Control apparatus of internal combustion engine
a control apparatus and internal combustion engine technology, applied in the direction of electric control, ignition automatic control, speed sensing governors, etc., can solve the problems of engine torque decline, unstable fuel condition, and unstable fuel stability of the engin
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
[0071] First Embodiment
[0072] A first embodiment of the present invention applied to a direct injection engine is described by referring to FIGS. 1 to 3 as follows.
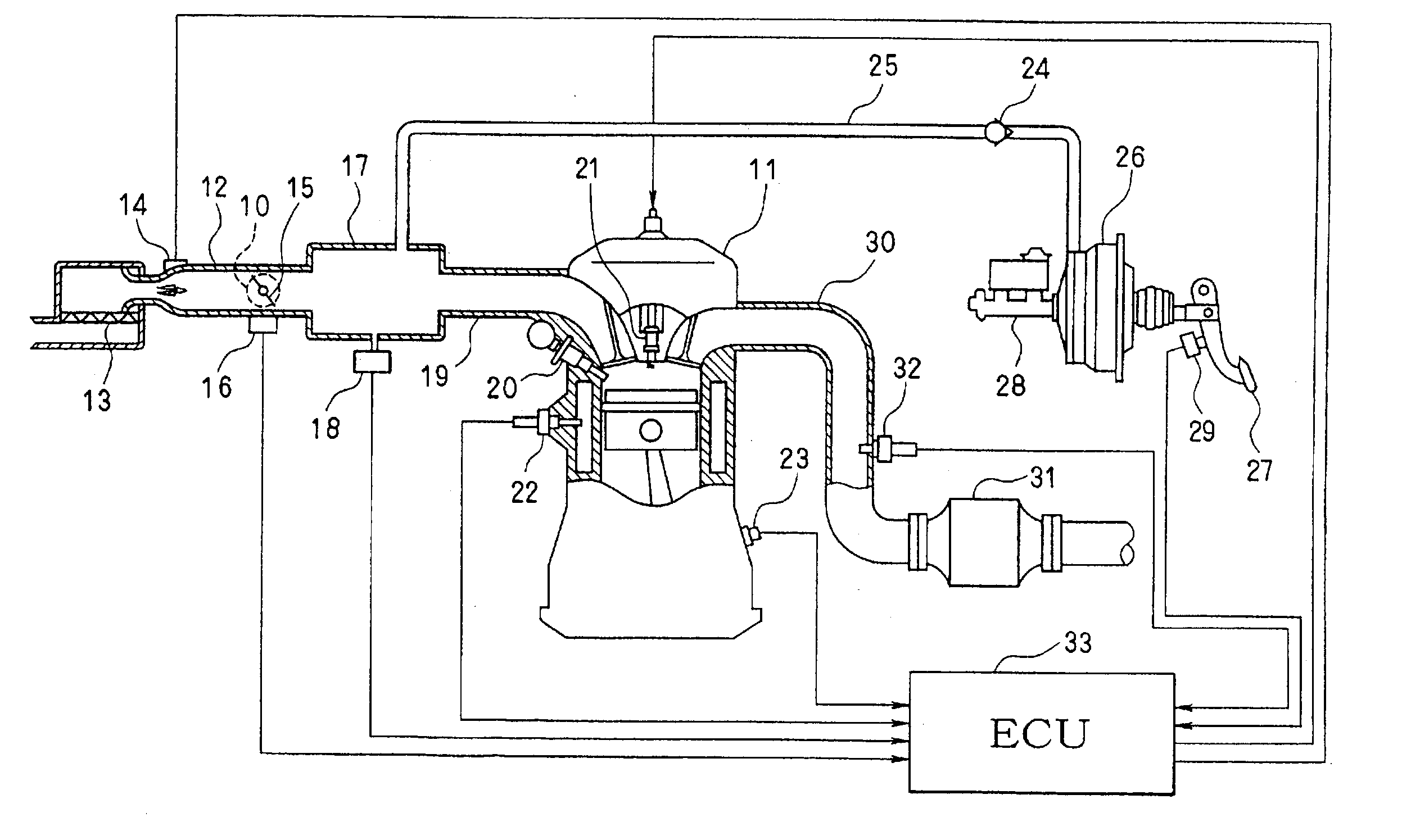
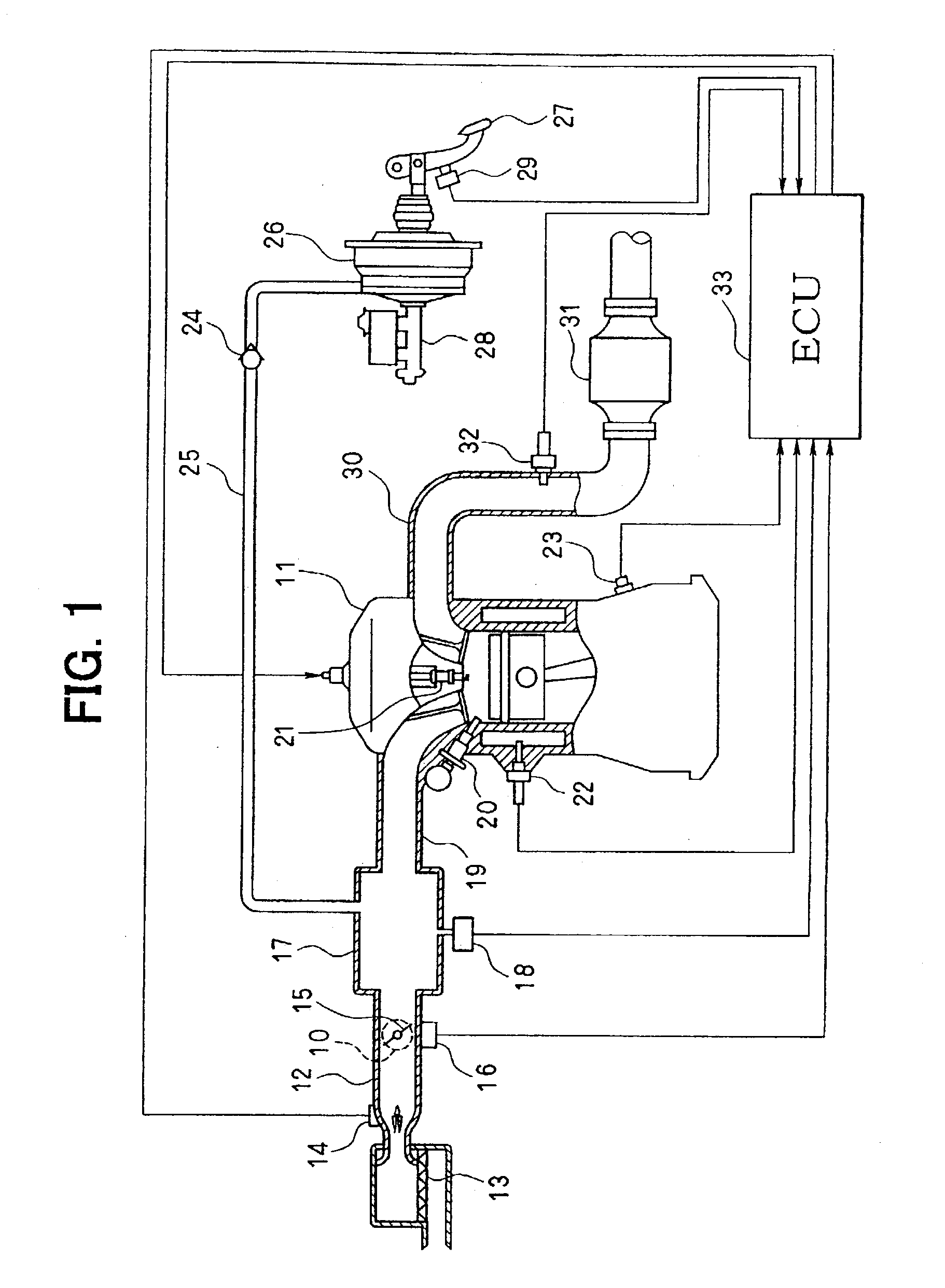
[0073] The description begins with an explanation of the entire engine control system's configuration, which is shown in FIG. 1. At the upper end of the upstream side of an intake pipe 12 employed in an engine 11 working as an internal combustion engine, an air cleaner 13 is provided. On the downstream of this air cleaner 13, an airflow meter 14 for detecting an intake airflow volume is provided. On the downstream side of the airflow meter 14, there are provided a throttle valve 15 driven by an actuator such as a motor 10 and a throttle angle sensor 16 for detecting a throttle angle.
[0074] On the downstream side of the throttle valve 15, a surge tank 17 is provided. On the surge tank 17, there is provided an intake pressure sensor 18 (negative pressure recognizing means) for detecting a negative pressure of an intake pipe...
second embodiment
[0093] Second Embodiment
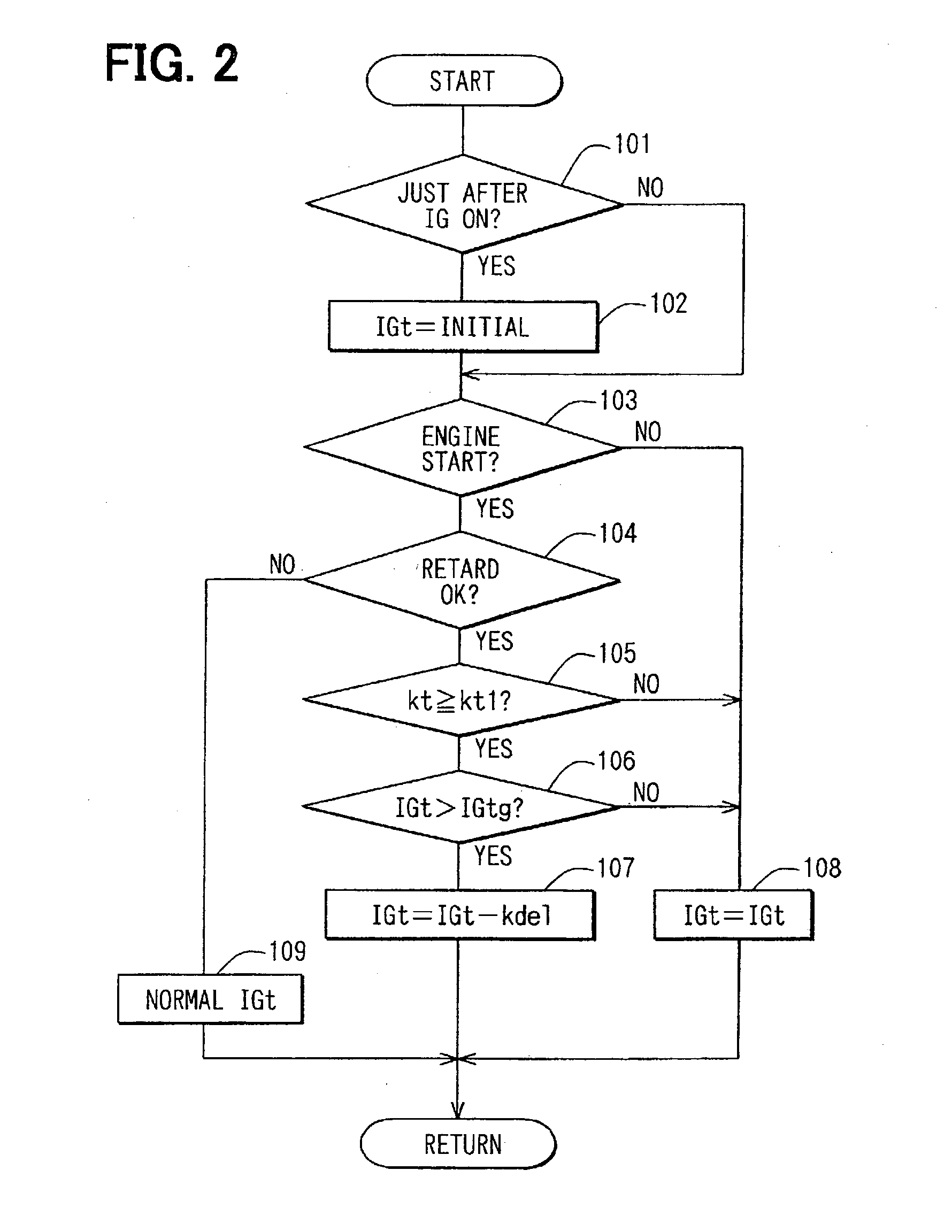
[0094] In the case of the first embodiment, a timing of a state in which a proper negative pressure of the brake booster can be assured after a start of the engine is confirmed when a predetermined time lapses since the start of the engine. Such a timing is taken as a timing to start the control of retarding ignition. In the case of a second embodiment shown in FIG. 4, on the other hand, at a step 105a, an intake pipe negative pressure Pm detected by an intake pipe negative pressure sensor 18 is examined to determine whether the pressure Pm has decreased to a predetermined value kpm1 or a lower value. The predetermined value kpml is an intake pipe negative pressure at which a proper negative pressure of the brake booster can be assured. During a period between a start of the engine and a time the intake pipe negative pressure Pm decreases to the predetermined value kpm1 or a lower value, the ignition timing is sustained at an initial value instead of being re...
third embodiment
[0098] Third Embodiment
[0099] In the first and second embodiments, during a period between a start of the engine and a state in which a proper negative pressure of the brake booster can be sustained, the ignition timing is sustained at an initial value instead of being retarded. In the case of a third embodiment shown in FIGS. 5 and 6, on the other hand, during a predetermined period kt2 beginning at a start of the engine, the retardation speed of the ignition timing is lowered and, after the period, the retardation speed is increased. The period is a time it takes to lower the intake pipe negative pressure Pm to a predetermined value kpm1.
[0100] In the actual processing, at a step 103 of a flowchart shown in FIG. 5, completion of an engine start is confirmed. If the completion is confirmed, the flow of the routine goes on to a step 104 to determine whether the conditions for execution of the ignition retarding control to heat the catalyst at an early time are satisfied. If the cond...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com