Repair method of decommissioned lead-acid battery, repair electrolyte and preparation method of repair electrolyte
A lead-acid battery, electrolyte technology, applied in the direction of lead-acid battery, secondary battery repair/maintenance, electrolyte/reactant regeneration, etc. Capacity decline and other problems, to achieve the effect of enhancing deep cycle performance, improving service life, and promoting dissolution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
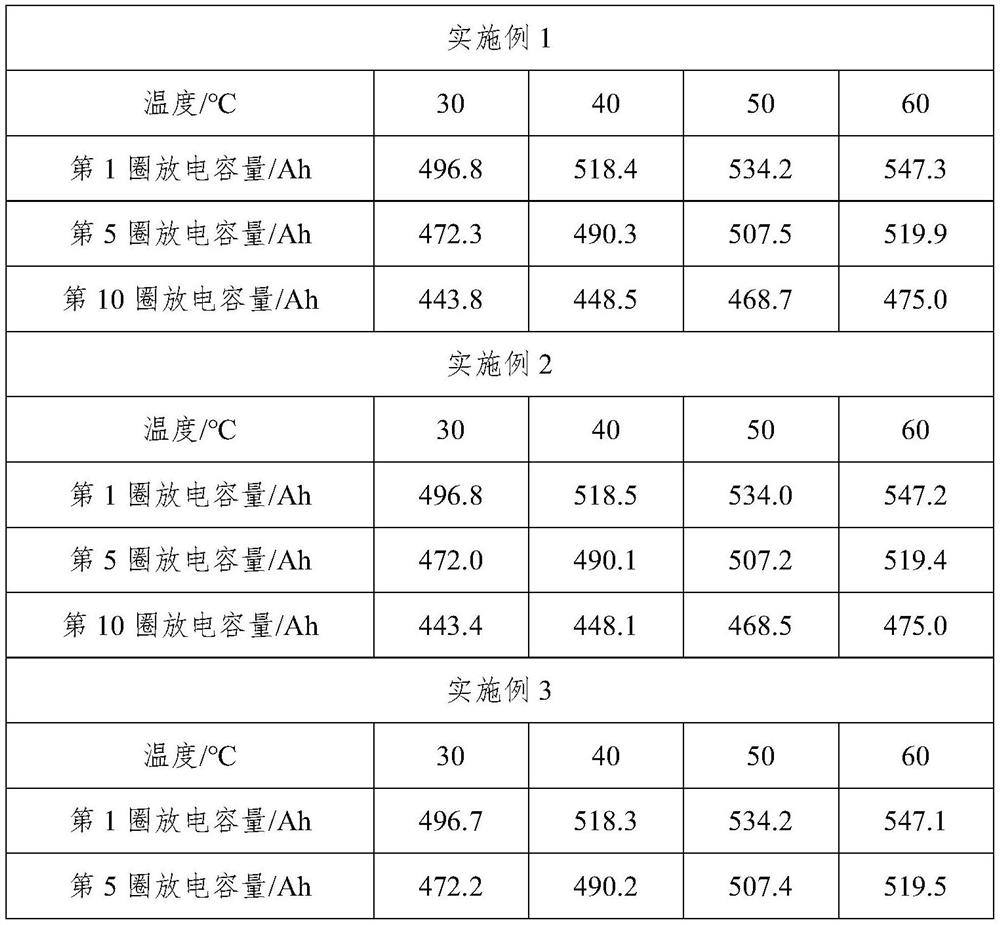
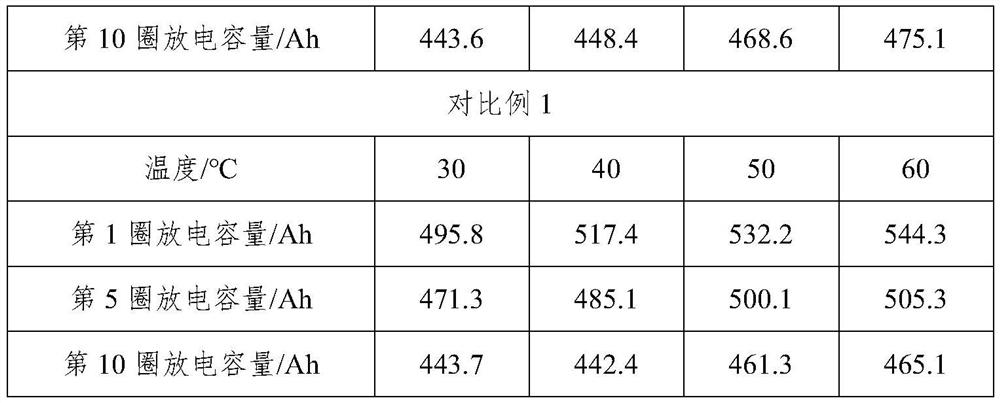
Embodiment 1
[0023] A kind of decommissioned lead-acid battery repair electrolyte of the present invention comprises the following components, recorded in parts by weight, followed by 0.5 parts of polyvinylpyrrolidone, 2.8 parts of activated carbon fibers, 6.5 parts of sodium silicate, 1.5 parts of nano silicon dioxide, sulfuric acid 4 parts of sodium, 4 parts of zinc sulfate, 3 parts of copper sulfate, 86 parts of ultra-pure distilled water.
[0024] A preparation method for repairing electrolyte of decommissioned lead-acid battery, comprising the following steps:
[0025] (1) To prepare an aqueous solution of polyvinylpyrrolidone, add polyvinylpyrrolidone with a K value (significant average molecular weight) of 30 to ultrapure distilled water, heat to about 40°C, and stir until fully dissolved to obtain an aqueous solution of polyvinylpyrrolidone;
[0026] (2) sodium sulfate, zinc sulfate, copper sulfate, activated carbon fiber, polyvinylpyrrolidone aqueous solution are added to a large ...
Embodiment 2
[0029] A retired lead-acid battery repair electrolyte, comprising the following components, recorded in parts by weight, followed by 1 part of polyvinylpyrrolidone, 3 parts of activated carbon fiber, 7 parts of sodium silicate, 2 parts of nano silicon dioxide, 5 parts of sodium sulfate 5 parts, 5 parts of zinc sulfate, 5 parts of copper sulfate, 70 parts of ultrapure distilled water.
[0030] A preparation method for repairing electrolyte of decommissioned lead-acid battery, comprising the following steps:
[0031] (1) To prepare an aqueous solution of polyvinylpyrrolidone, add polyvinylpyrrolidone with a K value (significant average molecular weight) of 40 to ultrapure distilled water, heat to about 45°C, and stir until fully dissolved to obtain an aqueous solution of polyvinylpyrrolidone;
[0032] (2) sodium sulfate, zinc sulfate, copper sulfate, activated carbon fiber, polyvinylpyrrolidone aqueous solution are added to a large amount of ultrapure distilled water, fully stir...
Embodiment 3
[0035] A retired lead-acid battery repair electrolyte, comprising the following components, recorded in parts by weight, followed by 1.2 parts of polyvinylpyrrolidone, 3.8 parts of activated carbon fiber, 9.5 parts of sodium silicate, 2.5 parts of nano silicon dioxide, 6.5 parts of sodium sulfate 6.5 parts of zinc sulfate, 4 parts of copper sulfate, 80 parts of ultrapure distilled water.
[0036] A preparation method for repairing electrolyte of decommissioned lead-acid battery, comprising the following steps:
[0037] (1) To prepare an aqueous solution of polyvinylpyrrolidone, add polyvinylpyrrolidone with a K value (significant average molecular weight) of 60 to ultrapure distilled water, heat to about 50°C, and stir until fully dissolved to obtain an aqueous solution of polyvinylpyrrolidone;
[0038] (2) sodium sulfate, zinc sulfate, copper sulfate, activated carbon fiber, polyvinylpyrrolidone aqueous solution are added to a large amount of ultrapure distilled water, fully ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com