Aqueous zinc ion battery electrolyte as well as preparation method and application thereof
A zinc-ion battery and electrolyte technology, applied in water-based electrolytes, secondary batteries, secondary battery repair/maintenance, etc., can solve problems such as production difficulties and high costs, achieve low prices, alleviate zinc corrosion, and facilitate large-scale production Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] A preparation method for an aqueous zinc-ion battery electrolyte, comprising the following steps:
[0028] (1) Dissolve 0.2mol of zinc sulfate heptahydrate in 100mL of deionized water, stir and dissolve under normal temperature conditions to prepare a zinc sulfate solution with a concentration of 2mol / L as the matrix electrolyte;
[0029] (2) Dissolve 0.001 mol of catechol in 100 mL of zinc sulfate matrix electrolyte to prepare a zinc sulfate-catechol electrolyte with a concentration of 0.01 mol / L.
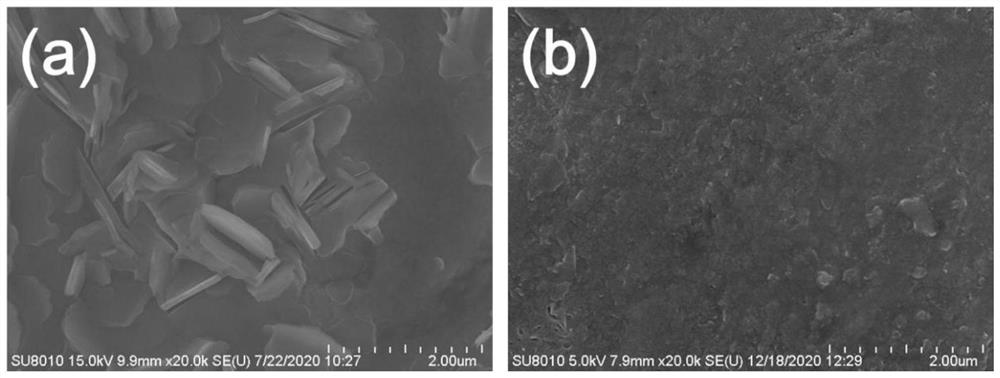
[0030] SEM was used to characterize the surface morphology of the zinc foils that were left to stand for 4h in zinc sulfate-catechol and blank zinc sulfate electrolytes, and the results were as follows figure 1 As shown, it can be clearly seen from the figure that compared with the blank zinc sulfate electrolyte, the surface of the zinc foil standing in the zinc sulfate-catechol electrolyte for 4 hours is smoother.
[0031] Assemble the zinc symmetric battery, test the dep...
Embodiment 2
[0035] A preparation method for an aqueous zinc-ion battery electrolyte, comprising the following steps:
[0036] (1) Dissolve 0.2mol of zinc sulfate heptahydrate in 100mL of deionized water, stir and dissolve under normal temperature conditions to prepare a zinc sulfate solution with a concentration of 2mol / L as the matrix electrolyte;
[0037] (2) Dissolve 0.0005 mol of tannic acid in 100 mL of zinc sulfate solution to obtain a 0.005 mol / L zinc sulfate-tannic acid electrolyte.
[0038] Assembled zinc symmetric cells were tested for electrochemical performance, as Figure 5 As shown, in the electrolyte with tannic acid added to the symmetrical battery, when the concentration of tannic acid is 0.005mol / L, the current density is 4mA / cm 2 , the deposition rate is 4mAh / cm2 Under certain conditions, the cycle life can be as long as 120h.
Embodiment 3
[0040] A preparation method for an aqueous zinc-ion battery electrolyte, comprising the following steps:
[0041] (1) Dissolve 0.2mol of zinc sulfate heptahydrate in 100mL of deionized water, stir and dissolve under normal temperature conditions to prepare a zinc sulfate solution with a concentration of 2mol / L as the matrix electrolyte;
[0042] (2) Dissolve 0.0001 mol α-methyldopa in 100 mL of zinc sulfate matrix electrolyte, stir and dissolve to obtain 0.001 mol / L zinc sulfate-α-methyldopa electrolyte.
[0043] Assembled zinc symmetric cells were tested for electrochemical performance, as Figure 6 As shown, when the concentration of α-methyldopa is 0.001mol / L in the electrolyte solution with α-methyldopa added, the current density is 4mA / cm 2 , the deposition rate is 4mAh / cm 2 Under certain conditions, the cycle life can be as long as 160h.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com