Voltage controlled oscillator
A voltage-controlled oscillator and oscillation frequency technology, applied in power oscillators, automatic power control, pulse generation, etc., can solve the problems of oscillation frequency fluctuation, current value swing, cost increase, etc., and achieve low phase noise and reduced phase noise. Volatile, low-cost effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
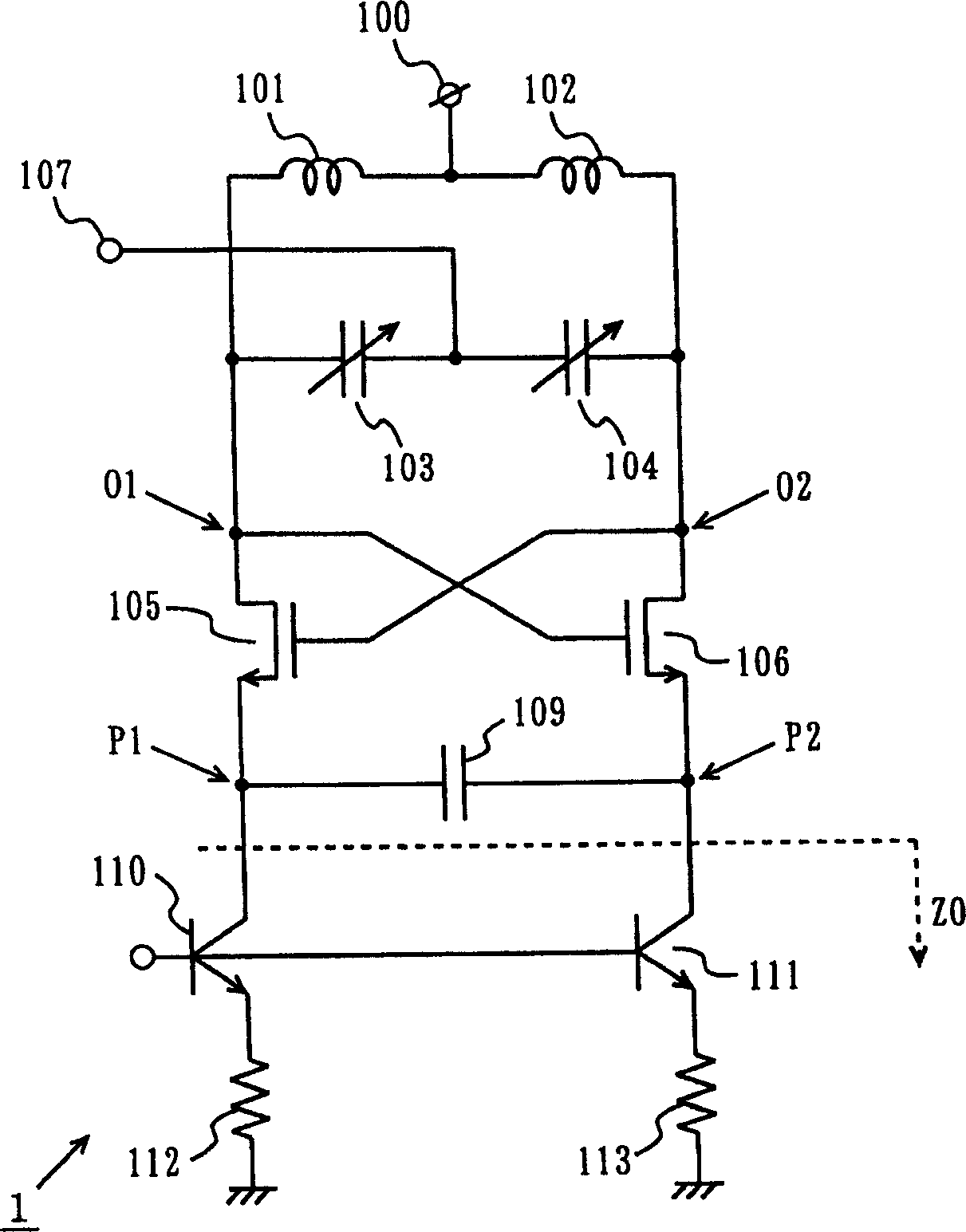
[0080] figure 1 It is a circuit diagram showing the structure of the voltage-controlled oscillator 1 according to the first embodiment of the present invention. exist figure 1The VCO 1 includes a power supply terminal 100, inductors 101 and 102, variable capacitance elements 103 and 104, oscillation transistors 105 and 106, a frequency control terminal 107, a coupling capacitor 109, current source transistors 110 and 111, and resistors 112 and 113. exist figure 1 , the bias circuit and the like are omitted.
[0081] The variable capacitance elements 103 and 104 utilize the gate capacitance of a variable capacitance diode or a field effect transistor (FET). The oscillation transistors 105 and 106 are field effect transistors (both referred to as "FETs" hereinafter). The coupling capacitor 109 is a capacitor having a predetermined capacitance value. Current source transistors 110 and 111 are bipolar transistors.
[0082] Inductors 101 and 102 are connected in series. The...
no. 2 example
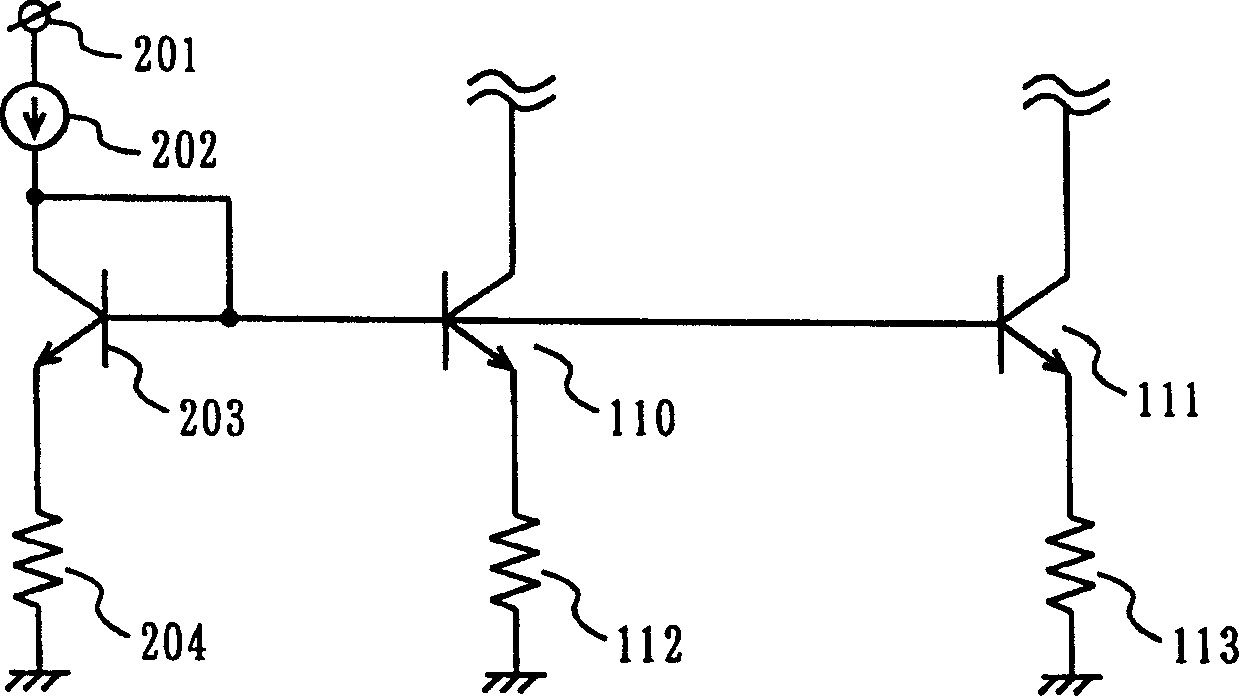
[0106] Figure 5 It is a circuit diagram showing the structure of the voltage-controlled oscillator 2 according to the second embodiment of the present invention. exist Figure 5 The VCO 2 includes a power supply terminal 100, inductors 101 and 102, variable capacitance elements 103 and 104, oscillation transistors 105 and 106, a frequency control terminal 107, a coupling capacitor 109, current source transistors 110 and 111, a resistor 112 and 113, and inductors 120 and 121. exist Figure 5 , the bias circuit and the like are omitted. exist Figure 5 , the same parts as those in the first embodiment have the same reference numerals and will not be described further.
[0107] In the first embodiment, the parasitic capacitance between the emitters and collectors of the current source transistors 110 and 111 reduces the impedance Z0 viewed from the terminals P1 and P2 to the current source side with respect to the higher oscillation frequency . For example, when the oscil...
no. 3 example
[0122] Figure 8 It is a circuit diagram showing the structure of the voltage-controlled oscillator 3 according to the third embodiment of the present invention. exist Figure 8 In the above, the voltage controlled oscillator 3 includes a power supply terminal 100, inductors 101 and 102, variable capacitance elements 103 and 104, oscillation transistors 105 and 106, a frequency control terminal 107, a coupling capacitor 109, current source transistors 110 and 111, and inductors 132 and 106. 133. Figure 8 The bias circuit and the like are omitted. Figure 8 , the same parts as those in the first embodiment have the same reference numerals and will not be further described.
[0123] Inductors 132 and 133 are connected to the emitters of current source transistors 110 and 111 and grounded. The impedances of the inductors 132 and 133 can suppress the signal at the two terminals of the coupling capacitor 109 whose frequency is twice the oscillation frequency, which is similar ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com