Self-driven short-wave infrared response organic photoelectric synapse flexible device and application thereof
A short-wave infrared and flexible device technology, applied in the direction of electric solid-state devices, photovoltaic power generation, electrical components, etc., can solve problems affecting device performance and achieve high relative permittivity, strong absorbance, and good solubility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] This embodiment provides a conjugated polymer based on benzobisthienediazole and tellurphene, the structural formula of which is shown in formula (I);
[0027]
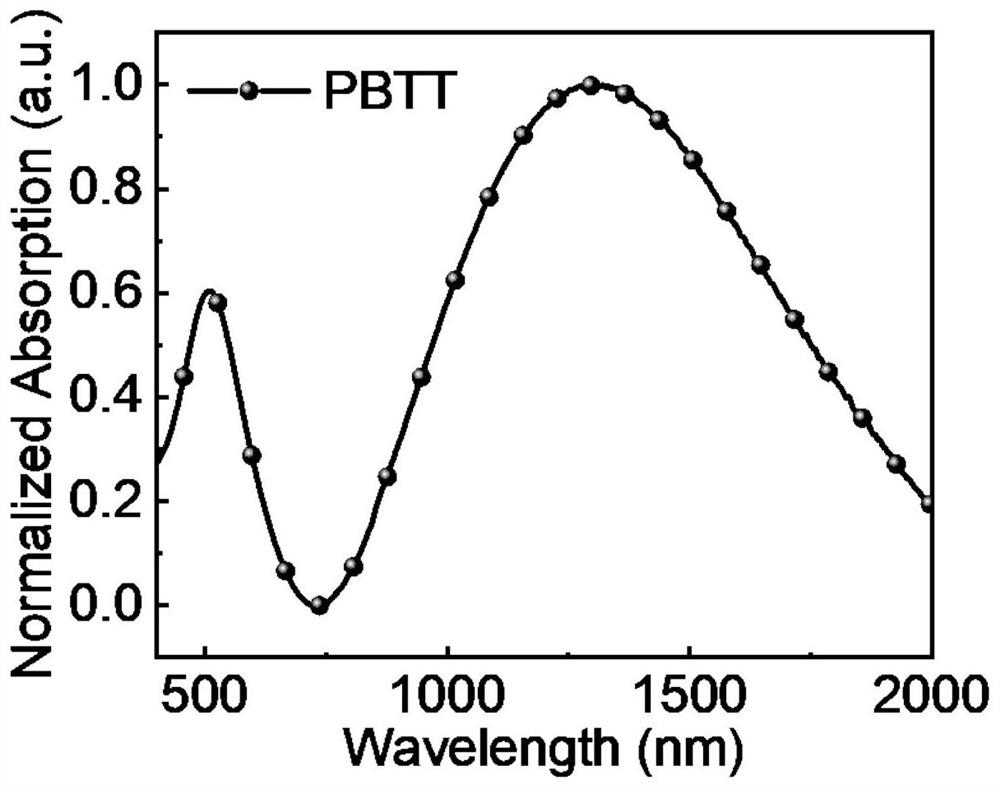
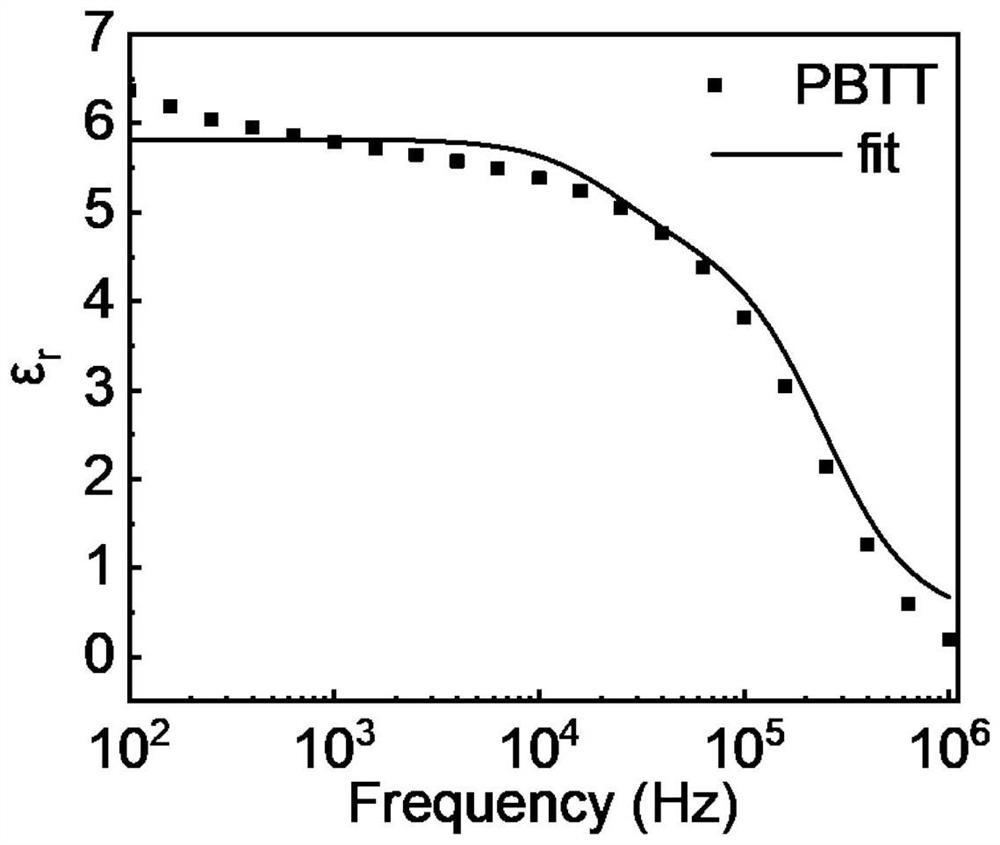
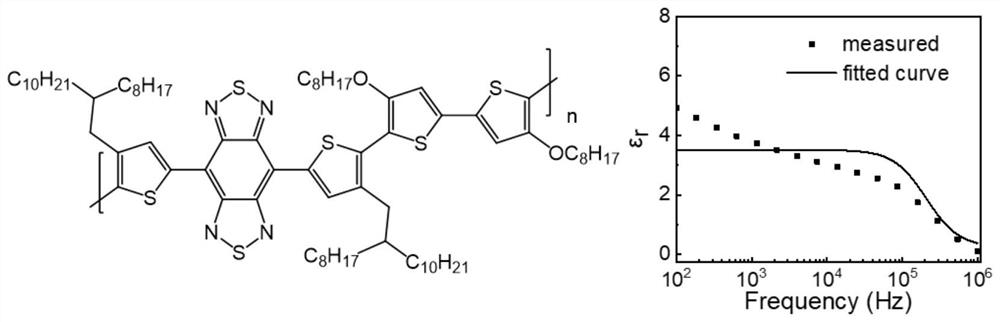
[0028] In the general structural formula of formula I, n is an integer greater than or equal to 4 and less than 20. And the polymer in formula I is denoted as PBTT. exist figure 1 The UV-visible-infrared absorption spectrum of the polymer is shown in , it can be seen from the spectral absorption that the polymer has a wide absorption in the visible and most short-wave infrared regions, and is a good short-wave infrared material, so it can be used to prepare organic Short-wave infrared optoelectronic synapse. figure 2 It is the frequency-permittivity curve fitted by the device with the structure of ITO / PEDOT:PSS / PBTT / Al. It can be obtained that the relative permittivity of the polymer is 5.8, which is a relatively high value among organic polymers. And polymers such as PBBT-2OT The dielectric constant i...
Embodiment 3
[0030] This example provides a method for preparing the polymer PBTT represented by the above formula (II).
[0031] (1) Protected by inert gas, under the catalysis of tris(dibenzylideneacetone) dipalladium and tris(o-methylphenyl)phosphorus, 4,8-Bis[5-bromo-4-(2-octyldodecyl )-2-thienyl]-2λ4δ2-benzo[1,2-c:4,5-c']-bis[1,2,5]thiadiazole(M1) and 2,5-bis(trimethylstannyl)tellurophene(M2) A mixed solution is obtained in an organic solvent.
[0032] In this method, 4,8-Bis[5-bromo-4-(2-octyldodecyl)-2-thienyl]-2λ4δ2-benzo[1,2-c:4,5-c']-bis[1,2 ,5] The molar ratio of thiadiazole to 2,5-bis(trimethylstannyl)tellurophene is 1:0.99-1.05, preferably 1:1. The amount of tris(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium is 4,8-Bis[5-bromo-4-(2-octyldodecyl)-2-thienyl]-2λ4δ2-benzo[1,2-c:4,5- 2-4% of c']-bis[1,2,5]thiadiazole molar dosage, the dosage of tris(o-methylphenyl)phosphorus is 4,8-Bis[5-bromo-4-(2-octyldodecyl) -2-thienyl]- 2λ4δ2-benzo[1,2-c:4,5-c']-bis[1,2,5]thiadiazole 8%-12% of molar do...
Embodiment 4
[0045] In this embodiment, the method of using narrow bandgap copolymers for preparing photoelectric synapse devices includes:
[0046] Weigh 10mg of the polymer obtained in Example 3, dissolve it in 0.25mL ultra-dry o-dichlorobenzene, heat and stir at 60°C for 2h until it is completely dissolved, and prepare the polymer on a PET substrate coated with gold electrodes by spin coating or other methods A photoactive layer film with uniform thickness; in a specific embodiment, the thickness of the active layer is 80nm. Finally prepared as Figure 5 The device structure shown. The device includes: flexible substrate (PET) / electrode (Au) / photoactive layer (narrow bandgap conjugated polymer).
[0047] Image 6 Current-time curves at different wavelengths for the use of conjugated polymers in photoelectric synapses with a bias voltage of 0V. It can be seen that the dark current is stable when no light is added, and under the same light intensity (100mW / cm 2 ), under the irradiati...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com