Protective film agent for laser dicing and wafer processing method using the protective film agent
a technology of protective film and laser dicing, which is applied in the direction of radiation-absorbing paint, manufacturing tools, welding/soldering/cutting articles, etc., can solve the problems of deteriorating the quality of semiconductor chips, affecting the adhesion of the insulating film required of circuit elements formed on the chip face, and the inability to completely prevent the deposition of debris, etc., to achieve effective deposition of debris and high adhesion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0104] A protective film agent of the following composition was prepared:
[0105] Water-soluble resin: 20 g [0106] Polyvinyl alcohol having a saponification degree of 88% and a polymerization degree of 300
[0107] Water-soluble laser light absorber: 0.2 g [0108] Ferulic acid
[0109] Water: 80 g
[0110] g absorption coefficient k of the solids=1.56×10−1
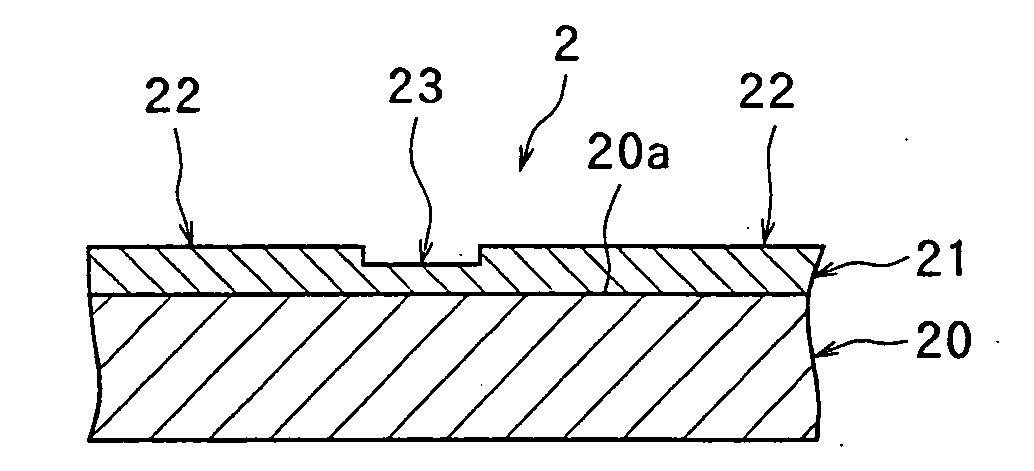
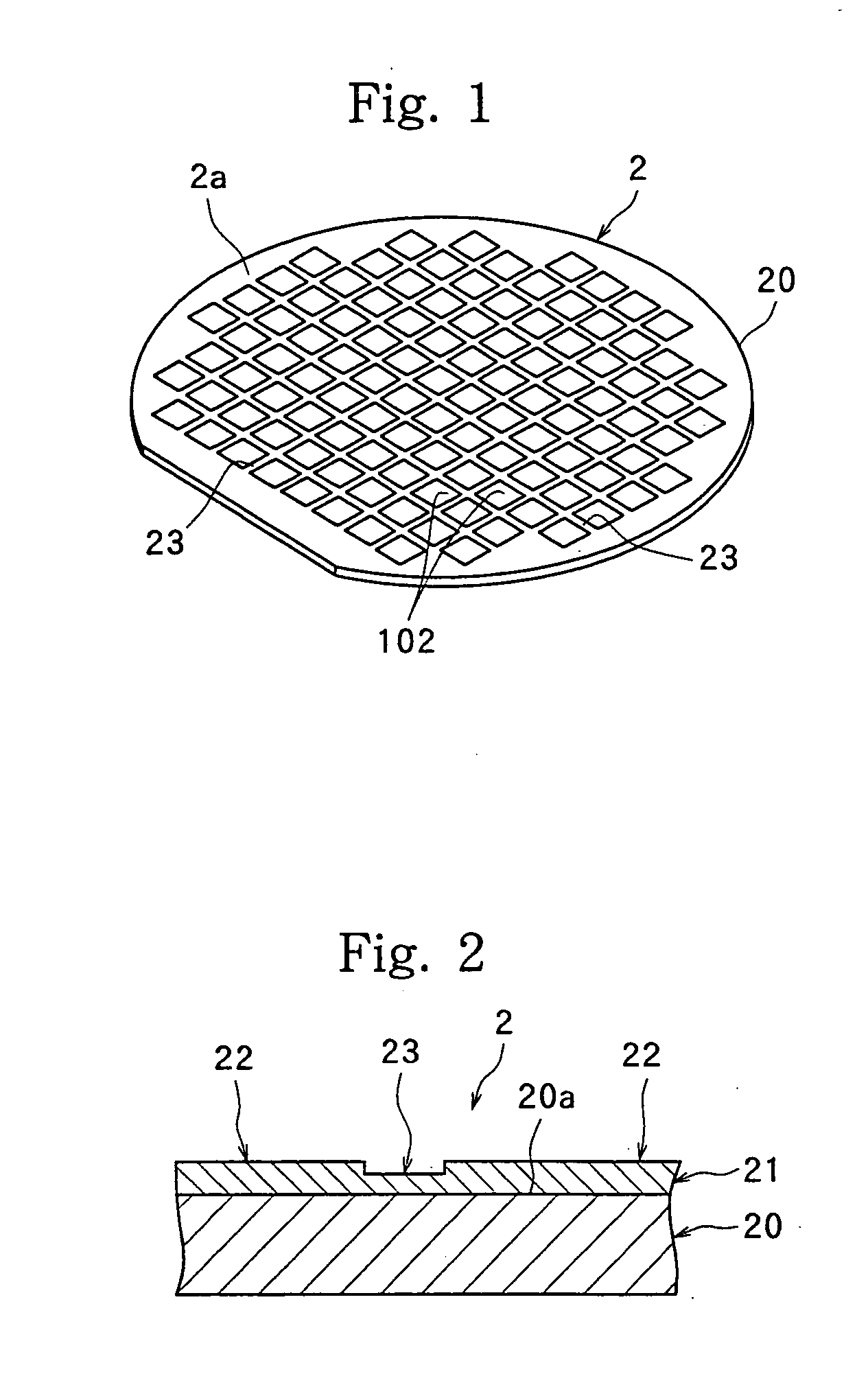
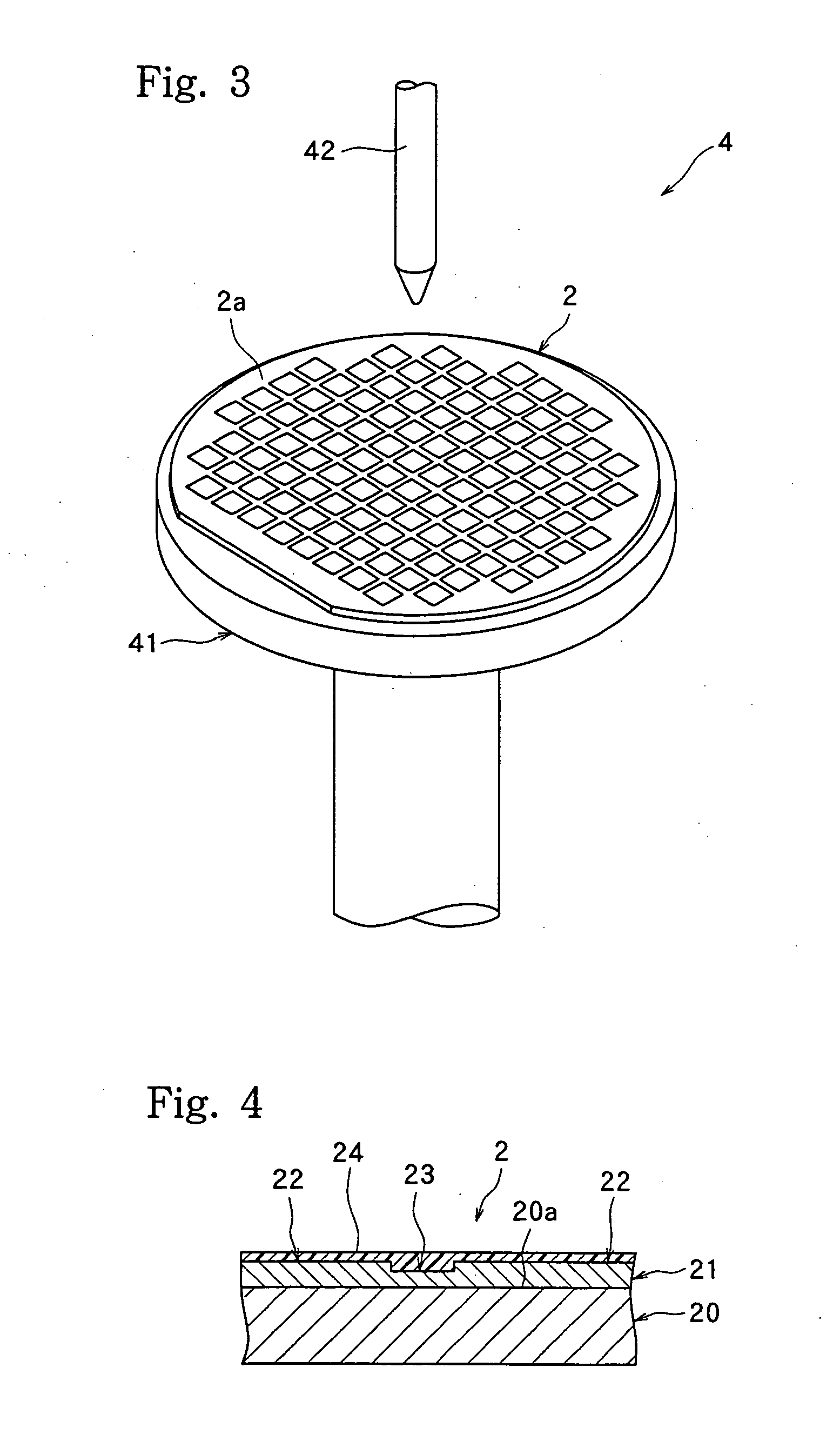
[0111] The above protective film agent was coated on a silicon wafer by a spinner, and dried to form a protective film having a thickness on the street of 0.5 to 1.5 μm. Then, the silicon wafer having the protective film formed thereon was mounted on the laser processing apparatus complying with the above specifications, and was subjected to laser processing. Then, the protective film was washed off with pure water, and the surroundings of the laser scans were observed. Bulges of the edge areas were observed, but no deposition of debris on the surroundings was noted. Thus, the silicon wafer was at a usable level. The width of processing w...
example 2
[0112] A protective film agent was prepared in exactly the same manner as in Example 1, except that the amount of ferulic acid, a water-soluble laser light absorber, was changed to 0.8 g. The g absorption coefficient k of the solids of the protective film agent was 5.61×10−1.
[0113] Using the above protective film agent, a protective film having a thickness of 0.2 μm was formed on a silicon wafer in the same manner as in Example 1. Laser processing was performed in the same manner, and the protective film was washed off with water. Observation of the surroundings of the laser scans, which was made in the same manner as in Example 1, showed no deposition of debris. The width of processing was slightly larger than the laser spot diameter, but the silicon wafer was at a usable level.
example 3
[0114] A protective film agent was prepared in the same manner as in Example 1, except that polyvinyl alcohol having a saponification degree of 75% and a polymerization degree of 500 was used as the water-soluble resin. The g absorption coefficient k of the solids of the protective film agent was 1.56×10−1 as in Example 1.
[0115] Using the above protective film agent, a protective film having a thickness of 0.5 to 1.5 μm was formed on a silicon wafer in the same manner as in Example 1. Laser processing was performed in the same manner, and the protective film was washed off with water. Observation of the surroundings of the laser scans, which was made in the same manner as in Example 1, showed no deposition of debris. The width of processing was comparable to the laser spot diameter without having influence from the thickness of the coating film.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| grain size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com