Alpha-glucosidase QsGH97a derived from deep-sea bacteria as well as coding gene and application thereof
A technology of glucosidase and encoding gene, which is applied in the fields of glucose production, application, bacteria, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient application of α-glucosidase, low enzymatic activity, poor thermal stability, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Cloning of α-glucosidase gene qsgh97a and construction of recombinant plasmid
[0040] Deep-sea sediment samples were collected from Pacific seamount margins. The bacterial genome library was provided by the Second Institute of Oceanography, State Oceanic Administration, a cooperative unit.
[0041] Primers used to construct recombinant prokaryotic expression vectors include:
[0042] Upstream primer: 5'-GGCGGATGATCCGCCATATCGCCCTCTTCATC-3', as shown in SEQ ID NO.3;
[0043] Downstream primer: 5'-AAACTCGAGTCACCCCTGCGGCACGAACTCG-3', as shown in SEQ ID NO.4.
[0044] The enzyme cutting sites are BamHI and XhoI, respectively, and the selected expression vector is pSMT3 vector. The cloned target gene fragment and vector are confirmed by agarose electrophoresis, and the size of the band is correct, and then restriction double enzyme digestion is performed. The enzyme cutting sites are BamHI and XhoI, and then the enzyme-cleaved products were tapped to recover. Using T4 DN...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Transformation of recombinant plasmid of α-glucosidase gene qsgh97a
[0048] The positive clones with correct sequencing were cultured in LB liquid medium at 37°C, and then plasmids were extracted using a plasmid extraction kit (Axygen, USA) to obtain recombinant plasmids. Aliquot 30 μl of E.coli strain BL21(DE3) plus (full type gold, China) competent cells taken out of the -80°C refrigerator into EP tubes, add 1 μl of plasmid, and incubate on ice for 30 minutes, then store at 42°C Heat shock for 1 min, incubate on ice for 2 min, then add 500 μl LB medium, incubate on a shaker at 37°C for 1 hour, centrifuge to remove 200 μl supernatant, take the remaining bacterial solution and spread evenly on LB agar containing 50 μg / mL kanamycin resistance on the tablet.
Embodiment 3
[0050] Expression and purification of α-glucosidase QsGH97a
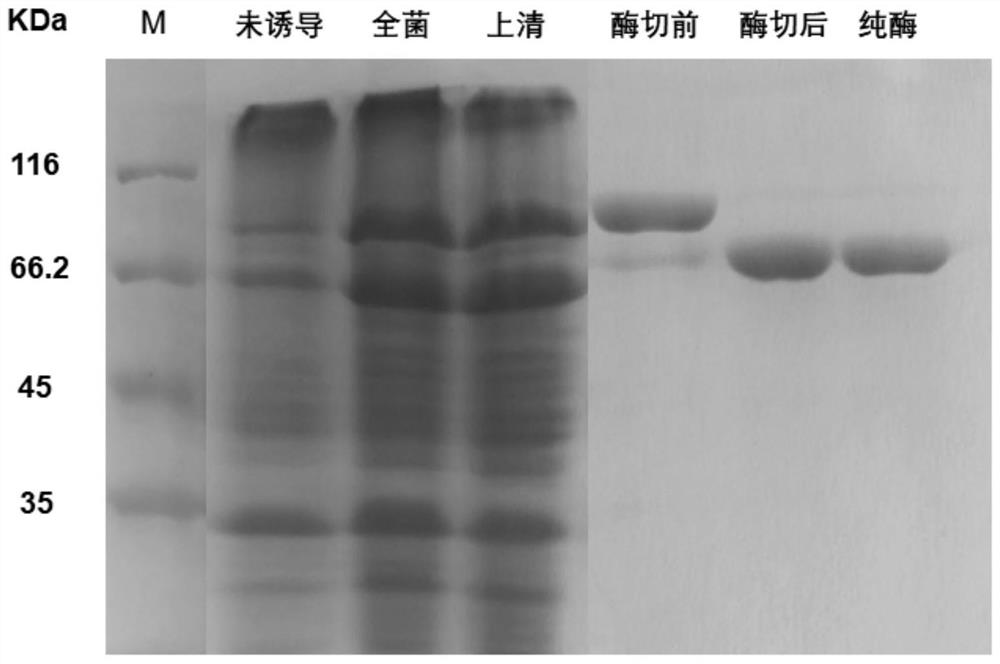
[0051] Pick the positive clones transformed into E.coli strain BL21(DE3)plus competent cells, and culture them in 500ml LB liquid medium containing 50μg / mL kanamycin resistance at 37℃ until OD 600 After reaching 0.8-1.0, add IPTG (isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactopyranoside) with a final concentration of 0.5mM at 16°C and place it on a shaker at 200rpm for 20h, then collect the bacteria by centrifugation at low temperature, and weigh Suspended in Buffer A solution (50 mM Tris-hydrochloric acid, pH 8.0, 500 mM sodium chloride, 10 mM imidazole, volume concentration 1% glycerol), placed the resuspension on ice and crushed the cells with an ultrasonic breaker. The supernatant was collected by low-temperature centrifugation, and the supernatant was incubated with Ni-NTA medium for 0.5 h, and then purified by a gravity column. Since the expressed recombinant protein contains a His tag, it can be affinity-adsorbed to the nickel c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com