Application of salvia miltiorrhiza transcription factor SmbHLH124 in improvement of yield character of salvia miltiorrhiza hairy roots
A technology of transcription factor and hairy root, applied in the field of plant biology, can solve the problems of increasing the growth of hairy roots of Salvia miltiorrhiza, and achieve the effects of improving yield traits, biomass and tanshinone content, and good application prospect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] The construction of embodiment 1 Salvia miltiorrhiza SmbHLH124 overexpression vector
[0055] (1) SmbHLH124 cDNA fragment acquisition
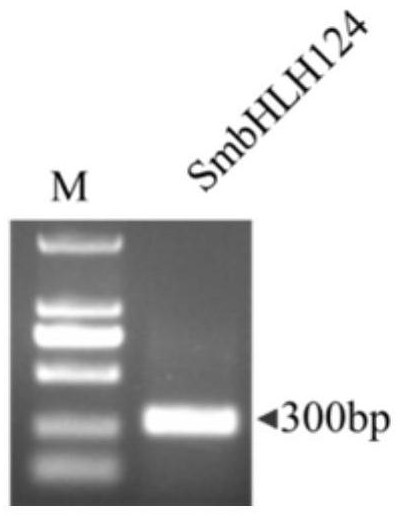
[0056] Design specific primers SmbHLH124-F and SmbHLH124-R according to the sequence information of the SmbHLH124 gene in the published Salvia miltiorrhiza genome and transcriptome data. synthesis. Using the cDNA (20ng / μL) of the underground root of Salvia miltiorrhiza as a template, the SmbHLH124 gene fragment was amplified. The target fragment amplification system: 10×KOD Plus Buffer 5μL, dNTP (2.5mM) 5μL, MgSO4 (25mM) 3μL, KODPlus Neo (1U / μL) 1 μL, SmbHLH124-F (10 μM) 1 μL, SmbHLH124-R (10 μM) 1 μL, cDNA 1 μL, ddH 2 O 33 μL. The PCR amplification program is as follows: 95°C / 5min→(95°C / 30s→56°C / 30s→68°C / 30s)×40cycles→68°C / 5min→12°C / 10min. The PCR product was subjected to agarose electrophoresis, and the target fragment of about 300bp was recovered using the AxyPrep DNA Gel Recovery Kit. figure 1 , and sent the gel-recovered produ...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Example 2 Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy roots
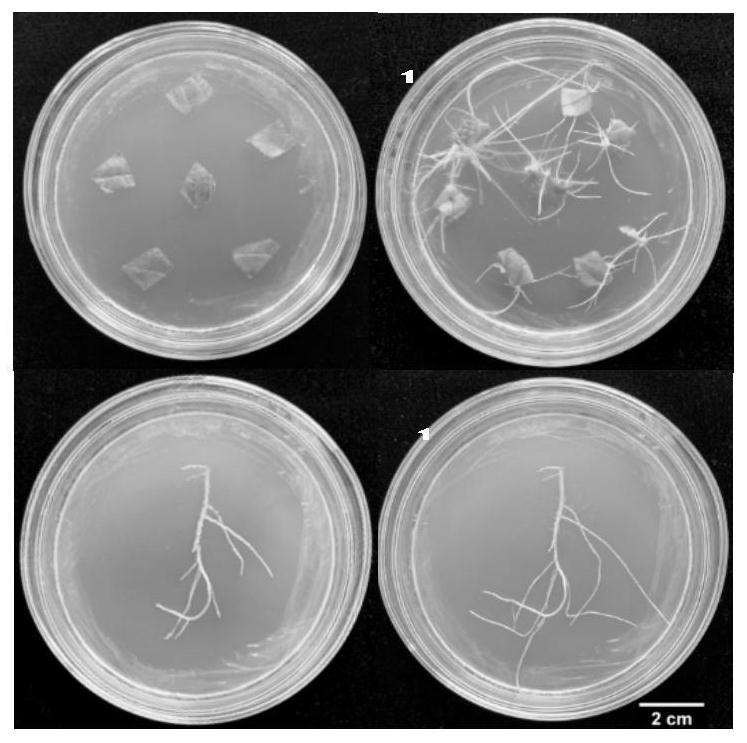
[0068] Agrobacterium-mediated Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root genetic transformation reference (Toki et al., Early infection of scutellum tissue with Agrobacterium allows high-speed transformation of rice. The Plant Journal, 2006, 47 (6): 969-976.) disclosed method . The steps of genetic transformation of Salvia miltiorrhiza are as follows, and the flowchart is shown in image 3 :
[0069] (1) Agrobacterium preparation
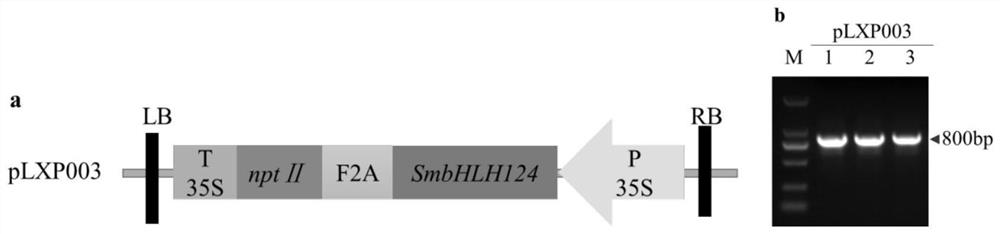
[0070]Pick up Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58C1 carrying the target vector pLXP003 (Shanghai Titan Technology Co., Ltd.) stored at -80°C with an inoculation loop, streak on LB+50mg / L Kan+50mg / L Rif plate and culture it upside down at 28°C Pick up a single colony on the above LB plate with a toothpick, inoculate it in a test tube (or 10 mL EP tube) containing 5 mL LB+50 mg / L Kan+50 mg / L Rif liquid medium, activate at 28°C and 180 rpm Cultivate for 48 hours; on t...
Embodiment 3
[0081] Example 3 Molecular identification of Salvia miltiorrhiza overexpressing SmbHLH hairy roots
[0082] (1) Genomic DNA extraction from the hairy root of Salvia miltiorrhiza
[0083] The DNA extraction of Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root adopts CTAB method, and the specific operation steps are as follows:
[0084] The CTAB extract was preheated in a 65°C water bath. Take a single root 1-2cm away from the root tip and put it into a 2mL centrifuge tube with steel balls, put it into liquid nitrogen for quick freezing, and then shake it into powder. Add 500 μL of preheated CTAB extract, bathe in water at 65°C for 30-50 min, and mix well during this period. Add 500 μL of chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (24:1), mix thoroughly by inversion, and centrifuge at 12000 rpm for 10 min at room temperature. Take the supernatant, add an equal volume of isopropanol to precipitate, and precipitate at -20°C for 1 h. Centrifuge at 12000rpm for 10min at room temperature to collect the precipitate...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com