Tetragenococcus halophilus and application of tetragenococcus halophilus in production of anti-cancer exopolysaccharides
A technology of halophilic tetradococcus and exopolysaccharide, which is applied in the field of new halophilic tetradococcus and its application in the production of anti-cancer exopolysaccharide, which can solve the problems of body damage and side effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] The isolation and screening of embodiment 1 bacterial strain
[0064] 1. Screening samples
[0065] The experimental samples were 192 naturally fermented soybean paste samples collected from 12 different regions in Liaoning Province (Jinzhou, Shenyang, Zhuanghe, Benxi, Dalian, Gongzhuling, Dandong, Huludao, Tieling, Anshan, Liaozhong and Liaoyang).
[0066] 2. Preliminary screening of tetradococci
[0067] Take 1g of soybean paste sample, add 9mL of 0.9% sterile normal saline, mix thoroughly and soak for 15min; then take 1mL of sample solution and inoculate it into the enrichment culture set, and after static culture at 30°C for 1-2d, use the plate coating method Cultured on solid separation medium for 5-6d.
[0068] Pick a single colony that is small, has obvious calcium-dissolving circle, is milky white and opaque, and has a shape similar to that of a lactic acid bacteria colony, and performs Gram staining. The results of microscopic examination showed that there w...
Embodiment 2
[0079] Identification of embodiment 2 LZ4 bacterial strain
[0080] 1. Identification of colony morphology
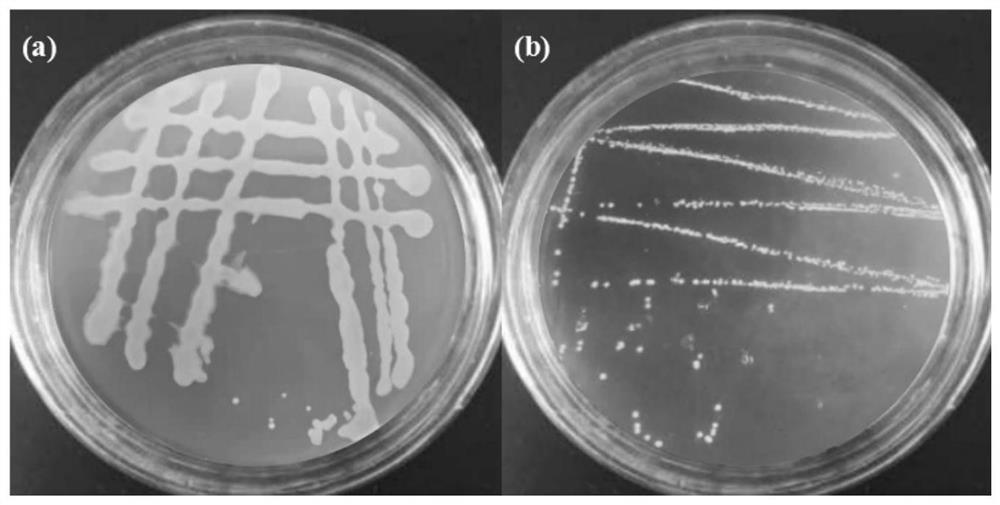
[0081] The colony of the LZ4 strain is small, milky white, opaque, smooth and glossy, sticky, with neat edges; Gram staining is positive, the cells are spherical, and generally exist in quadruple or in pairs. Colony morphology and cell morphology figure 1 and figure 2 shown.
[0082] 2. Physiological and biochemical characteristics
[0083] Physiological and biochemical characteristics of the LZ4 strain were tested and identified: sugar fermentation test; catalase test; gelatin liquefaction test; ammonia production test; glucose production acid and gas test; hydrogen sulfide test;
[0084] 3. Molecular biological identification
[0085] (1) Bacterial DNA extraction:
[0086] Pipette 100 μL of the bacterial suspension of the LZ4 strain into the sterilized MRS liquid medium, and culture it in a shaking incubator at 37°C for 24 hours. The genome of the strain was e...
Embodiment 3
[0100] Example 3 Analysis of Fermentation Conditions of Tetradendococcus halophilus SNTH-8
[0101] 1. Effect of carbon source and its concentration on polysaccharide synthesis and strain growth
[0102] On the basis of sugar producing medium, 2% (w / v) glucose, sucrose, mannose, fucose, galactose, arabinose, rhamnose and xylose were respectively used as carbon sources to determine the For polysaccharide production and strain biomass, the optimal carbon source was determined according to the production and growth of exopolysaccharide of the strain, and its optimal concentration was investigated.
[0103] From Figure 5 It can be seen that the halophilic Tetradendococcus SNTH-8 cannot ferment rhamnose and xylose to produce sugar, and the growth of the strain is not good. Although glucose can promote the growth of the strain to a certain extent, the production of exopolysaccharide is less than that of sucrose. Therefore, sucrose is the best carbon source among the tested carbo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com