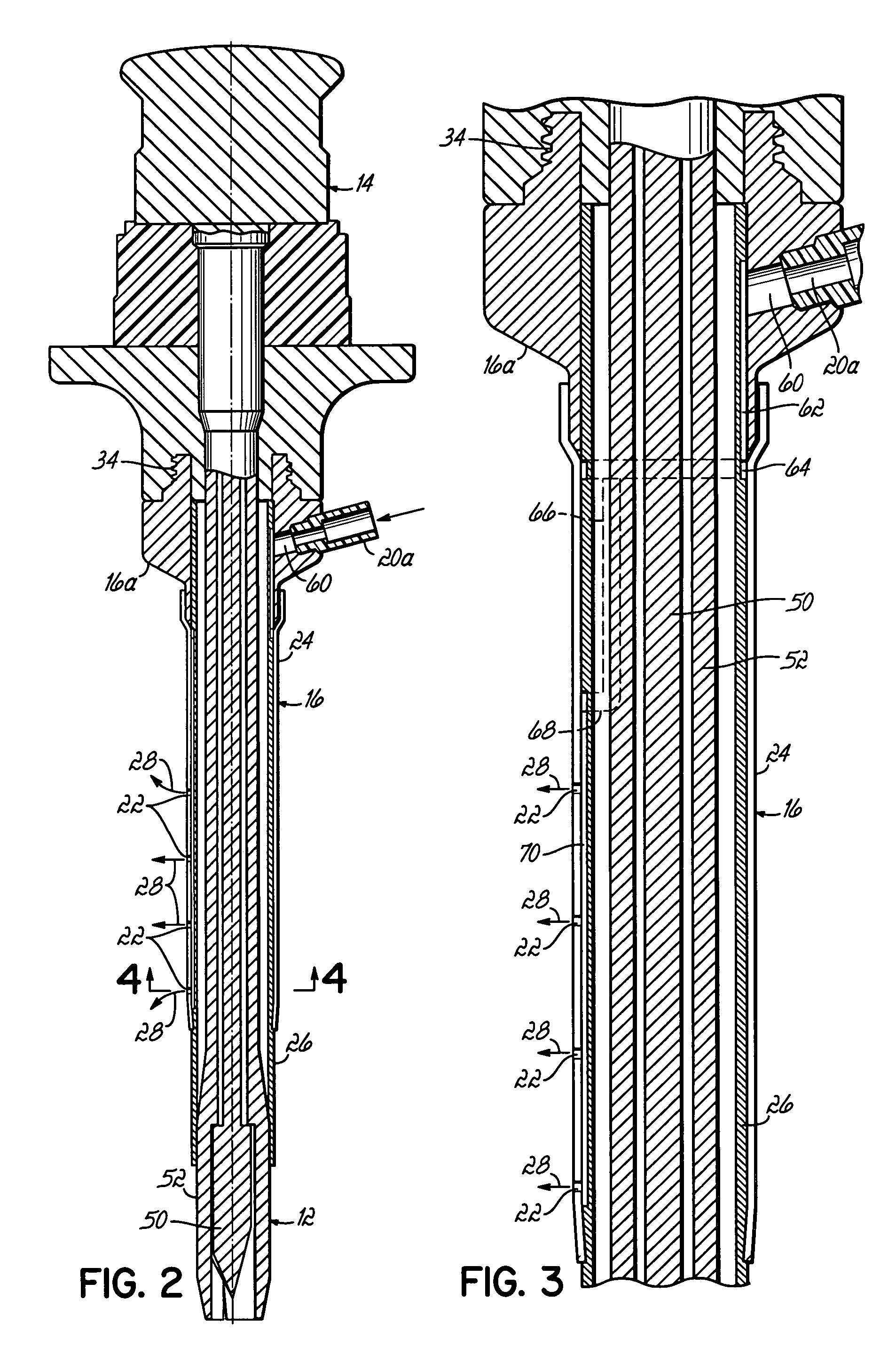
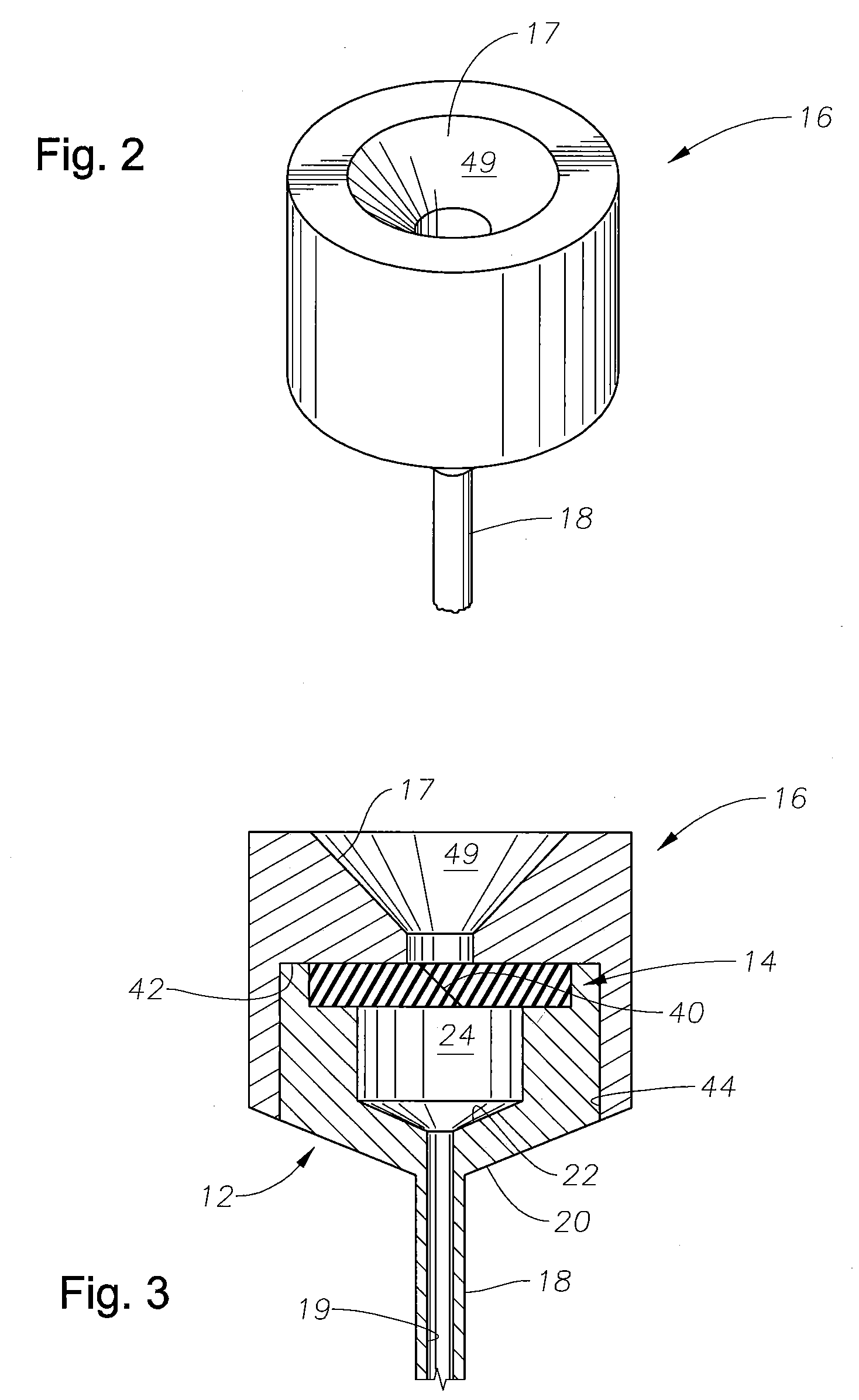
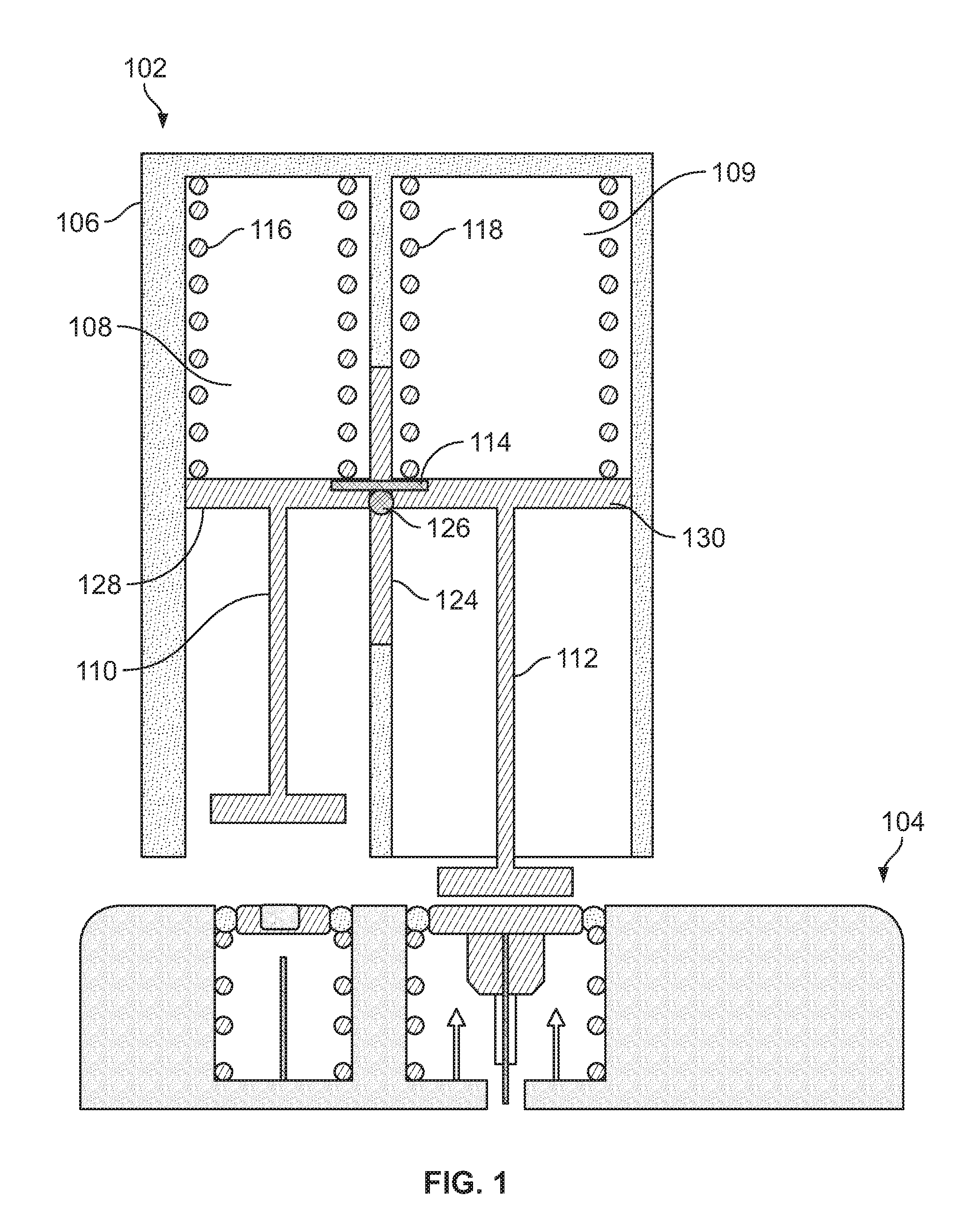
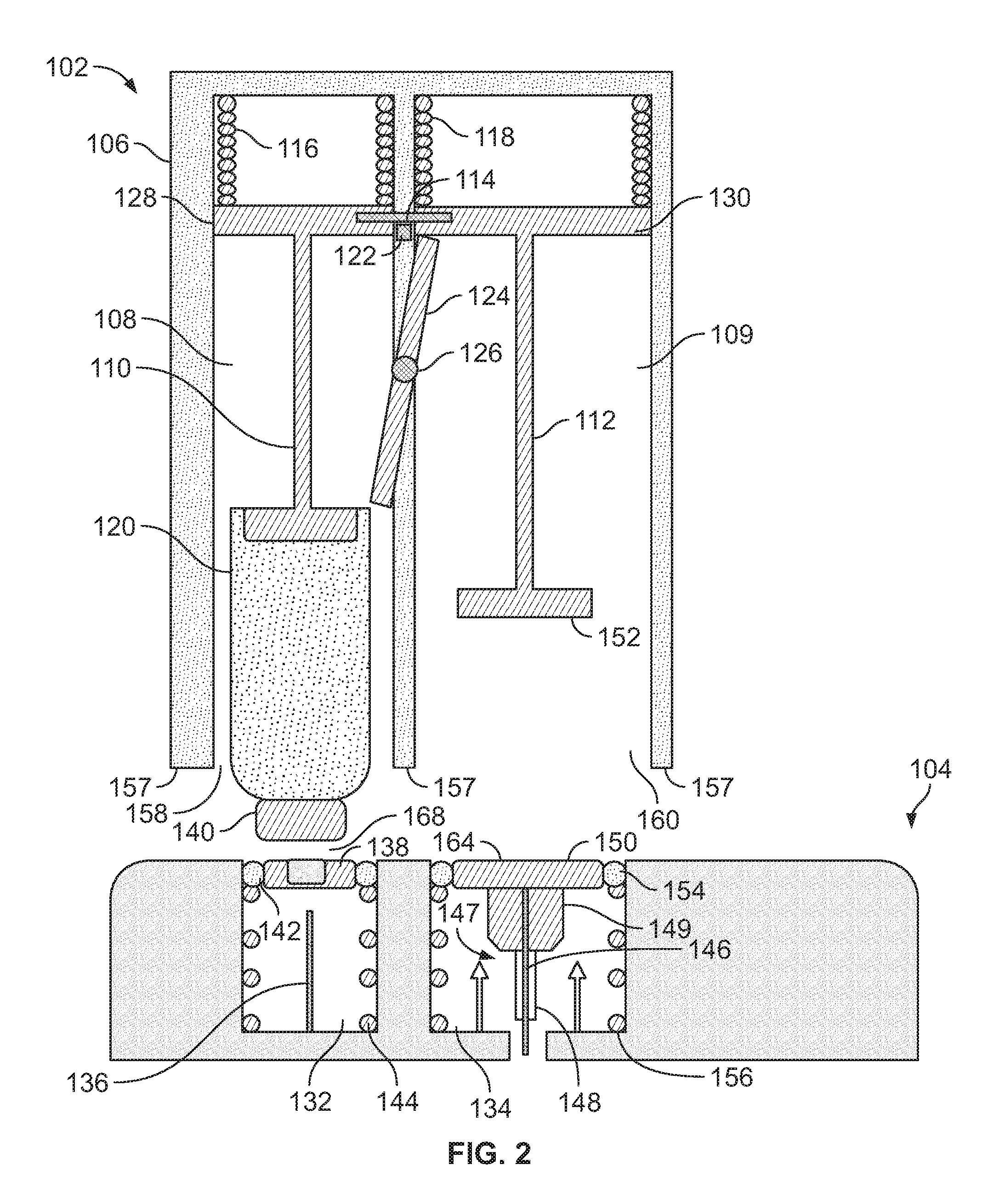
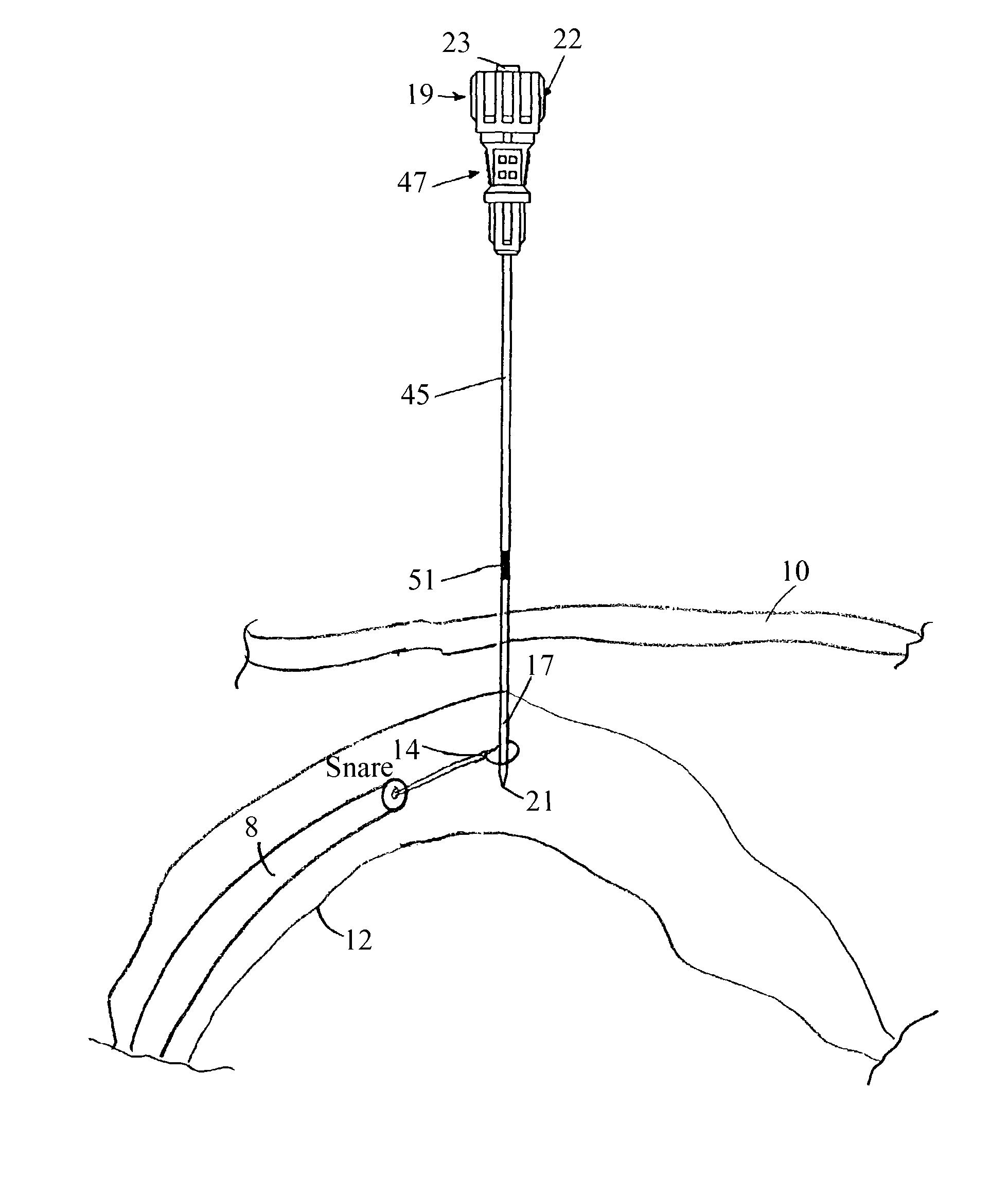
Systems and methods for sustained medical infusion and devices related thereto
Embodiments of the invention are directed to systems, methods and devices for sustained medical infusion with controlled rate injection of a liquid into a body. Such a system may include a first separate reusable unit, a second separate depletable unit a third separate disposable unit having a cannula, and may include a fourth separate remote control unit. Emission of appropriate instructions from the fourth unit, when the first unit, the second unit, and the third unit are coupled together in associative operation and disposed on the skin, power is supplied to an engine for generating motion to a fluid transfer system, and when the cannula is inserted in the well and in the body, liquid is transferred from the reservoir to the body, via the tube and the cannula, under control of the controller and transceiver.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
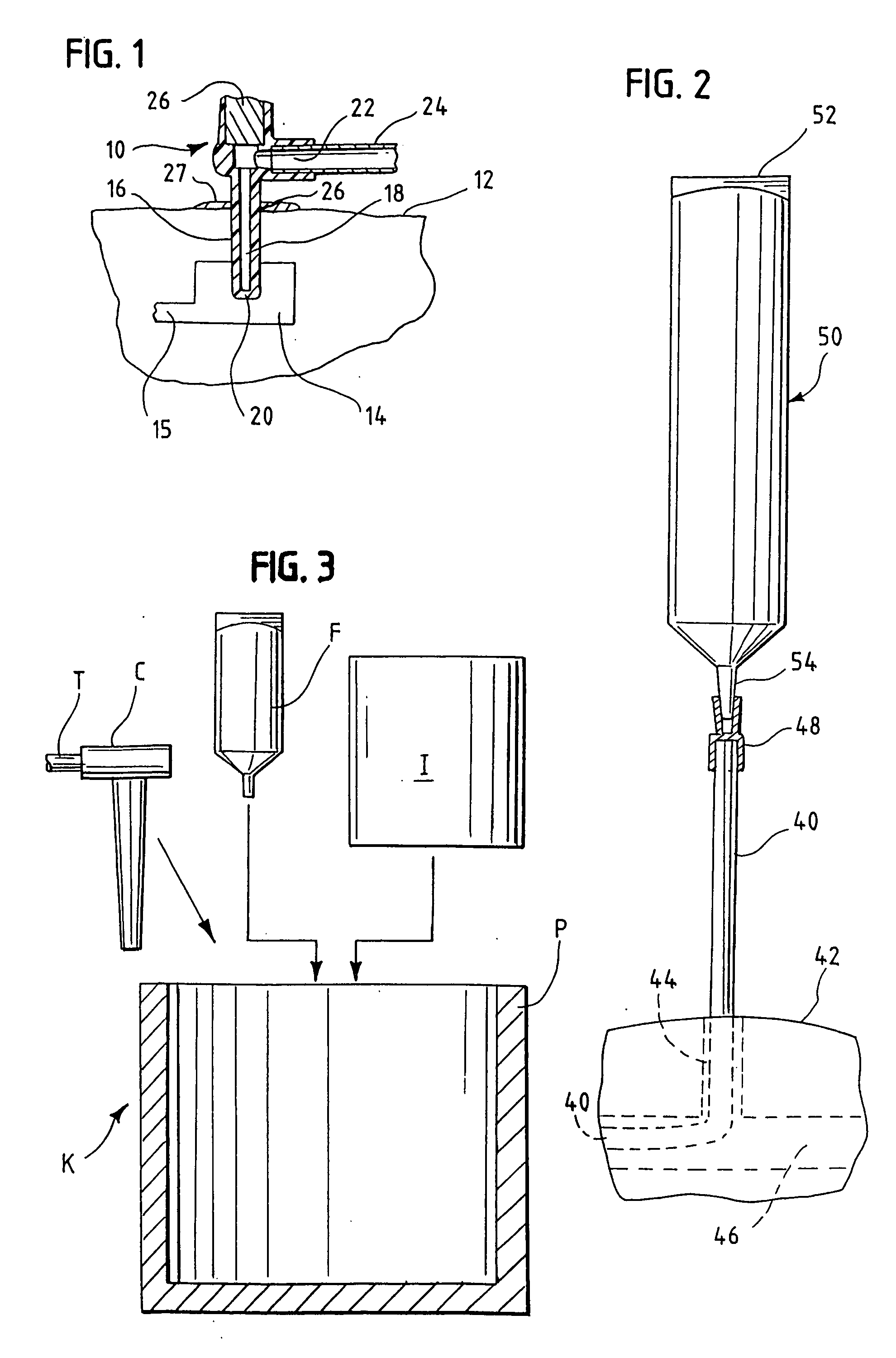
Infusion medium delivery system, device and method with needle inserter and needle inserter device and method
An infusion medium delivery system, device and method for delivering an infusion medium to a patient-user, includes a needle inserter device and method for inserting a needle and / or cannula into a patient-user to convey the infusion medium to the patient-user. The needle inserter device and method operate to insert a needle and cannula into a patient-user's skin and automatically withdraw the needle from the patient-user, leaving the cannula in place and in fluid flow communication with a reservoir. The delivery device may include a base portion and a durable portion connectable to the base portion, and wherein the base portion can be separated from the durable portion and disposed of after one or more specified number of uses. The base portion supports the reservoir and the needle inserter device, while the durable portion supports a drive device for selectively driving the infusion medium out of the reservoir and into the needle and / or cannula.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
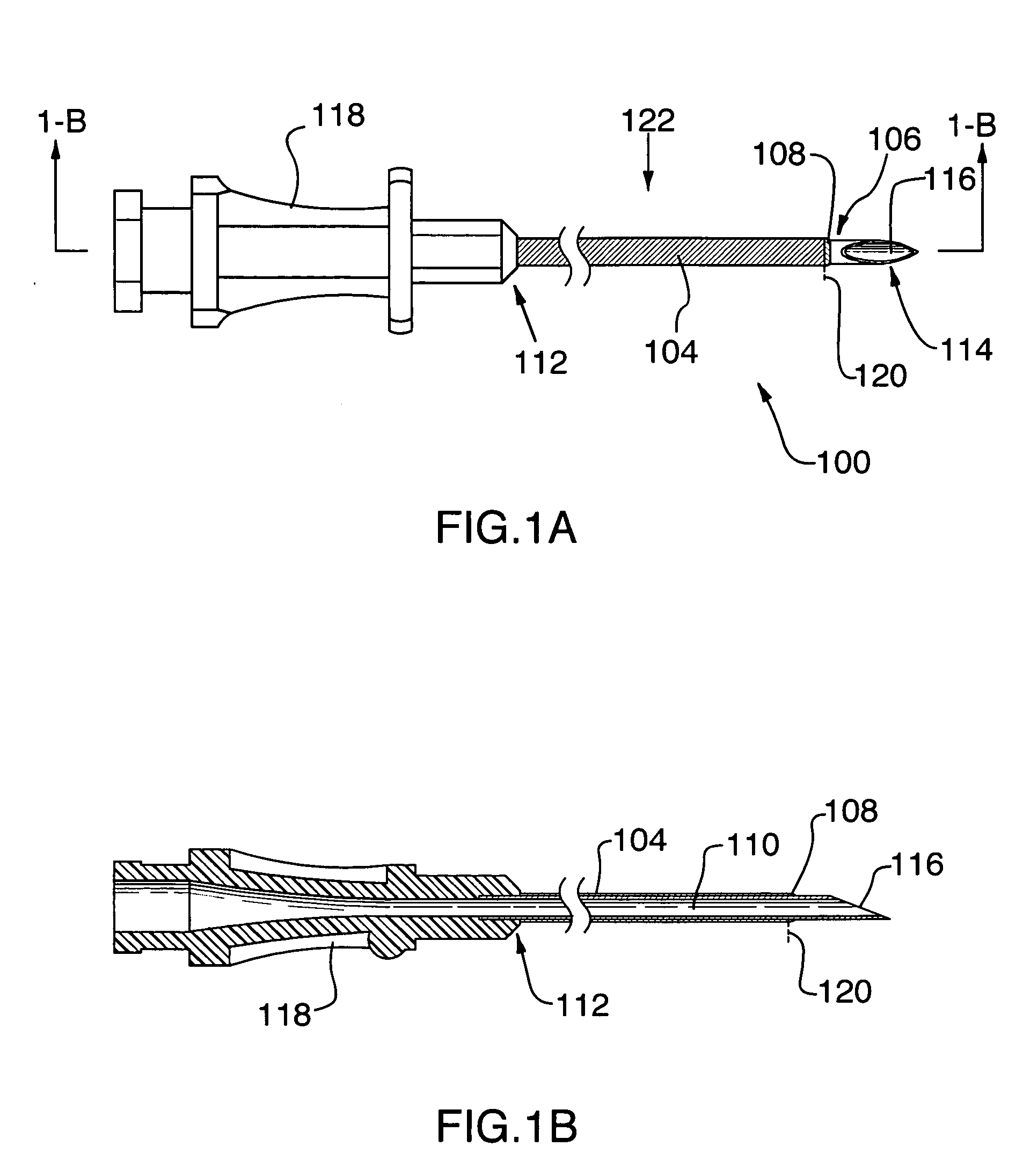
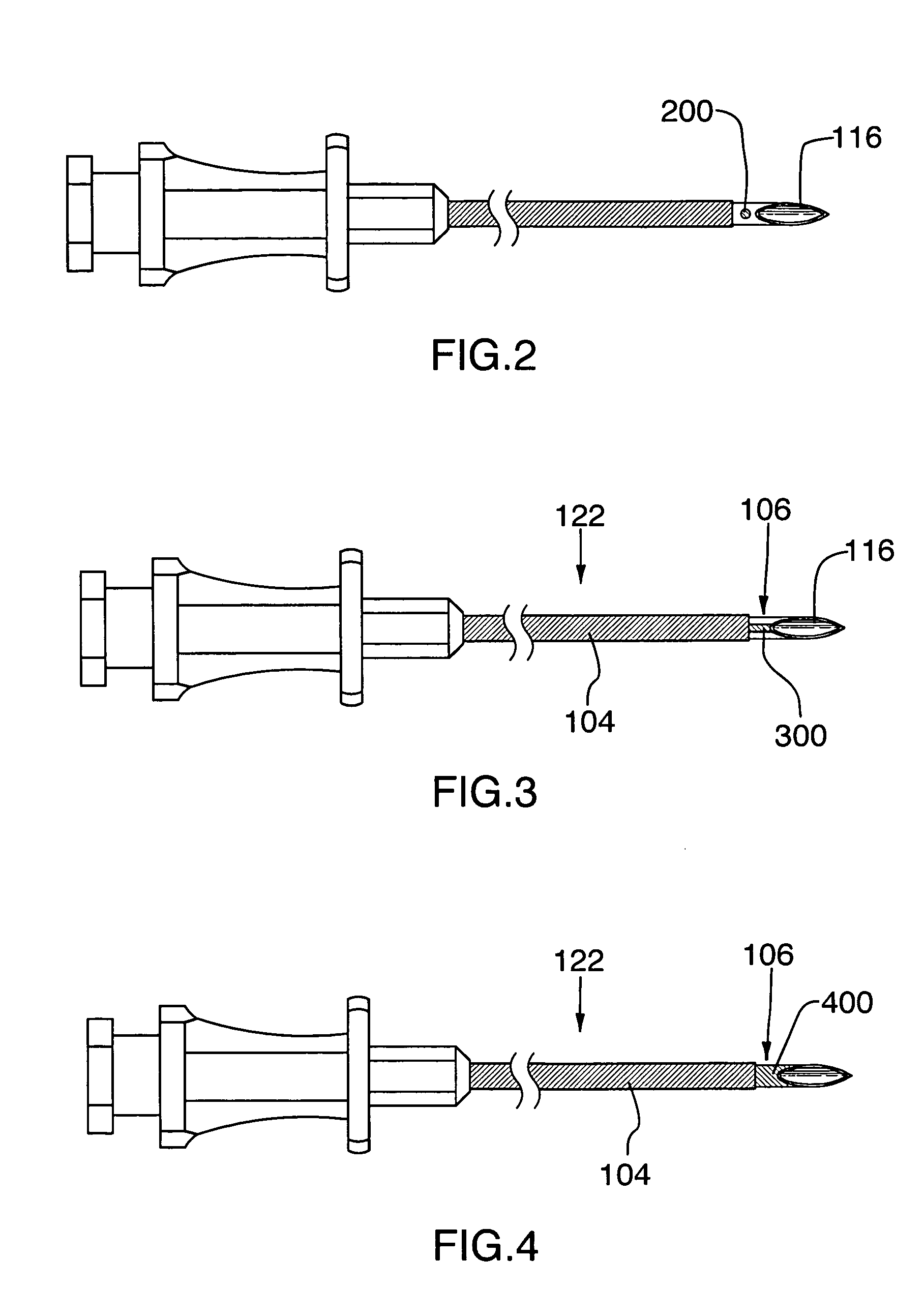
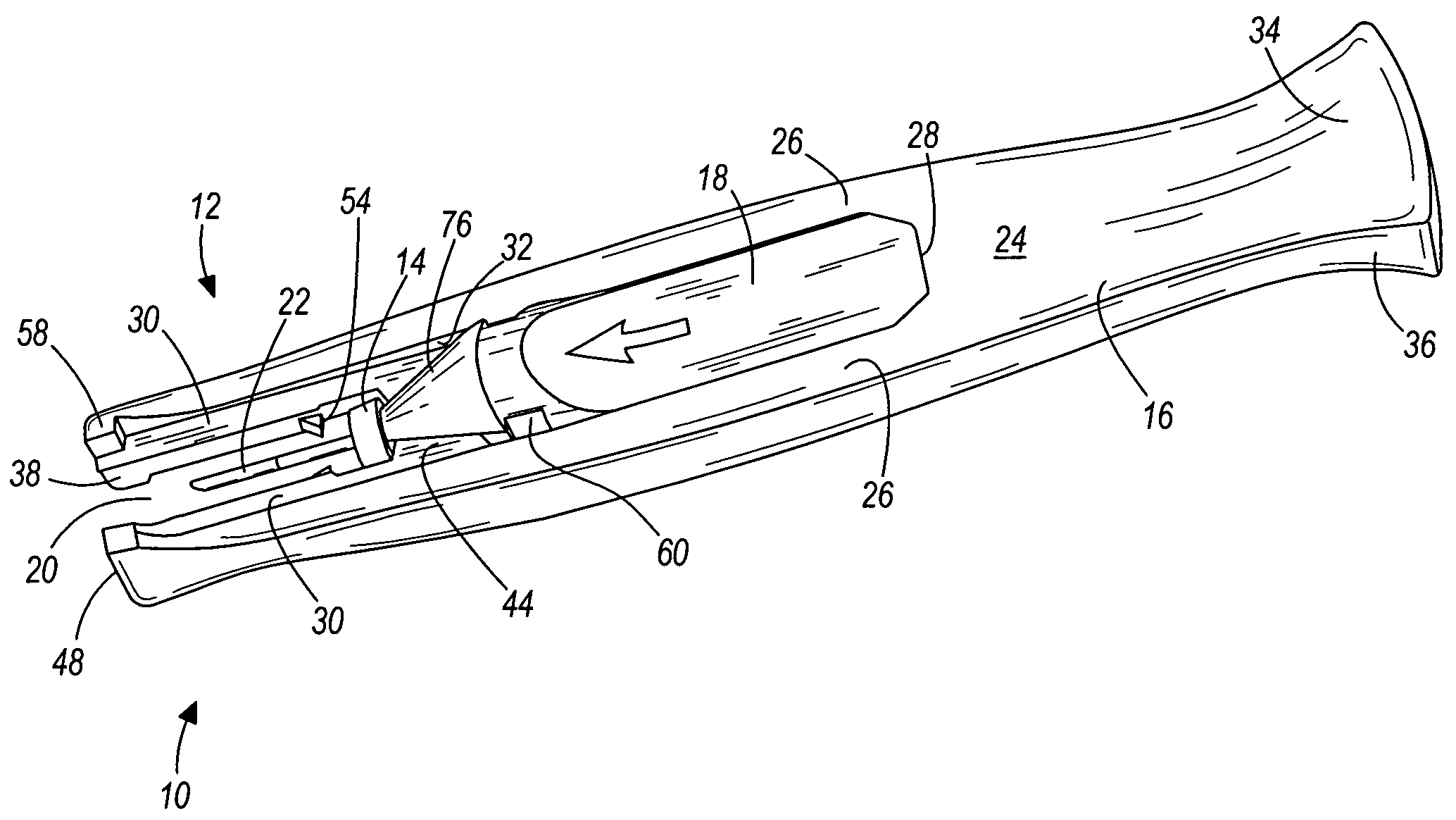
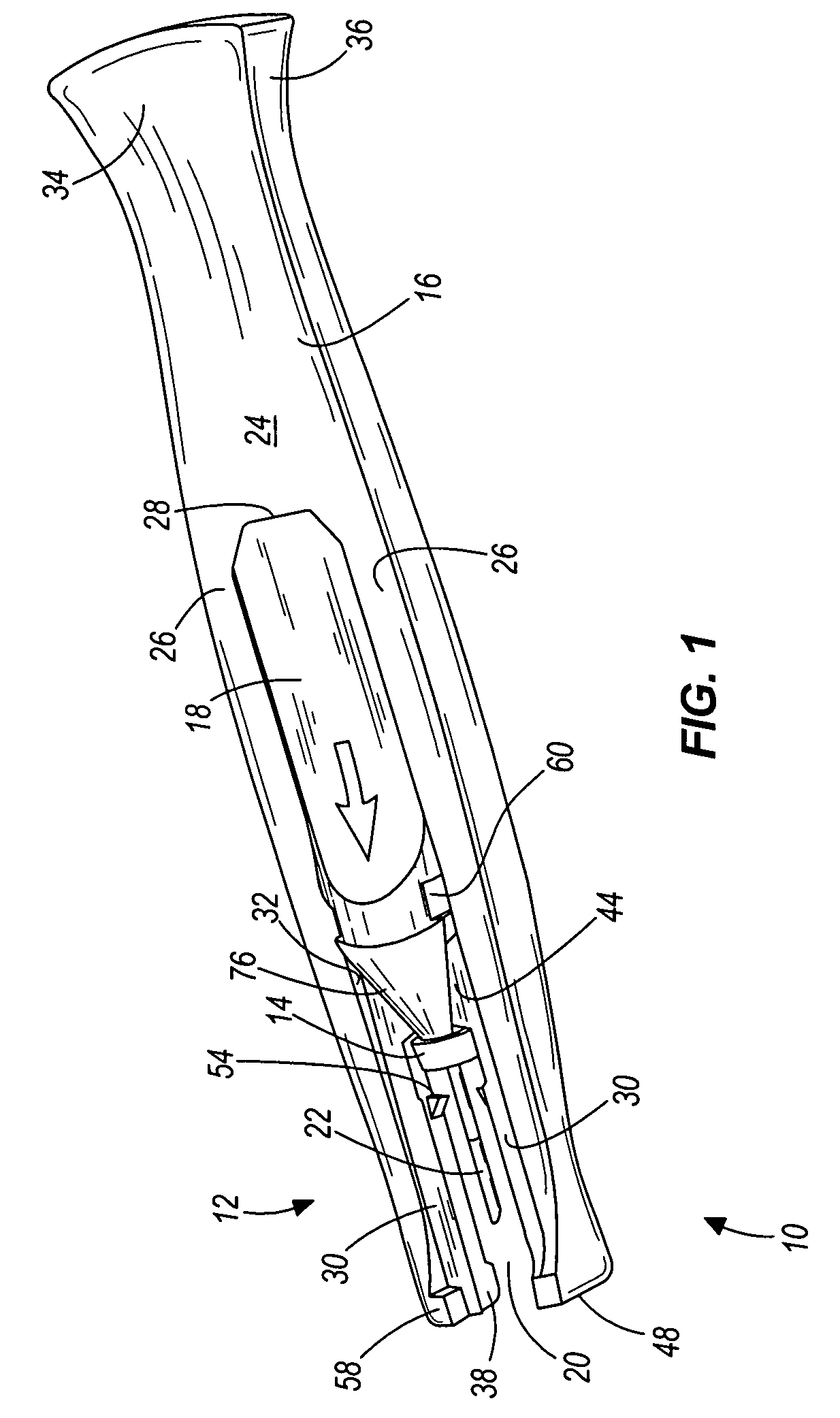
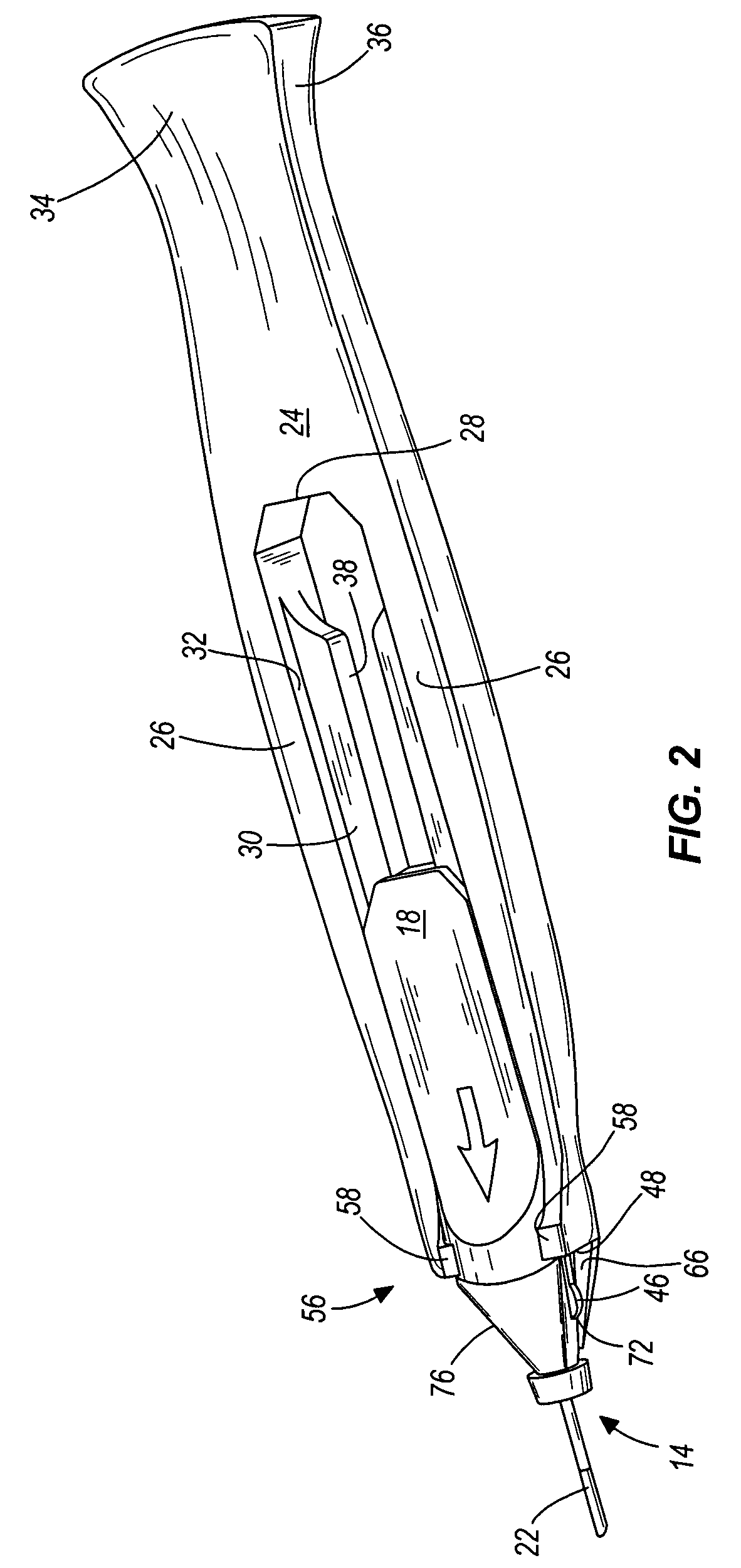
Cannula insertion device and related methods
ActiveUS7846132B2Improve comfortWithdrawn quickly and automaticallyAutomatic syringesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCannula insertionGeneral surgery
Owner:CEQUR SA
Cannula Insertion Device and Related Methods
ActiveUS20090099521A1Improve comfortWithdrawn quickly and automaticallyAutomatic syringesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCannula insertionGeneral surgery
A cannula insertion device includes a housing defining an opening for receiving therethrough a cannula and further defining a channel, and a cannula forming a lumen, the cannula adapted for sliding movement within the housing from a retracted position to an extended position. When the cannula is in the retracted position, the lumen is located remotely from the channel and the channel is in fluidic communication with the opening. When the cannula is in the extended position, the lumen is in fluidic communication with the channel.
Owner:CEQUR SA
Systems and methods for reducing fractured bone using a fracture reduction cannula
InactiveUS20070118143A1Raise the possibilitySooner resumptionSurgical furnitureSurgical needlesFracture reductionMedicine
Systems and methods provide for the fixation of osteoporotic and non-osteoporotic long bones, especially Colles' fractures. A cannula having a circumferential opening is inserted into cancellous bone and directed such that the circumferential opening faces the fracture. The cannula is further adapted to receive an expandable structure, the expandable structure being inserted through the cannula until it is in registration with the circumferential opening. The expandable structure is expanded through the circumferential opening into cancellous bone and toward the fracture. The expansion of the expandable structure through the circumferential opening toward the fracture causes compression of cancellous bone and moves fractured cortical bone, thus creating a cavity proximal to the fracture. The cavity is then filled with a flowable bone filling material and the material allowed to harden.
Owner:ORTHOPHOENIX
High viscosity antibacterials
InactiveUS20060024372A1Low viscosityReduce evaporationBiocidePowder deliveryAlcoholGrommet Insertion
An antibacterial fluid may be applied to a tubular medical cannula for access to a patient. The fluid comprises a typically metabolizable antibacterial formulation having a viscosity preferably greater than 150,000 cp. The cannula may then be inserted into the patient with an increased lubricity for a reduction of pain, while at the same time, unlike silicones, preferred materials do not readily accumulate in the patient. The fluid may be placed on the skin. The tubular medical cannula may be a rigid, hollow needle, sharp or blunt, a spike, or a flexible catheter. Also, the viscous antibacterial fluid may be used to lock a catheter or other cannula while implanted in the patient, for storage purposes. The formulation is typically an alcohol plus a viscosity increasing agent and optionally a surfactant, a clotting agent, and / or EDTA.
Owner:DSU MEDICAL
Apparatus for delivery of therapeutic and/or diagnostic agents
A system for delivery of therapeutic and / or diagnostic agents into a living body includes a port assembly having a cannula extending from the mounting side, a port opening away from the mounting side and a resilient barrier between the port and the cannula. An access hub includes a connector positionable at the port for opening the resilient barrier. The access hub is movable in the port assembly, is engaged therewith through a resilient ring coupling and forms a seal with the resilient barrier, reducing the amount of volume to be primed. Inserters, both disposable and reusable, include the cannula insertion member as part of the assembly. A spring loaded port driver is operatively mounted within the housing with movement controlled by a latch. The driver includes a seat for receipt of a port assembly. The cannula insertion member is nonremovably fixed in a socket in the port driver in the disposable assembly. In the reusable inserter, the cannula insertion member is slidably mounted within a socket associated with the latch. Slidable movement is limited by locking shoulders. The socket is split and may be splayed to release the cannula insertion member following use.
Owner:MEDSOLVE TECH
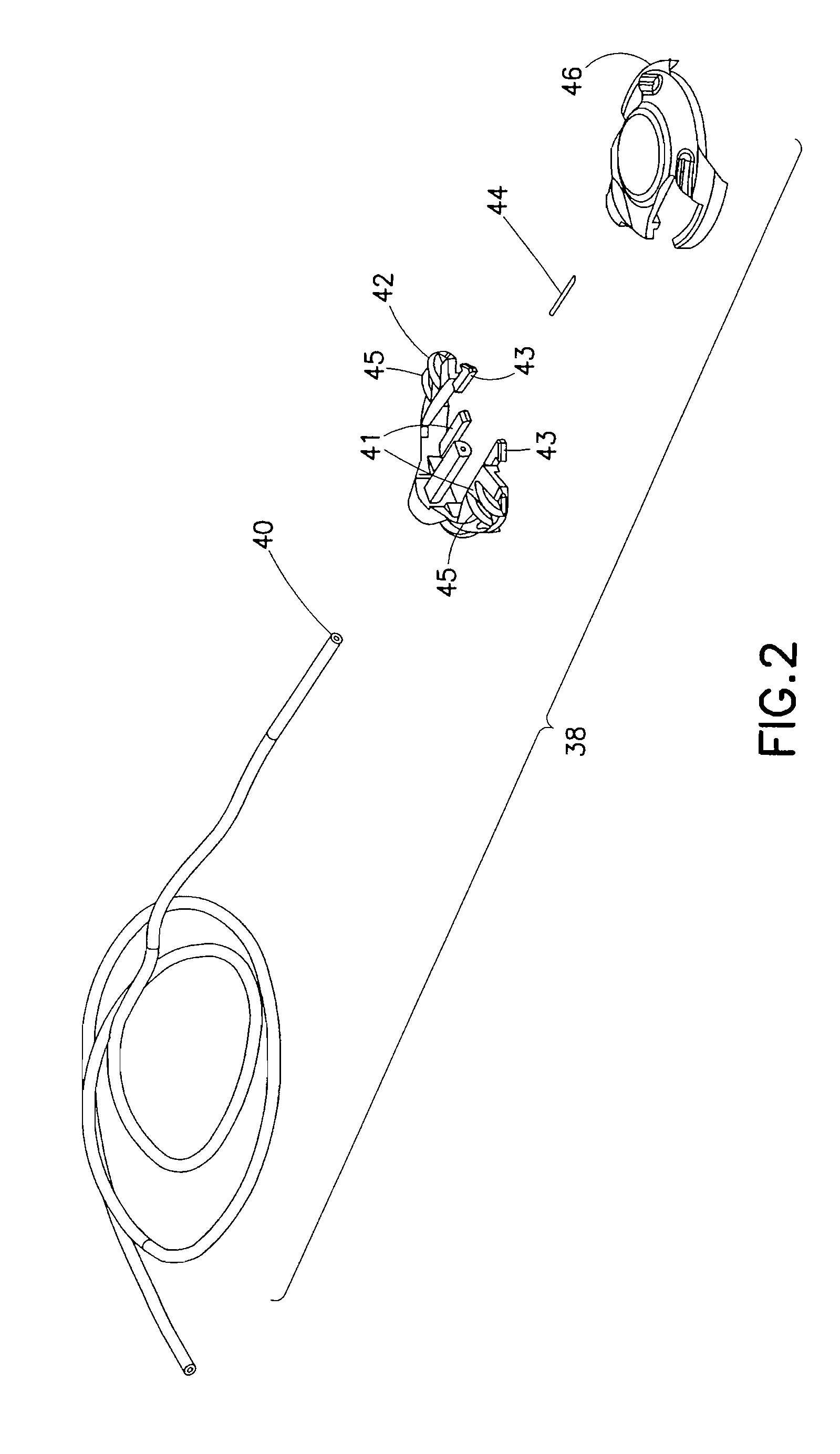
Cannula deployment mechanism
ActiveUS20150306307A1Reduce the overall heightLess componentsAutomatic syringesMedical devicesCannula insertionCatheter
A cannula insertion device is disclosed. The device includes a needle carriage, a rail device on which the needle carriage is slidable, a yoke having a channel, a linkage connected to the needle carriage and extending into the channel, a torsion spring with one end connected to the linkage, and locking device for locking the torsion spring in tension and maintaining the needle carriage and the linkage in a locked position prior to activation. Upon release of the locking device, the tension of the torsion spring is released, which causes the linkage to move in the channel and slide the needle carriage along the rail device. A catheter carriage may also be provided for actuation by the linkage.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
In-situ formed intervertebral fusion device and method
InactiveUS20150173914A1MinimallyIncrease heightLuminescence/biological staining preparationBone implantOrthopedic devicesGonial angle
An orthopedic device for implanting between adjacent vertebrae comprising: an arcuate balloon and a hardenable material within said balloon.In some embodiments, the balloon has a footprint that substantially corresponds to a perimeter of a vertebral endplate. An inflatable device is inserted through a cannula into an intervertebral space and oriented so that, upon expansion, a natural angle between vertebrae will be at least partially restored. At least one component selected from the group consisting of a load-bearing component and an osteobiologic component is directed into the inflatable device through a fluid communication means.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
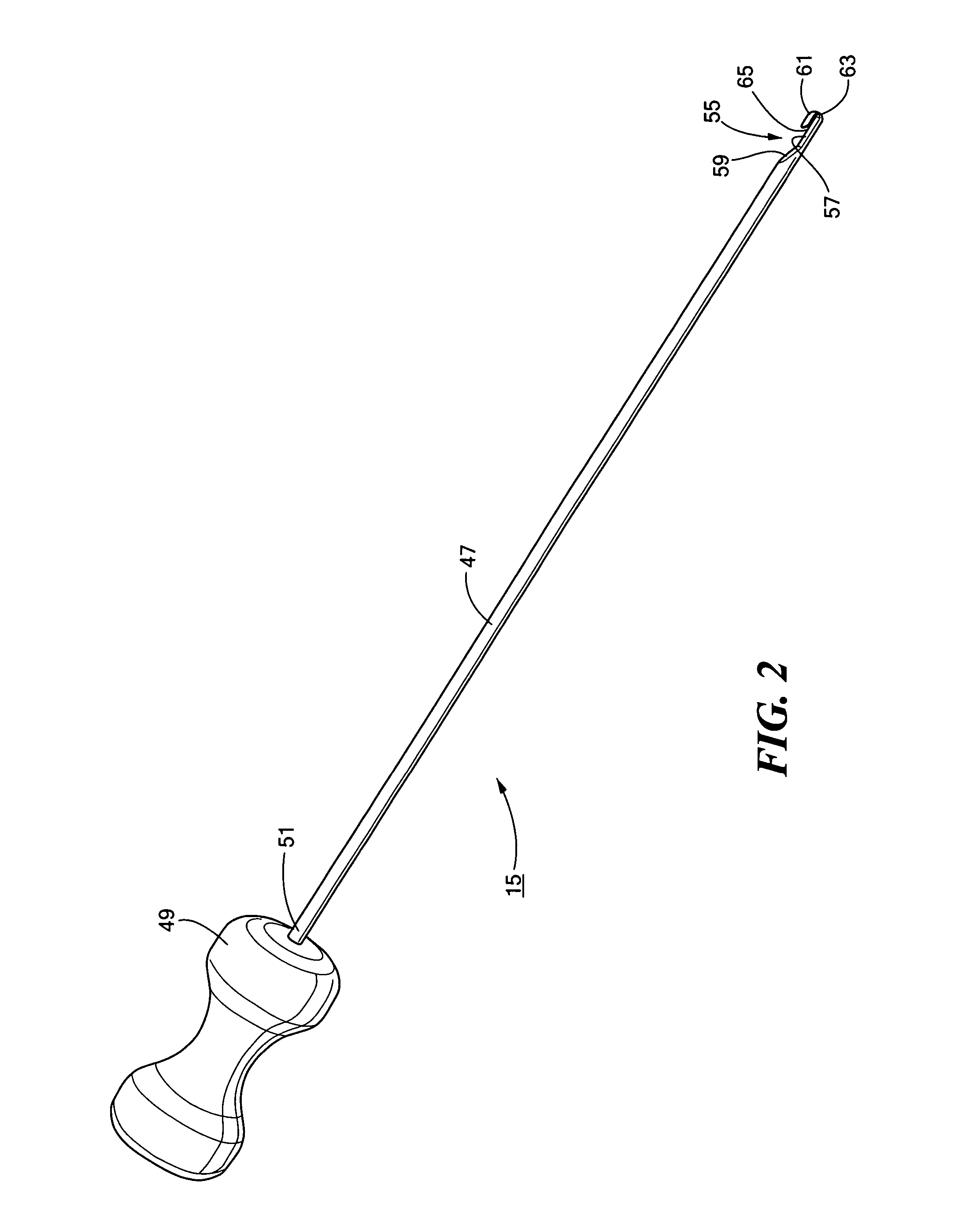
Ophthalmic cannula insertion tool and method
A cannula insertion tool having a needle movable between a retracted position and an extended position. In some embodiments, the needle can be retracted within the periphery of a handle of the insertion tool when not in use to protect the needle. When the needle is needed for surgical use, the needle can be extended at least partially beyond the outer periphery of the handle. The needle can be coupled to a slide movable relative to the handle between the retracted position and the extended position. The slide can be secured in each position to prevent unintentional movement of the slide. A cannula can be positioned on the needle when the needle is in the retracted position, and can be retained upon the needle by a member extending toward the cannula.
Owner:MEDICAL INSTR DEVMENT LAB
Method for use of dilating stylet and cannula
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Method for use of dilating stylet and cannula
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
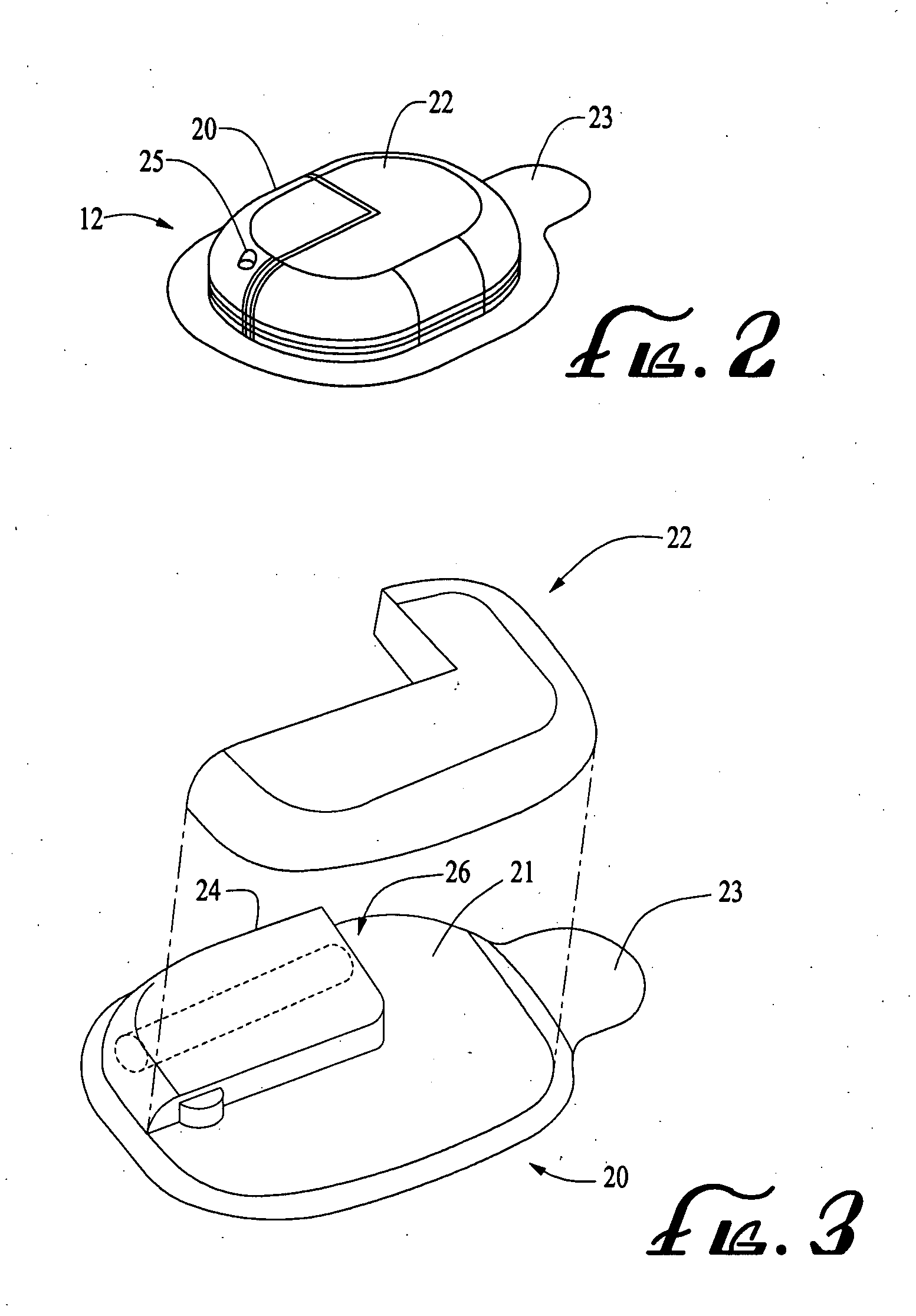
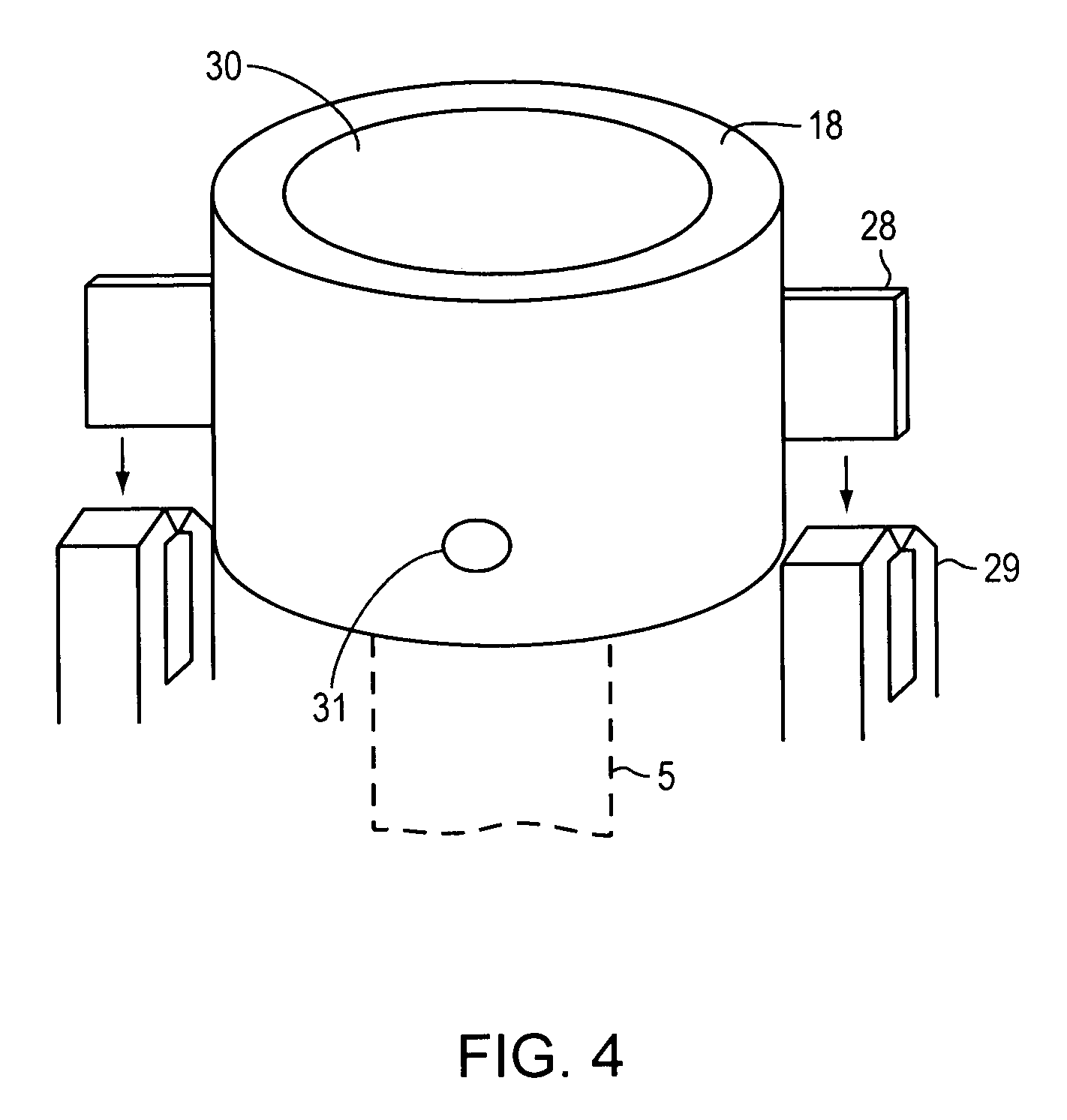
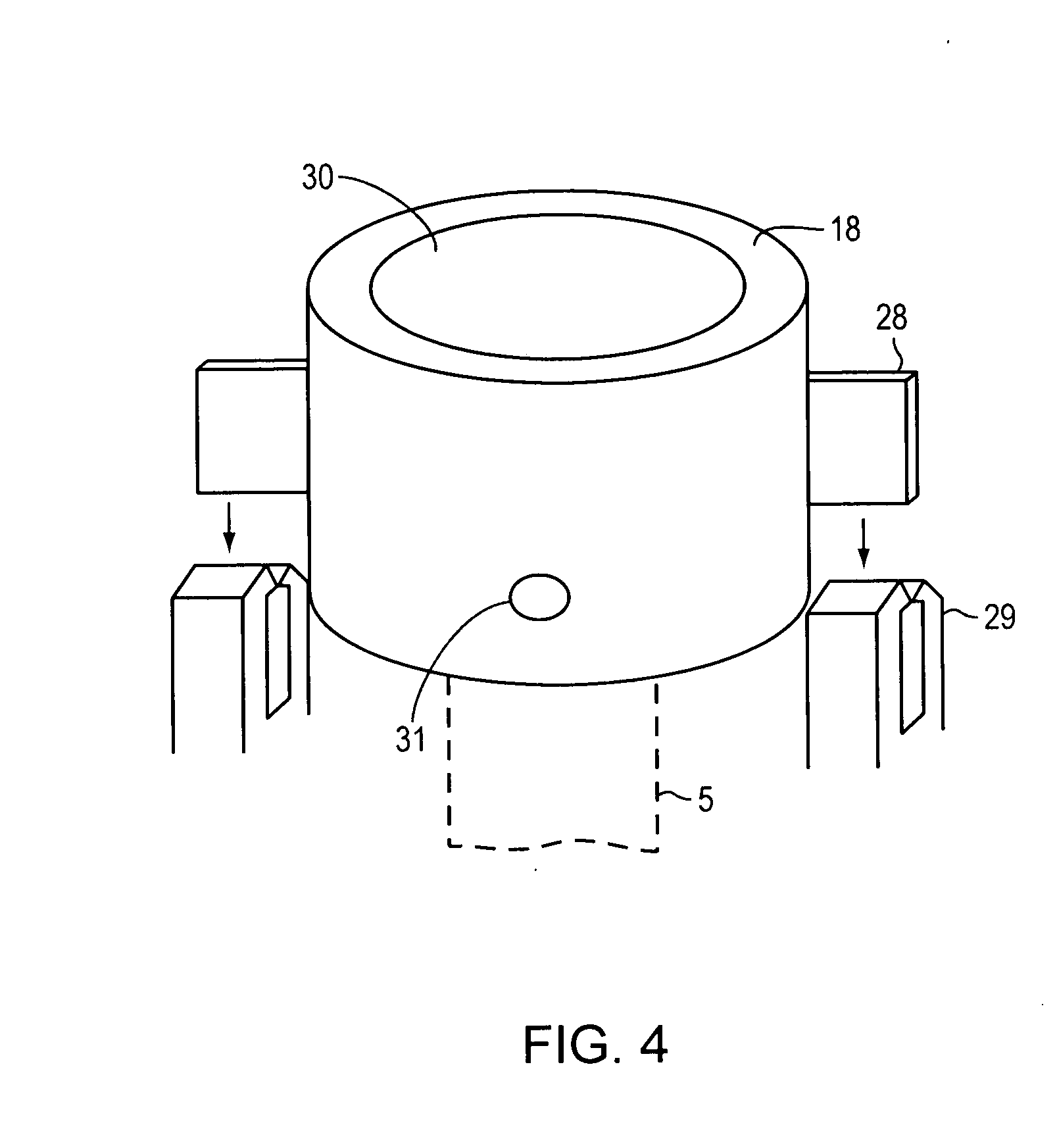
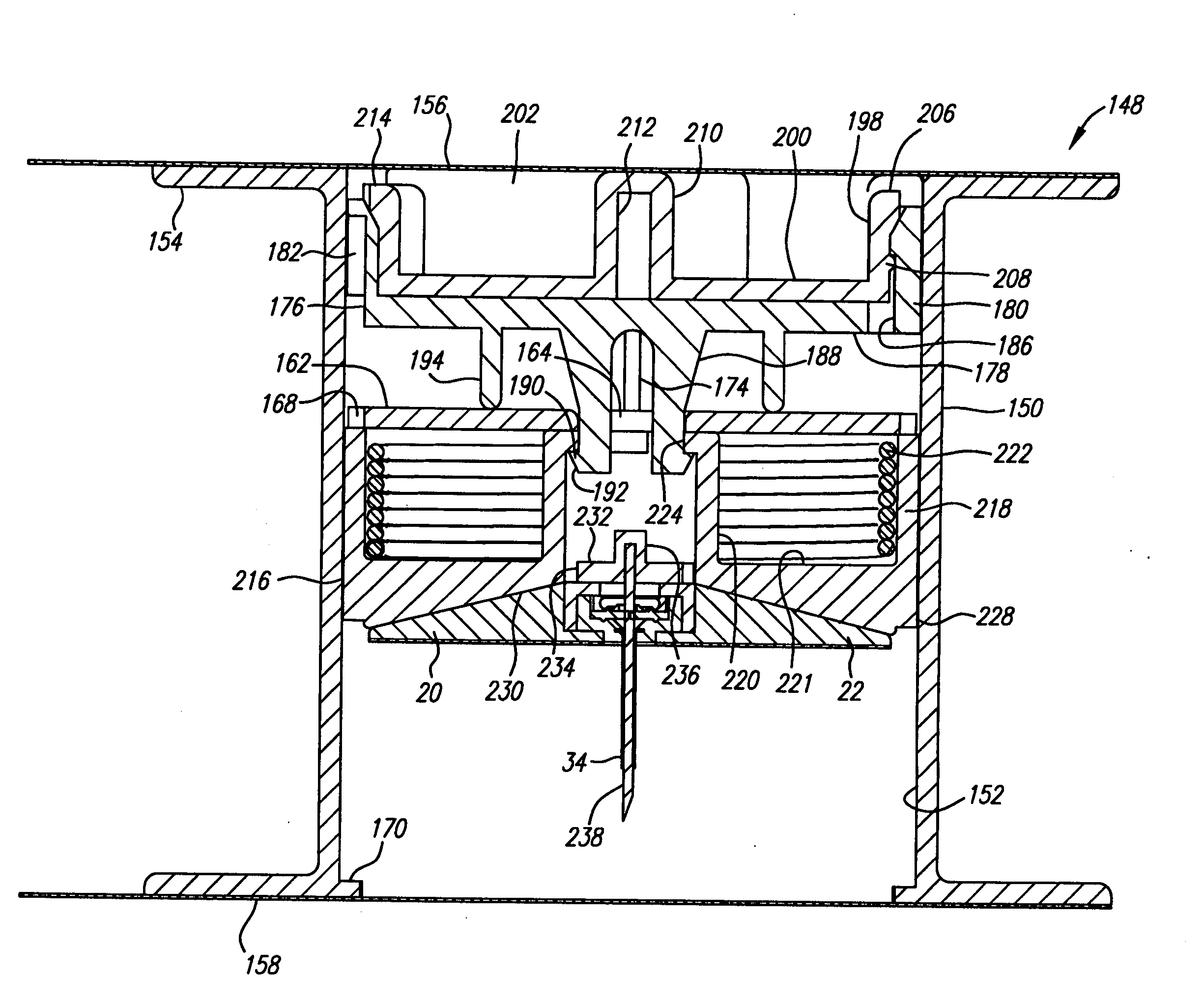
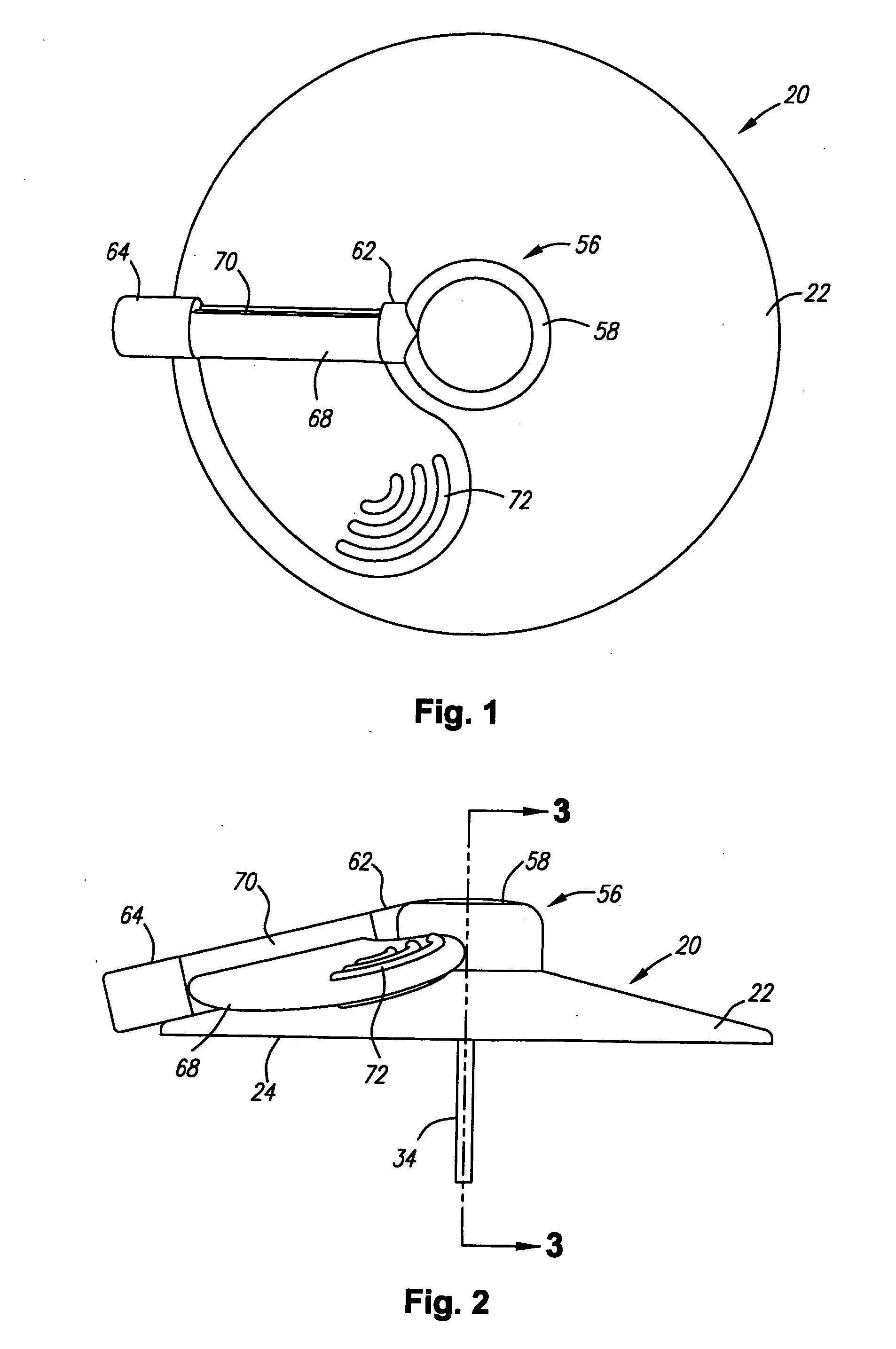
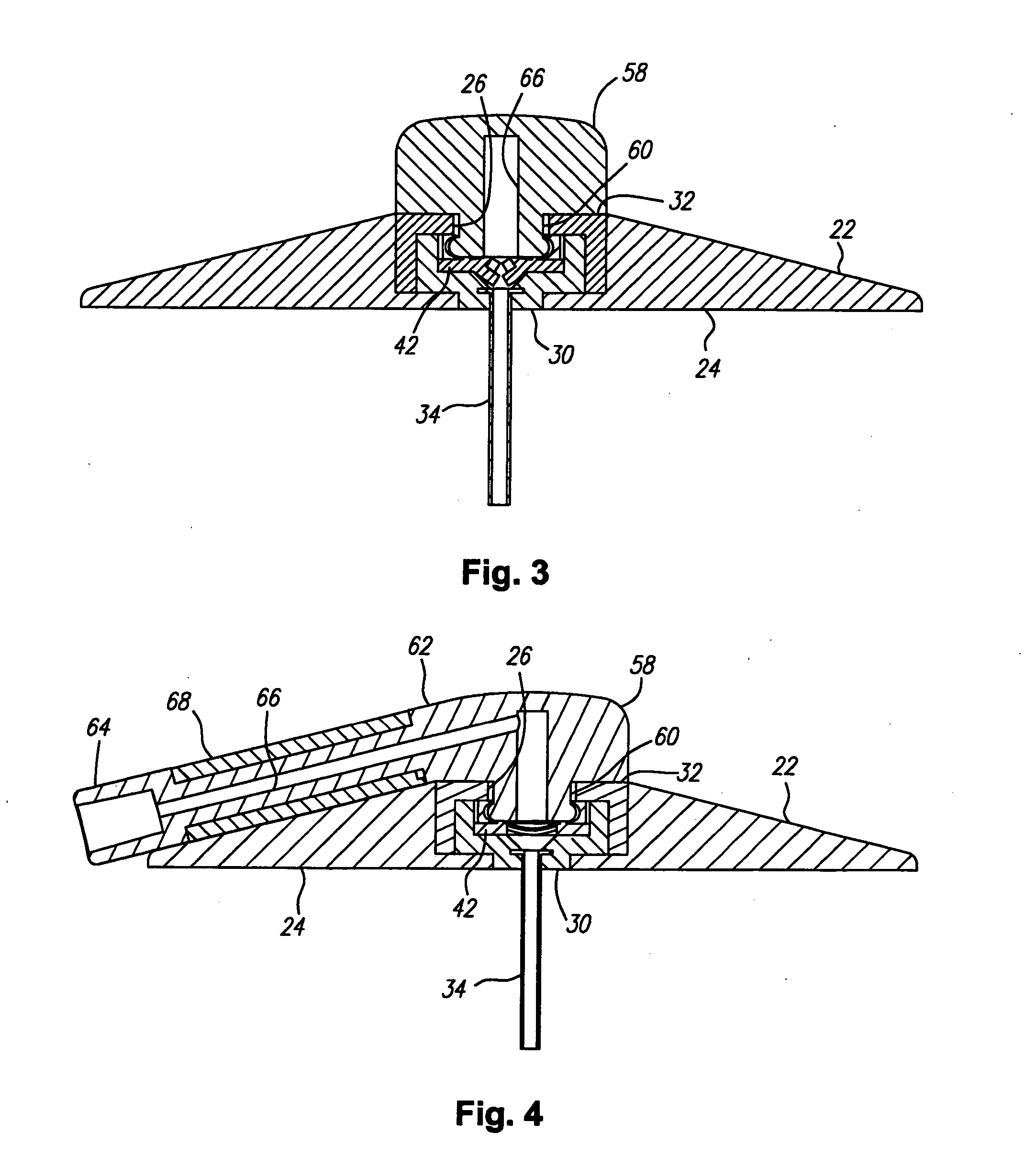
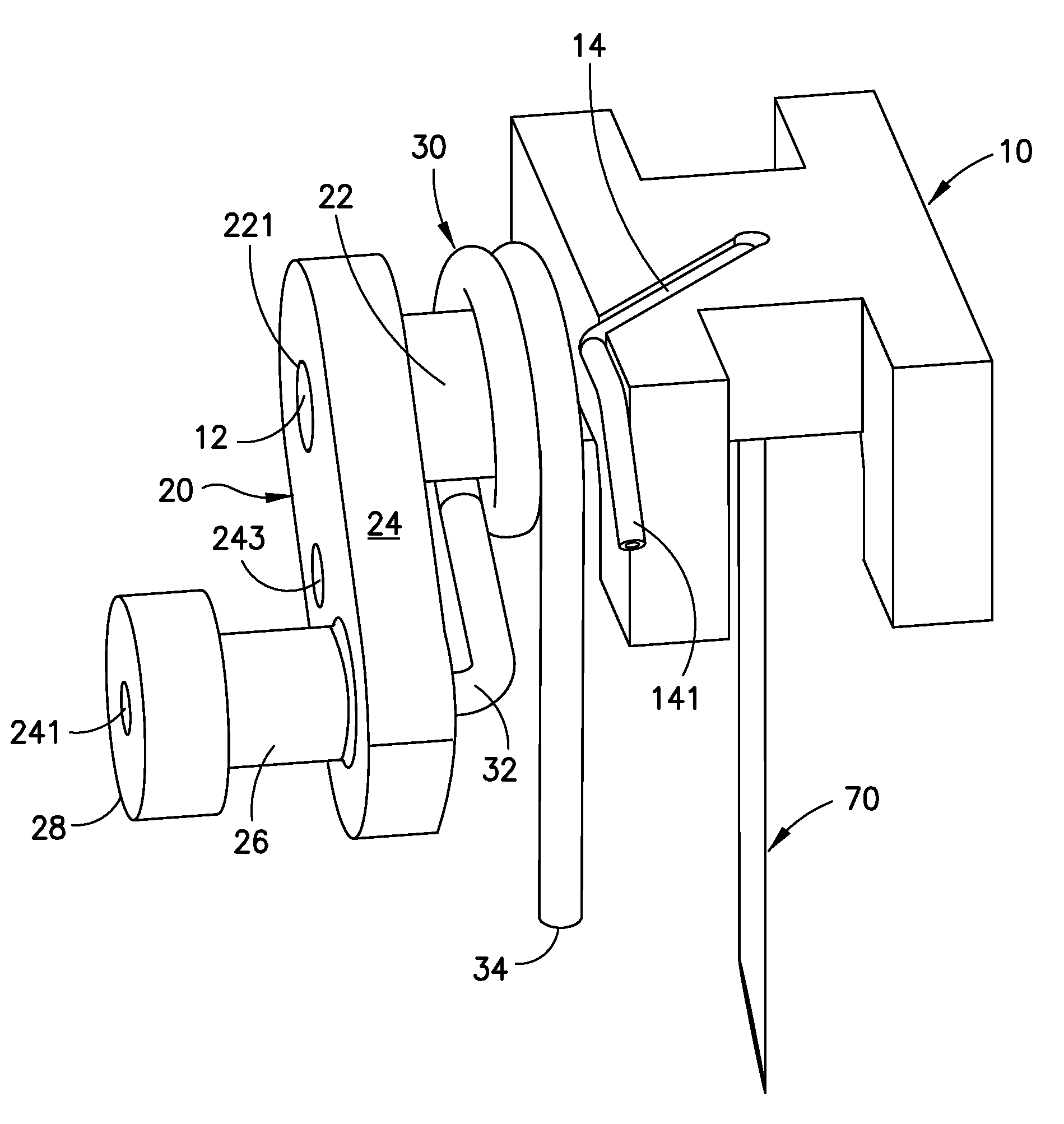
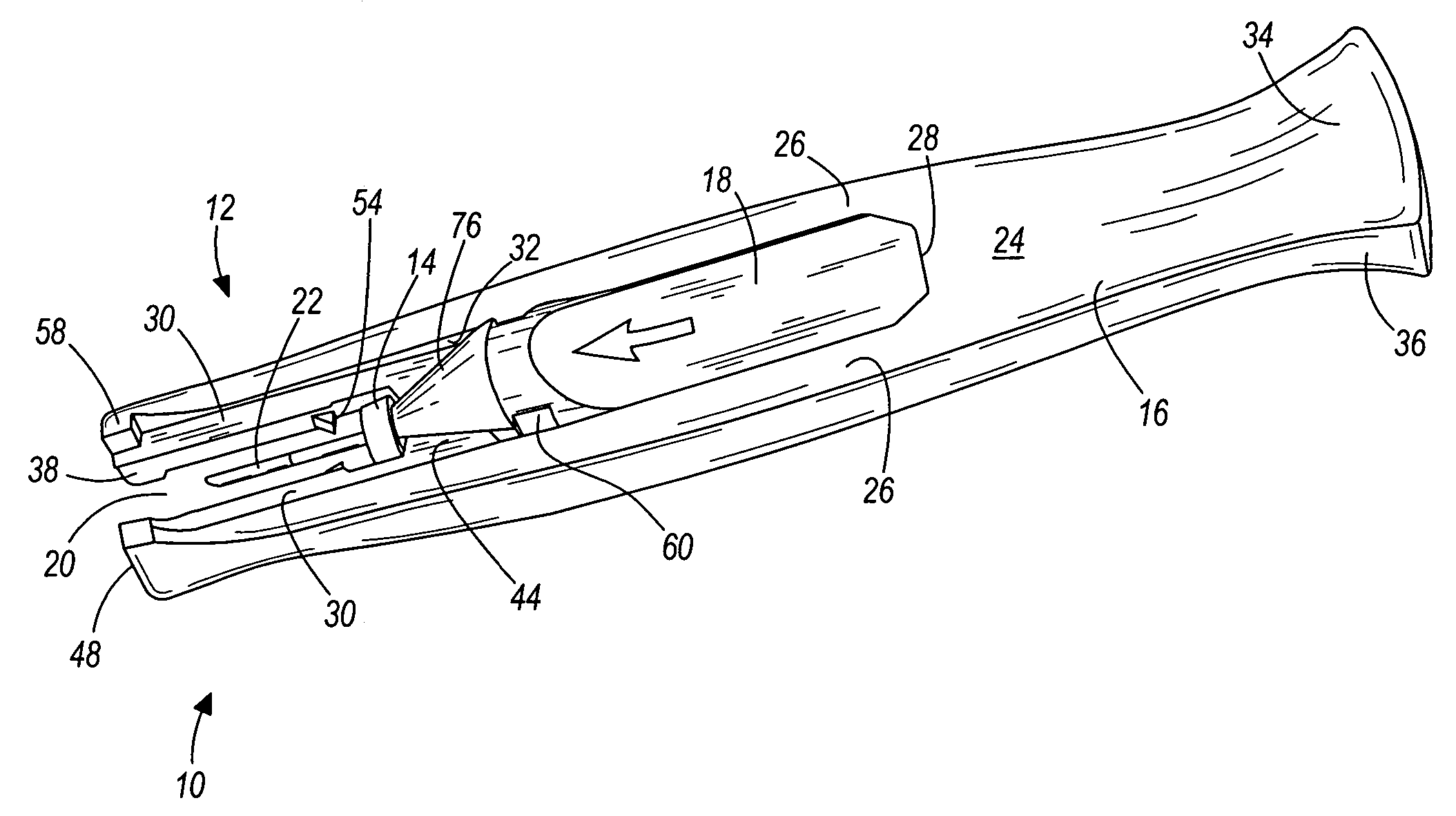
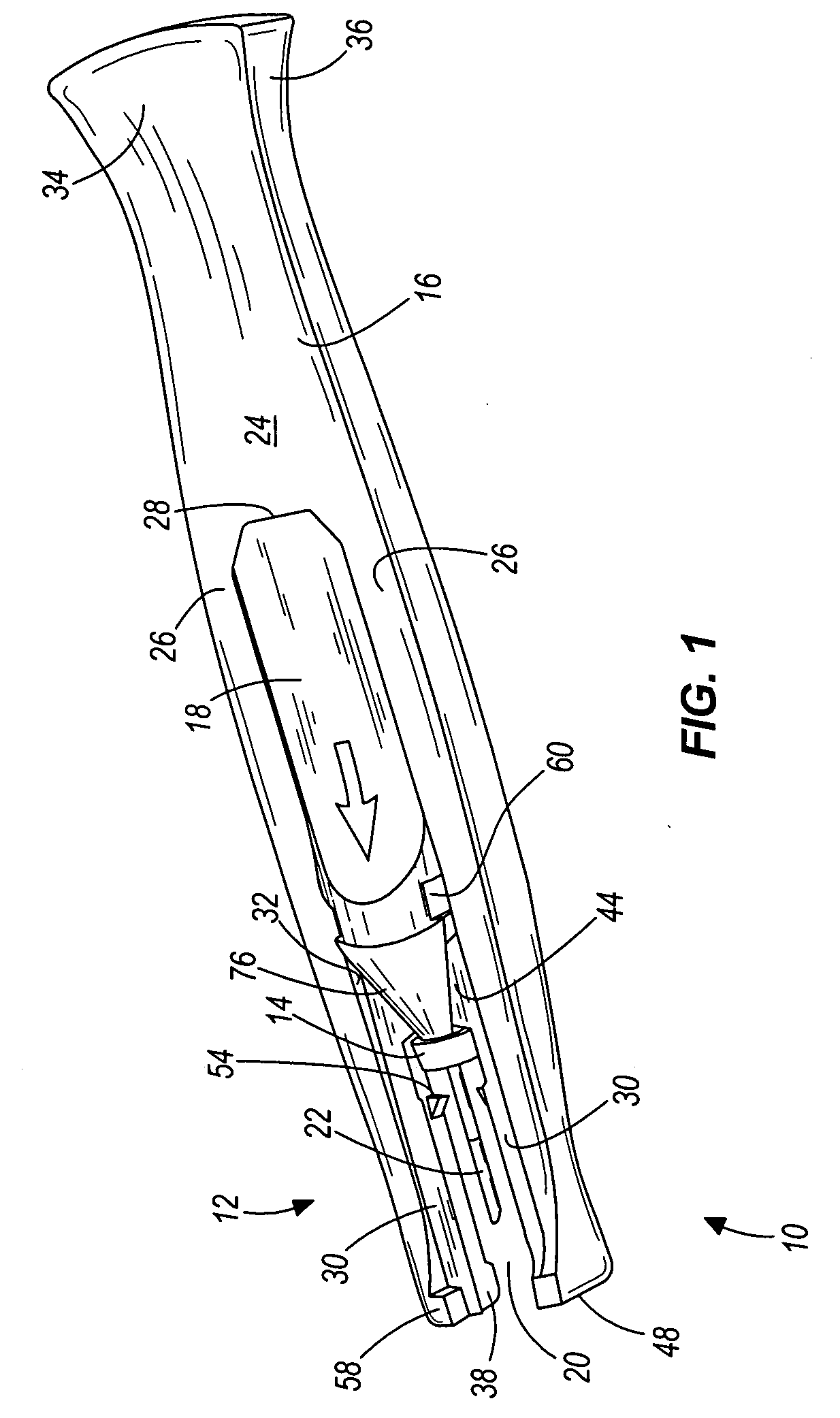
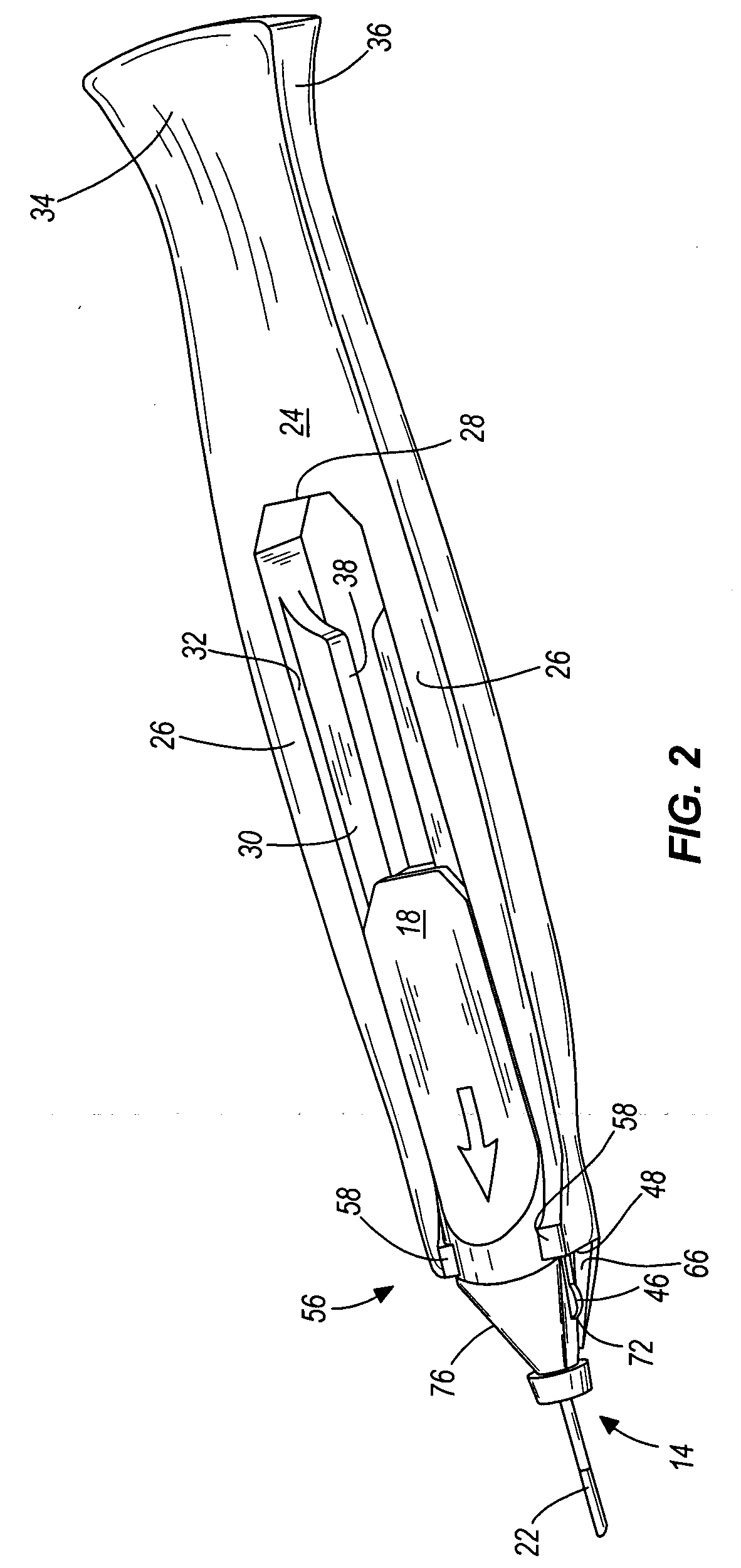
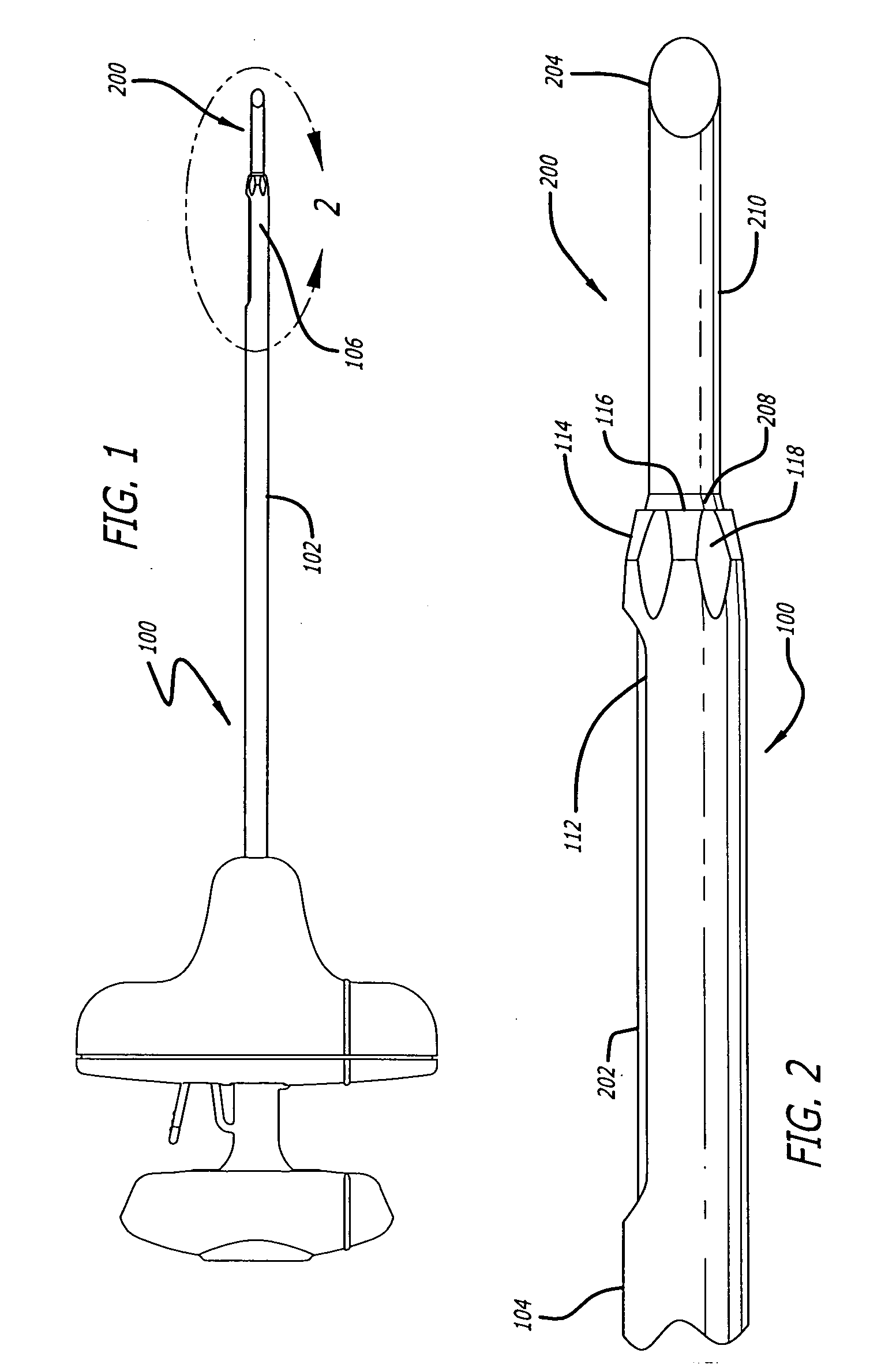
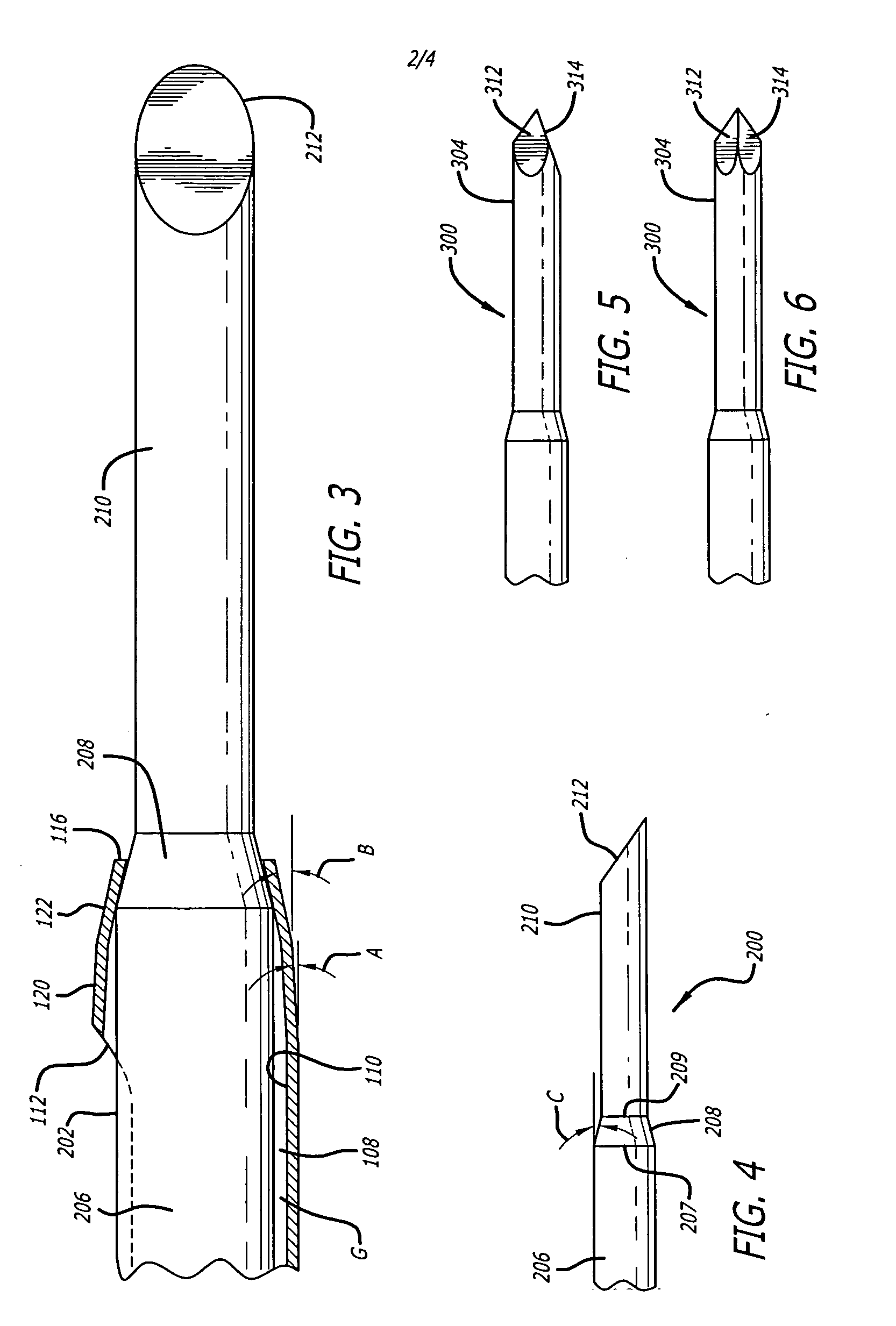
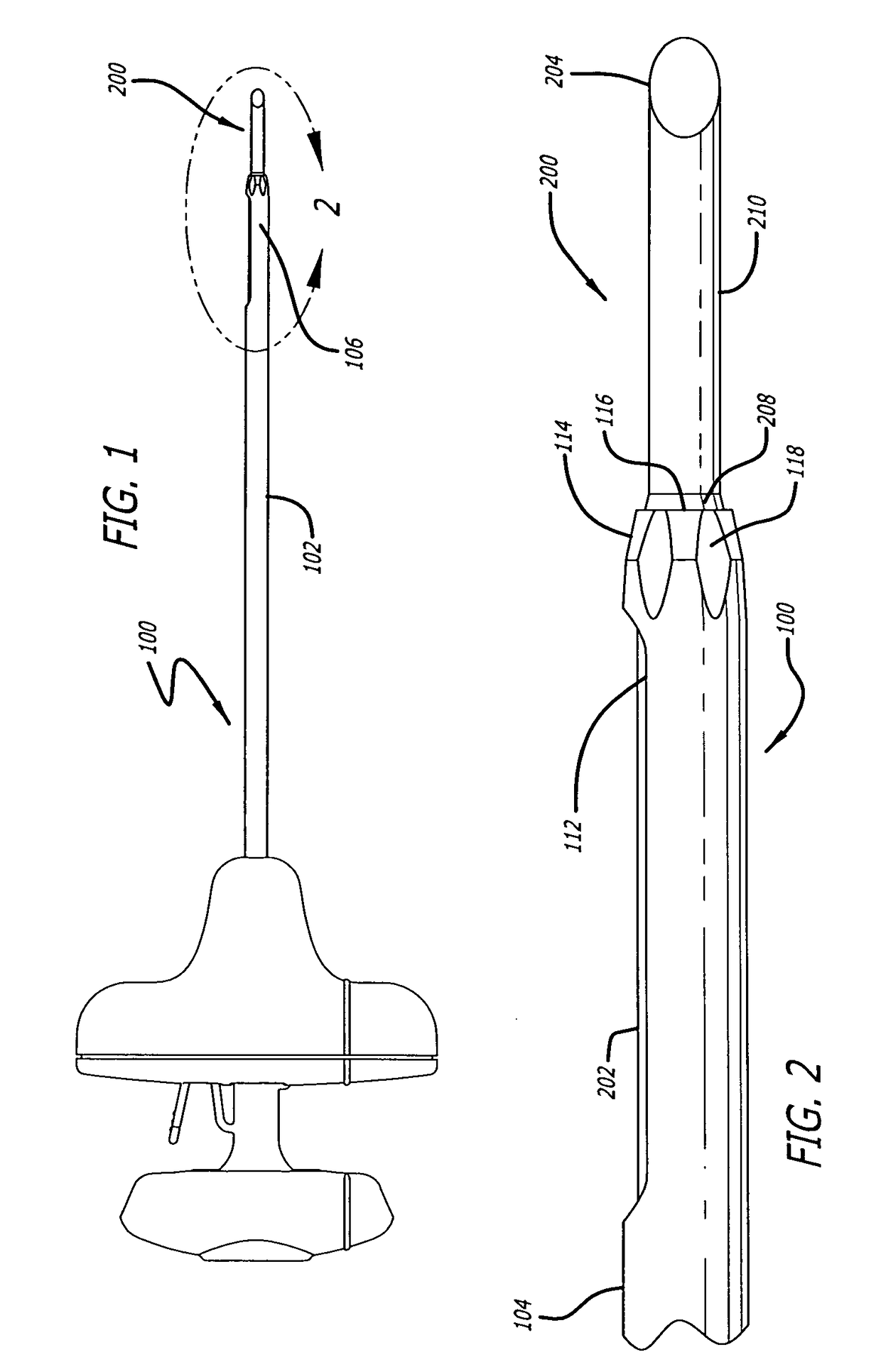
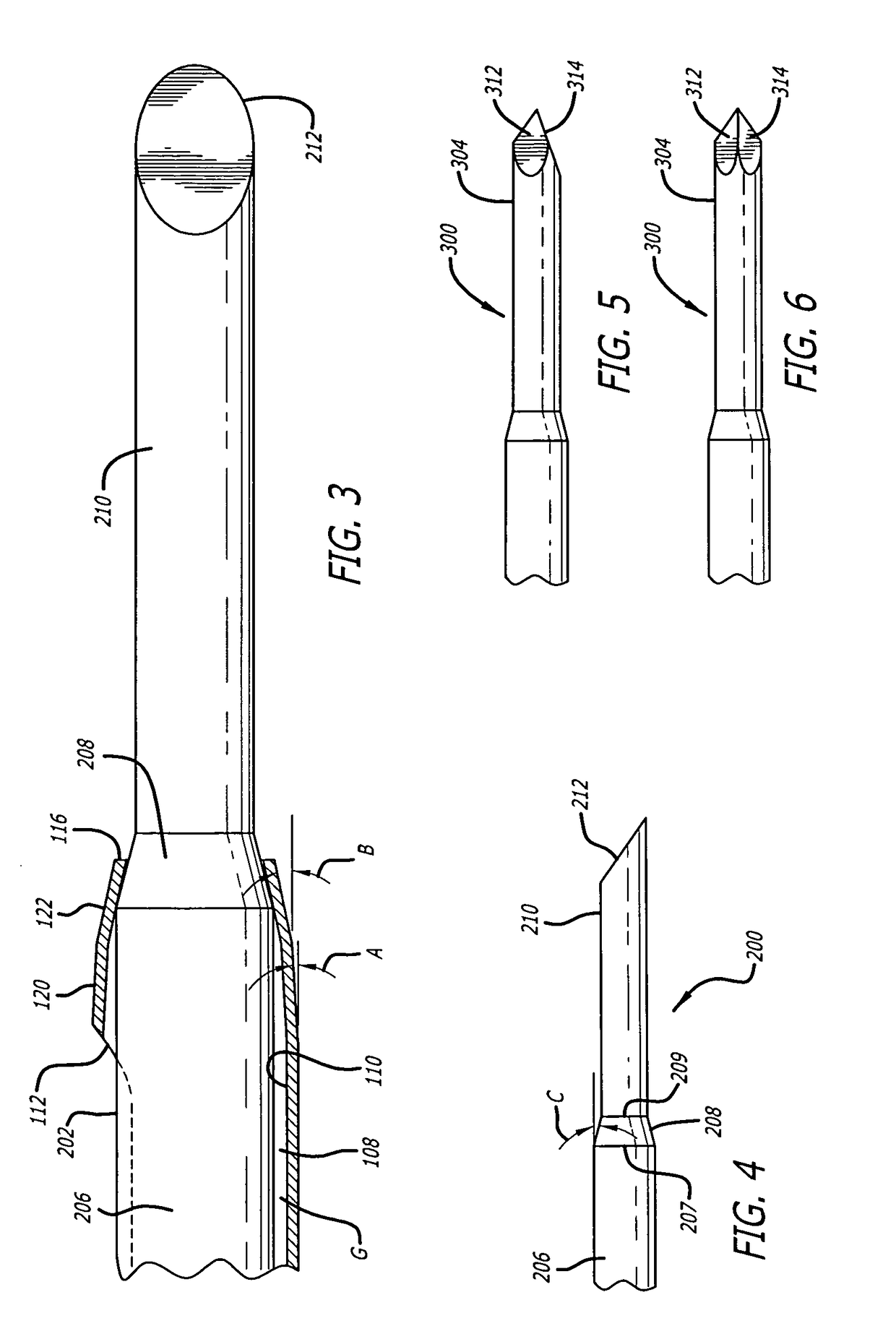
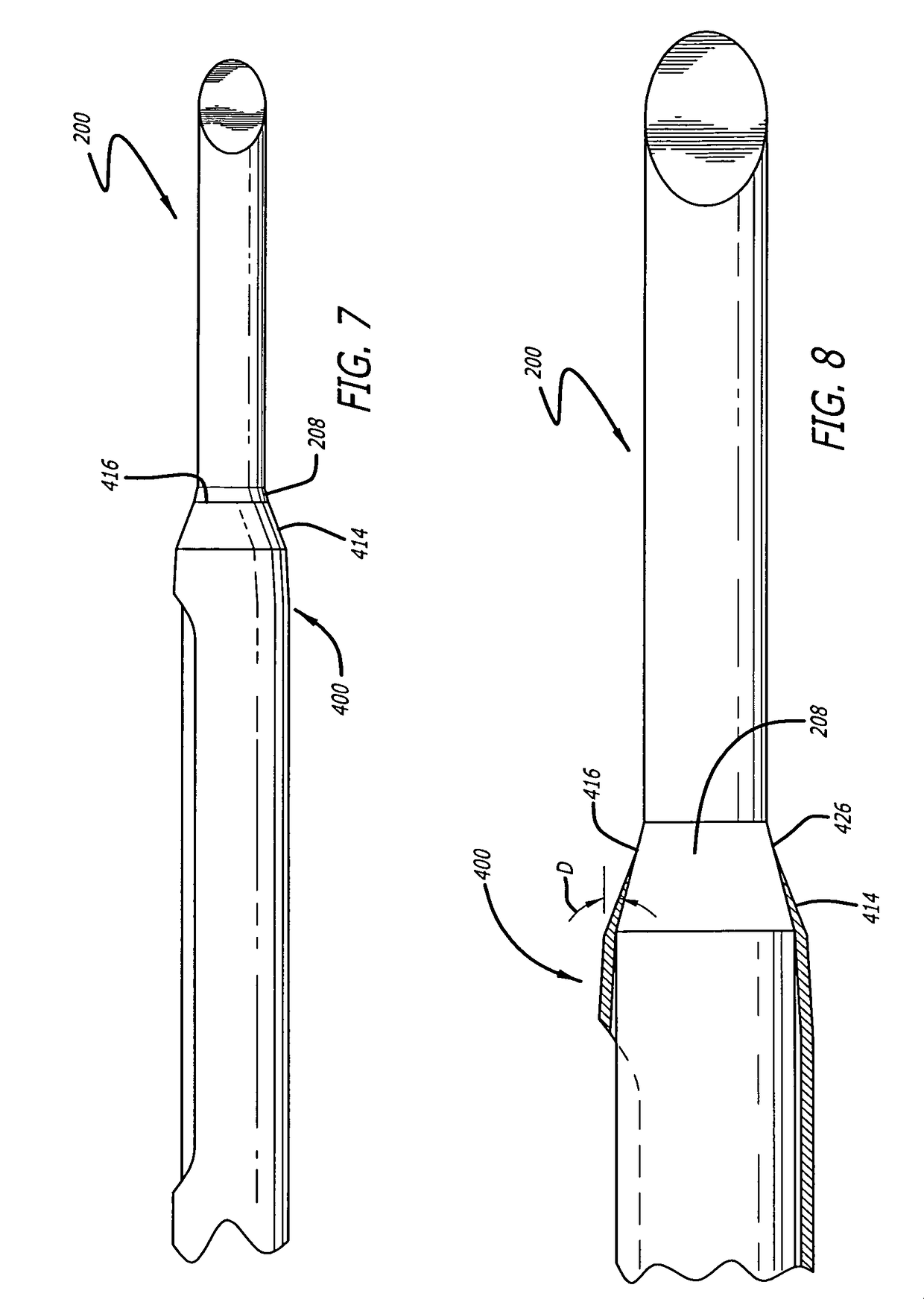
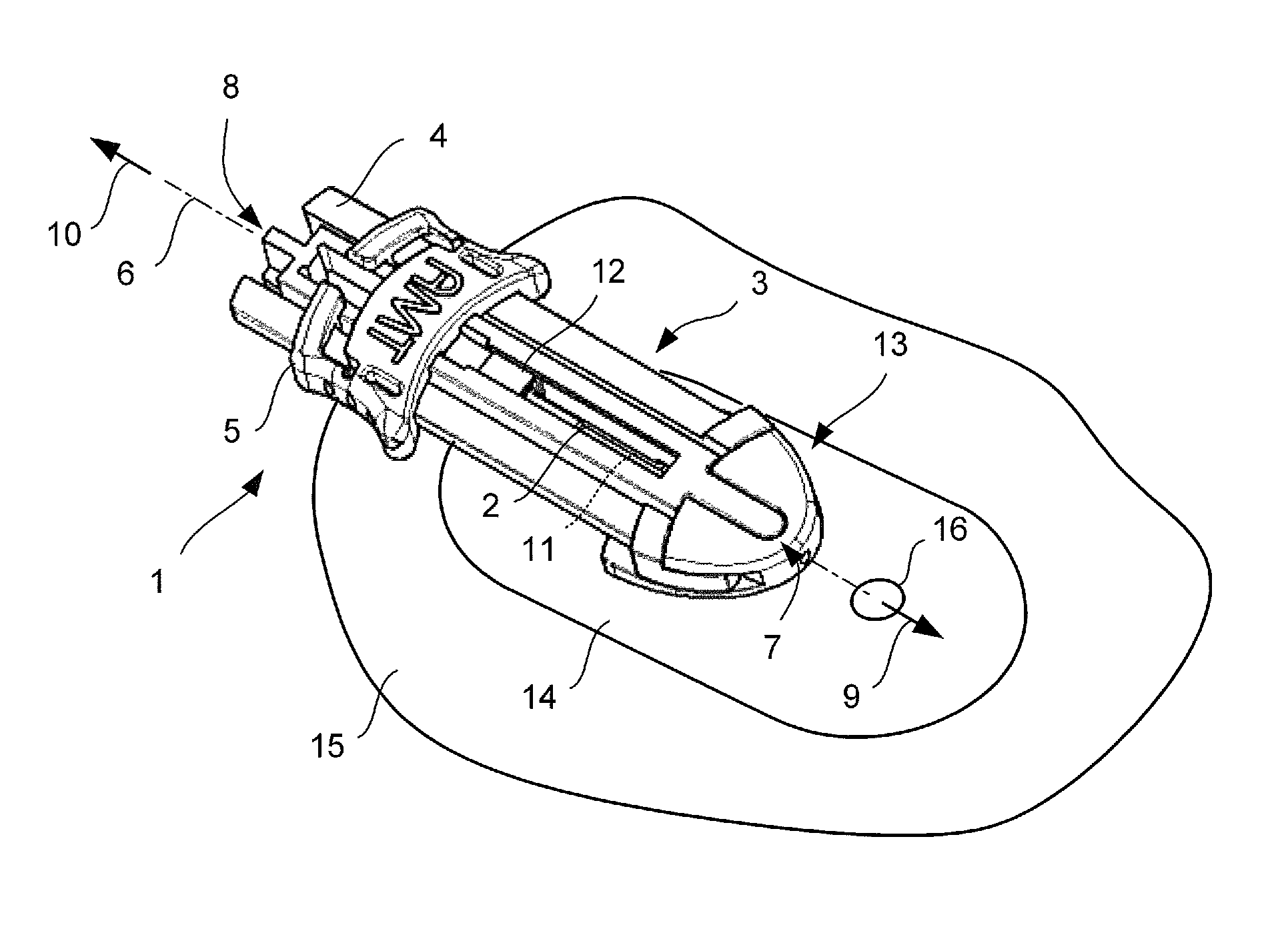
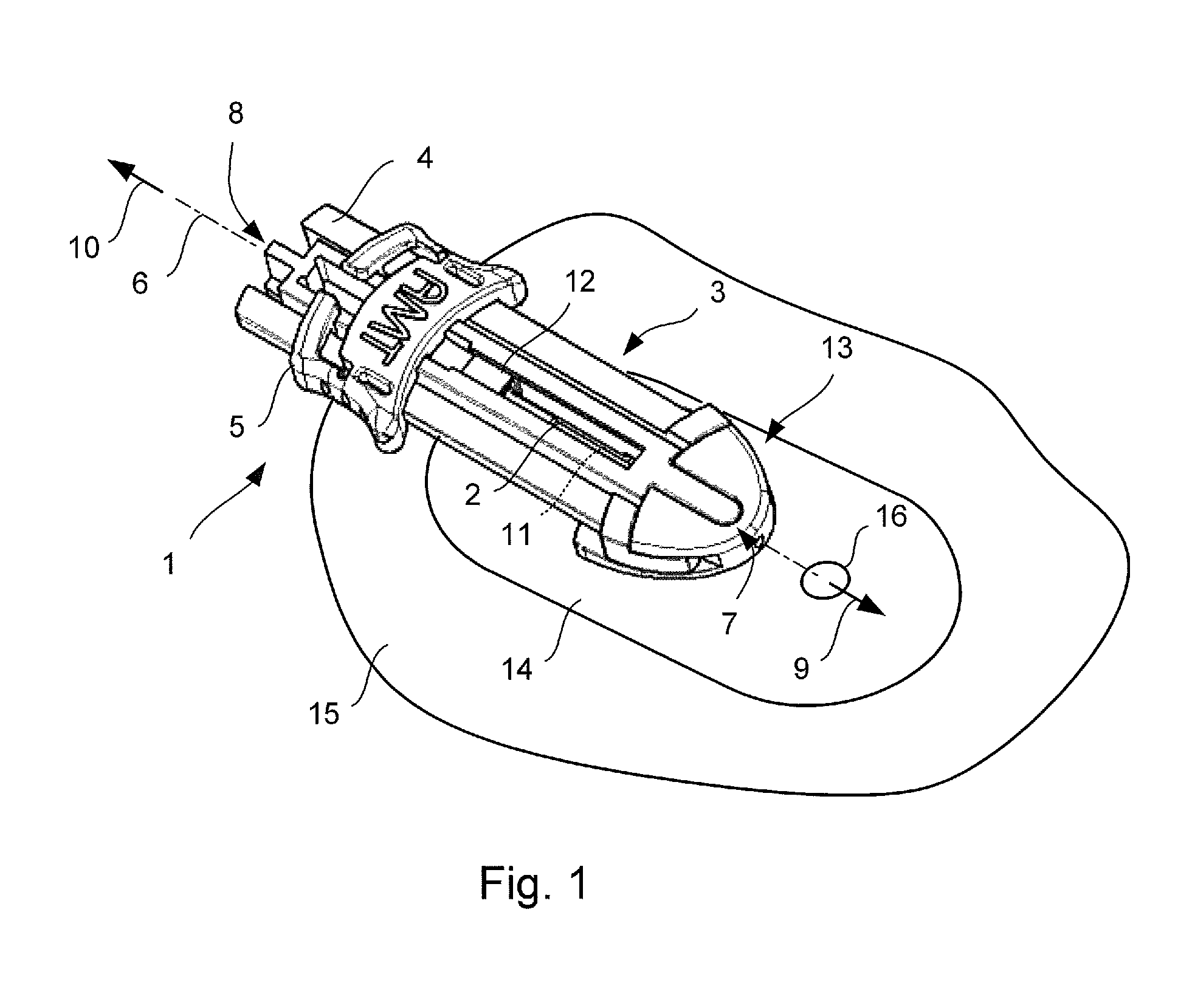
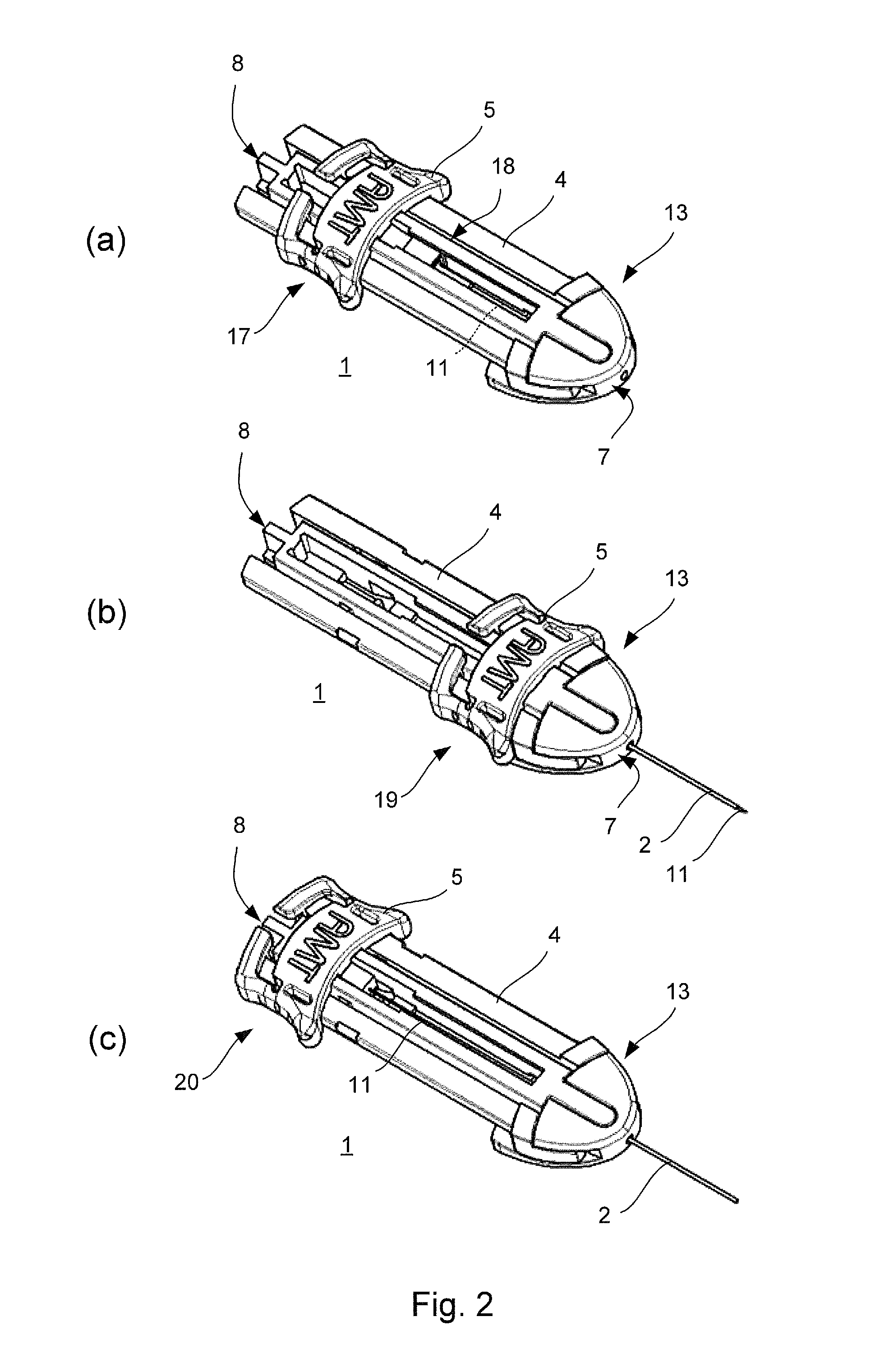
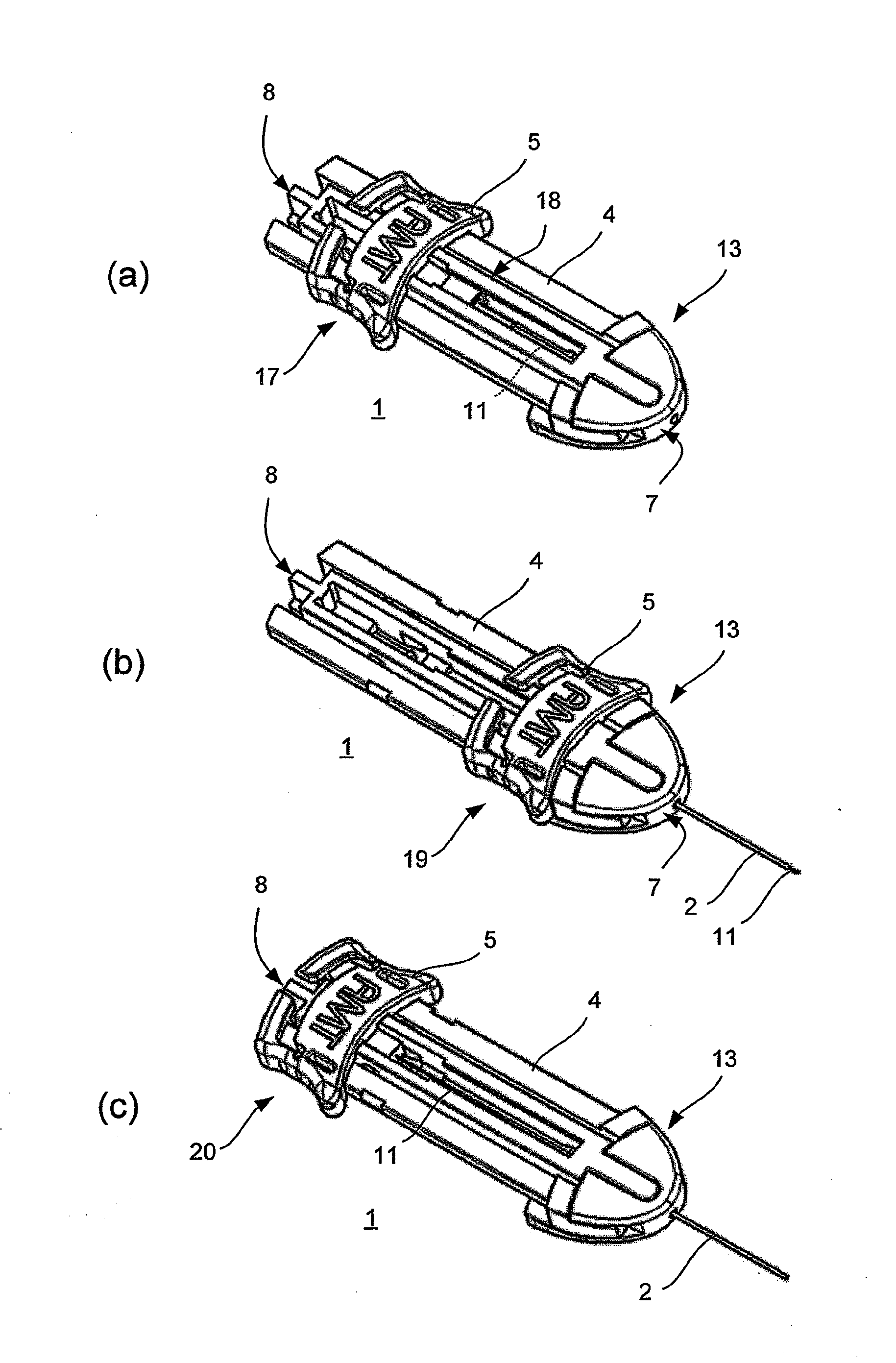
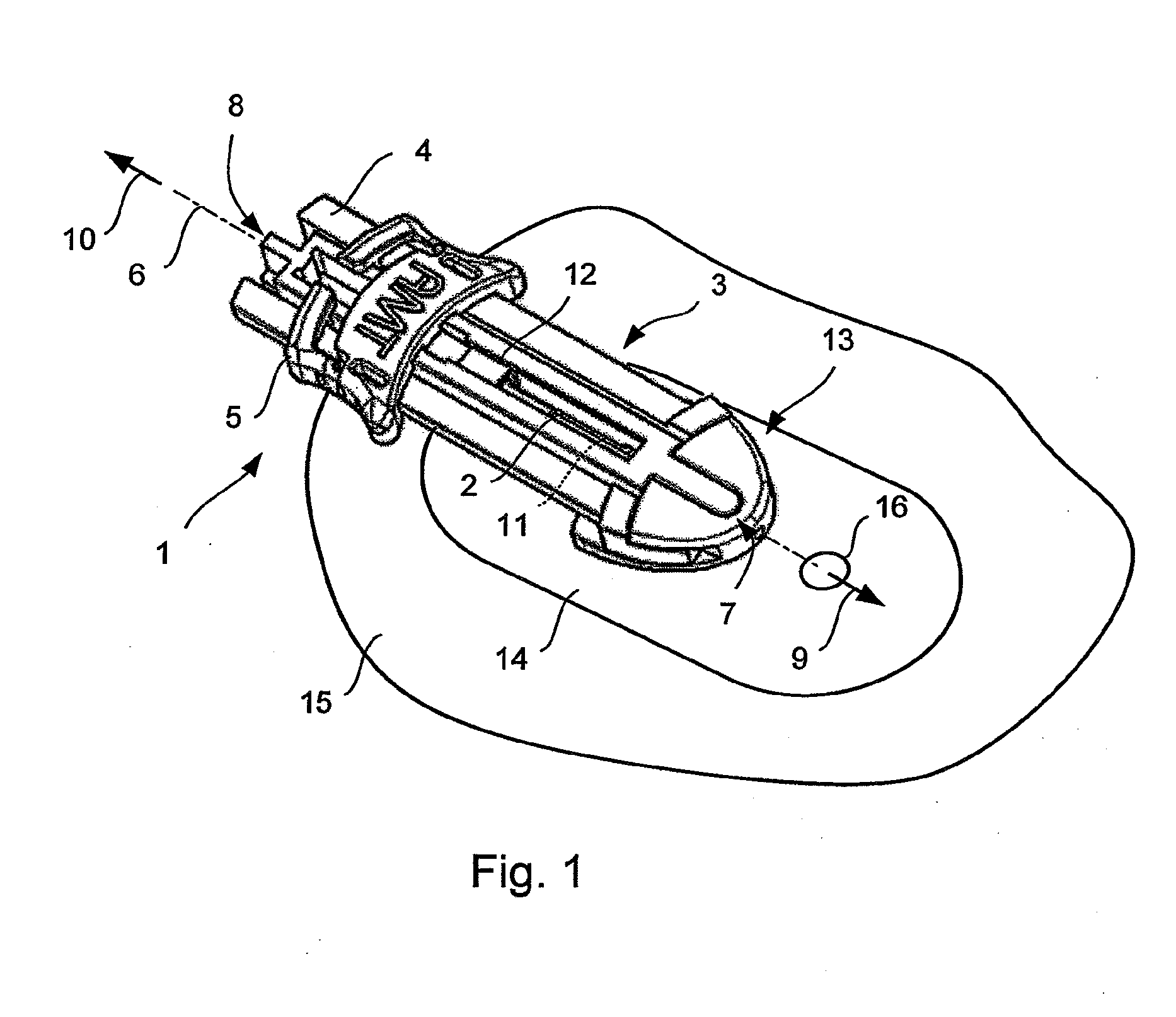
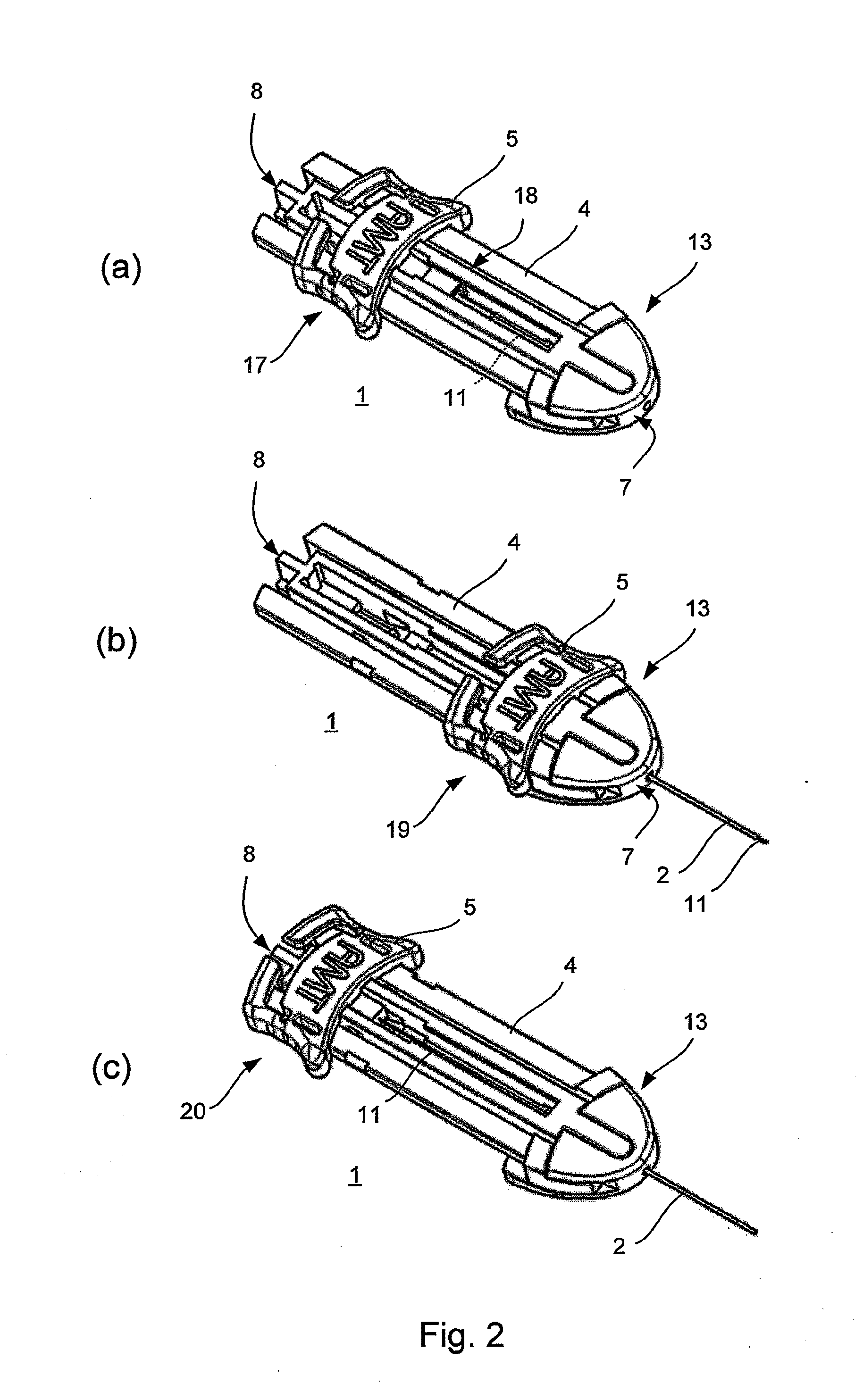
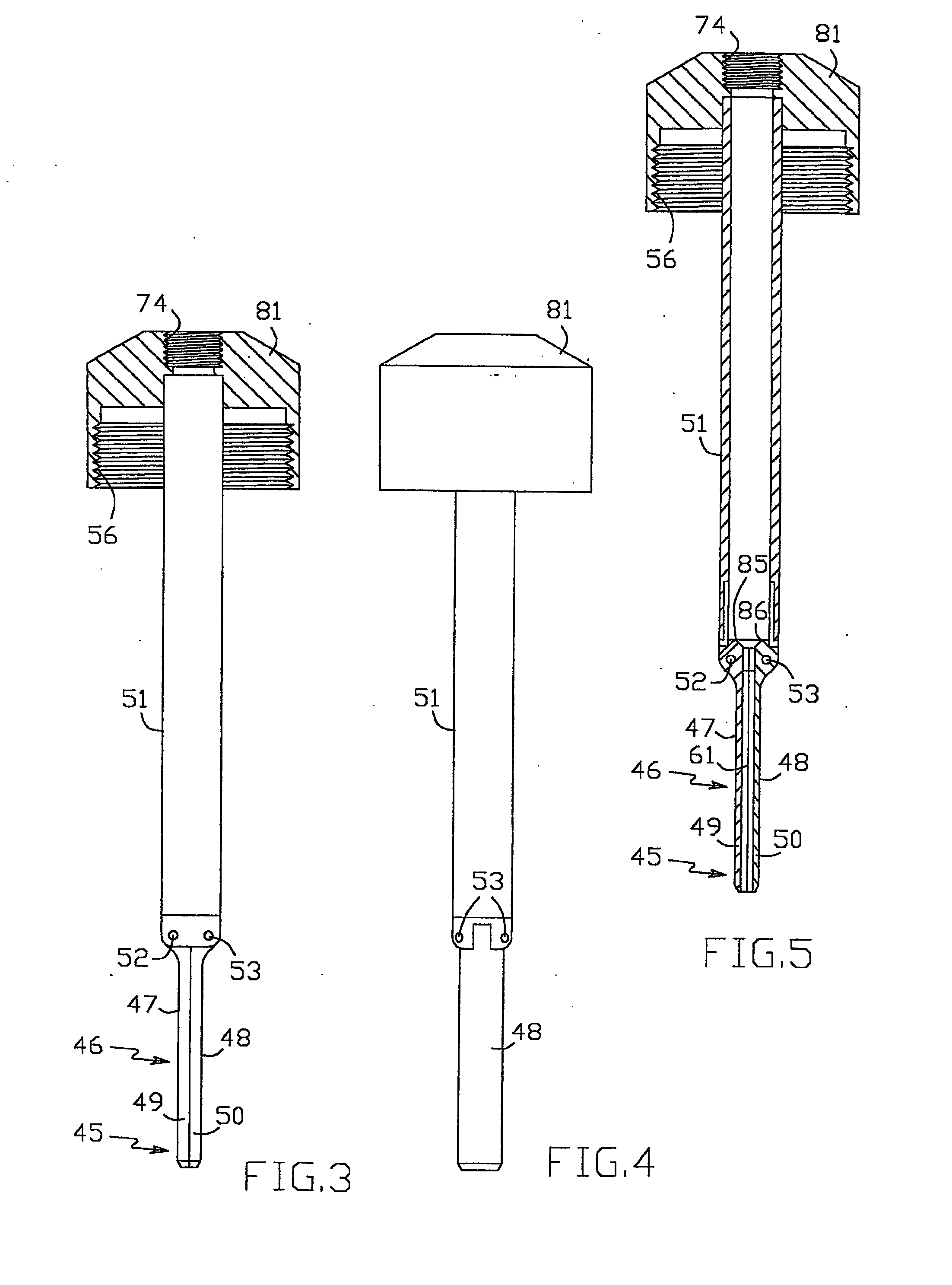
Cannula insertion device
ActiveUS8172803B2Minimise contaminationMinimise injuryCannulasInfusion syringesCannula insertionEngineering
A cannula insertion device comprises an elongate frame (4) and a hub (5) mounted to the frame and arranged to be slidably moveable from a first position forwards along a longitudinal axis to a second position relative to the frame and a needle (11) projecting forwards from the hub and carrying a detachable cannula (2) assembly including a cannula. The frame and hub are arranged to allow the hub to be moved forwards from the first position to the second position so as to insert the cannula into a patient and to be drawn backwards to a withdrawn position. The needle is shielded by the frame when the hub is in the first position and also when in the withdrawn position.
Owner:INFUTECH LTD
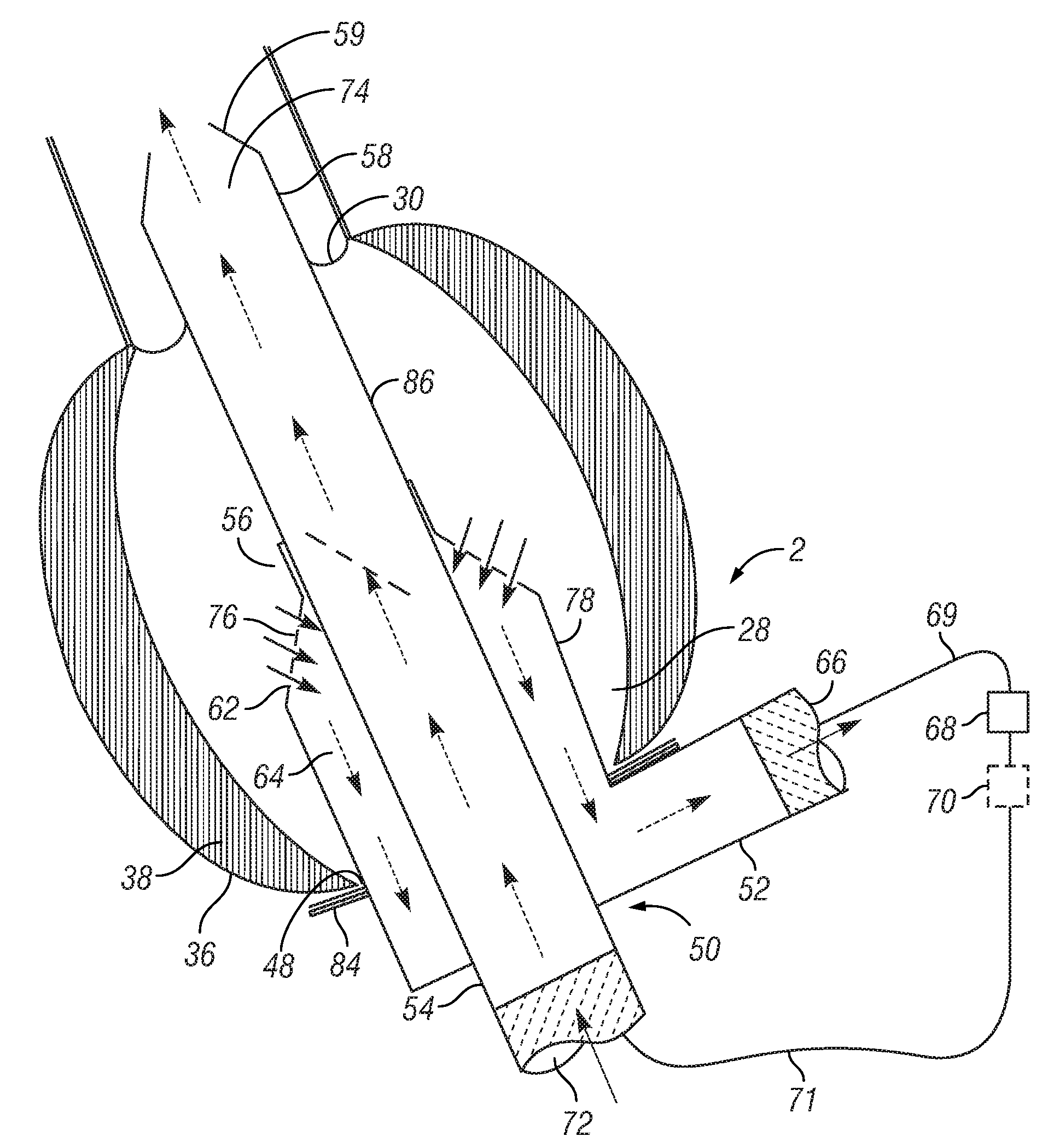
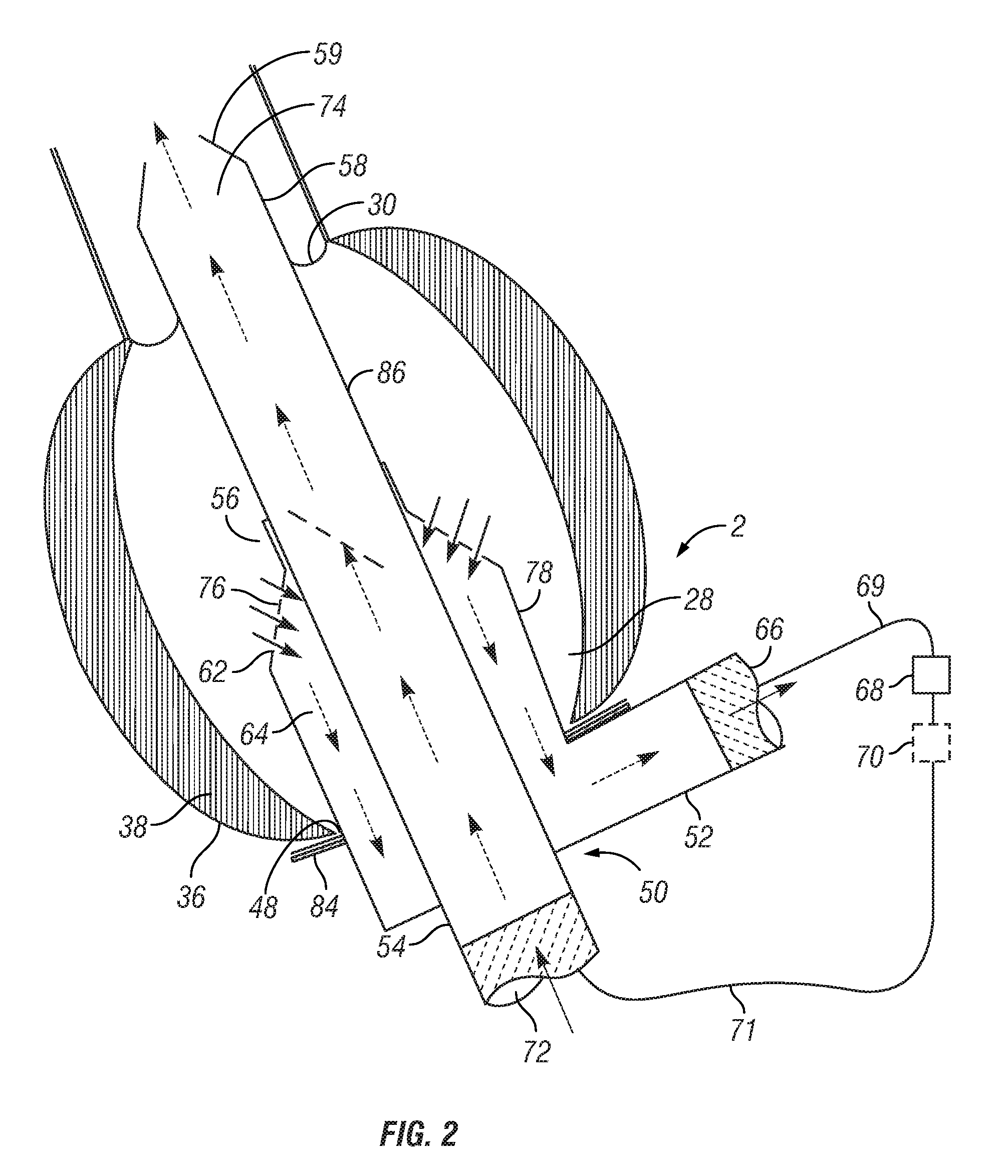
Trocar-cannula complex, cannula and method for delivering fluids during minimally invasive surgery
A fluid delivery cannula which provides an interface between an access point or port site in the body of a patient and a working channel which may receive tools or instruments used during surgical procedures which may be less invasive surgical procedures than traditional open procedures. The cannula allows introduction of fluid(s) into the port site and then into tissue generally at or near that location within the body of the patient. The fluid delivery cannula includes an expandable sleeve that may itself comprise a cannula through which a needle, or trocar assembly is inserted. At least one fluid passageway, is defined, for example, in either the expandable sleeve itself, or defined, by the combination of the needle or trocar assembly and the expandable sleeve. Visual identifiers are used with the fluid delivery cannula to visually distinguish the location of the fluid passageway relative to an adjacent area.
Owner:RED DRAGON INNOVATIONS LLC +1
Method for positioning a catheter guide element in a patient and kit for use in said method
A method for positioning a guide element in a patient and a kit for use in the method. In one embodiment, the method involves transorally inserting an endoscope into a patient's stomach. An incision site is externally indicated by transilluminating the stomach and abdominal walls of the patient from within the stomach. Next, a scalpel incision is made at the indicated incision site, and an access needle is inserted into the incision, the proximal end of the access needle remaining external to the patient and the distal end of the access needle extending into the patient's stomach. The stylet of the access needle is then removed from the patient while keeping the cannula in place. Next, the distal end of a grasping tool is inserted through the cannula and into the patient's stomach. The looped leading end of a pullwire is then inserted through the endoscope and into the stomach. The tool is then manipulated until a distal hook on the tool catches the looped leading end. Next, the tool and the looped leading end are withdrawn from the patient through the cannula. The endoscope is then withdrawn from the patient over the trailing end of the pullwire. In this manner, the pullwire is positioned so that the trailing end of the pullwire extends from the patient's mouth and the leading end of the pullwire extends from the incision.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
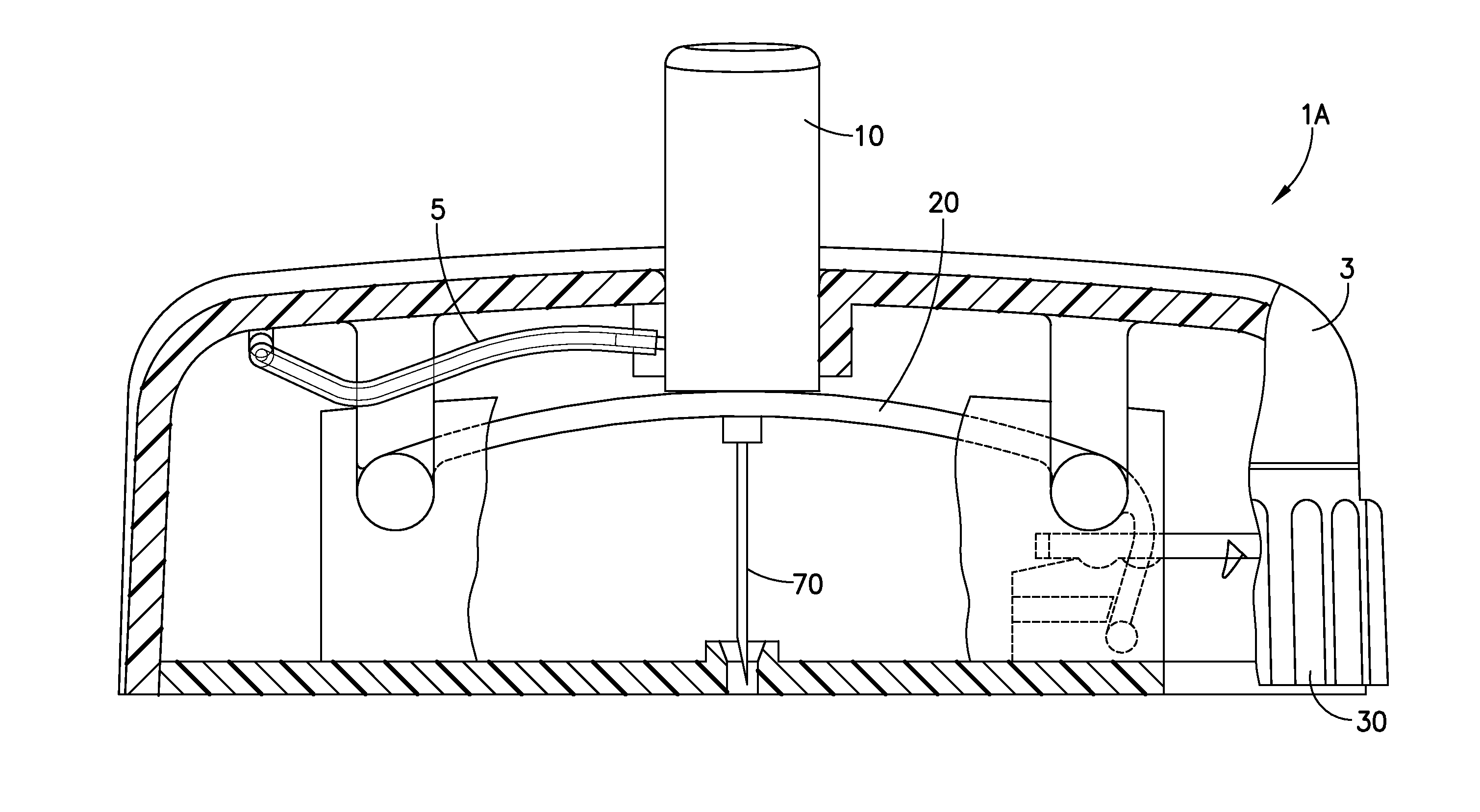
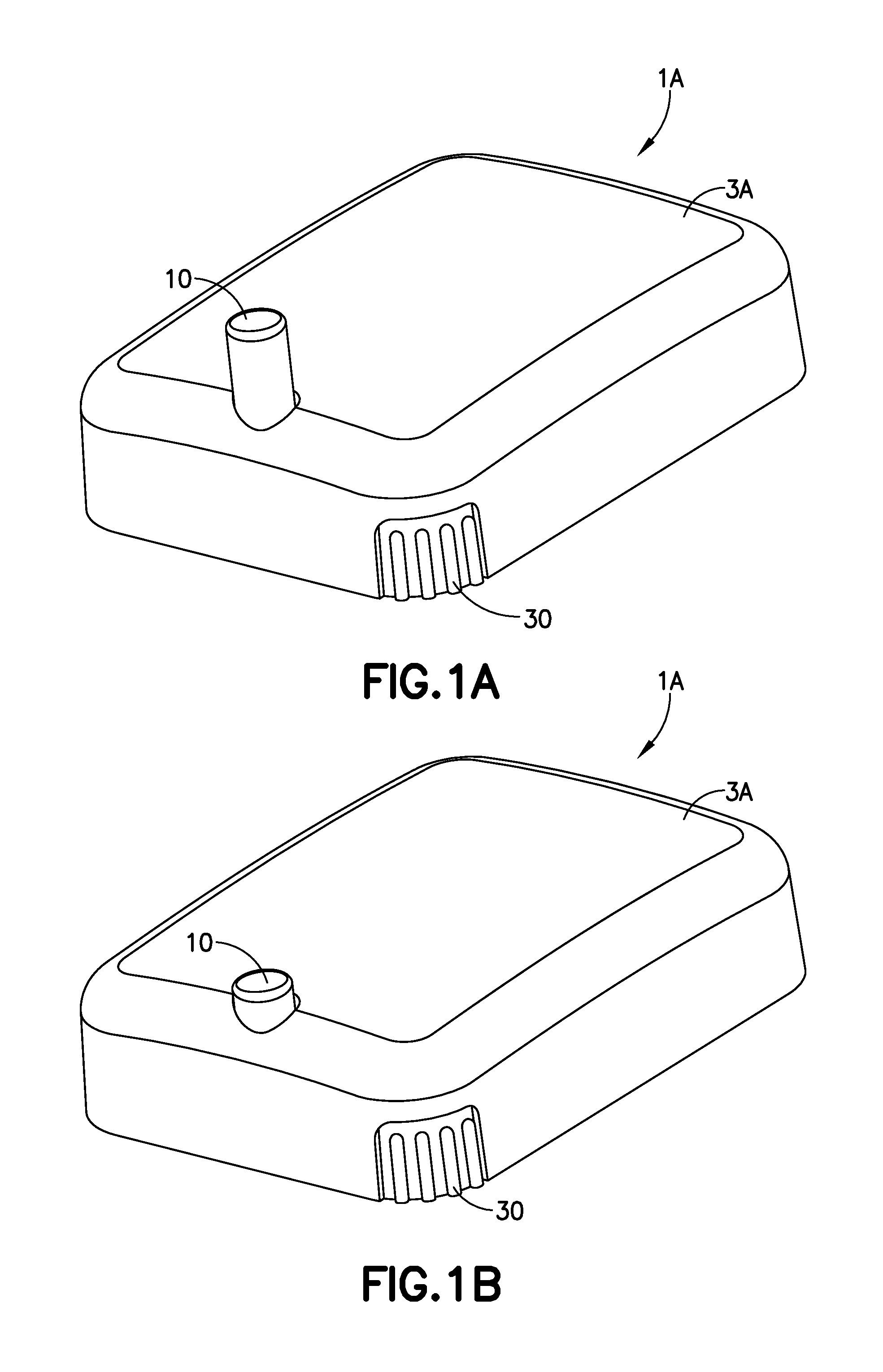
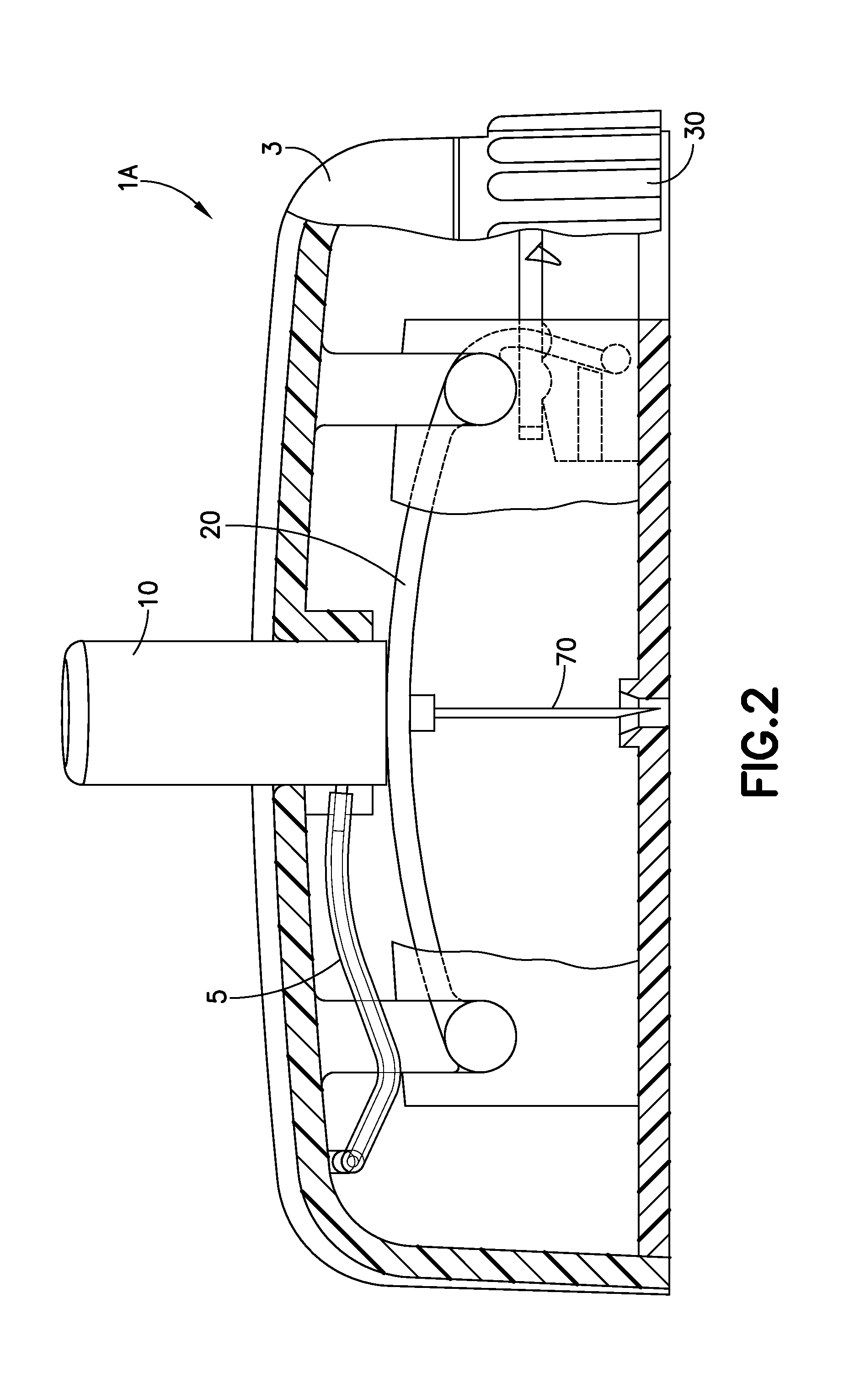
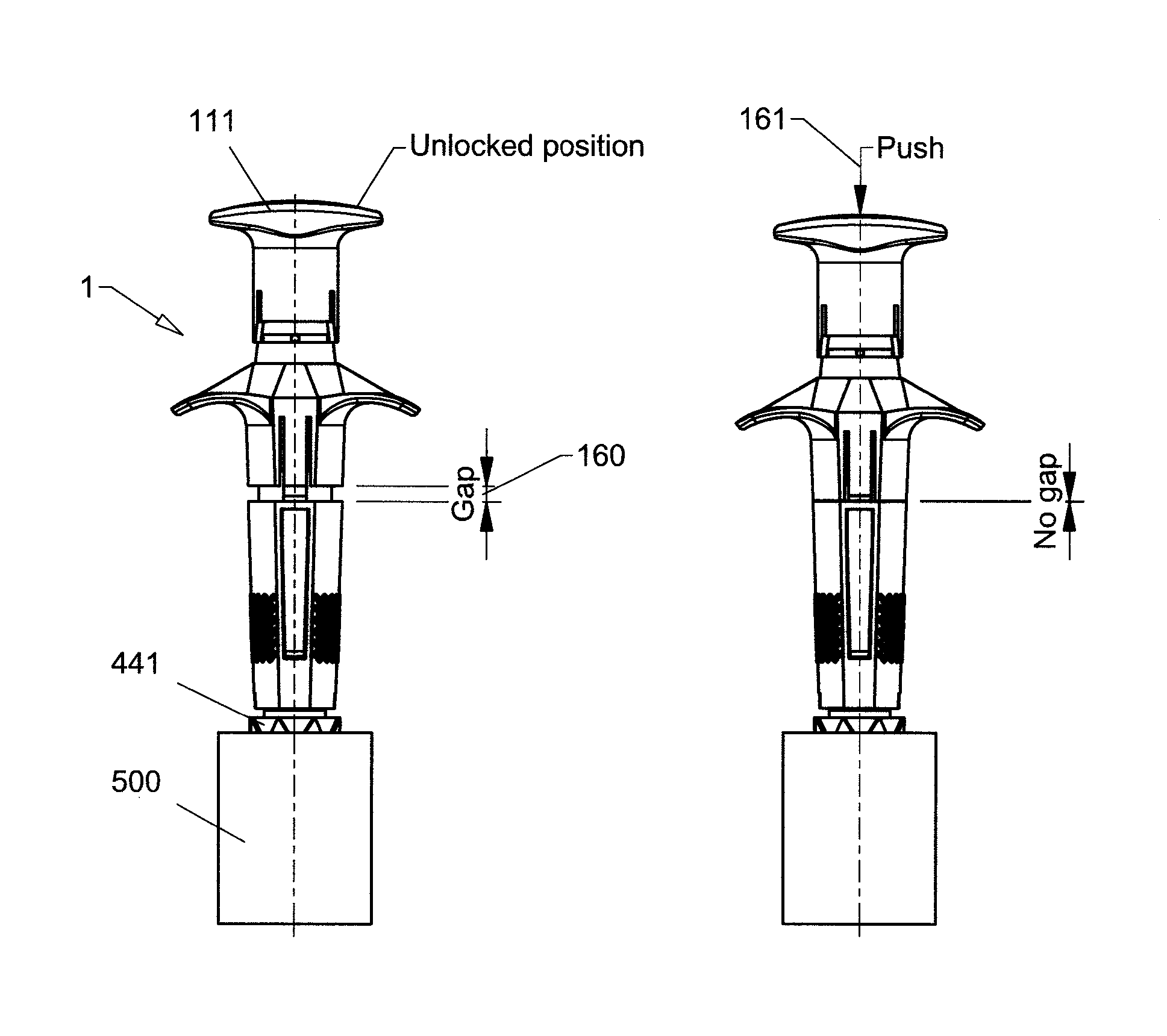
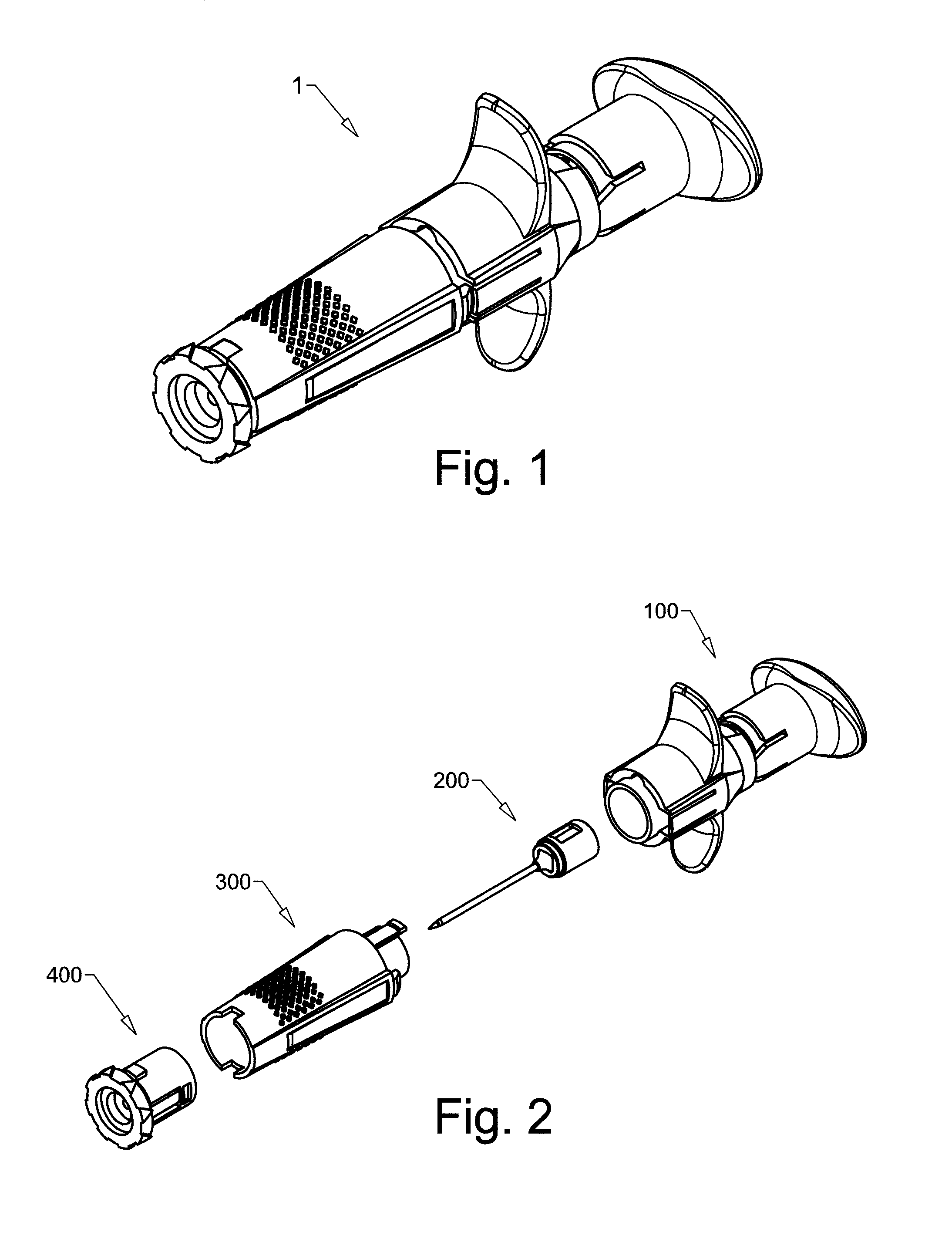
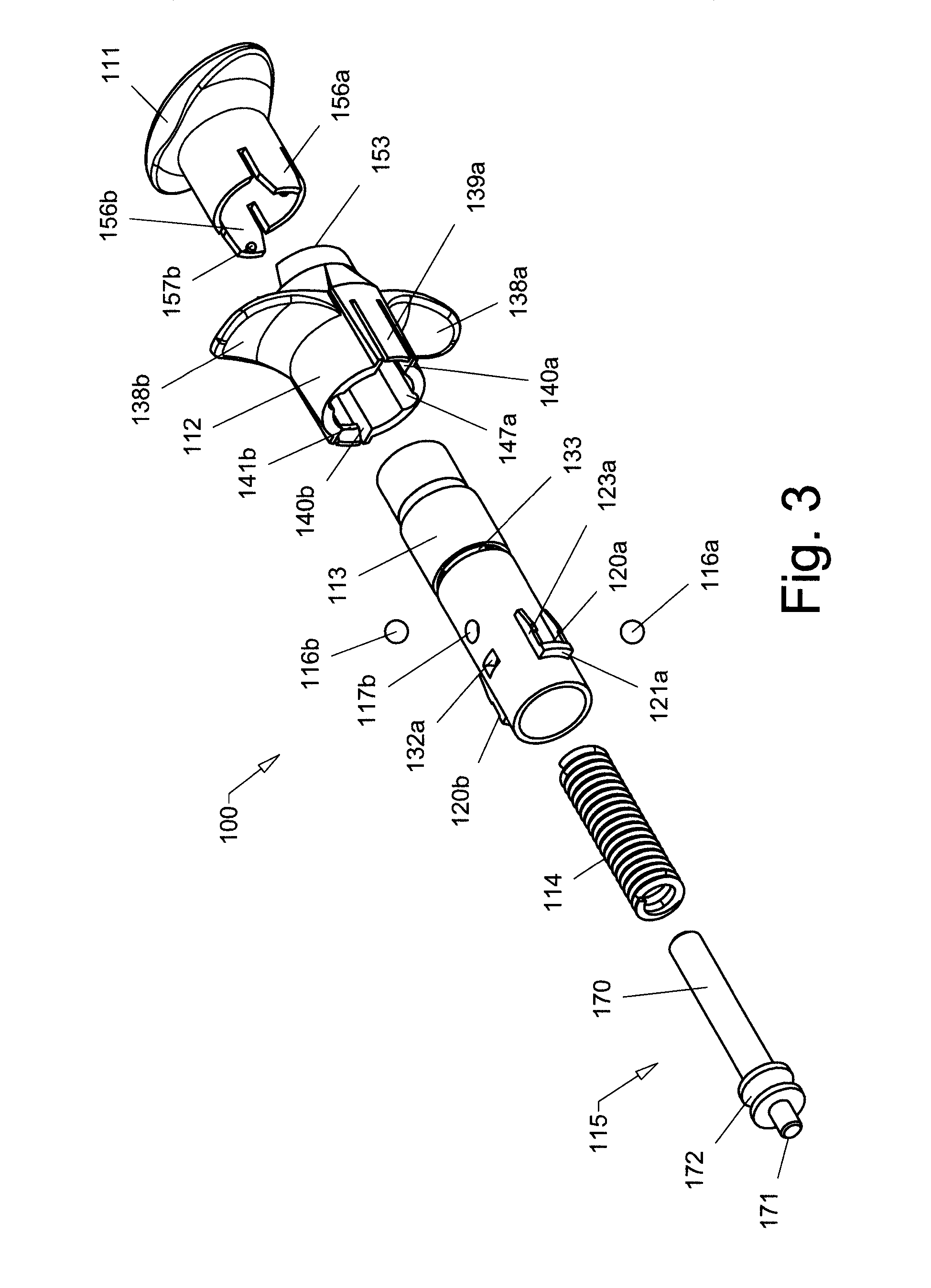
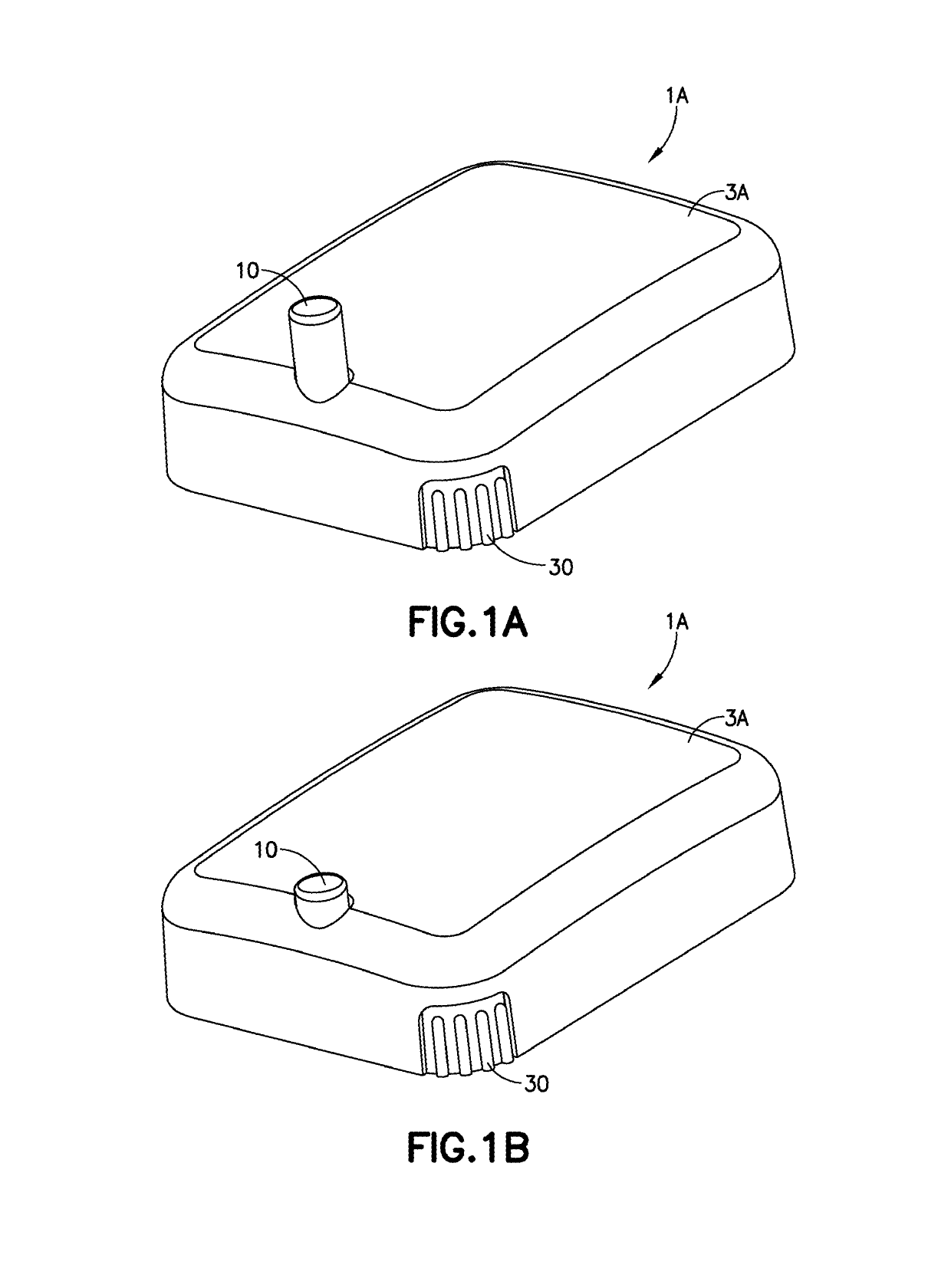
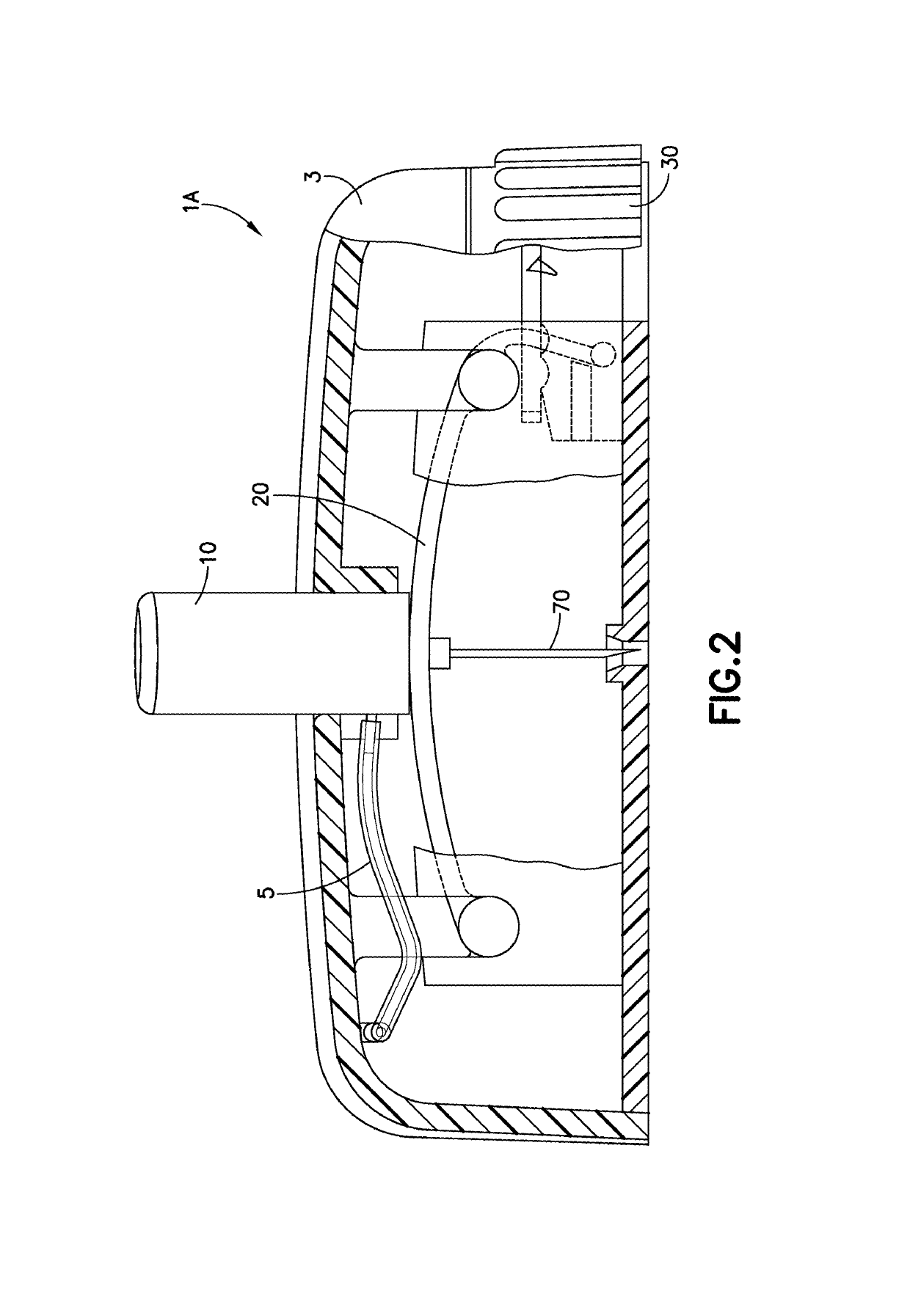
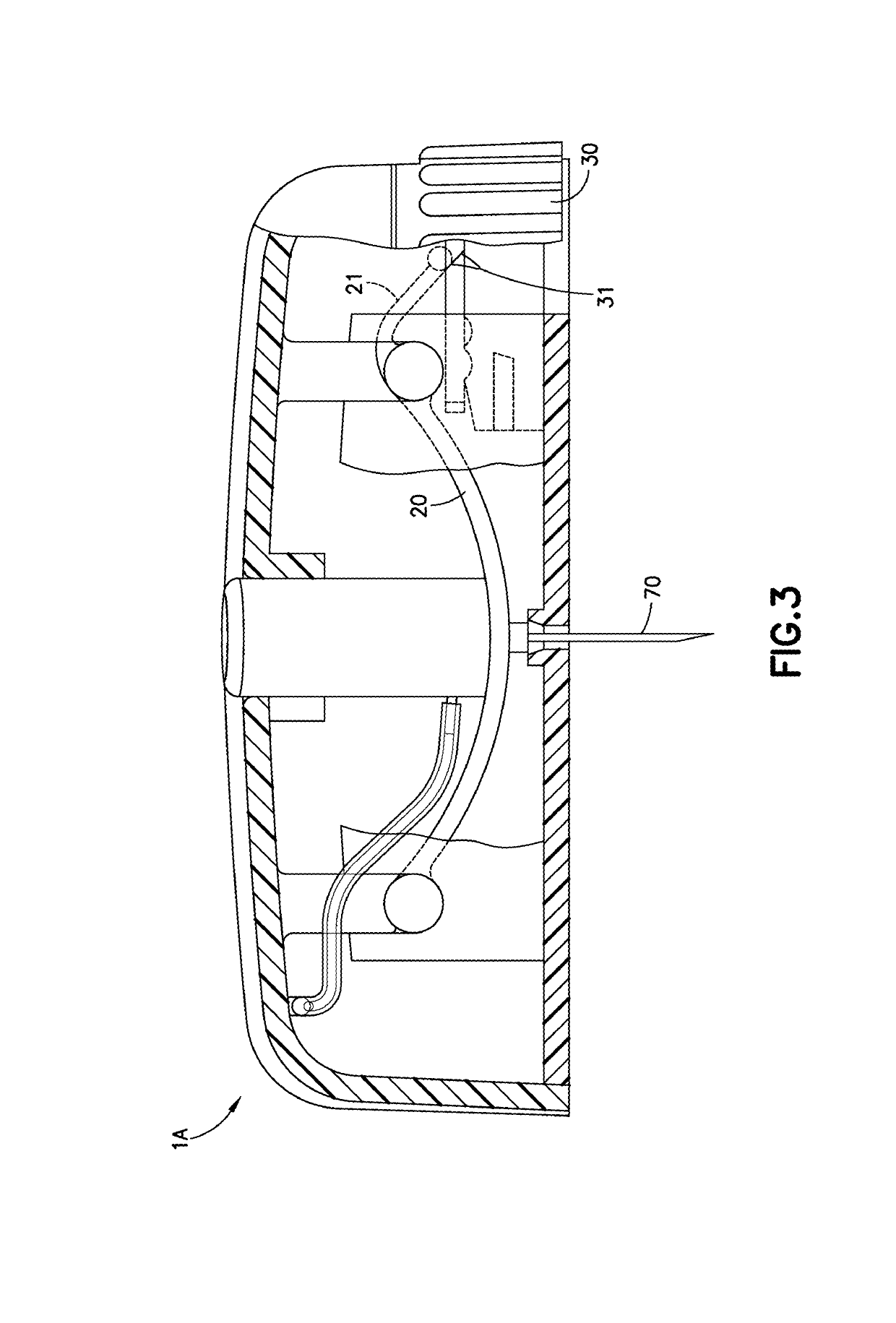
Cannula Insertion and Retraction Device for Infusion Device
ActiveUS20170021096A1Easy to insertReduce in quantityPressure infusionInfusion needlesInsulin infusionCannula insertion
An insulin infusion device (1A) is disclosed. The device includes a body (3A), cannula (70) housed in the body (1A), a cannula insertion device (10, 20, 23) and a cannula retraction device (20, 23, 30). When the cannula insertion device is activated, the cannula (70) extends at least partly out of the body (1A) and into an infusion site and when the cannula retraction device is activated after the cannula insertion device has been activated, the cannula (70) retracts into the body (1A).
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Electrosurgical device with improved visibility
InactiveUS20050159797A1Improving radiographic visualizationLittle strengthElectrotherapySurgical needlesCannula insertionElectric current flow
A method and apparatus are disclosed for improving accuracy of placement of a cannula during delivery of electrical energy proximate to bodily tissue, e.g. neural structures. The apparatus optionally includes a cannula operable to deliver electrical current where a portion of the cannula is electrically insulated and a portion of the cannula is exposed and electrically conductive. The cannula further includes a radiopaque marker to identify a specific portion of the cannula, for example to differentiate the electrically insulated region from the electrically exposed region, by allowing it to be more clearly delineated using fluoroscopy or other radiographic imaging techniques. The radiopaque marker is optionally tapered in order to reduce the force required to insert a cannula comprising a radiopaque marker into the patient's body.
Owner:AVENT INC
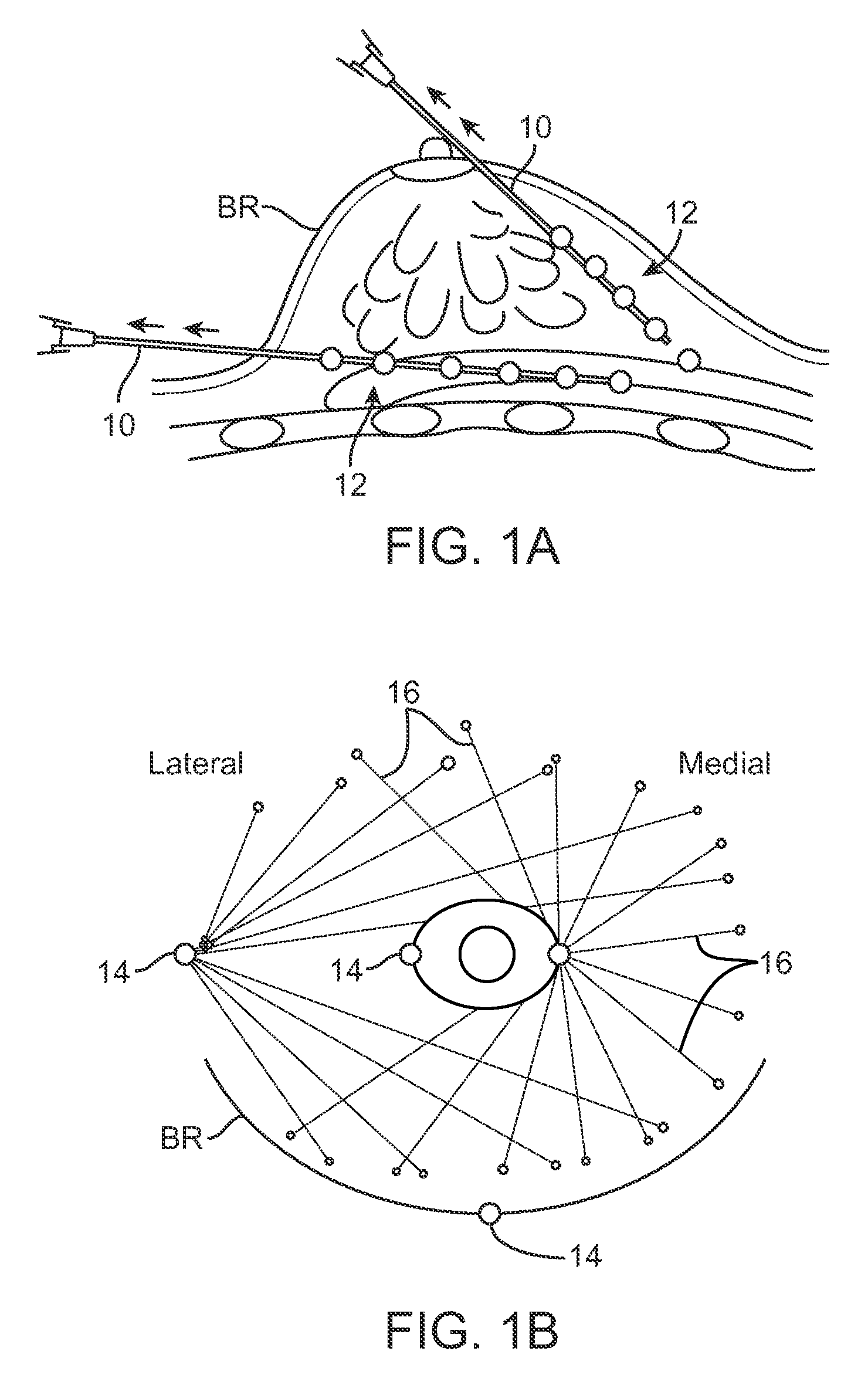
Devices and methods for tissue transfer
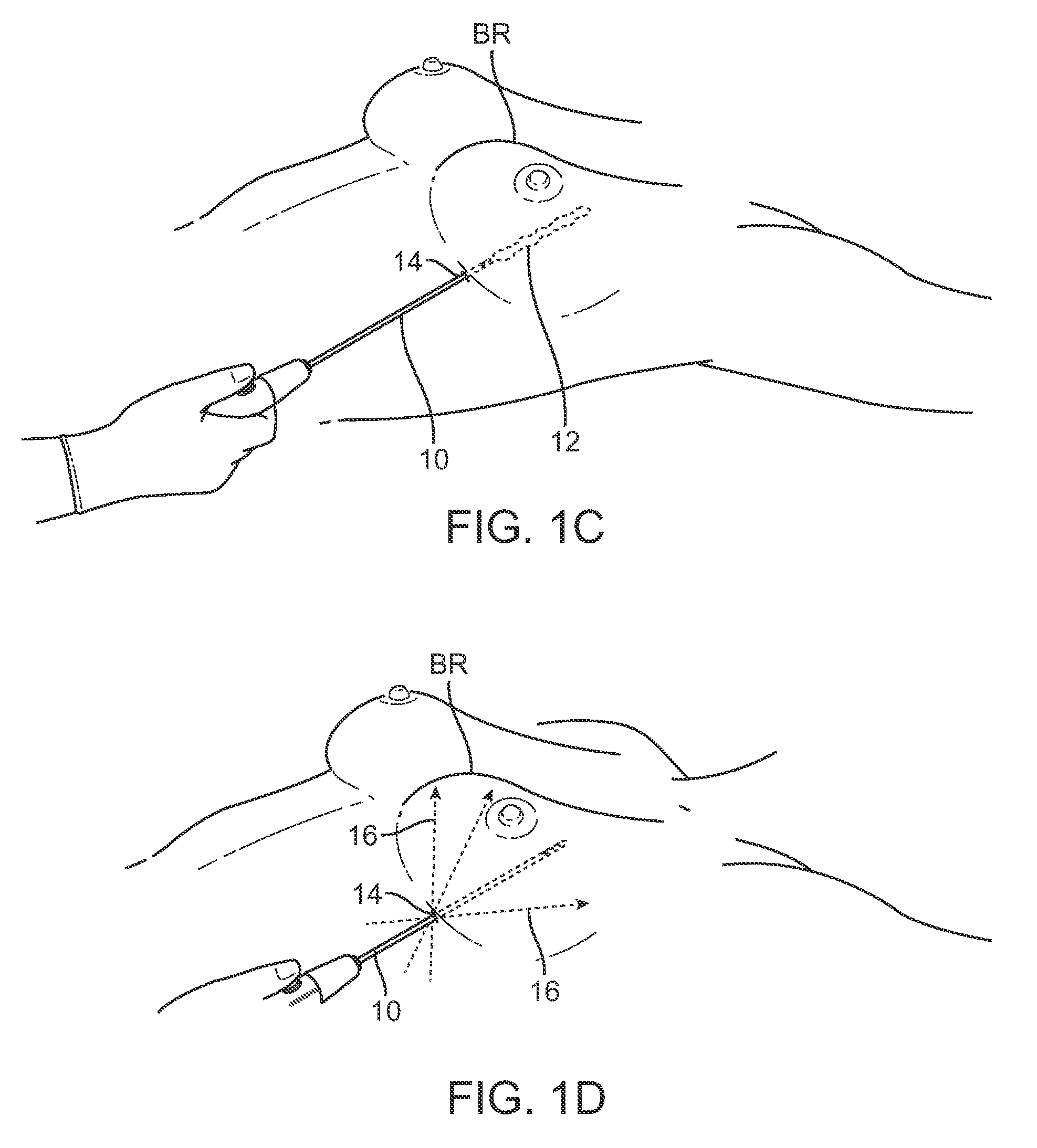
ActiveUS9314568B2Precision injectionEasy to controlMedical devicesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsAnatomyCannula insertion
Devices and methods for tissue transfer are described where a cannula may be inserted into the breast of a subject at one of several points of entry. Insertion of the cannula into the breast may be accomplished by using a guidance system to distinguish between tissue types. Once desirably positioned, the cannula may be withdrawn from the breast while automatically (or manually) injecting the fat in multiple deposits of adipose tissue or fat such that the deposited fat remains within the tract formed by the withdrawn cannula. Multiple tracts of the deposited fat may be injected within the breast until the breast has been desirably remodeled and / or augmented.
Owner:LIFECELL
Ophthalmic cannula insertion tool and method
A cannula insertion tool having a needle movable between a retracted position and an extended position. In some embodiments, the needle can be retracted within the periphery of a handle of the insertion tool when not in use to protect the needle. When the needle is needed for surgical use, the needle can be extended at least partially beyond the outer periphery of the handle. The needle can be coupled to a slide movable relative to the handle between the retracted position and the extended position. The slide can be secured in each position to prevent unintentional movement of the slide. A cannula can be positioned on the needle when the needle is in the retracted position, and can be retained upon the needle by a member extending toward the cannula.
Owner:MEDICAL INSTR DEVMENT LAB
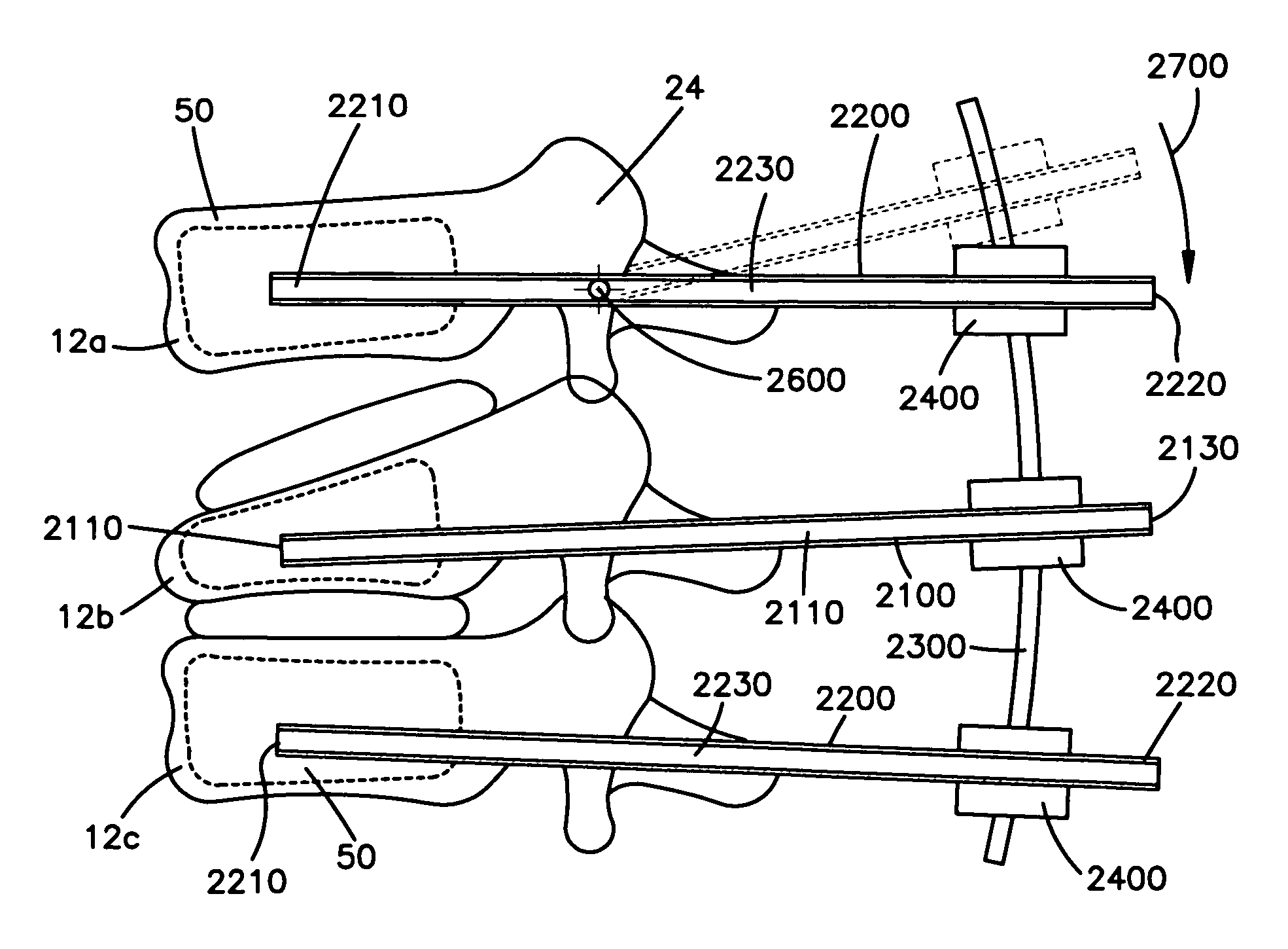
Apparatus and methods for vertebral augmentation
ActiveUS8157806B2Augment the vertebral bodyReduce compressionInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnNormal spine
Apparatuses and methods of treating a collapsed vertebra may include inserting cannulae into the damaged vertebral body and one or more adjacent vertebral bodies and repositioning the one or more adjacent vertebral bodies by manipulating one or more of the cannulae. Before or after repositioning the vertebral bodies, the method may further include passing through the cannula and into the damaged vertebra a disruption tool for fracturing the damaged vertebral body. Once the cortical bone is broken or otherwise disrupted, the height of the damaged vertebral body may be restored, for example by removing the disruption tool and inserting through the cannula another tool, implant, device and / or material to restore the height of the vertebral body and to restore normal spinal curvature in the affected area. Bone cement, bone chips, demineralized bone or other grafting material or filler may be added with or without an implanted device to augment the damaged vertebral body.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
Cannula insertion device
ActiveUS20100204652A1Minimise contaminationMinimise injuryCannulasInfusion syringesCannula insertionBiomedical engineering
A cannula insertion device comprises an elongate frame (4) and a hub (5) mounted to the frame and arranged to be slidably moveable from a first position forwards along a longitudinal axis to a second position relative to the frame and a needle (11) projecting forwards from the hub and carrying a detachable cannula (2) assembly including a cannula. The frame and hub are arranged to allow the hub to be moved forwards from the first position to the second position so as to insert the cannula into a patient and to be drawn backwards to a withdrawn position. The needle is shielded by the frame when the hub is in the first position and also when in the withdrawn position.
Owner:INFUTECH LTD
Self Sealing Cannula / Aperture Closure Cannula
A cannula having a body, a sealing disc, and a cap. The sealing disc is located within the body and is compressed by the cap. An angled cut in the sealing disc allows microsurgical instruments to be inserted through the cannula into the eye. Upon removal, the cut in the sealing disc closes, preventing the loss of intraocular pressure.
Owner:ALCON INC
C-tourniquet
ActiveUS20160045203A1Easy and quick to placeEasy to insertTourniquetsTourniquet timeCompression device
A blood vessel compression device including a C-shaped spring and a clamp at an end of the spring to compress a blood vessel. The clamp may have a flat shaped cross section or spatulate cross section with an edge where the edge confronts a blood vessel to compress it. The clamp may have a channel and a sac inflatable with air to compress the blood vessel. The device may be positioned on body to clamp an external jugular vein or cephalic vein for cannula insertion. The C-shaped spring may be spaced from a front of the neck to not compress a windpipe of the neck.
Owner:POLLOCK JAMES ERIC
Apex to aorta cannula assembly
ActiveUS7524277B1Reduce thrombosisEnsure sealing performanceBlood pumpsIntravenous devicesCannula insertionThrombus
An apparatus, system, and method for assisting a heart in circulating blood that has been damaged, for example, by a myocardial infarction. In at least one aspect, an apparatus, system, and method are used for inserting a single cannula assembly comprising at least an inner and outer cannula into the left ventricle, advancing the inner cannula portion of the cannula assembly past the aortic valve, and into the aorta without requiring a secondary cannula insertion through an external portion of the aorta. In another aspect, an intraventricular assistant device (IVAD) having a motor and impeller can be inserted directly into the heart, such as in the left ventricle. The IVAD uniquely provides a pump within the heart through a single insertion that can reduce thrombosis and lessen the complexities typically associated with such efforts.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Combined medicament fill and cannula insertion device
InactiveUS20160296695A1Performance of and safe and easyImprove user experiencePharmaceutical containersMedical devicesCannula insertionBiomedical engineering
A device for filling a medicament delivery device (e.g., a patch pump) with medicament or fluid and inserting a cannula subcutaneously enables improved results and user safety, while simplifying the set up process for a user. The device can include a housing with a first chamber portion having a first deployment mechanism and a second chamber portion having a second deployment mechanism. The device can also include a trigger mounted to the housing to activate at least one of the first deployment mechanism and the second deployment mechanism and an interface adapted to mate releasably with the medicament delivery device. The filling of the device with medicament and the insertion of the cannula may occur sequentially or simultaneously, and both actions can be initiated by a single user step or a limited number of user steps, as compared to conventional approaches.
Owner:CEQUR SA
Insulin pump dermal infusion set having partially integrated mechanized cannula insertion with disposable activation portion
ActiveUS8784383B2Maintaining degree of comfortPromote absorptionInfusion syringesInfusion needlesSkin surfaceMedicine
An infusion set has a partially integrated ballistic inserter that can insert a needle at a controlled rate of speed to a depth to deliver content to the upper 3 mm of skin surface, and a skin-securing adhesive layer to secure the skin surface at the insertion site such that the inserter that can insert a needle with a reduced risk of tenting of the skin surface. A removable turnkey or pushable handle can be provided to release a driving spring of the ballistic inserter to insert a needle at a controlled rate of speed, of 3.3 ft / sec. (1.0 m / sec.) up to and including those greater than 10 ft / sec. (3.0 m / sec.), then release from the set for disposal. The infusion set can further include an extendable interface ring that retracts when the inserter is removed from the infusion set.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
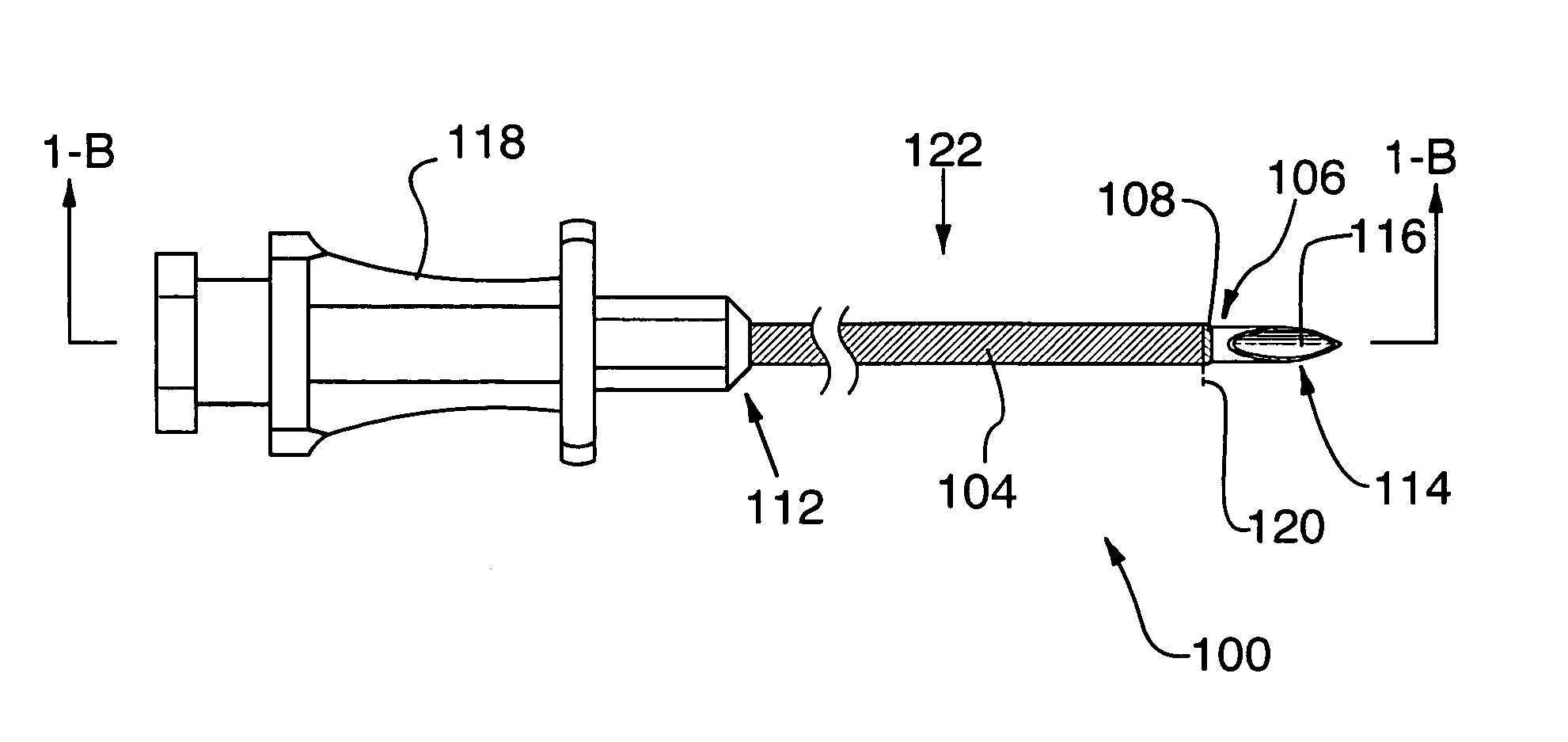
Method for implanting a percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy/jejunostomy tube in a patient and access needle for use in said method
InactiveUS8382770B2Overcome difficultiesEar treatmentSurgical needlesPercutaneous endoscopic jejunostomyCannula insertion
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
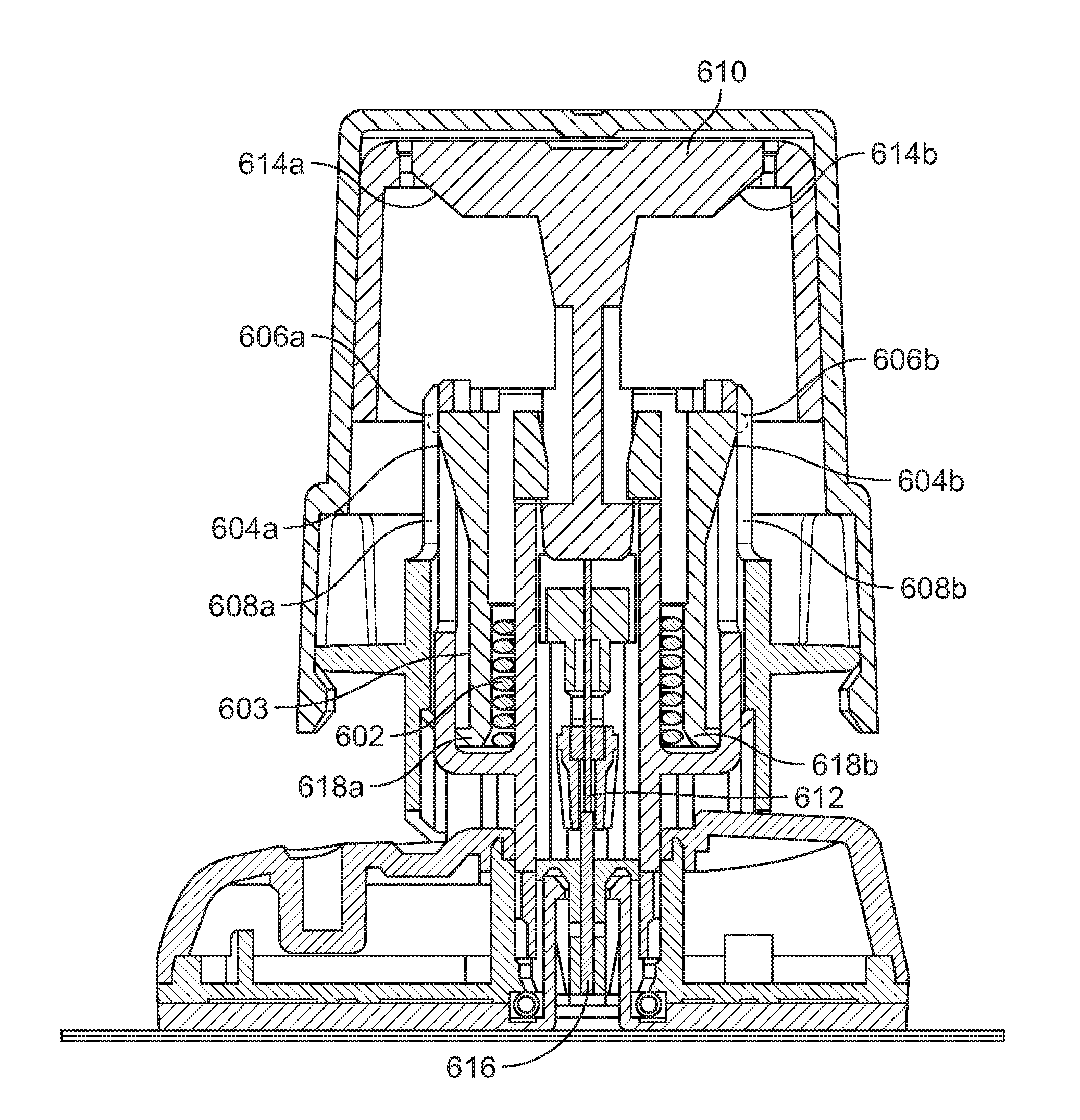
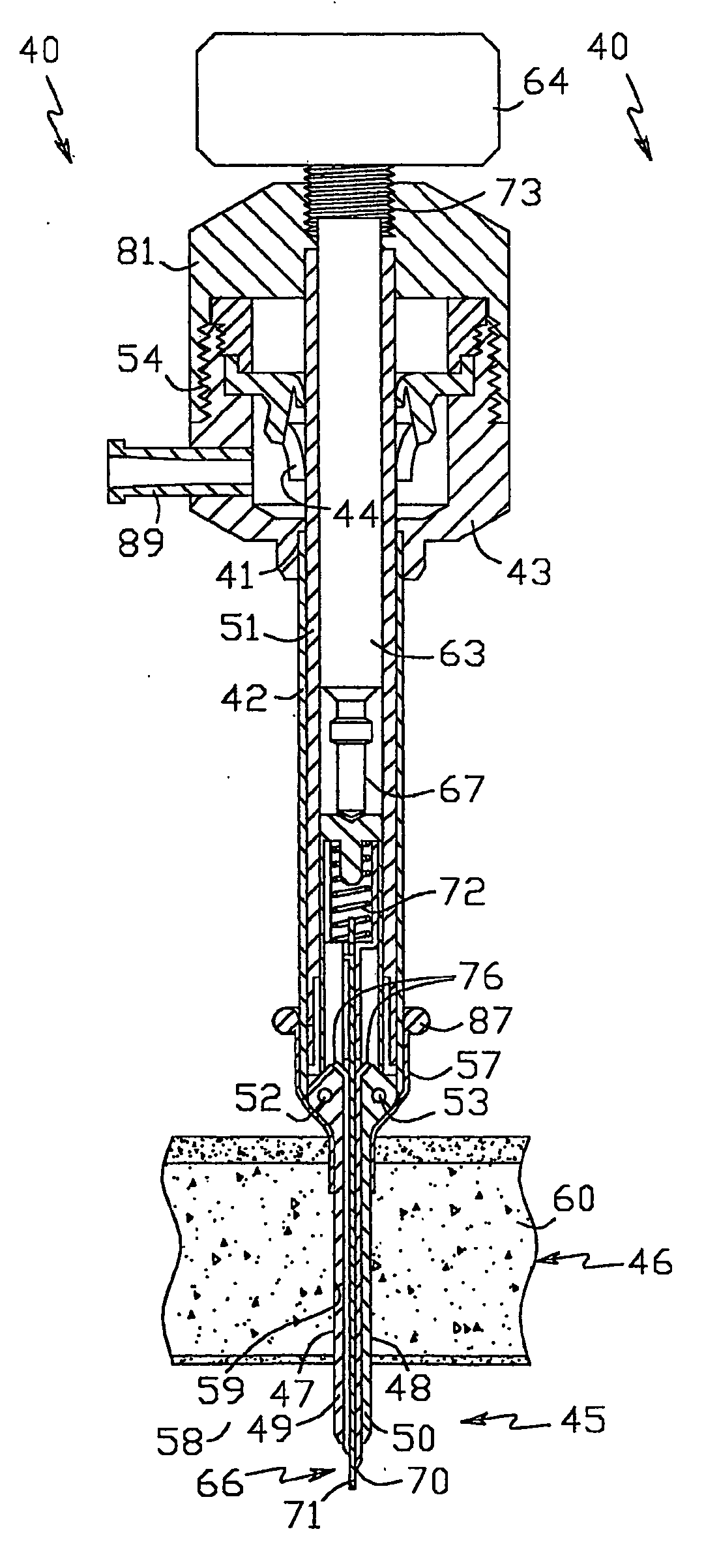
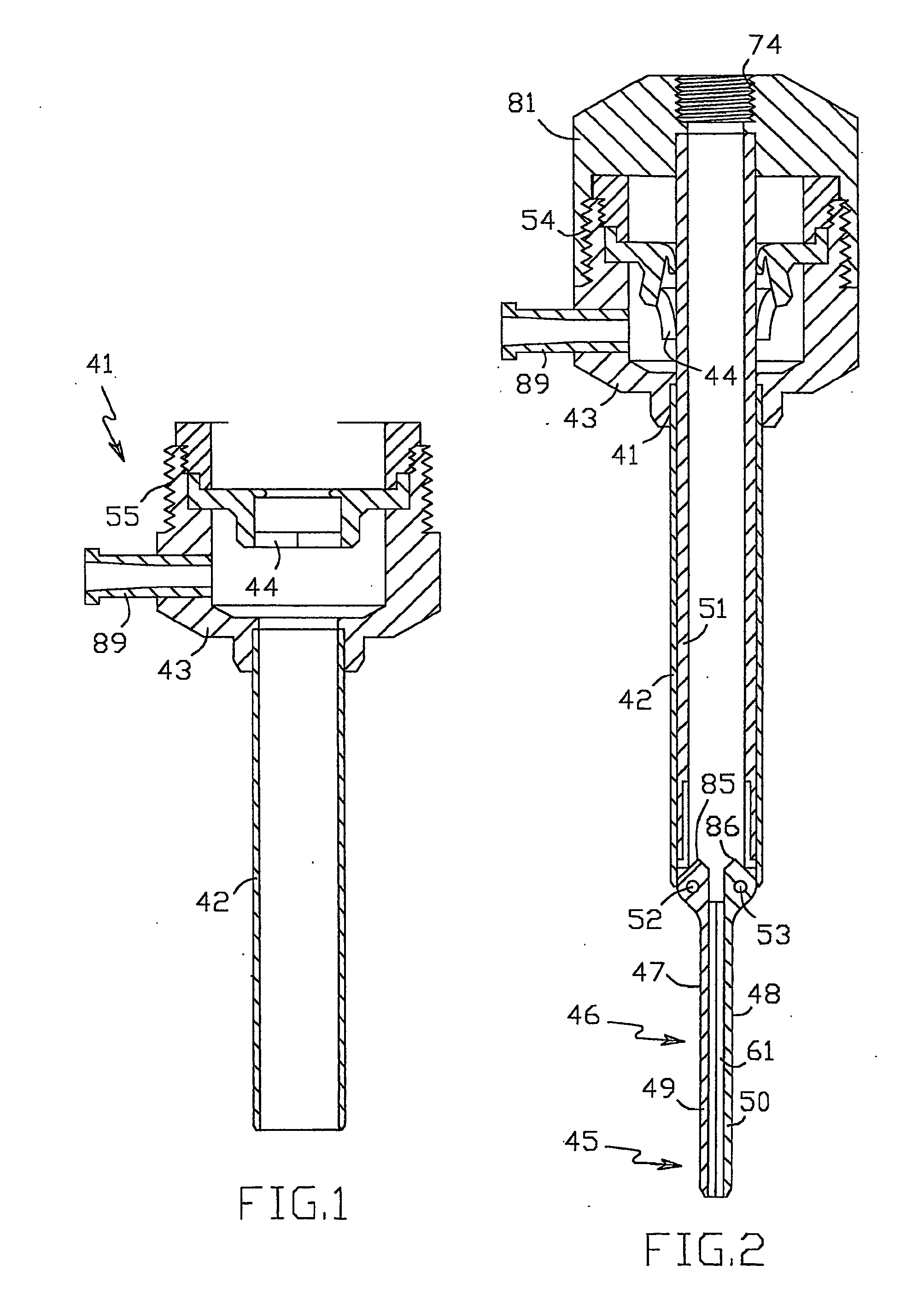
Intraosseous device for inserting a cannula into a bone
The invention relates to a device for the insertion of a cannula into a bone of a patient, which comprises: (a) an activator assembly for activating the device; (b) needle assembly which comprises a stylet and cannula; (c) barrel assembly for containing said stylet and cannula in a loaded state prior to the device activation; and (d) a setting assembly for adjusting the penetration depth of said cannula into the patient's bone.
Owner:WAISMED
Cannula insertion and retraction device for infusion device
ActiveUS10493201B2Easy to insertReduce in quantityPressure infusionInfusion needlesInsulin infusionCannula insertion
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Dilating Trocar
InactiveUS20070282365A1Inexpensive and reliableLittle resistanceCannulasInfusion syringesCannula insertionBody cavity
Dilating trocar (40) (see FIG. 14) comprises cannula (42) containing carrier (51) with pivotable dilating members (49, 50) of small transversal dimensions protruding distally of the cannula. Obturator (63) is housed inside the carrier and has sharp element (70) with underspringed protective shield (71) protrudind distally of the dilating members. After inserting the closed dilating members into a small opening primary made in patient's body cavity wall (60) by sharp element (70), user removes the obturator, introduces an actuating rod into carrier (51) and forces apart the dilating members rotating them about axes (52, 53) and thereby stretching the primary opening to provide the cannula insertion therein. Finally, user removes the actuating rod, carrier and dilating members from cannula (42) remaining the cannula in patient's body.
Owner:POPOV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com