Preparation method and application of constructed wetland dephosphorization matrix
A technology of constructed wetlands and substrates, applied in the field of water pollution control, can solve problems such as high organic matter interference that is difficult to overcome
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] Embodiment 1: Comparative embodiment of sintering temperature and load type selection parameters
[0053] A preparation method for a constructed wetland dephosphorization substrate, comprising the following steps:
[0054] (1) Take the attapulgite raw ore (medium-grade or high-grade attapulgite raw ore; calcium oxide content≤10% in the attapulgite raw ore), physically sieve, remove impurities, mechanically pulverize after drying, and sieve (the mesh number is greater than 100 mesh ), obtain the attapulgite clay powder, for subsequent use; get biochar, mechanically pulverize, sieve (mesh number greater than 100 orders), obtain biochar powder, for subsequent use;
[0055] (2) Take the attapulgite clay powder and biochar powder with a mass ratio of 1:1 and mix them evenly, then mix the mixed material with the load liquid, fully infiltrate for 30 hours, and obtain the mixed material, the moisture content of the mixed material is 15%, and extrude , making a columnar carrier w...
specific Embodiment
[0058] Concrete embodiment parameter sees the following table one:
[0059]
[0060] Table I
[0061] Detection experiment:
[0062] According to the scheme disclosed in Example 1 (A1-A5, B1-B5, C1-C5), the corresponding phosphorus removal substrates were prepared, and detected respectively according to the following methods:
[0063] 1. Material loss rate: Take 1-2g of phosphorus removal matrix, put it in 100ml deionized water, shake it at constant temperature for 24 hours, and calculate the material loss rate. Material loss rate (%) = lost material dry weight / material weight.
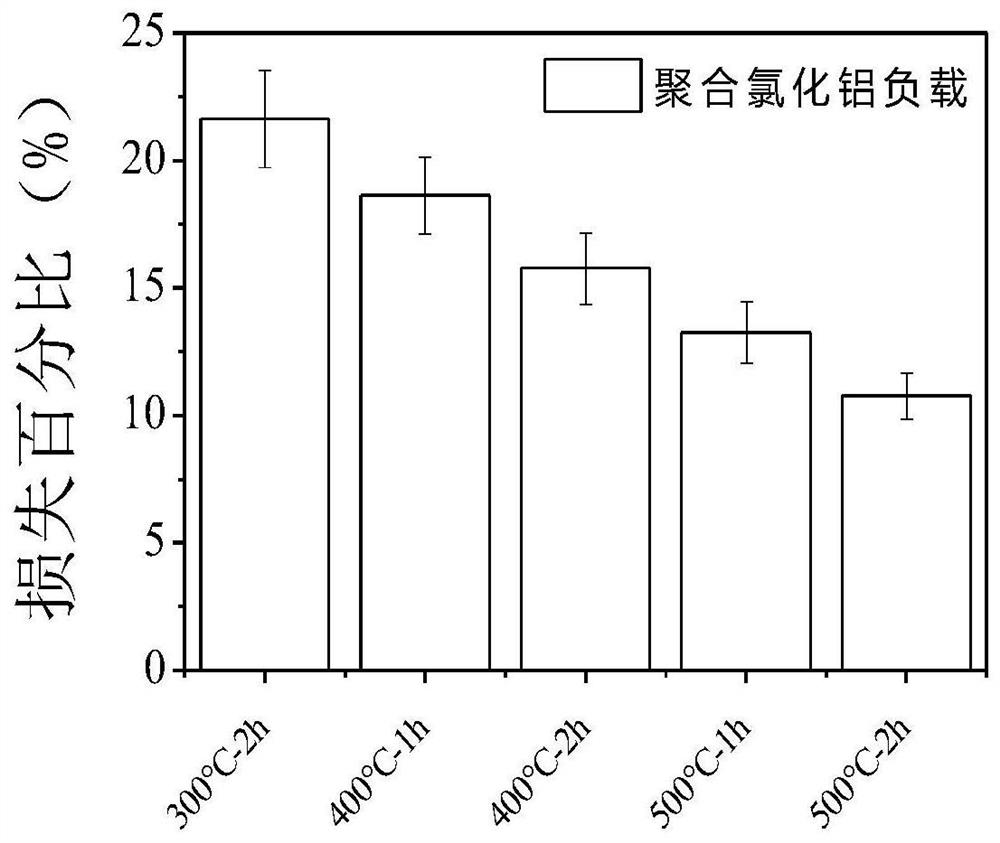
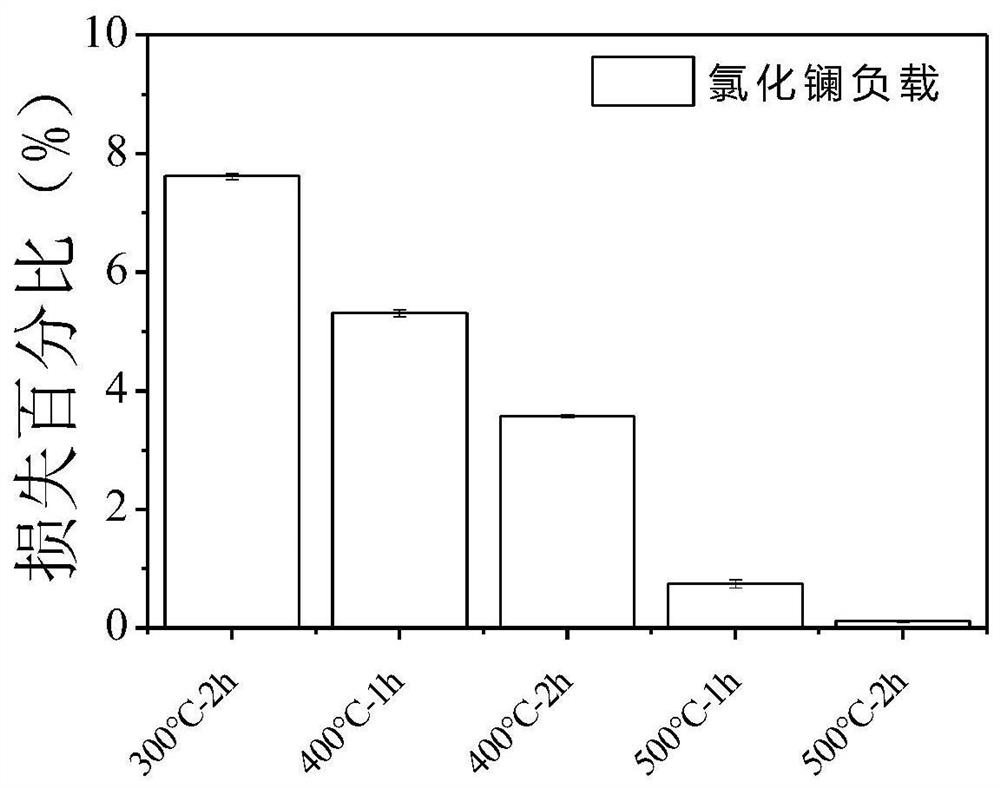
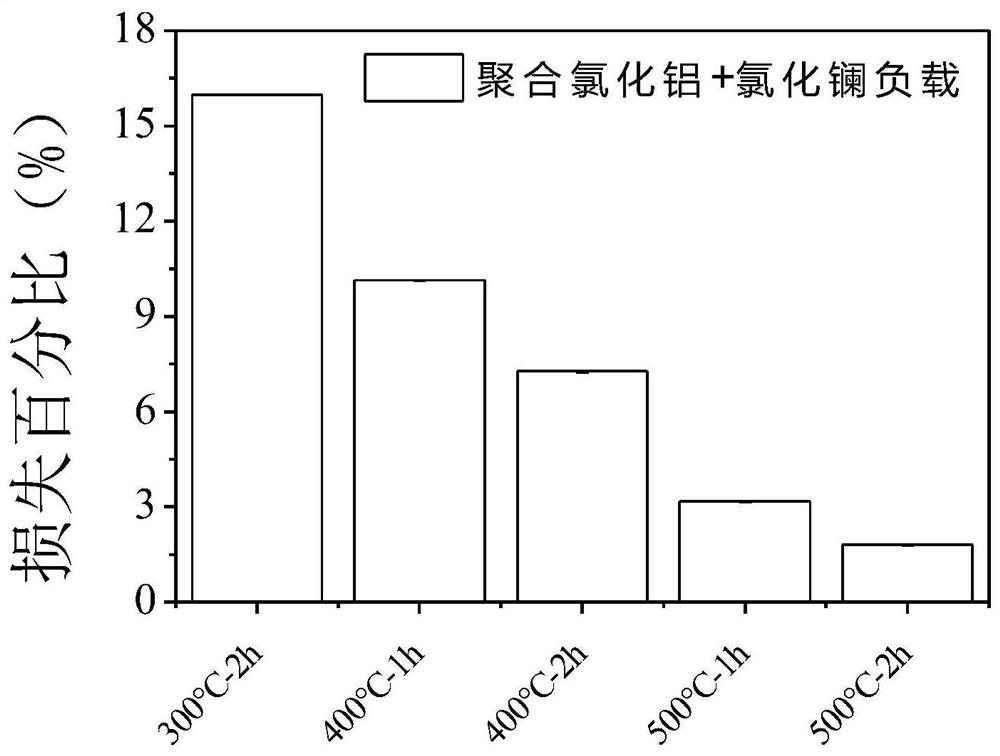
[0064] Specific test results such as figure 1 , figure 2 , image 3 Shown: where figure 1 Material loss rate of phosphorus removal substrates prepared for schemes A1-A5; figure 2 Material loss rate of phosphorus removal substrates prepared for schemes B1-B5; image 3 Material loss rates of phosphorus removal substrates prepared for schemes C1-C5.
[0065] Depend on Figure 1-Figure 3 It...
Embodiment 2
[0070] Embodiment 2: Parameter control test of load liquid load mass fraction
[0071] A preparation method for a constructed wetland dephosphorization substrate, comprising the following steps:
[0072] (1) Take the attapulgite raw ore (medium-grade or high-grade attapulgite raw ore; calcium oxide content≤10% in the attapulgite raw ore), physically sieve, remove impurities, mechanically pulverize after drying, and sieve (the mesh number is greater than 100 mesh ), obtain the attapulgite clay powder, for subsequent use; get biochar, mechanically pulverize, sieve (mesh number greater than 100 orders), obtain biochar powder, for subsequent use;
[0073] (2) Take the attapulgite clay powder and biochar powder with a mass ratio of 1:1 and mix them evenly, then mix the mixed material with the load liquid, fully infiltrate for 30 hours, and obtain the mixed material, the moisture content of the mixed material is 15%, and extrude , making a columnar carrier with a diameter of 6 mm a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com