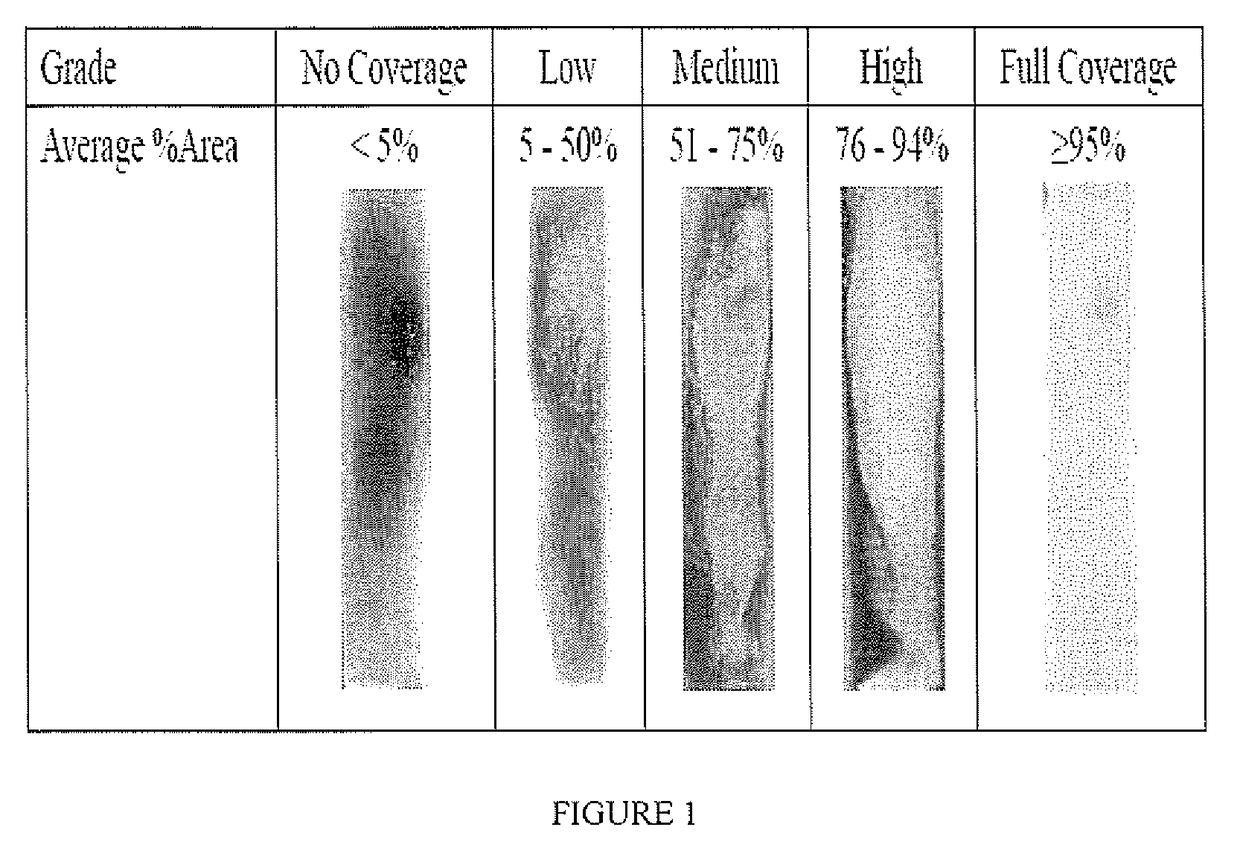
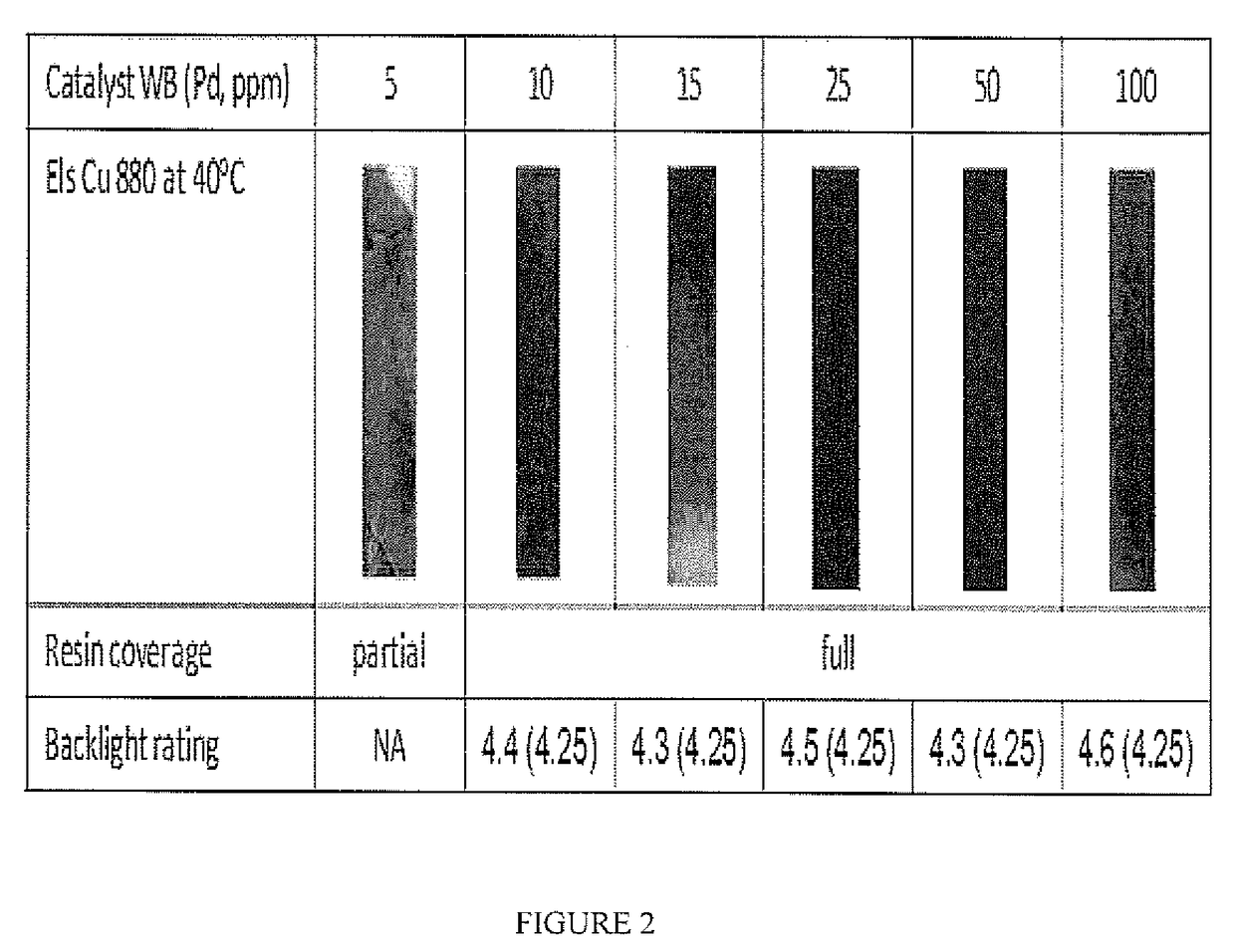
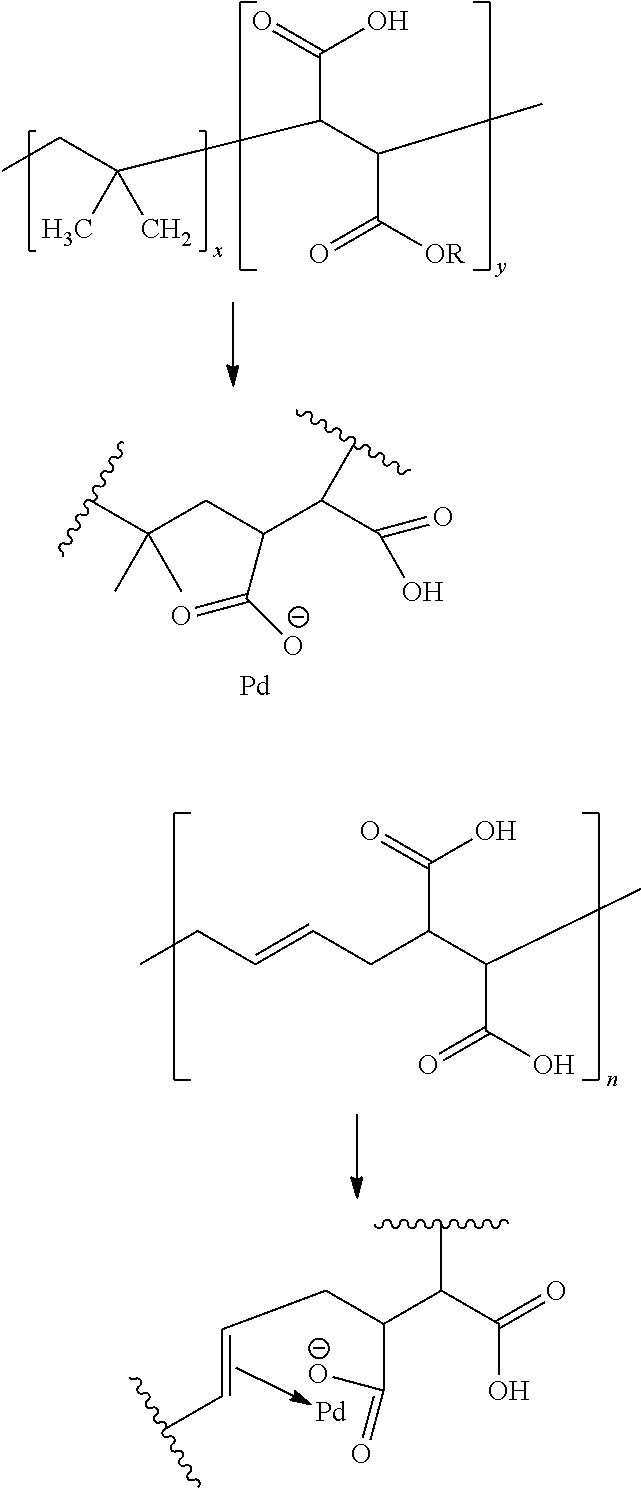
Plating catalyst and method
a plating catalyst and catalyst technology, applied in the direction of organic compound/hydride/coordination complex catalyst, physical/chemical process catalyst, chemical coating, etc., can solve the problems of catalyst particle size increase, catalyst particle loss, and catalyst particle size loss,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
Test Methods
[0055]The properties of the catalyst were evaluated by observing test coupons plated by electroless copper plating according to the process described below. As the test coupon, conventional FR-4 laminate and SY-1141 from Shengyi were used. For surface coverage test, bare laminate was used. For backlight test, Cu clad laminate with inner layer copper was used.
(1) Test coupon was cut into 1×6 cm2 and its edges were sandblasted by SiC#240, then cleaned in RO (Reverse osmosis) water for several times and blown dried.
(2) Processed through the swelling, oxidizing, neutralizing, conditioning and microetching steps shown in Table 1.
(3) The test coupon was then dipped in the catalyst solution at 40° C. for 10 minutes at various pH values of 2.9 to 10.9 as shown in each example. The test coupon was washed with deionized water.
(4) Electroless copper plating was conducted at 35° or 40° C. for 15 minutes.
TABLE 1process flow for electroless Cu deposition testsTemper-Dur-Rinse atureati...
example 1
[0061]Step 1—Measured 2.38 g of poly (butadiene-maleic acid) 1:1 molar (Mw=10,000-15,000) solution (42%), and dissolved it with 25 ml of deionized (DI) water; mixed it with 780 ml of DI water into a 3 liter beaker with stirring; and added 1.0 g of dichlorodiammine palladium (II) into the solution with stirring. The pH was adjusted by NaOH to 3.0 to 4.0.
Step 2—Quickly injected 7 mL of freshly prepared 1.0 mol / L dimethylaminoborane (DMAB) into the above solution with strong stirring at 500 rpm using a magnetic stirrer and continued stirring for over 1 h and obtained Pd nanoparticles (Pd catalyst concentrate).
Step 3—For storing the prepared nanoparticles, the pH was adjusted to 9.0-9.5 after 3-4 hours from the injection of the reducing agent. The total volume was topped up to a final volume of 1 liter.
The ingredients of Pd concentrate are written below.
Pd catalyst concentrate:
Pd ion: 0.5 g / L
[0062]PBDMA as stabilizer: 1.0 g / L
DMAB: 7.0 mM
[0063]The Pd catalyst concentrate which was obtain...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| mole ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com